Secondary battery, method for manufacturing same, and thermal adhesive insulating film for secondary battery
A secondary battery and insulating film technology, which is applied in secondary battery, electrolyte battery manufacturing, electrode manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of affecting battery performance and foreign matter in the battery, so as to increase the exposed area, prevent peeling, and improve tolerance sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
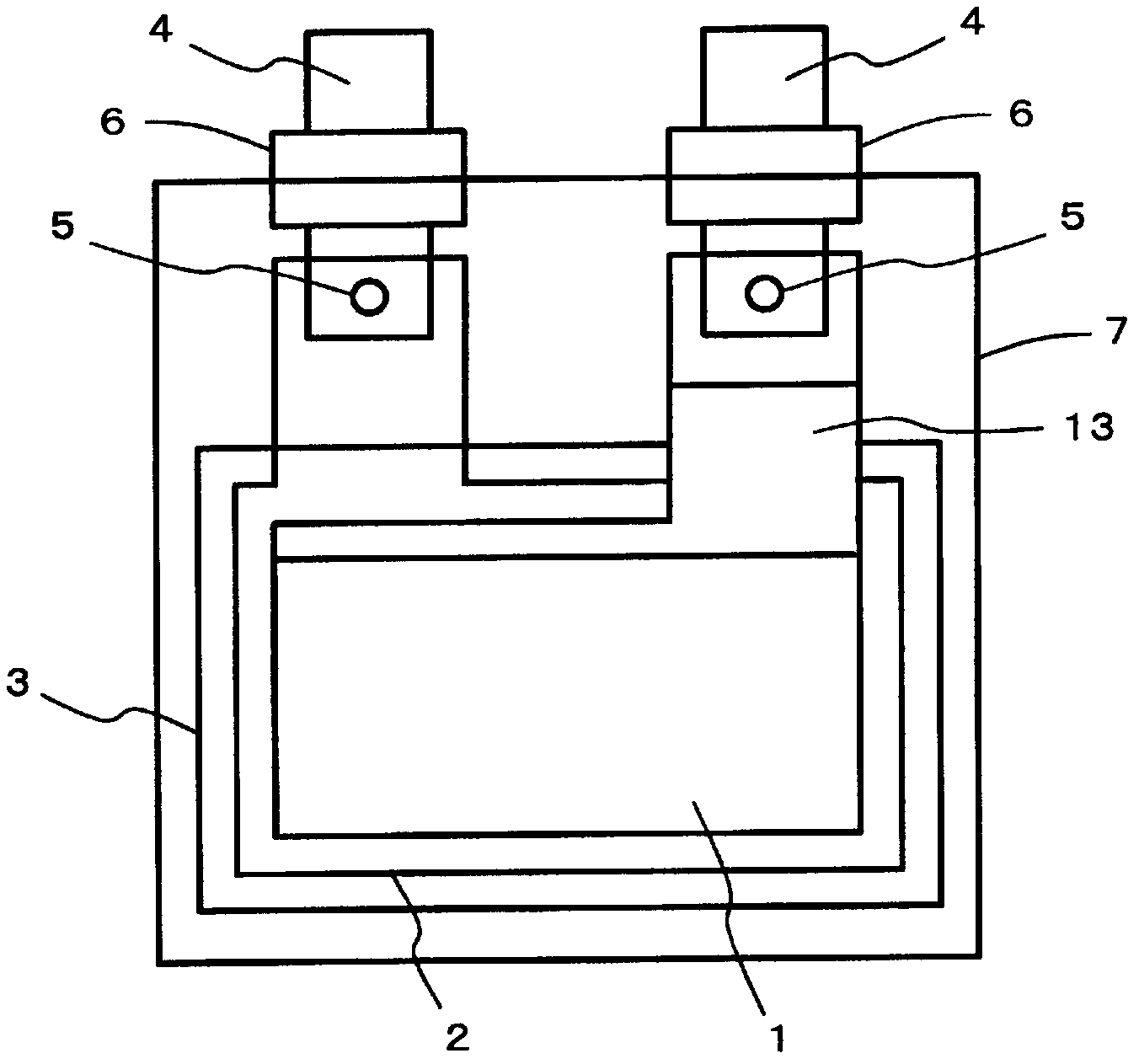
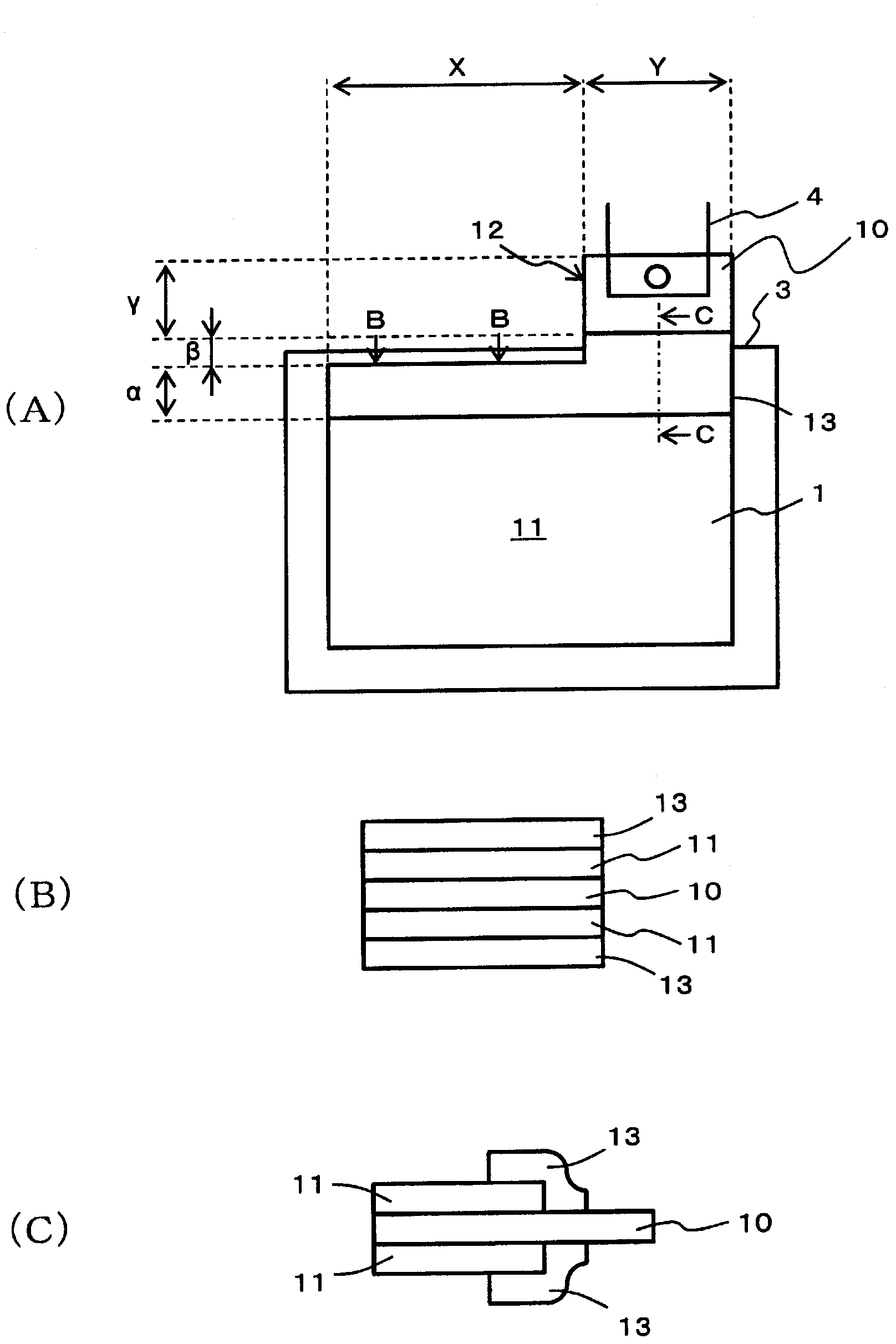
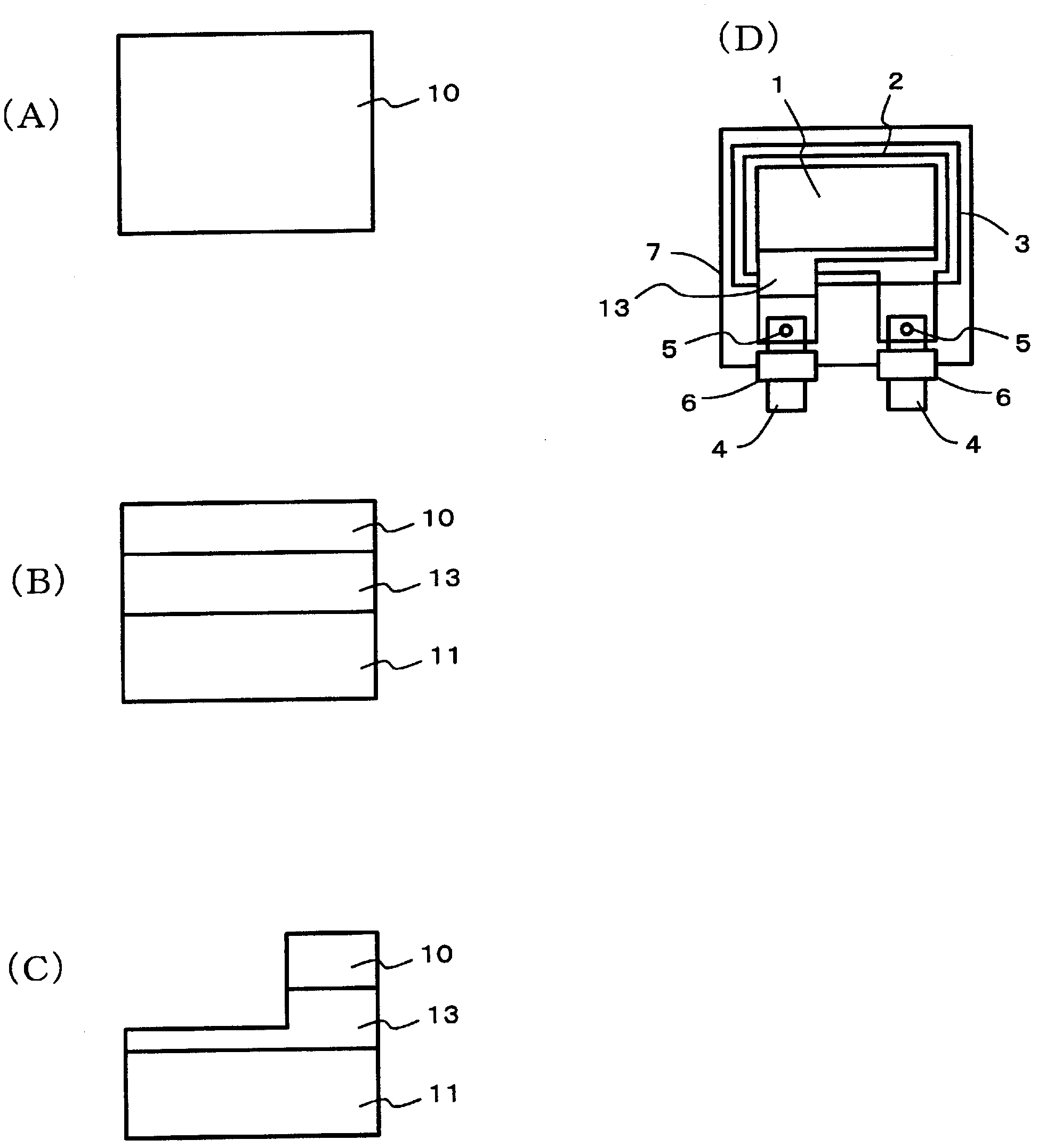
[0046] according to image 3 In the manufacturing process shown, a lithium-ion secondary battery is produced by using rolled aluminum foil for the positive electrode collector foil and electrolytic copper foil for the negative electrode collector foil. For the positive active material, LiMn as the transition metal lithium acid 2 o 4 The main component is polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) as a binder, the positive