Method for removing Se(IV)/Se(VI) from water by magnetic field enhanced zero-valent iron
A magnetic field strengthening, zero-valent iron technology, applied in the fields of magnetic field/electric field water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, etc. Achieve the effect of low price, improved reaction rate and long service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
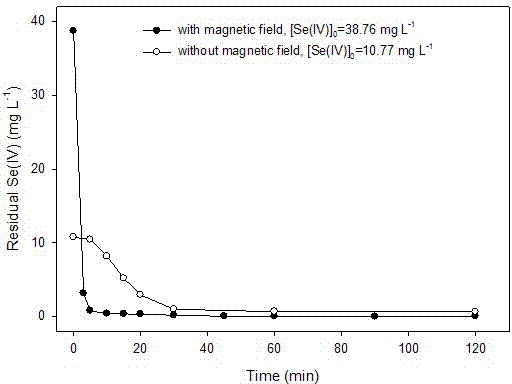
[0025] Specific embodiment one: a kind of magnetic field strengthening zero-valent iron in this embodiment removes the method for Se(IV) / Se(VI) in water is in complete mixing reactor, to containing 38.76 mg L -1 Add 1 g L of Se(IV) to the water -1 The zero-valent iron (particle size is 3 microns), the mass ratio of zero-valent iron to Se is about 25:1, pH=4.0, the magnetic field used is an alternating magnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 0.2~10 mT. In the presence of a magnetic field, zero-valent iron can remove more than 99% of Se(IV) within 0.25 h. In the absence of a magnetic field, when the initial Se(IV) concentration was reduced to 10.77 mg L -1 , even if the reaction is 2 h, only about 94% of Se(IV) can be removed. see details figure 1 .
specific Embodiment approach 2
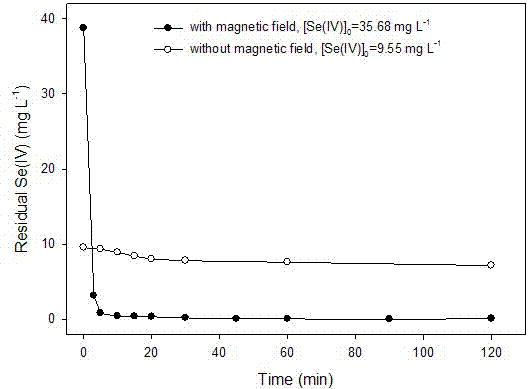
[0026] Specific embodiment two: a kind of magnetic field strengthening zero-valent iron in this embodiment removes the method for Se(IV) / Se(VI) in water is in complete mixing reactor, to containing 35.68 mg L -1 Add 1 g L of Se(IV) to the water -1 The zero-valent iron (particle size is 3 microns), the mass ratio of zero-valent iron to Se is about 25:1, pH=5.0, the magnetic field used is an alternating magnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 0.2~10 mT. In the presence of a magnetic field, zero-valent iron can remove more than 99% of Se(IV) within 0.25 h. In the absence of a magnetic field, when the initial Se(IV) concentration was reduced to 9.55 mg L -1 , even if the reaction is 2 h, only about 25% of Se(IV) can be removed. see details figure 2 .
specific Embodiment approach 3
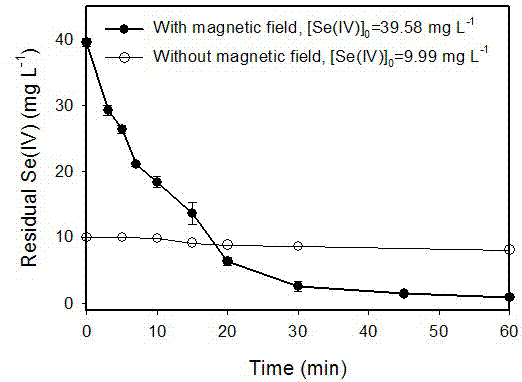
[0027] Specific embodiment three: a kind of magnetic field strengthening zero-valent iron in this embodiment removes the method for Se(IV) / Se(VI) in water is in complete mixing reactor, to containing 39.58 mg L -1 Add 1 g L of Se(IV) to the water -1 The zero-valent iron (particle size is 3 microns), the mass ratio of zero-valent iron to Se is about 25:1, pH=6.0, the magnetic field used is an alternating magnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 0.2~10 mT. In the presence of a magnetic field, zero-valent iron can remove more than 98% of Se(IV) within 1 h. In the absence of a magnetic field, when the initial Se(IV) concentration was reduced to 9.99 mg L -1 , even if the reaction is 2 h, only about 26% of Se(IV) can be removed. see details image 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com