Charging method in monocrystalline silicon ingot casting, and monocrystalline silicon ingot casting method
A single crystal silicon and ingot casting technology is applied in the field of single crystal silicon ingot and single crystal silicon ingot charging, which can solve the problems of easy-to-melt single crystal ingot casting process and difficult control of seed crystals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clarified below with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention.
[0031] clearly and completely, it is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, not
[0032] All examples. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, those of ordinary skill in the art do not create
[0033] All other embodiments obtained under the premise of sexual labor fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
[0034] In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more clearly understood, the present invention is hereinafter described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0035] The following examples are described in further detail.
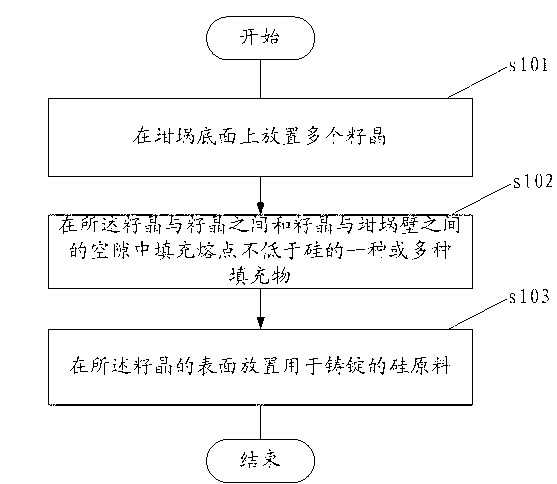
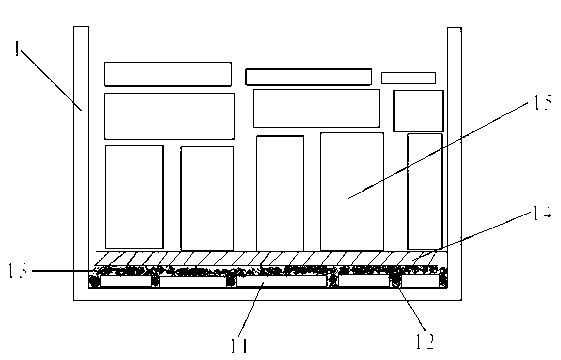
[0036] refer to figure 1 It is a flow chart of the charging method of the single crystal silicon ingot according to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com