Solid waste sorting process based on thermal conductivity difference of different materials
A solid waste and process technology, which is applied in the field of solid waste sorting treatment process, can solve the problems of complicated sorting process, high equipment cost, single sorting object, etc., and achieve huge economic benefits, efficient sorting, and simplified sorting The effect of steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
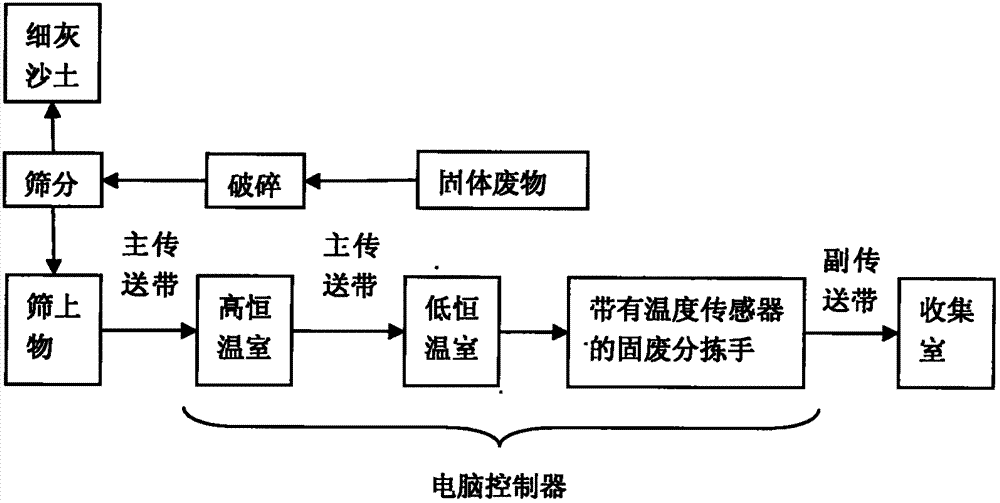
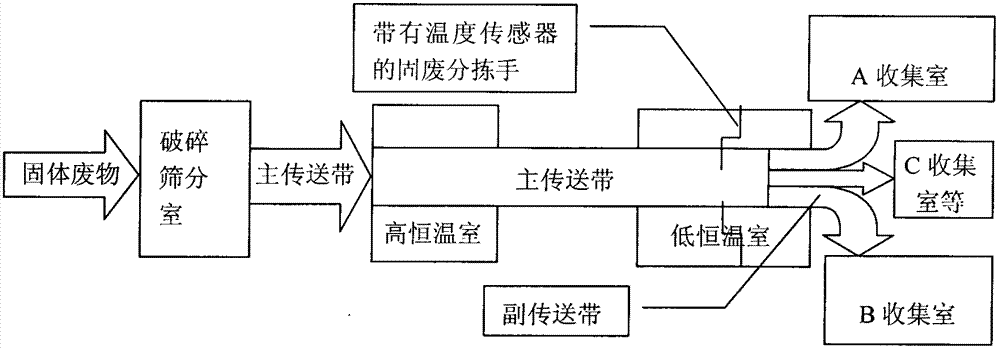
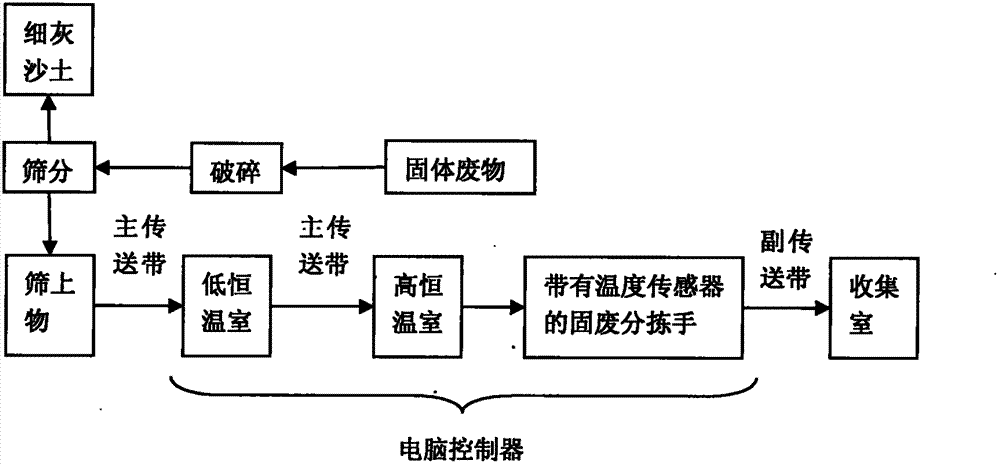
[0027] Under the condition that the room temperature is about 27°C, the mixed solid waste first passes through a low-temperature thermostatic chamber with a temperature of 27°C for 5 minutes, and the temperature of the mixed solid waste is completely kept at 27°C. At this time, the main conveyor belt transports the mixed solid waste to a high-temperature room with a temperature of 55 °C, and collects data through a PC-based data acquisition system. The sensor data shows that metal materials such as stainless steel, lead, aluminum, gold, copper, silver, etc. will rise by 15°C within 1.5-4min, and the heating rate is 3.75-10°C / min. At this time, several groups of solid waste sorting hands can sort out metal materials such as stainless steel, lead, aluminum, gold, copper, silver, etc., and move them to the secondary conveyor belt for conveying metal materials. The auxiliary conveyor belt then transports the metal material to the metal material collection room.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Under the condition that the room temperature is about 27°C, the mixed solid waste first passes through a low-temperature thermostatic chamber with a temperature of 27°C for 5 minutes, and the temperature of the mixed solid waste is completely kept at 27°C. At this time, the main conveyor belt transports the mixed solid waste to a high-temperature room with a temperature of 55 °C, and collects data through a PC-based data acquisition system. The sensor data shows that inorganic materials such as glass, soil, concrete, etc. will rise by 15°C within 5.5-8.5min, and the heating rate will be 1.76-2.72°C / min. At this time, several groups of solid waste sorting hands can sort inorganic materials such as glass, soil, concrete, etc., and move them to the secondary conveyor belt for transporting inorganic materials. The auxiliary conveyor belt then transports the inorganic material to the inorganic material collection chamber.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Under the condition that the room temperature is about 27°C, the mixed solid waste first passes through a low-temperature thermostatic chamber with a temperature of 27°C for 5 minutes, and the temperature of the mixed solid waste is completely kept at 27°C. At this time, the main conveyor belt transports the mixed solid waste to a high-temperature room with a temperature of 55 °C, and collects data through a PC-based data acquisition system. The sensor data shows that organic polymer materials such as rubber, [polymer] polypropylene, and epoxy resin rise by 15°C within 10-14min, and the heating rate is 1.07-1.5°C / min. At this time, several groups of solid waste sorting hands can sort out organic polymer materials such as rubber, [macromolecule] polypropylene, epoxy resin, etc., and move them to the secondary conveyor belt for conveying organic polymer materials. The secondary conveyor belt then transports the organic polymer material to the organic polymer material coll...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com