Industrial piptanthus nepalensis f.leiocarpus seedling rearing method
A yellow flower, factory-like technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, horticulture, soilless cultivation, etc., can solve the problem that it is difficult to obtain a large number of neat and robust seedlings, the distribution of light fruit yellow flowers is remote, and the emergence rate is less than 5%. and other problems, to achieve the effect of shortening the time of sowing and emergence, shortening the time of imbibition and improving the survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
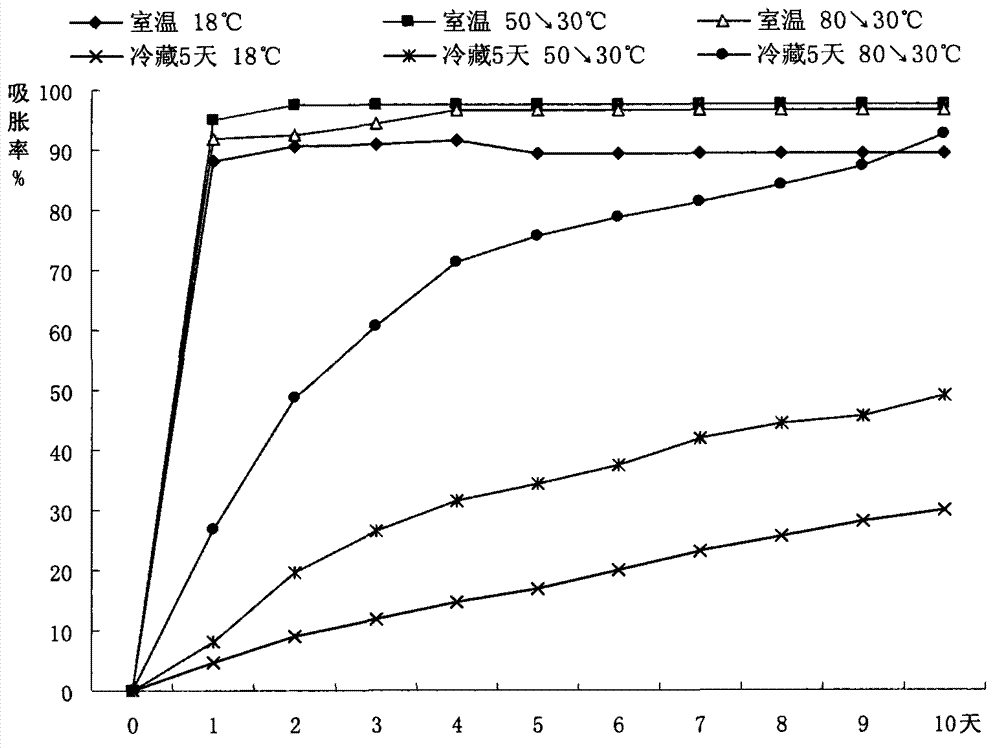
[0035] Embodiment 1, the influence of different treatments on the imbibition rate and germination rate of Chrysanthemum glabra seeds
[0036] The method of measuring the imbibition rate is as follows: randomly select a certain number of A. glabrata seeds; soak the seeds in normal temperature water on the first day, and then change the initial temperature every day to 15-25°C, 50°C-60°C and 80°C-100°C. Soak the seeds in clear water at a higher temperature, so that the water temperature will naturally drop to room temperature. Soak the seeds for a total of 10 days. Pick out the imbibition seeds before changing the water at different temperatures, record the number of imbibition seeds per day, and use the following formula to calculate the imbibition rate of different water temperatures:
[0037]
[0038] The calculation method of hard solid rate is:
[0039] Hard solid rate (%)=1-imbibition rate
[0040] 1. Effects of soaking seeds in different water temperatures on the imbi...
