Resistive random access memory unit and resistive random access memory
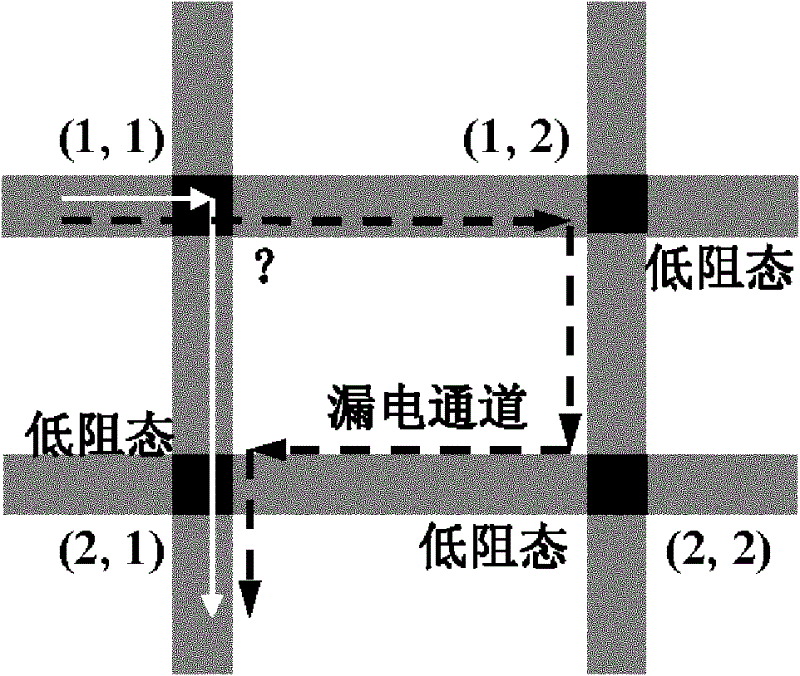
A resistive memory, random access storage technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problem of bipolar resistive random access memory not being found, unable to provide enough current, etc., to eliminate the phenomenon of read crosstalk , the effect of reducing the leakage channel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
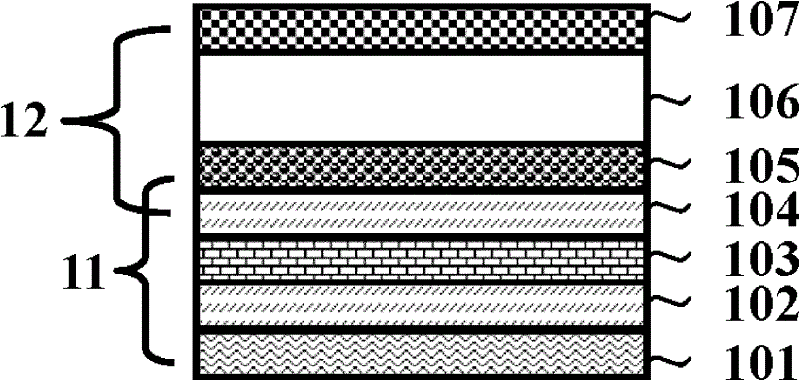
[0038] Embodiment 1 of the present invention is the unit structure and the design of the read / write mode of the resistive random memory unit composed of a bi-state resistor and a unipolar resistive memory in series.
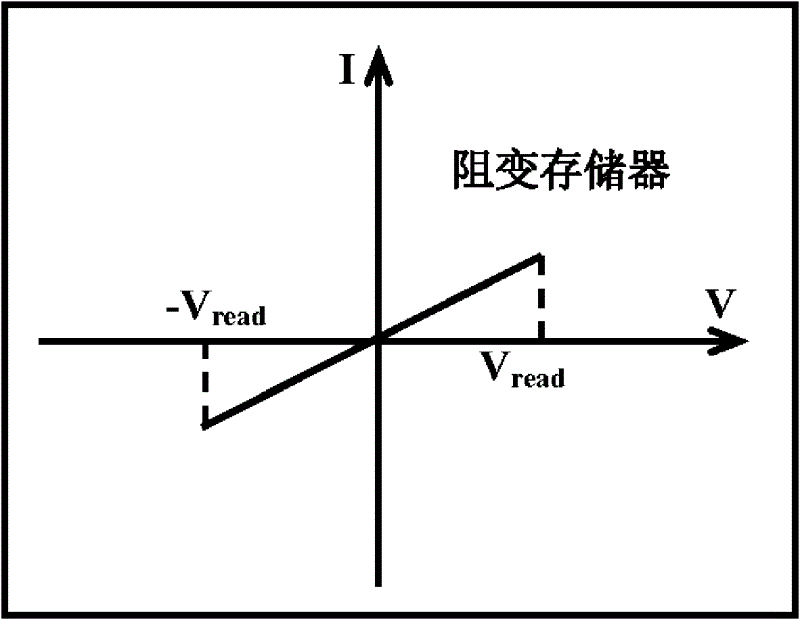
[0039] Figure 4 It is a current-voltage characteristic curve diagram of a bi-state resistor in a resistive random access memory unit in a DC scanning mode according to an embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the bi-state resistor of this embodiment is initially in a high-impedance state, and when the forward scanning voltage reaches V 1 When the two-state resistor is turned on, the two-state resistor is in a low-impedance state at this time, when the scanning voltage is changed by V 1 to V 2 During retrace, the low resistance state of the bi-state resistor can be maintained, but when the device voltage is less than V 2 , the two-state resistor returns from a low-impedance state to a high-impedance state. Bi-state resistors also h...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: Another embodiment of the present invention is the design of the cell structure and read / write mode of the resistive non-volatile memory composed of a two-state resistor and a bipolar resistive memory in series.
[0044] In this embodiment, the bi-state resistor has the same current-voltage characteristics as in Example 1.
[0045] Figure 7 It is the current-voltage characteristic curve of the bipolar resistive random access memory in the resistive random access memory unit in the embodiment of the present invention under the DC scanning mode. Such as Figure 7 As shown, the bipolar RRAM in the embodiment of the present invention starts to be in a high-impedance state, and under the forward scanning voltage (using the current limiting mode), when the voltage reaches V set , the RRAM changes from a high-resistance state to a low-resistance state, and when the voltage is removed, the RRAM can still remain in a low-resistance state; unlike Example 1, the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com