Identification method for rice leaves contaminated by heavy metals based on near infrared spectroscopy
A near-infrared spectroscopy and heavy metal technology is applied in the field of heavy metal pollution detection of plants, which can solve the problems of high instrument requirements, high detection cost, cumbersome preprocessing operation, etc., and achieves the effects of high identification accuracy, low cost, and non-destructive detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] 1. Build a model
[0037] (1) Set the mercury content to 1.5mg·Kg respectively -1 , containing cadmium 1.0mg·Kg -1 , lead 500mg·Kg -1 1. Four soils that do not contain heavy metals, and rice is planted on the four soils; rice is selected from 11 seeds of Zhonghua, and after 15 days of raising seedlings, transplant the seedlings in the three soils with heavy metal content, apply enough base fertilizer, irrigate in time, and regularly Apply nitrogen and compound fertilizers.
[0038] (2) When the rice is at the five-leaf stage, 20 rice leaf samples are collected from four soils as a calibration set, and the Nicolet Nexus870 (Thermo Corporation USA) Fourier transform near-infrared spectrometer is used to transmit to the back of the rice leaf samples The range of wave number is 4000~12000cm -1 near-infrared spectrum, and collect the diffuse reflectance spectrum information of all rice leaf samples; the near-infrared spectrometer sets the number of scans to 32 times, and...
Embodiment 2
[0059] 1. Model establishment
[0060] (1)~(2) are with embodiment 1;
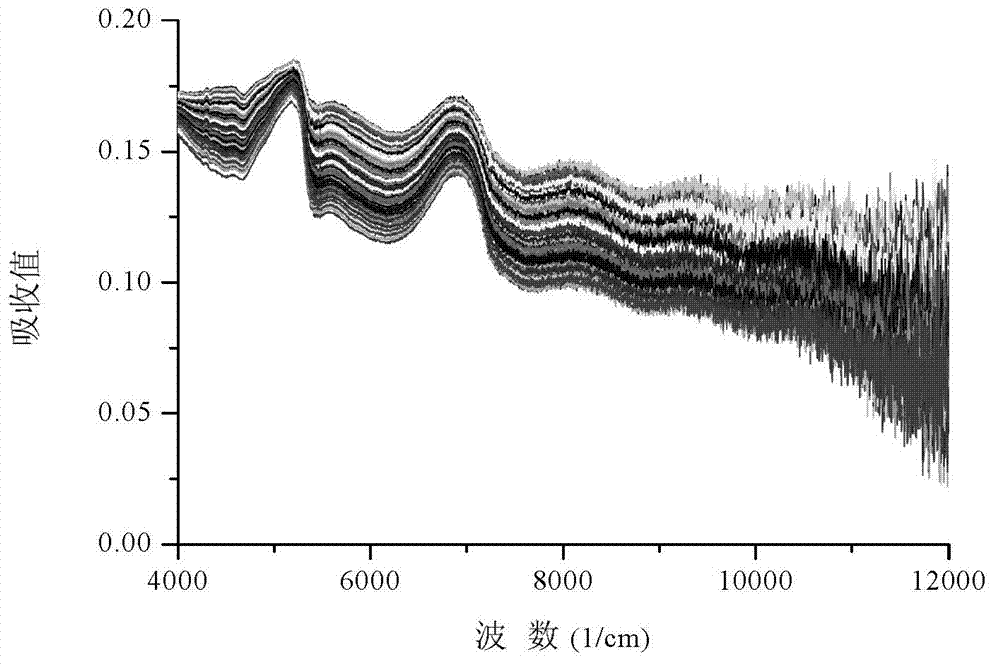
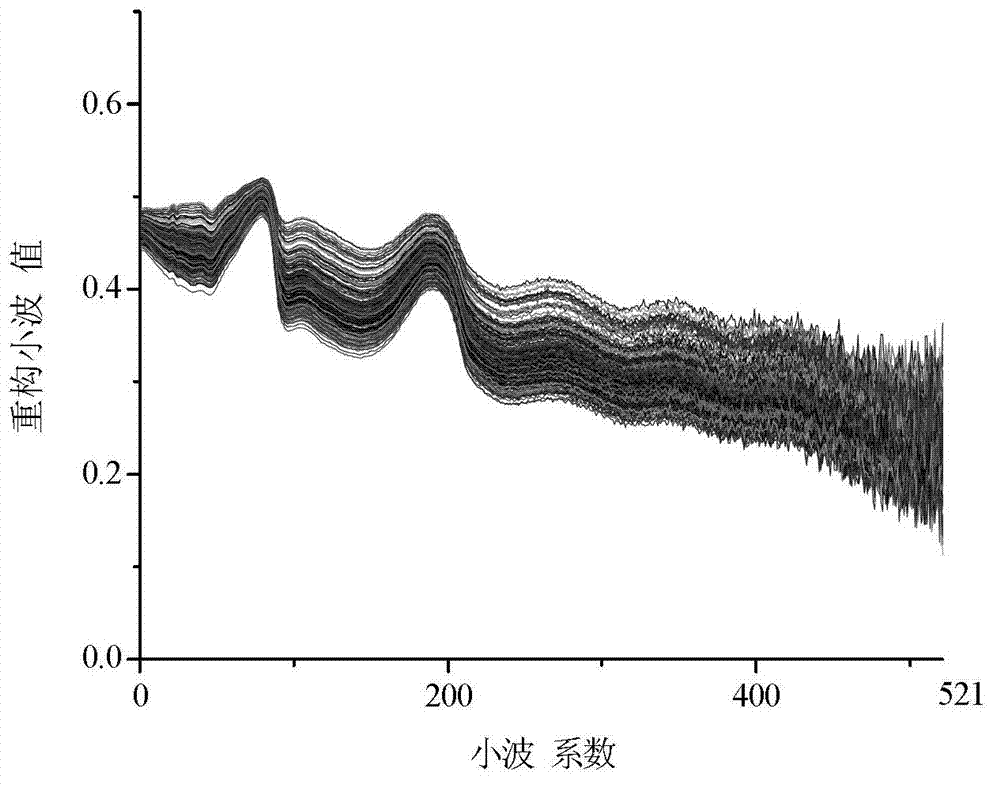
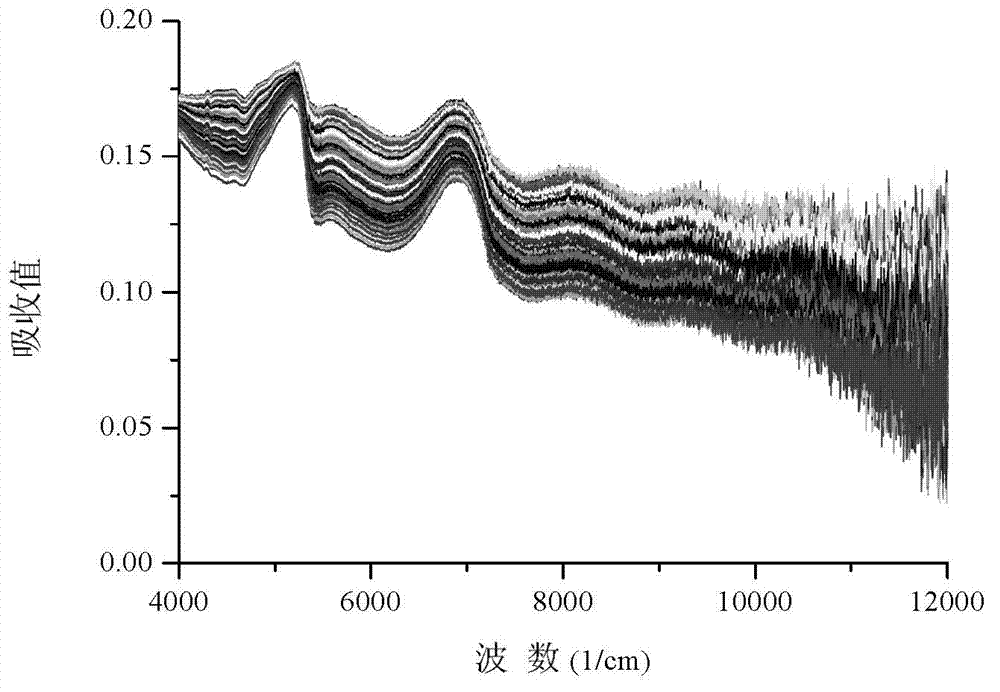