Embodiment 2
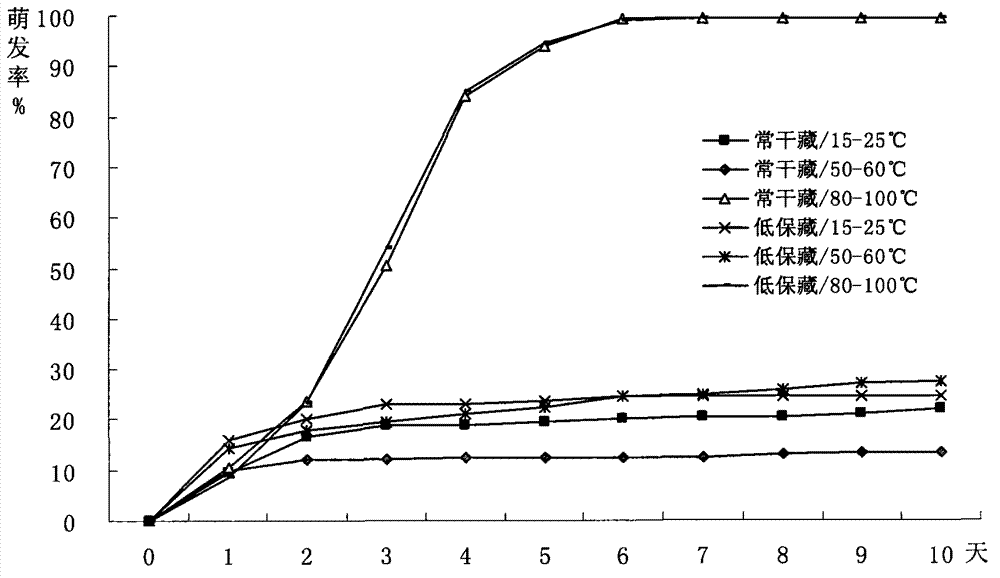
[0053] Embodiment 2, the comparative experiment of conventional sowing of glabra japonica seeds and the raising of seedlings of the present invention
[0054] In this experiment, the seeds of A. glabrata collected in October 2009 were selected. Threshing and net seeding by conventional methods, put them into sealed plastic bags and store them in a refrigerator at 0°C to 5°C to keep them moist and refrigerated. Randomly select 400 seeds for each treatment, and divide them into 4 repetitions, with 100 seeds per repetition; soak the seeds in water for 48 hours before storing in sand, and use Wet sand was layered for 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 months; on February 28, 2011, seeds were sown in a non-heated glass greenhouse at the same time. The method of the present invention was used as a contrast, soaking seeds in clear water for 1 day on March 1, soaking seeds in 80-100°C high-temperature water naturally down to room temperature for 5 days from March 2 to March 6, and 98% concentrated sul...
Embodiment 3
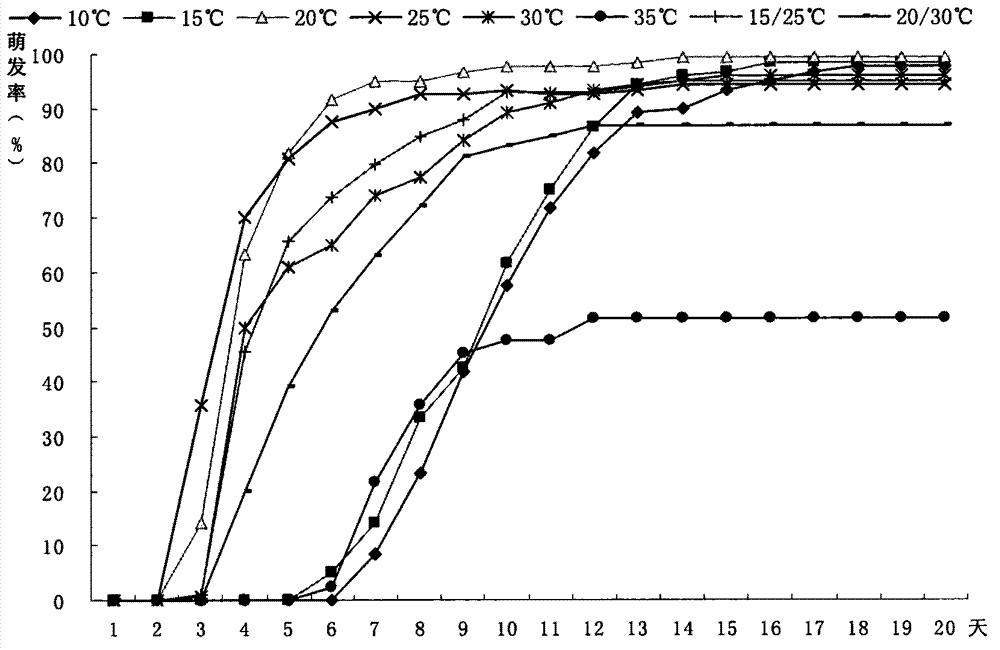
[0056] Embodiment 3, comparative test of industrialized seedling raising technology of A. glabrata
[0057] The sowing depth experiment of industrialized seedling cultivation selects the uniform seedlings germinated by this technology, and uses 3 treatments with soil covering depths of 1 cm, 2 cm, and 3 cm in the uniformly prepared uniform cultivation medium for comparative experiments, and each treatment has 30 seedlings. Seeds germinated on the same day, 3 repetitions, observed and recorded the number of emergences per day, measured the height of the seedlings after 30 days, calculated the emergence rate and survival rate, the results are shown in Figure 7 . Figure 7 The picture on the left shows the emergence of seedlings at different sowing depths within 30 days of sowing. The first emergence time of 1 cm, 2 cm, and 3 cm was 6 days, 8 days, and 18 days respectively; the time to reach the maximum emergence rate was 17 days, 26 days, After 28 days, the maximum emergence r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com