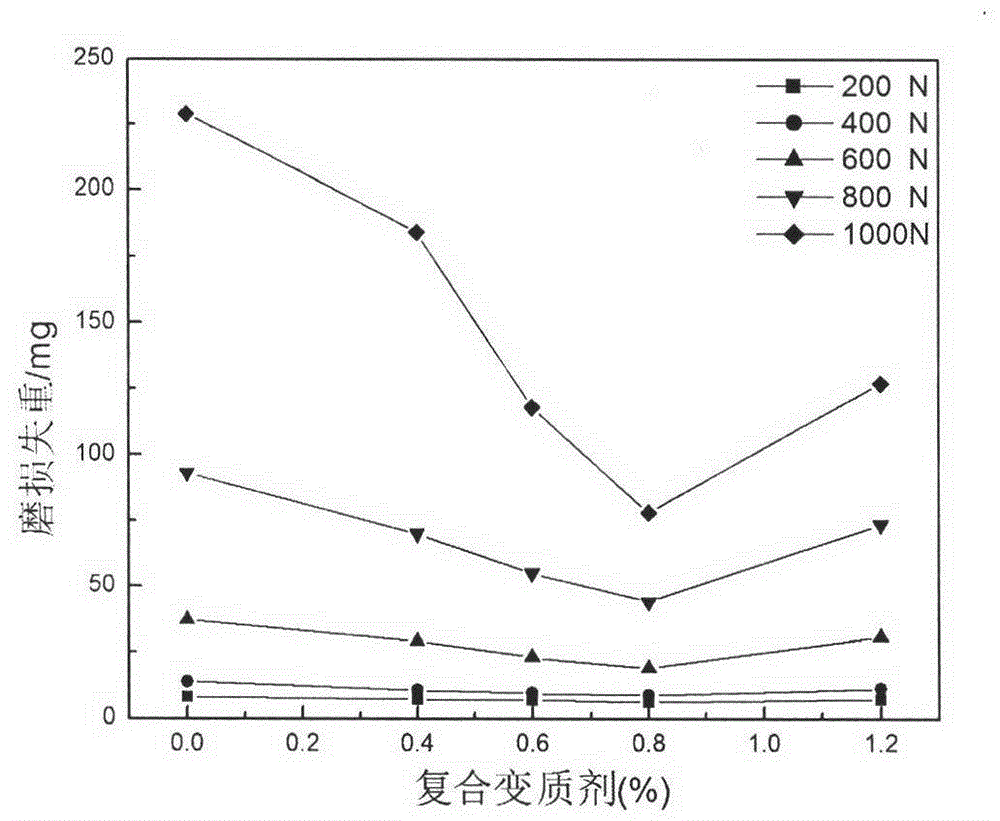
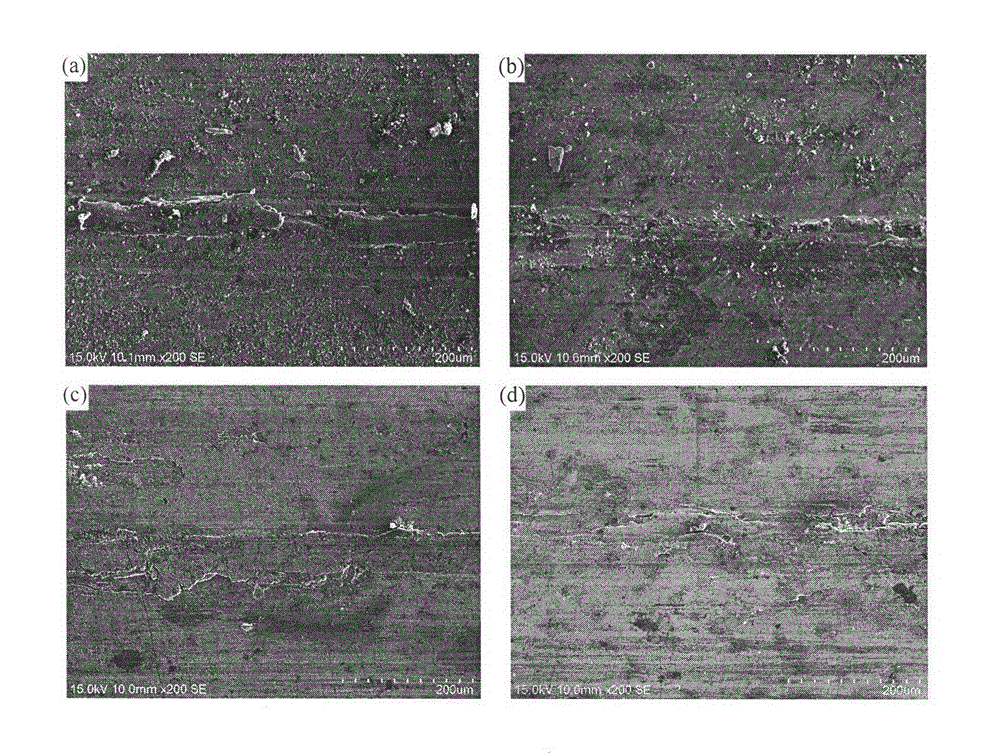
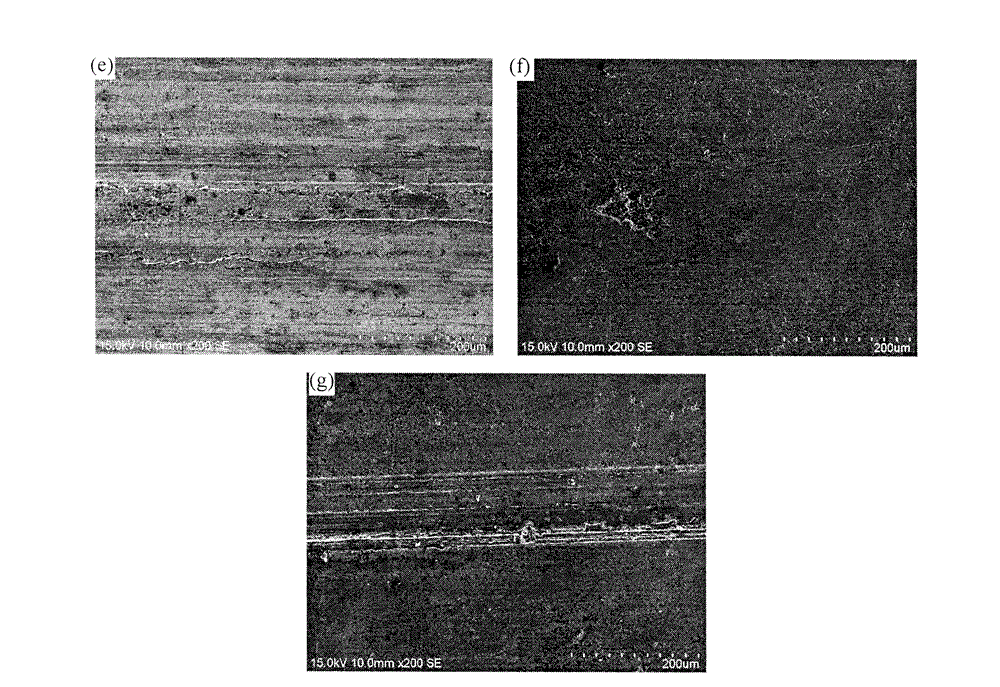
Multielement zinc-aluminum alloy capable of improving frictional wear performance
A zinc-aluminum alloy, friction and wear technology, applied in the field of zinc-aluminum alloy preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Industrial aluminum ingot No. A00, zinc ingot No. 0, electrolytic copper, composite modifier (including Ni20-30%, Ti15-25%, Mn5-15%, Cr5-15%, Si5-10%, Ce5-10%, La5-10%, Y1-6%, Nb1-6%, V1-6%, the rest is aluminum), pure magnesium as raw materials. The composition is calculated by weight percentage, after weighing according to the proportion of Al28%, Cu2.3% (added in the form of aluminum-copper master alloy containing 50% copper), composite modifier 0.2%, Mg0.015%, and the balance is Zn. Melted in an induction melting furnace. The smelting process is as follows: first add aluminum ingots, zinc ingots, aluminum-copper intermediate alloys, and composite modifiers. After the materials are completely melted, heat them up to 600-650°C and keep them warm for 6min-8min to homogenize each element, in order to reduce the burning loss of magnesium. Use a bell jar to press magnesium into molten metal, and use 0.2% dehydrated ZnCl containing molten metal 2 For refining, use a bell...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Industrial aluminum ingot No. A00, zinc ingot No. 0, electrolytic copper, composite modifier (including Ni20-30%, Ti15-25%, Mn5-15%, Cr5-15%, Si5-10%, Ce5-10%, La5-10%, Y1-6%, Nb1-6%, V1-6%, the rest is aluminum), pure magnesium as raw materials. The composition is calculated by weight percentage, after weighing according to the ratio of