Chloroprene 'activity'/controllable radical polymerization method
A chloroprene and polymerization method technology, applied in the field of polychloroprene, can solve the problems of uncontrollable polymer molecular weight, no re-initiating monomer, obvious tendency of branching and cross-linking, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
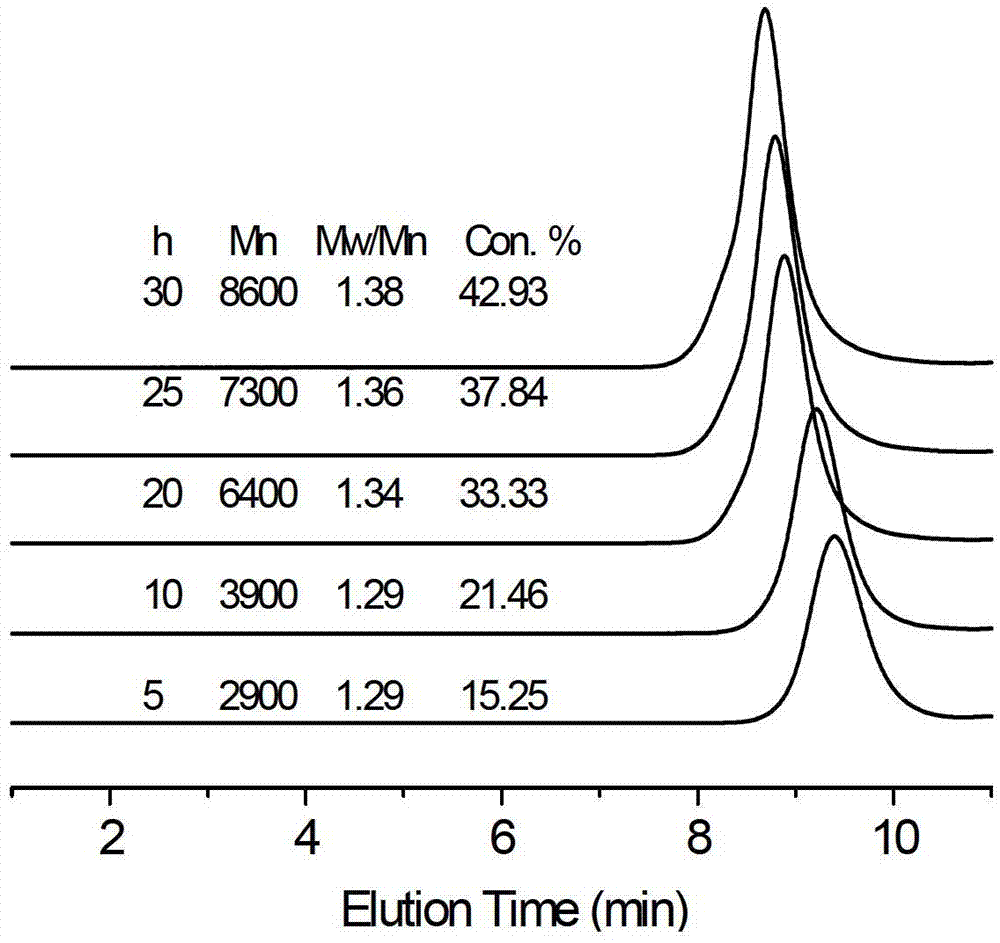
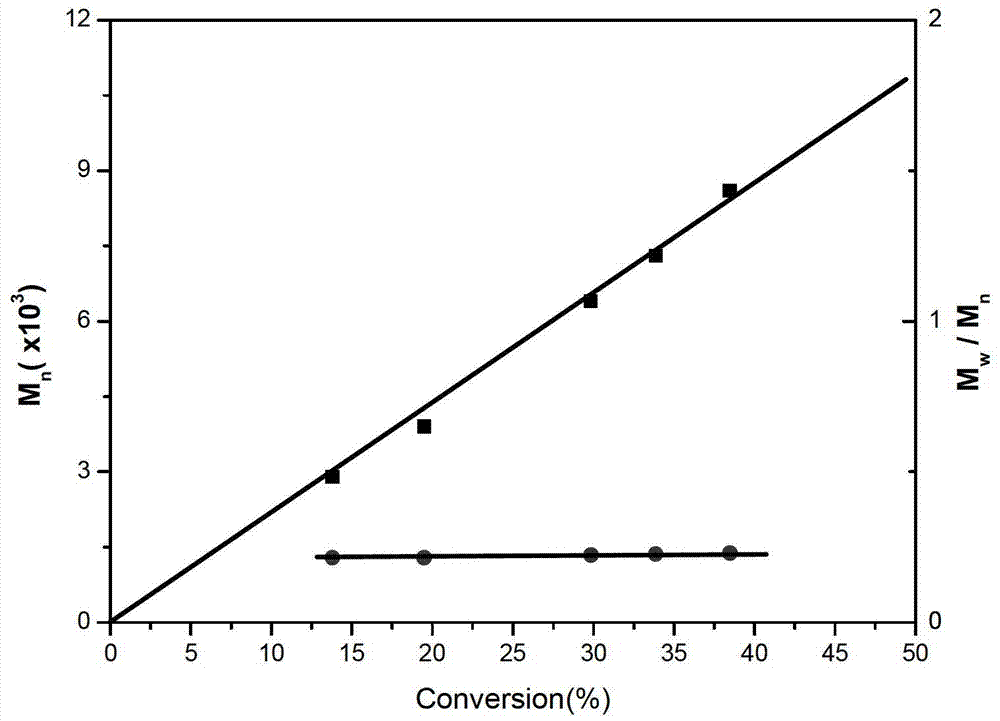
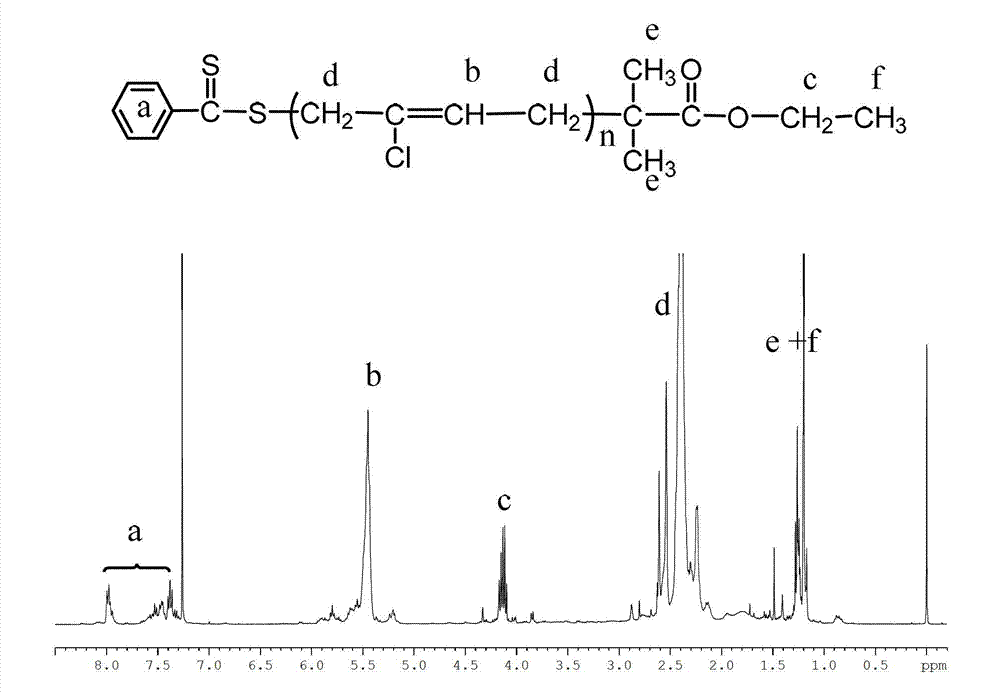
[0029] RAFT reagent (2-ethoxycarbonyl propane-2-dithiobenzoate) is a chain transfer agent, AIBN is an initiator, and the molar ratio of RAFT and AIBN is 4:1. The molar ratio of solvent benzene, monomer chloroprene and chain transfer agent RAFT is 200:1. The above components were sequentially added to a 50 mL round-bottom branched-tube flask, and a magnet was placed; after argon was introduced for 10 minutes, vacuum degassing-argon filling was repeated three times, and the tube was sealed in an oxygen-free atmosphere. The sealed round-bottom branched-tube flask was placed in an oil bath at a constant temperature for the reaction, and the reaction temperature was 60°C, and samples were taken during the reaction. The polymer was precipitated with a large amount of petroleum ether, and dried in a vacuum oven at room temperature to constant weight. Weighing to calculate the monomer conversion rate; GPC to test the relative molecular mass and molecular weight distribution of the po...
Embodiment 2
[0032] RAFT reagent (2-ethoxycarbonyl propane-2-dithiobenzoate) is a chain transfer agent, AIBN is an initiator, and the molar ratio of RAFT and AIBN is 4:1. The molar ratio of solvent toluene, monomer chloroprene and chain transfer agent RAFT is 400:1. The above components were