Grain clear beverage and production method thereof
A technology for grains and beverages, applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of strong sourness, insufficient dissolution of flavor substances, and inconvenient drinking.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0148] Step 1: Get 100 kilograms of rice (commercially available indica rice) after cleaning up and pulverize, cross 10 mesh sieves, obtain 80 kilograms of powder,
[0149] spare;
[0150] Step 2: Add 80 kg of water to the above powder, soak at 30°C for 60 minutes to fully swell the material, and drain the water.
[0151] Step 3: steam the material obtained in step 2 for 60 minutes at 80° C. to fully ripen the starch inside the rice.
[0152] Step 4: Roast the above-mentioned steamed materials. First, bake them at a high temperature of 150°C for 9 minutes until the raw materials are puffed and crispy, and then bake them at a low temperature of 60°C for 20 minutes until they are golden yellow and have a burnt grain smell.
[0153] Step 5: Weighing 3 kg of green tea leaves, 3 kg of licorice, 2 kg of lotus seed core, and 0.02 kg of coptis, roasting at 100° C. for 25 minutes to obtain auxiliary materials.
[0154] Step 6: Mix the roasted raw materials and auxiliary materials, ad...
Embodiment 2
[0162] Step 1: Take 100 kilograms of rice (commercially available indica rice) after cleaning up and pulverize, pass through a 10-mesh sieve to obtain 80 kilograms of powder, and set aside;
[0163] Step 2: Add 80 kg of water to the above powder, soak at 30°C for 60 minutes to fully swell the material, and drain the water.
[0164] Step 3: steam the material obtained in step 2 for 60 minutes at 80° C. to fully ripen the starch inside the rice.
[0165] Step 4: Roast the above-mentioned steamed materials. First, bake them at a high temperature of 150°C for 9 minutes until the raw materials are puffed and crispy, and then bake them at a low temperature of 60°C for 20 minutes until they are golden yellow and have a burnt grain smell.