Al28%, Cu2.3% (added in the form of aluminum-copper master alloy containing 50% copper), composite modifier 0.8%, Mg0.015%, and the balance is Zn. Melted in an induction melting furnace. The smelting process is as follows: first add aluminum ingots, zinc ingots, aluminum-copper intermediate alloys, and composite modifiers. After the materials are completely melted, heat them up to 600-650°C and keep them warm for 6min-8min to homogenize each element, in order to reduce the burning loss of magnesium. Use a bell jar to press magnesium into molten metal, and use 0.2% dehydrated ZnCl containing molten metal 2 For refining, use a bell jar to...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Industrial aluminum ingot No. A00, zinc ingot No. 0, electrolytic copper, composite modifier (including Ni20-30%, Ti15-25%, Mn5-15%, Cr5-15%, Si5-10%, Ce5-10%, La5-10%, Y1-6%, Nb1-6%, V1-6%, the rest is aluminum), pure magnesium as raw materials. The composition is calculated by weight percentage, after weighing according to the proportion of Al28%, Cu2.3% (added in the form of aluminum-copper master alloy containing 50% copper), composite modifier 1.2%, Mg0.015%, and the balance is Zn. Melted in an induction melting furnace. The smelting process is as follows: first add aluminum ingots, zinc ingots, aluminum-copper intermediate alloys, and composite modifiers. After the materials are completely melted, heat them up to 600-650°C and keep them warm for 6min-8min to homogenize each element, in order to reduce the burning loss of magnesium. Use a bell jar to press magnesium into molten metal, and use 0.2% dehydrated ZnCl containing molten metal 2 For refining, use a bell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com