IP data packet identification method and gateway
An IP data packet and identification method technology, applied in electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of low IP data packet identification efficiency, long waiting time for data packets, inaccurate port numbers, etc., to reduce computing resources. The effect of consumption, high accuracy and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
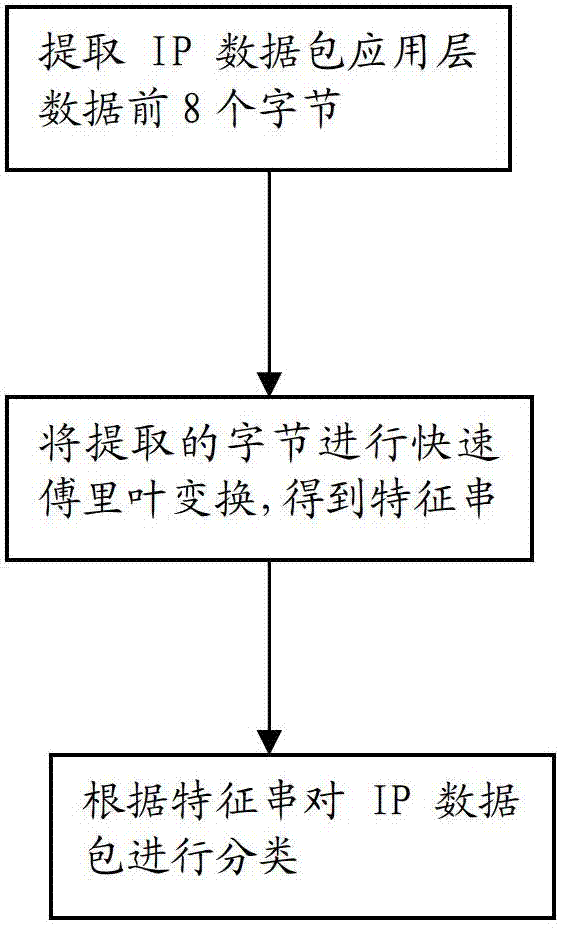
[0051] Such as figure 2 As shown, the IP data packet identification method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0052] Step 1: Extract the first 8 bytes of the application layer data of the IP packet; the 8 bytes are 71.00, 69.00, 84.00., 32.00, 47.00, 112.00, 114.00, and 110.00 in sequence
[0053] Step 2: Perform Fast Fourier Transform on the extracted 8 bytes to obtain the 8-byte frequency domain feature string; the feature string is obtained by fast Fourier transform from the extracted 8 bytes It is composed of 8 bytes corresponding to the above 8 bytes; the 8 bytes corresponding to the frequency obtained by the above 8 bytes are 640.00, 49.45+116.27i, -80.00-38.00i, -1.45+56.26i, -8.00,- 1.45-56.26i, -80.00+38.00i, 49.45-116.26i. The above-mentioned 8 frequency domain bytes constitute a characteristic string.
[0054] Step 3: Use the SVM (Support Vector Machine) algorithm to classify the above-mentioned feature strings to identify the type of IP data packet; thr...
Embodiment 2
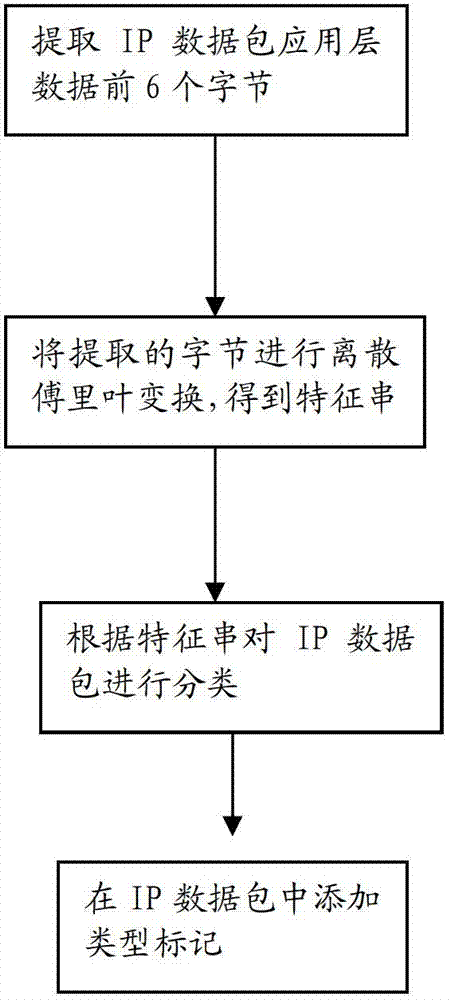
[0062] Such as image 3 As shown, the IP data packet identification method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0063] First: Extract the first 6 bytes of the application layer data of the IP packet; the 6 bytes are 128.00, 107.00, 25.00, 212.00, 0.00, 29.00 in sequence;
[0064] Second: transform the 6 bytes extracted from the time domain signal into the corresponding 6 bytes in the frequency domain signal by discrete Fourier transform; the 6 bytes are 501.00, -28.00-89.20 in turn i, 259.00-15.90i, -195.00, 259.50+45.90i, -28.00+89.20i. 6 bytes in the frequency domain constitute the characteristic string in the frequency domain;
[0065] The frequency characteristic string obtained by calculation can also be calculated by fast Fourier transform; fast Fourier transform is a fast algorithm of discrete Fourier transform, which has the characteristics of small amount of calculation, high efficiency and accuracy;
[0066] Third: Use NB (Naive Bayes) Bayesian classification ...
Embodiment I
[0071] The IP data packet identification method in this embodiment is:
[0072] Extract the first 4 bytes of the application layer data of the IP packet; the 4 bytes are 36.00, 2.00, 2.00, 43.00 in sequence. The extracted 4 bytes are subjected to fast Fourier transform to obtain the 4 bytes The corresponding 4 bytes of the frequency domain are 83.00, 34.00+41.00i, -7.00, 34.00-41.00i, and the 4 bytes are converted into frequency domain signals to obtain the characteristic string of the frequency domain; using RART (Partial Decision Tree) Part of the decision tree algorithm classifies the above-mentioned characteristic strings to identify the type of IP data packets; the IP data packets described in this embodiment belong to RTSP application type data packets. According to the classification of the IP data packet, the type mark is added to the classified IP data packet, and the type mark corresponding to each application type is different. Using 4 byte pairs as the original data ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com