[0166] Step 5: Weighing 3 kg of black tea leaves, 3 kg of licorice, 2 kg of lotus seed core, and 0.02 kg of coptis, roasting at 100° C. for 25 minutes to obtain auxiliary materials.
[0167] Step 6: Mix the roasted raw materials and auxiliary mate...
Embodiment 3
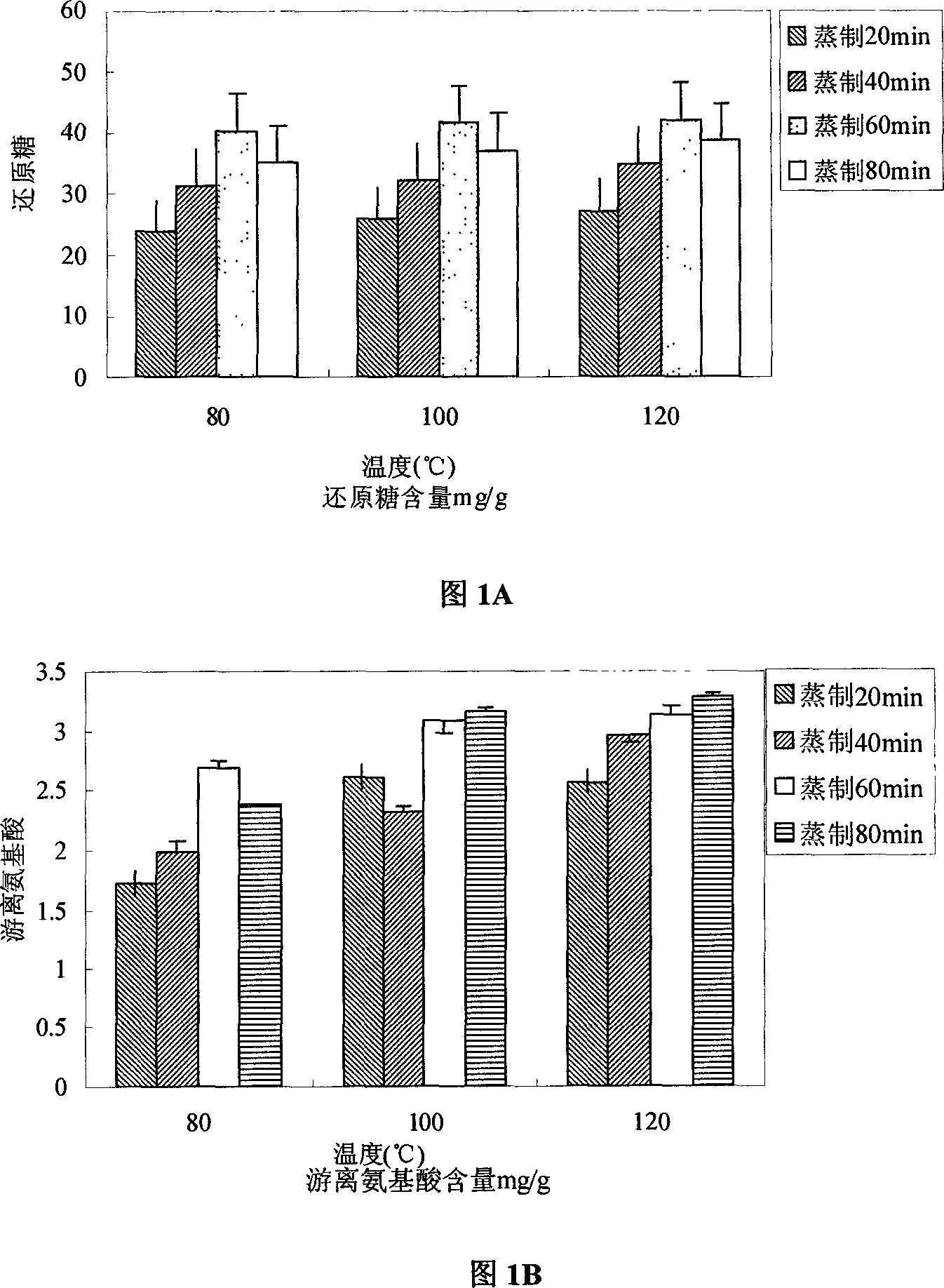
[0172] Embodiment 3: steaming effect example
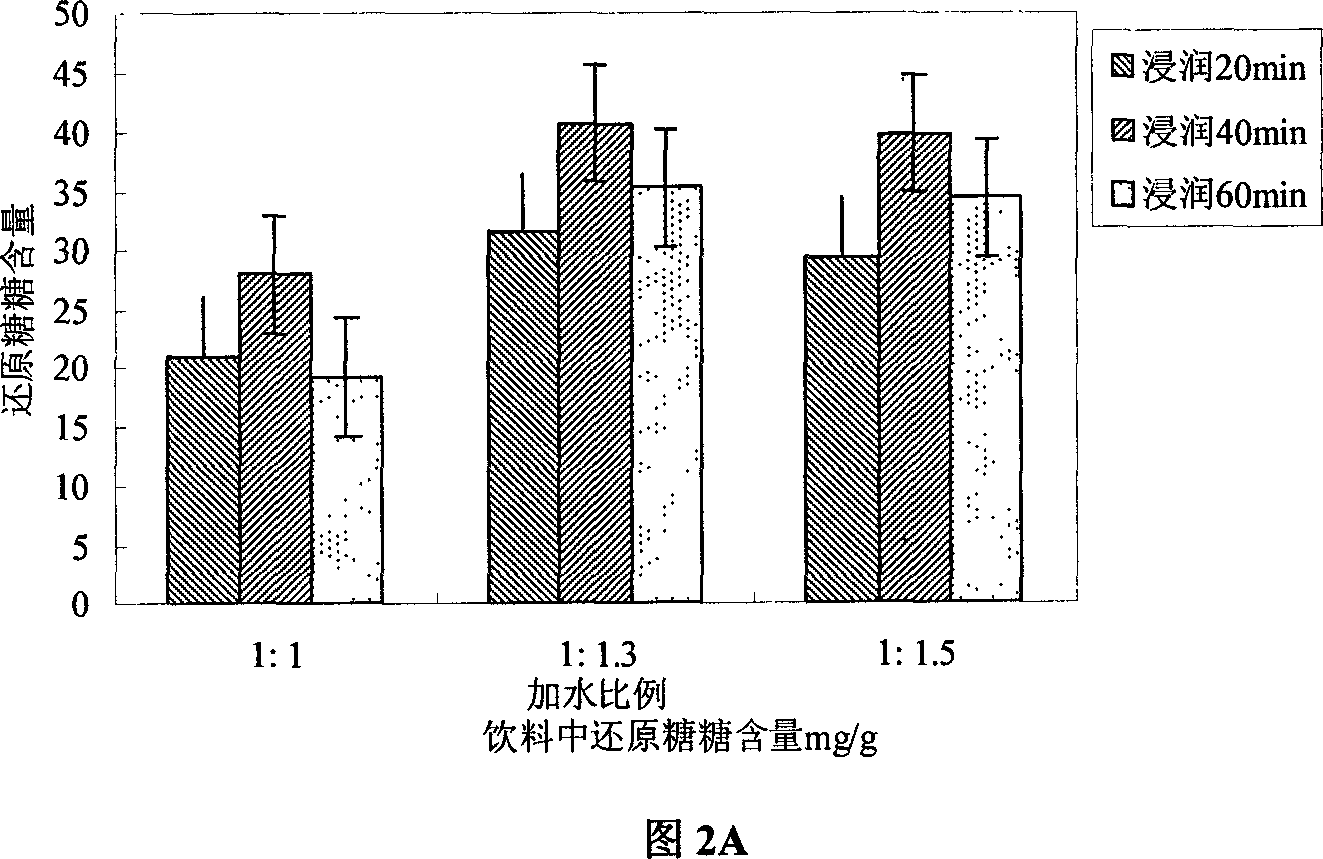
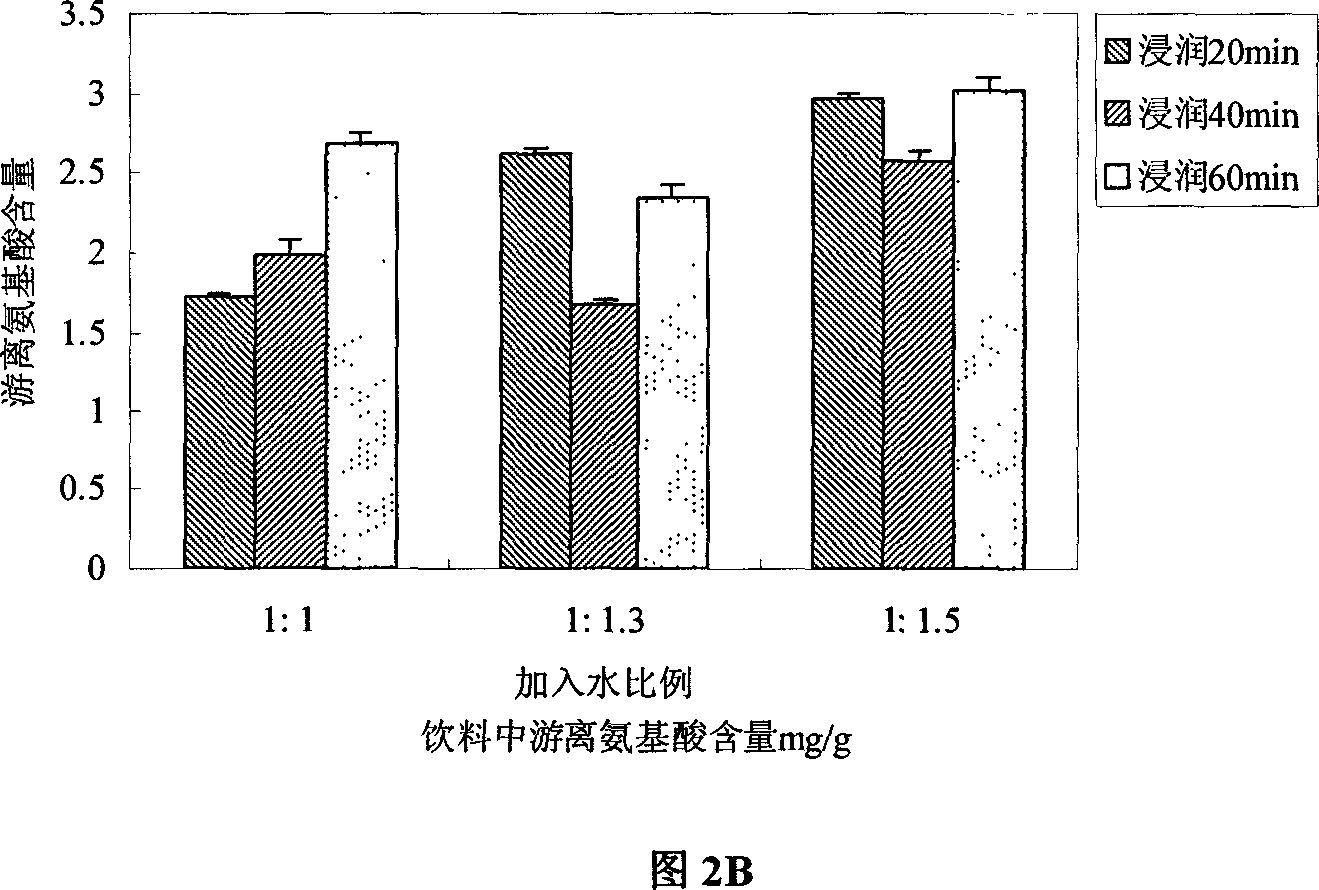
[0173] Follow the steps of Example 1. The grain of this embodiment is broken rice. Pass through a 30-mesh sieve after crushing. This embodiment only tested and compared the effects of steaming temperature and time on the content of reducing sugars and free amino acids in the product. See the effect of the invention figure 1 shown. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that increasing the steaming temperature can increase the reducing sugar content, and steaming the soaked broken rice at a temperature of 100-120°C for 40-60min is beneficial to the precipitation of free amino acids.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com