[0061] (3) Use the wavelet function Daubechies 2 (Db2), set the decomposition level to 2, process the diffuse reflectance spectra of all the collected rice samples, and obtain the corresponding 1039 wavelet features. The wavelet eigenvalues of the rice samples are shown in Table 4; The original diffuse reflectance spectra and wavelet reconstructed diffuse reflectance spectra of all rice sample leaves are as follows: image 3 , Figure 4 It can be seen from the figure that the processed spectrogram retains the basic spectral information.
[0062] (4) Take the wavelet feature of the rice leaf sample obtained in step (3) as input, and take the leaf pollution type setting value corresponding to the rice leaf sample as the output, and set four pollution types: mercury pollution, cadmium pollution, lead pollution and normal The set values of output are 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively, and the BP neural network mo...
Embodiment 3
[0079] 1. Build a model
[0080] (1)~(2) steps are with embodiment 1;
[0081] (3) Use the wavelet function Daubechies 2 (Db2), set the decomposition level to 4, process the diffuse reflectance spectrum information of all collected rice leaf samples, and obtain the corresponding 262 wavelet features; the original diffuse reflectance spectra of all rice leaf samples Figure and wavelet reconstructed diffuse reflectance spectrum as shown in Figure 5 , Image 6 As shown in the figure, it can be seen from the figure that the processed spectrogram retains the basic spectral information;
[0082] (4) Take the wavelet feature of the rice leaf sample obtained in step (3) as input, and take the leaf pollution type setting value corresponding to the rice leaf sample as the output, and set four pollution types: mercury pollution, cadmium pollution, lead pollution and normal The set values of output are 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively, and the RBF neural network model is established.
[008...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com