electrode active material is coated on an aluminum foil, dried, and formed by roll pressing. For the negative electrode active material, graphite is used as the main component, polyvinylidene fluoride is used as the binder, the negative electrode active material is coated on the electrolytic copper foil, dried, and formed by roll pressing. The electrolyte uses a mixture of diethyl carbonate and ethylene carbonate as the solvent and dissolves the electrolyte salt LiPF 6 the resulting liquid. In addition, the portion to which the insulating film was bonded on the alumi...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A lithium-ion secondary battery was manufactured under the same conditions as in Example 1 except that the base layer of the insulating film was changed to block PP whose melting point measured by DSC was 161° C., and the results are listed in Table 1. In addition, the secondary battery obtained under this condition also had sufficient adhesive force to the aluminum foil, and there was no peeling at the time of dicing or degradation of battery performance, but there was a slight tendency to fuse to the weather strip. In addition, this insulating film did not exhibit adhesiveness at normal temperature, and the insulating film also did not exhibit adhesiveness at ordinary temperature in Examples 3 to 9 and Comparative Example 1 shown below.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The adhesive layer of the insulating film was changed to a modified resin with a melting point of 161° C. as measured by DSC, that is, MODIC (registered trademark) P555 manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, and a lithium-ion battery was produced under the same conditions as in Example 1. batteries, and the results are listed in Table 1. In addition, the secondary battery obtained under these conditions did not suffer from peeling at the time of dicing or fusion with the weather strip, and the battery performance did not decrease, but the adhesive force with the aluminum foil tended to be slightly low.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com