Method for improving thermal cracking of heavy oil in sub (ultra) critical water
A technology of heavy oil and critical water, applied in the direction of non-catalytic thermal cracking, cracking, petroleum industry, etc., can solve the problems of no industrial reference, achieve good initiation efficiency, ingenious and unique conception, and be conducive to industrial production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
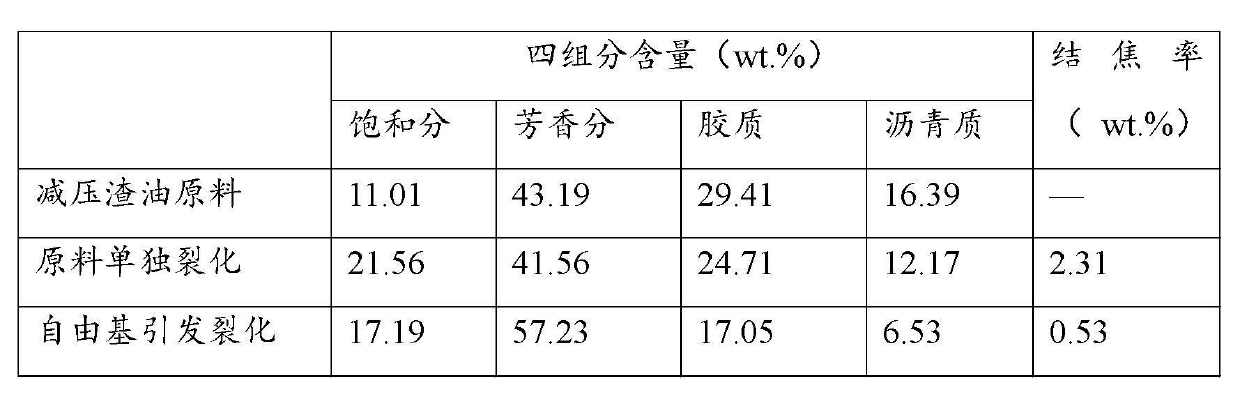
[0019] Sub (super) critical water intervening free radical initiator triggers residual oil cracking: 20 g vacuum residual oil, 30 g deionized water, 0.1 g azobisisobutylcyanide free radical initiator are added to a volume of 100 ml batch reactor. The reactor was rapidly heated to 380° C. and continued to react for 15 minutes and then cooled to room temperature. Separate the liquid and solid products in the reactor, take the liquid phase product for four-component analysis, collect the solid carbon residue and weigh it.
[0020] According to the above operation process, just do not add 0.1 g azobisisobutyrocyanide free radical initiator, the vacuum residue is thermally cracked under the same operating conditions, and the free radical initiator intervening with sub (super) critical water initiates The data comparison of residue cracking results can be seen in Table 1.
[0021] Table 1 Four-component analysis data of vacuum residue feedstock and cracked products.
[0022]
...
Embodiment 2
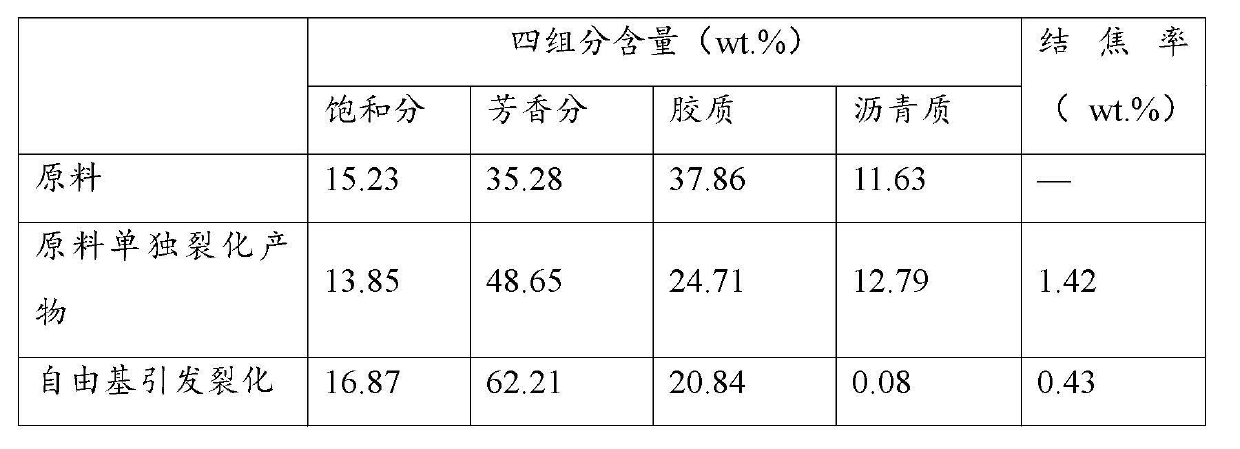
[0025] Sub (super) critical water intervening free radical initiator triggers catalytic cracking oil slurry cracking: the catalytic cracking oil slurry and deionized water dissolved in elemental iodine are respectively added to the continuous reactor with a metering pump, and the