Three-dimensional surface shaping of rotary cutting tool edges with lasers
A technology of rotating cutting tools and cutting edges, which is applied in the direction of rotating tools, tools for lathes, accessories of toolholders, etc., which can solve the problems of poor cutting edge quality, geometric shapes that cannot be defined point by point, high cost and processing time, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
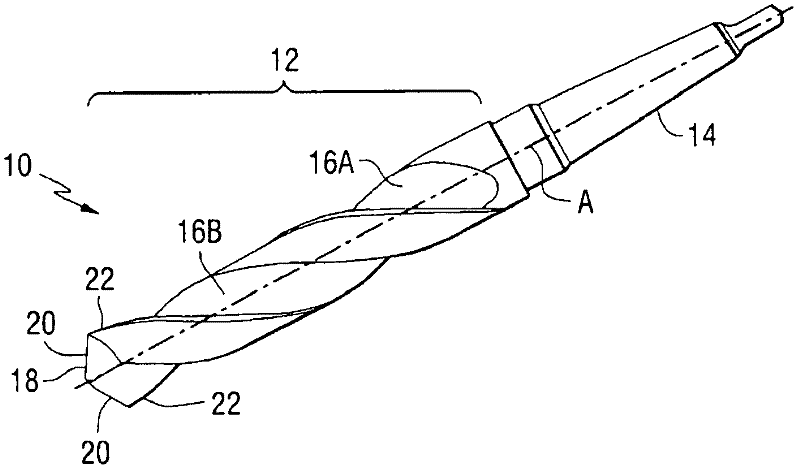
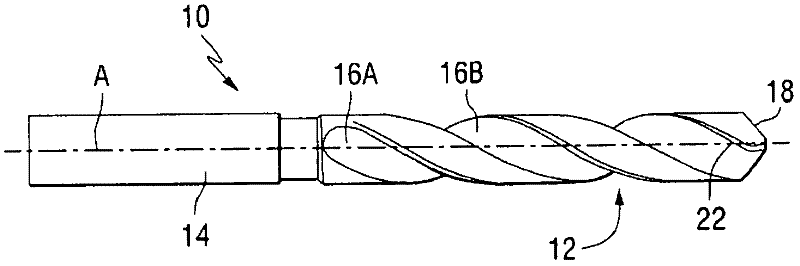
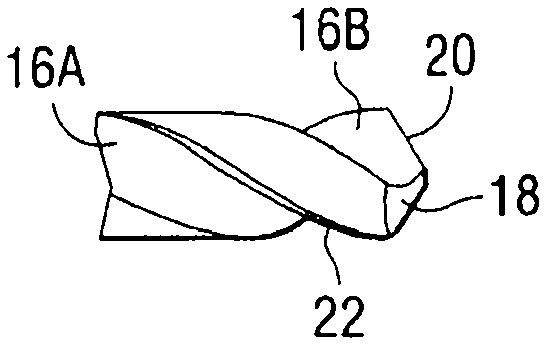
[0025] The laser forming method of the present invention can be used to form a plurality of cutting edges and surrounding contoured surfaces in a rotary cutting tool. As used herein, the term "rotary cutting tool" refers to a type of rotary tool used in chip evacuation machining. Examples of some types of rotary cutting tools that can be formed by the method of the present invention include: drills, drill tips, milling cutters, reamers, taps, graded drills, indexable drills, reamers, countersinks, orbitals Orbital tools, etc. The cutting edges of such tools can be made of very hard materials including: carbides; cermets such as cemented tungsten carbide; ceramics such as cubic boron nitride or alumina, polycrystalline diamond, and the like.
[0026] Figure 1 to Figure 4 Drill bits that can be made in accordance with the present invention are shown. However, it should be understood that any other type of rotary cutting tool having a similar type of cutting edge geometry is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com