Method for extracting a plurality of kinds of active ingredients from tea leaves simultaneously
A technology of active ingredients and tea leaves, applied in organic chemistry, carboxylic acid amide separation/purification, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory purity and yield of tea polyphenols, low content of active ingredients, and the presence of solvents, etc., achieving short extraction time, Less active material loss and easy resin regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
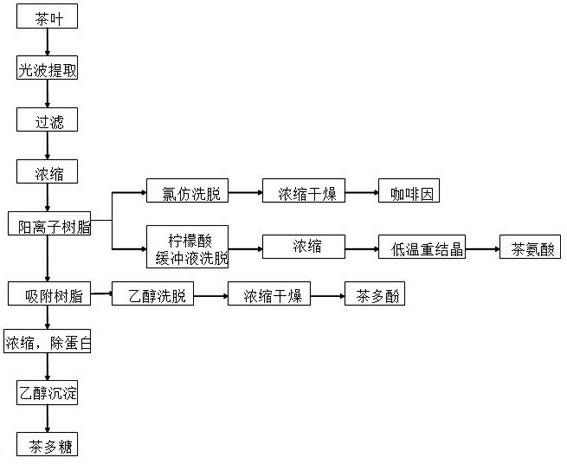
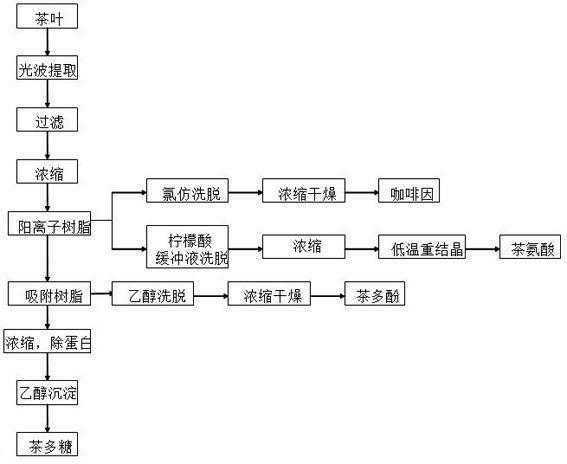
[0044] 1) 500g of tea powder, add 5Kg of water, soak and extract at 40-60℃ for 10-30 minutes under the action of light waves, filter, add 5Kg of water to the tea dregs, soak and extract at 40-60℃ for 10-30 minutes under the action of light waves, filter Remove the filter residue, combine the two soaking extracts, and concentrate the soaking extracts to 1 / 5 of the original volume;
[0045]2) After immersing the cationic resin in distilled water, repeat the treatment with acid and alkali twice, then transform it with acid, and finally wash it to neutral with distilled water. The cationic resin is WA-2;
[0046] 3) Soak the adsorption resin in distilled water, wash it with ethanol until it is colorless, and the adsorption resin is 92-2;
[0047] 4) The above-mentioned tea steeping extract was passed through the cationic resin column at a speed of 25mL / min, and the effluent was passed through the adsorption resin column at a speed of 20mL / min. First remove the caffeine on the cat...
Embodiment 2
[0051] 1) 500g of tea powder, add 6Kg of water, soak and extract at 40-60°C for 10-30 minutes under the action of light waves, filter, add 4Kg of water to the tea residue, soak and extract at 40-60°C for 10-30 minutes under the action of light waves, filter Remove the filter residue, combine the two soaking extracts, and concentrate the soaking extracts to 1 / 5 of the original volume;
[0052] 2) Soak the cationic resin in distilled water, repeat the treatment with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide twice, then transform it with hydrochloric acid, and finally wash it with distilled water until neutral. The cationic resin is D135;
[0053] 3) Soak the adsorption resin with distilled water, wash it with ethanol until it is colorless, and the adsorption resin is 92-3;
[0054] 4) The above-mentioned tea soaking extract was passed through the cationic resin column at a speed of 35mL / min, and the effluent was passed through the adsorption resin column at a speed of 25mL / min. Fi...
Embodiment 3
[0058] 1) 500g of tea powder, add 7.5Kg of water, under the action of light wave, soak and extract at 40-60°C for 10-30 minutes, filter, add 2.5Kg of water to the tea residue, and soak and extract at 40-60°C for 10-30 minutes under the action of light wave , filter to remove the filter residue, combine the two soaking extracts, and concentrate the soaking extracts to 1 / 5 of the original volume;
[0059] 2) After immersing the cationic resin in distilled water, repeat the treatment twice with 5% hydrochloric acid and 5% sodium hydroxide, then transform it with 5% hydrochloric acid, and finally wash it with distilled water to neutrality. The cationic resin is preferably 003× 7;
[0060] 3) After soaking the adsorption resin with distilled water, wash it with ethanol until it is colorless, and the adsorption resin is NK-S3;
[0061] 4) Pass the above-mentioned tea steeping extract through the cationic resin column at a speed of 40mL / min, and then pass the effluent through the ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com