reactor is immersed in a 390°C Fluidized sand bath. The mass ratio of water and oil is 1:2, and the amount of elemental iodine added is 15×10 -3 . The residence time of materials in the reactor was controlled at 15 min. After the product is separated, the liquid phase is taken for four-component analysis, and the solid carbon residue is collected and weighed.
[0026] According to the above operation process, except that elemental iodine is not added, the catalytic cracking oil slurry is cracked separately under the same operating conditions, and the data comparison with the cracking results of the catalytic cracking oil slurry by the free radical initiator intervened in sub (super) critical water c...
Embodiment 3
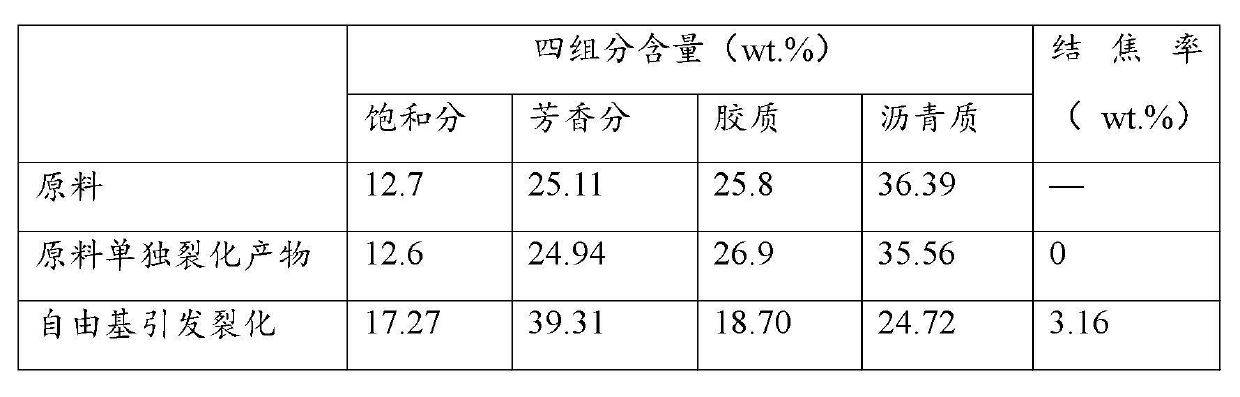
[0031] Sub (super) critical water intervened free radical initiators to initiate asphalt cracking: 8 g of asphalt, 32 g of deionized water, and 0.16 g of tertiary dibutyl peroxide were added to a batch reactor with a volume of 100 ml. The reactor was quickly immersed in a fluidized sand bath at 360 °C for 45 min. After the product is separated, the liquid phase is taken for four-component analysis, and the solid carbon residue is collected and weighed.
[0032] According to the above operation process, but without adding tertiary butyl peroxide, the bitumen was subjected to separate thermal cracking under the same operating conditions, and the comparison data with the results of asphalt cracking induced by sub-(super)critical water-mediated free radical initiators can be found in the table 3.
[0033] Table 3 Four-component analysis data of bitumen feedstock and cracked products.
[0034]
[0035] During the free radical-induced bitumen cracking process mediated by sub(su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com