sequentially added to a 50 mL round-bottom branched-tube flask, and a magnet was placed; after argon was introduced for 10 minutes, vacuum degassing-argon filling was repeated three times, and the tube was sealed in an oxygen-free atmosphere. The sealed round-bottom branched-tube flask was placed in an oil bath at a constant temperature for the reaction, and the reaction temperature was 60°C, and samples were taken during the reaction. The polymer was precipitated with a large amount of petroleum ether, and dried in a vacuum oven at room temperature to constant weight. Weighing, calculating the monomer conversion rate; GPC testing the relative molecular mass and molecular weight distribution of the po...
Embodiment 3
[0034]RAFT reagent (2-ethoxycarbonylpropane-2-dithiobenzoate) is a chain transfer agent, ABVN is an initiator, and the molar ratio of RAFT and ABVN is 4:1. The molar ratio of solvent toluene, monomer chloroprene and chain transfer agent RAFT is 800:1. The above components were sequentially added to a 50 mL round-bottom branched-tube flask, and a magnet was placed; after argon was introduced for 10 minutes, vacuum degassing-argon filling was repeated three times, and the tube was sealed in an oxygen-free atmosphere. The sealed round-bottom branched-tube flask was placed in an oil bath at a constant temperature for the reaction, and the reaction temperature was 55°C, and samples were taken during the reaction. The polymer was precipitated with a large amount of petroleum ether, and dried in a vacuum oven at room temperature to constant weight. Weighing, calculating the monomer conversion rate; GPC testing the relative molecular mass and molecular weight distribution of the poly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com