pH-sensitive nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery
一种纳米粒子、敏感性的技术,应用在纳米粒子和其制备领域,达到避免包封率、避免低、好胰岛素释放的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Preparation of Insulin-loaded PLGA / HP55 Nanoparticles
[0030] PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles were prepared by two different methods using HP55 as the pH sensitive substance / polymer. Method A: HP55 was dissolved in an organic phase of acetone and ethanol to form a mixture, which was used as a coating for PLGA nanoparticles to form PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles. Method B: Both PLGA and HP55 were dissolved in the organic phase dichloromethane and acetone to form a mixture which was directly used to form PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles.
[0031] Table 1
[0032]
[0033]As shown in Table 1, the encapsulation efficiency of nanoparticles in method B is higher than that in method A. The reasons for the lower encapsulation efficiency in method A are: (i) during prolonged magnetic stirring, insulin easily diffuses into the outer aqueous phase, and (ii) part of the HP55 dissolves during water washing, resulting in the protection of insulin The layer becomes thinner. In addition, the nanoparti...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Characterization of insulin-loaded PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles
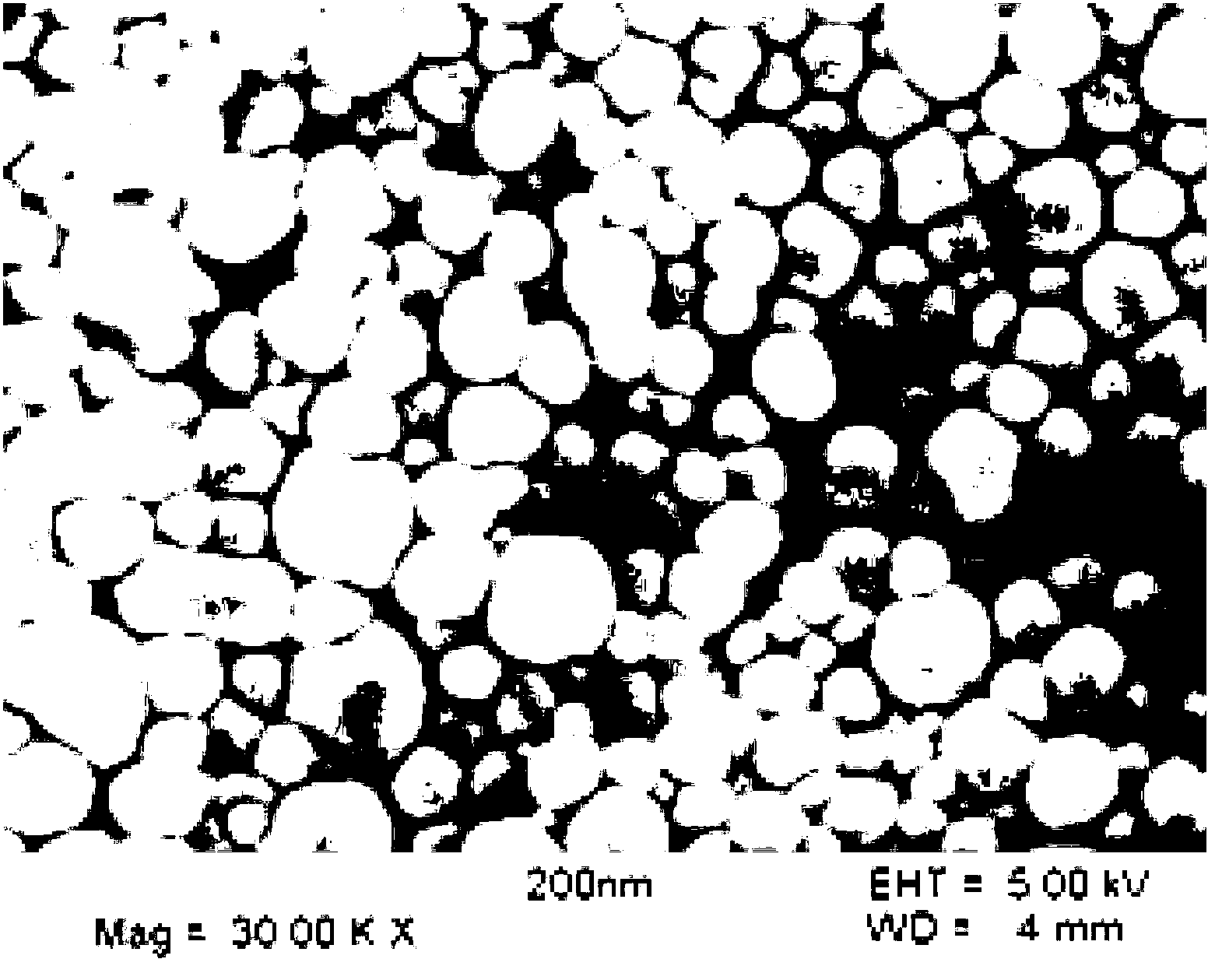
[0037] figure 1 The SEM images shown indicate that the insulin-loaded PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles have a white fine powder morphology. The PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles prepared from Method B in Example 1 had an average particle size of 181.9±19.0 nm with a PDI of 0.093±0.031. The insulin encapsulation efficiency was 90.85±1.09%. The insulin-loaded PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles prepared by the double emulsion solvent evaporation method used in the method of the present invention have high encapsulation efficiency and smaller nanometer size.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Insulin release study in vitro
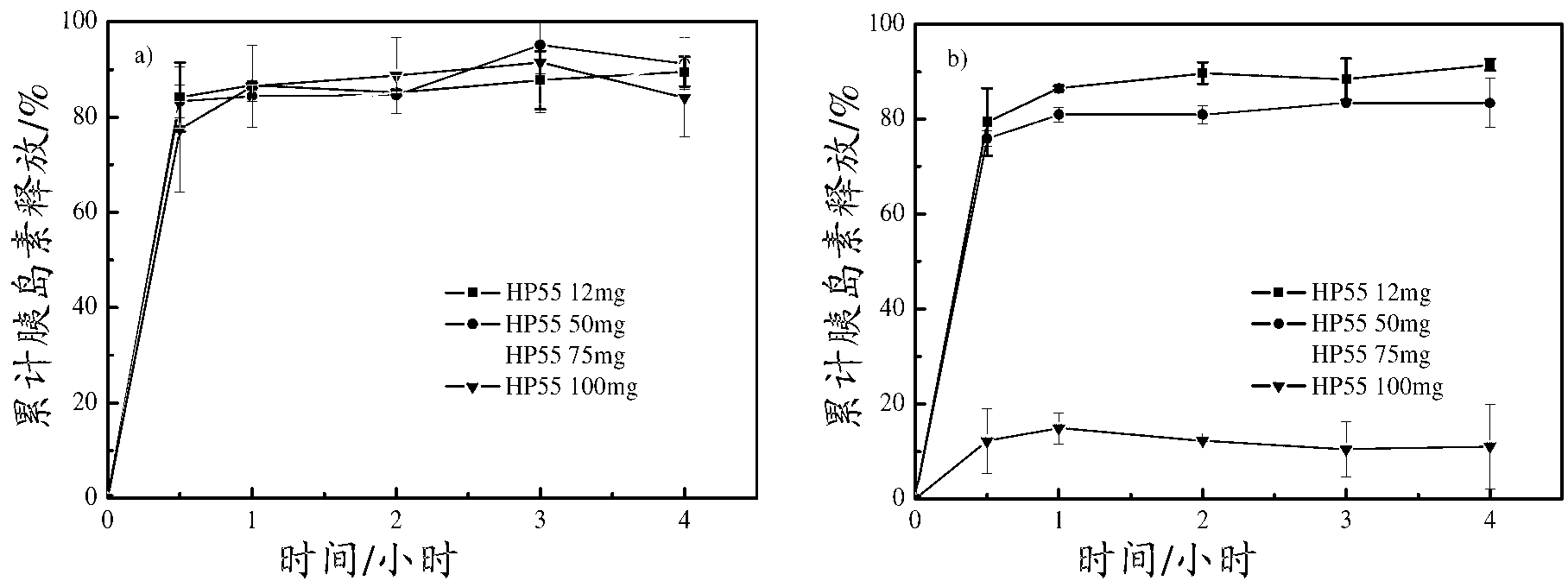
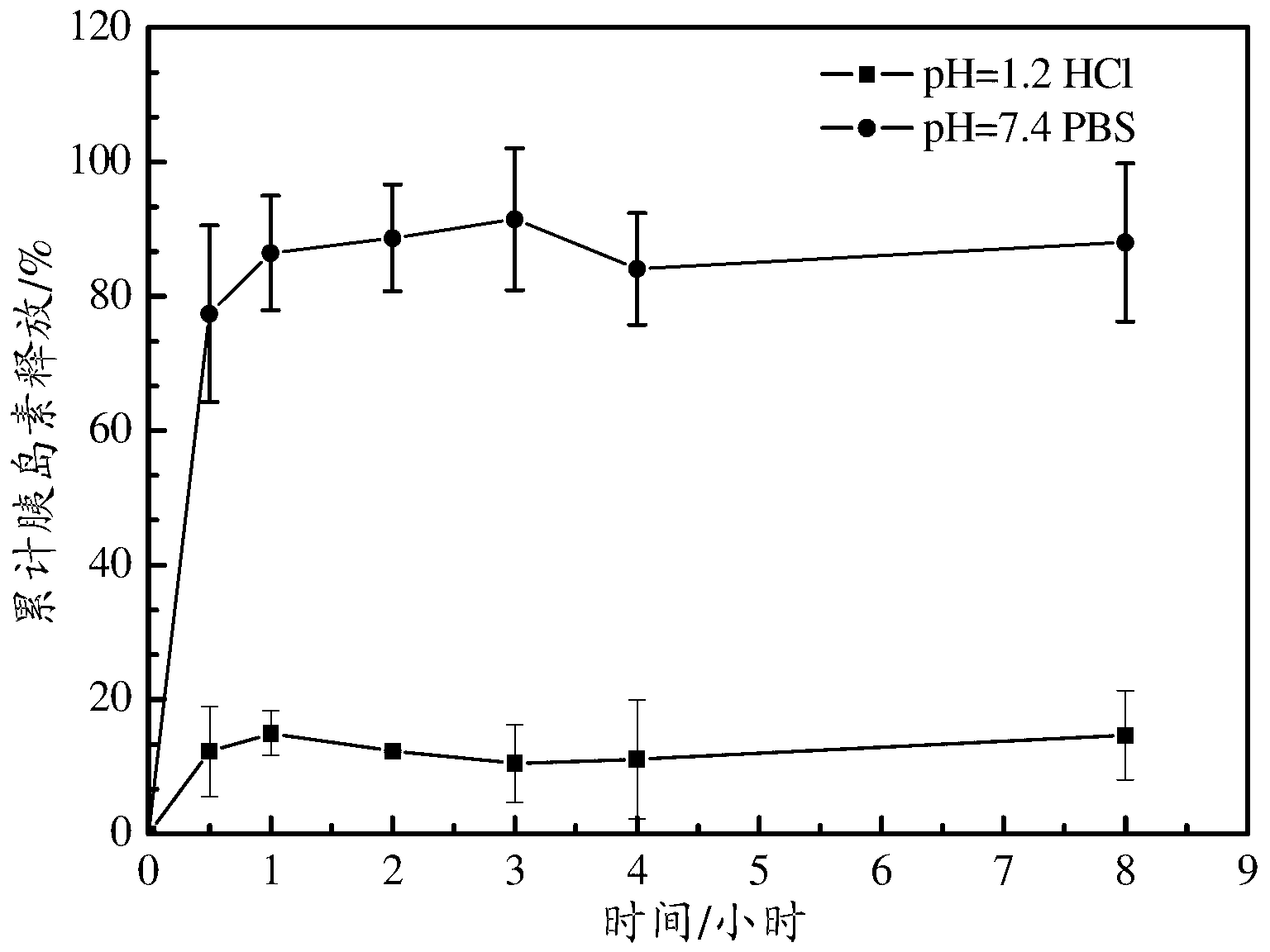
[0040] The amount of HP55 coated on PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles will affect the pH sensitivity of PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles. Therefore, an in vitro insulin release study was performed to determine the effect of different amounts of HP55 on the pH sensitivity of PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles. The effect of different amounts of HP55 on insulin release properties was evaluated in simulated gastrointestinal fluid. figure 2 In vitro release rates of insulin from nanoparticles with different amounts of HP55 are shown in solutions with pH=7.4 PBS (a) and pH=1.2 HCl (b), respectively.
[0041] PLGA / HP55 nanoparticles with different amounts of HP55 released more than 75% of insulin at pH = 7.4 PBS. When both PLGA and HP55 were dissolved in an organic solvent to capture insulin, the interaction between HP55 and insulin was stronger than that between PLGA and insulin; most insulin molecules tended to disperse in HP55 rather than PLGA. In the case of pH=7.4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com