Carbon negative electrode material of sodium ion battery
A carbon anode material, a technology for sodium ion batteries, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective insertion and extraction of sodium ions, and lack of sodium intercalation anode materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1. Polyphenylene pyrolytic carbon and electrochemical sodium storage performance
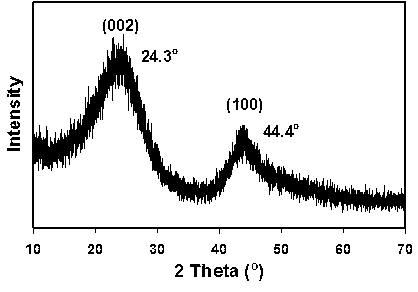
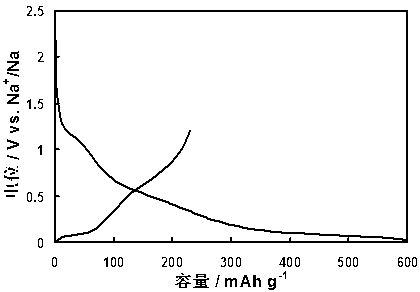
[0020] Place the polyphenylene material in a high-temperature furnace filled with nitrogen, at 1000 o C was pyrolyzed for 6h, and the resulting carbon material was analyzed by transmission electron microscopy and X-ray structure. Viewed from the transmission electron microscope (attached figure 1 ) carbon layers are arranged in an irregular form with an interlayer spacing of about 0.37 nm, X-ray analysis (attached figure 2 ) is less graphitized, but the peaks of (002) and (101) planes can still be clearly distinguished (respectively at 24.3 o and 44.4 o ). The carbon material is uniformly mixed with vinylidene fluoride (PVDF) (dissolved in N-methylpyrrolidone) and acetylene black at a weight ratio of 90:5:5, and coated into an electrode film. With the electrode film as the working electrode and the metal sodium sheet as the counter electrode, 1mol L -1 NaPF 6 (EC-DEC=1...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Embodiment 2. Preparation and sodium storage performance of phenolic resin pyrolytic carbon material
[0023] Place the phenolic resin material in a high-temperature furnace filled with nitrogen at 1200 o C pyrolysis for 2 hours, the obtained carbon material is mixed with vinylidene fluoride (PVDF) (dissolved in N-methylpyrrolidone) and acetylene black in a weight ratio of 90:5:5, and coated into an electrode film. With the electrode film as the working electrode and the metal sodium sheet as the counter electrode, 1mol L -1 NaPF 6 (EC-DEC=1:1) Assembled the battery with the electrolyte to test its electrochemical performance, Figure 4 It is the galvanostatic cycle performance curve of phenolic resin pyrolytic carbon, the current density is 50 mA g -1 , the charging and discharging voltage range is 2.0~0V (Na + / Na). like Figure 4 The material shown has a reversible capacity of 260mAh g -1 , the capacity still maintains 220 mAh g after 100 cycles -1 .
[002...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3. Preparation of pitch pyrocarbon and its sodium storage performance
[0026] Place the asphalt material in a high-temperature furnace filled with nitrogen at 600 o C pyrolysis for 24 hours, the obtained carbon material is mixed with vinylidene fluoride (PVDF) (dissolved in N-methylpyrrolidone) and acetylene black in a weight ratio of 90:5:5, and coated into an electrode film. With the electrode film as the working electrode and the metal sodium sheet as the counter electrode, 1mol L -1 NaPF 6 (EC-DEC=1:1) Assembled the battery with the electrolyte to test its electrochemical performance, the current density was 50 mA g -1 , the charging and discharging voltage range is 1.2~0V (Na + / Na). The reversible capacity of the tested material is 175mAh g -1 , the capacity still maintains 150 mAh g after 100 cycles -1 .
[0027]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com