Cloning method of antibiotics biosynthetic gene cluster based on site-specific recombination
A technology for synthesizing genes and cloning methods, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of difficulty in cloning and biosynthesis of gene clusters, and achieve the effect of simple methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
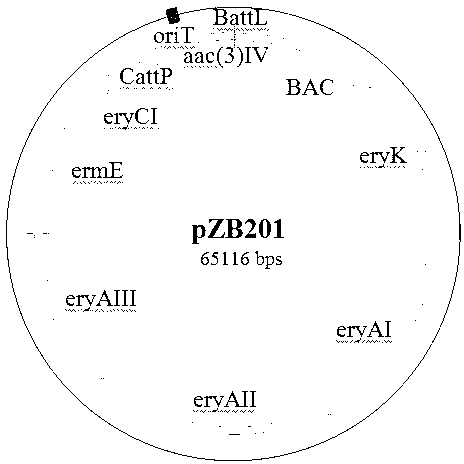
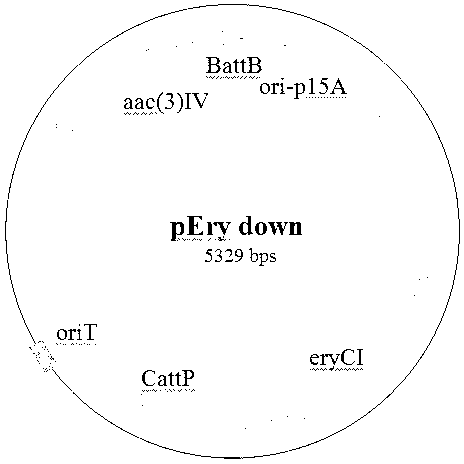
[0027] The present invention takes the cloning of the erythromycin biosynthetic gene cluster in Saccharopolyspora rubrum as an example, specifically introduces the method for cloning the antibiotic synthetic gene cluster, and the detailed operation process is as follows:
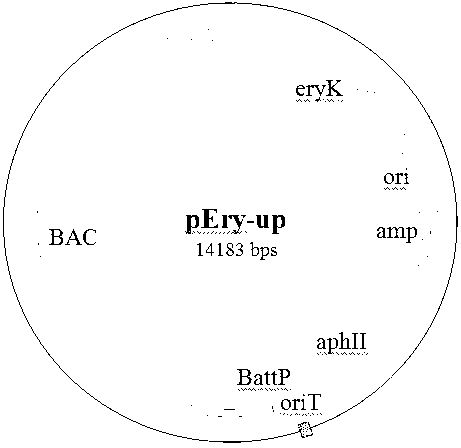
[0028] 1. Construction of the upstream homologous recombination vector pEry-up of the erythromycin gene cluster
[0029] Saccharopolyspora rubrum Saccharopolyspora erythraeThe genome of a is used as a template, and primers SEQ ID No. 2 and primers SEQ ID No. 3 are used to amplify the upstream homology arm fragment of the erythromycin gene cluster. The fragment size is 1993bp, and SEQ ID No. 2 is designed with MunI restriction endonuclease recognition site, make T-A clone of PCR product fragment and pMD19-T vector (TAKARA company) and transform Escherichia coli, pick positive transformant and extract plasmid DNA, select MunI site and XbaI site on T vector in the adjacent direction Plasmid, named T-ery-up. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com