Bioactive compositions comprising ficus serum fraction and methods to reduce the appearance of skin hyperpigmentation
A technology of figs and compositions, which is applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, skin care preparations, etc., and can solve problems such as environmental hazards, inability to obtain active substances, and inability to realize the potential of cosmetic preparations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] Preparation of Ficus Serum Fractions
[0050] The method used to isolate compounds from plant material (for example by extraction with a solvent) determines which compounds are isolated. Consistent with the general principle of "like dissolves like", the choice of extraction solvent largely determines the type and amount of compounds obtained by any particular extraction technique. For example, polar compounds are extracted with polar solvents, and non-polar compounds are extracted with non-polar solvents. This results in the isolation of only a narrow range of compounds from the total range of compounds that may be present. Table 1x below summarizes the different compound types typically extracted using common solvents in different polarity ranges.
[0051] Table 1x
[0052] conventional solvent extraction
[0053]
[0054] The Ficus serum fraction of the present invention is not prepared by solvent extraction, but by separating the fresh cell sap found in the...
Embodiment 1
[0184] Derived from fresh leaves of Ficus benghalensis Preparation of bioactive serum fractions
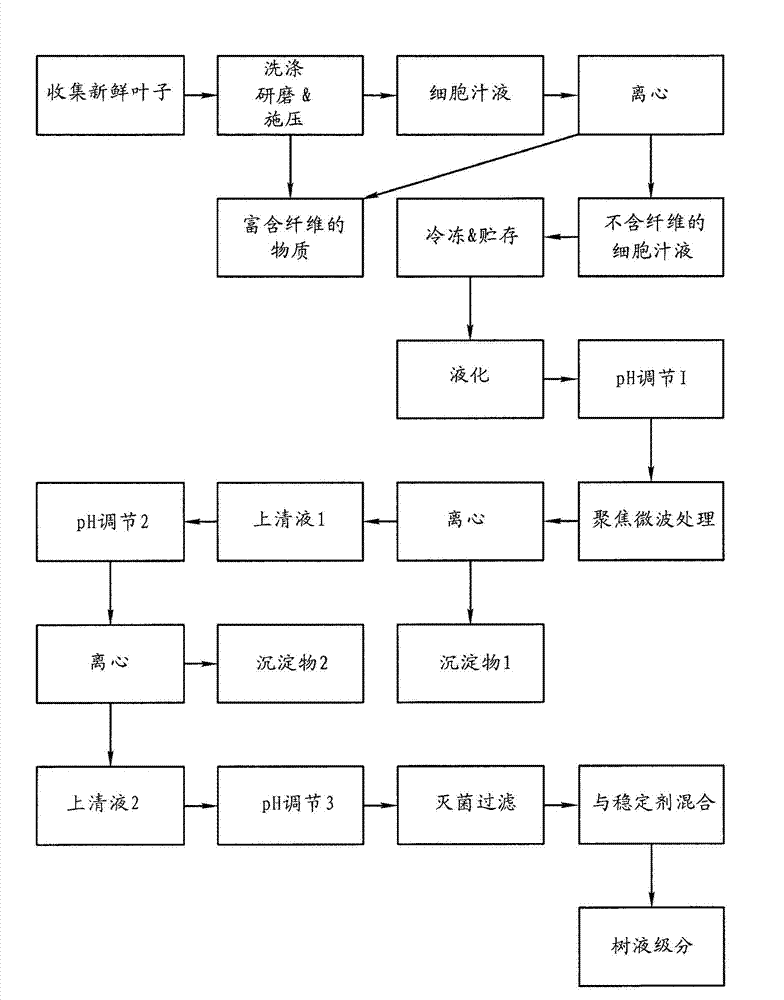
[0185] figure 1 is a schematic diagram showing one embodiment of a method of preparing a biologically active serum fraction from fresh Ficus leaves.
[0186] Sufficient fresh Ficus bengal leaves were collected to obtain approximately 100 kg dry matter. The level of dry matter in fresh leaves was determined to be 32.01%, which required the collection of about 312.4 kg of fresh plant leaves to obtain 100 kg of dry matter. Care is taken to preserve the inherent moisture content of fresh leaves and avoid wilting due to moisture loss. Collection is done in such a way as to avoid or minimize any damage to the collected fresh leaves. All steps are completed in the shortest possible time to minimize the exposure of the fresh leaves to sunlight, heat and other adverse environmental factors.
[0187] The collected leaves were then treated at ≤1 kg / cm before further processing 2 Wat...
Embodiment 2
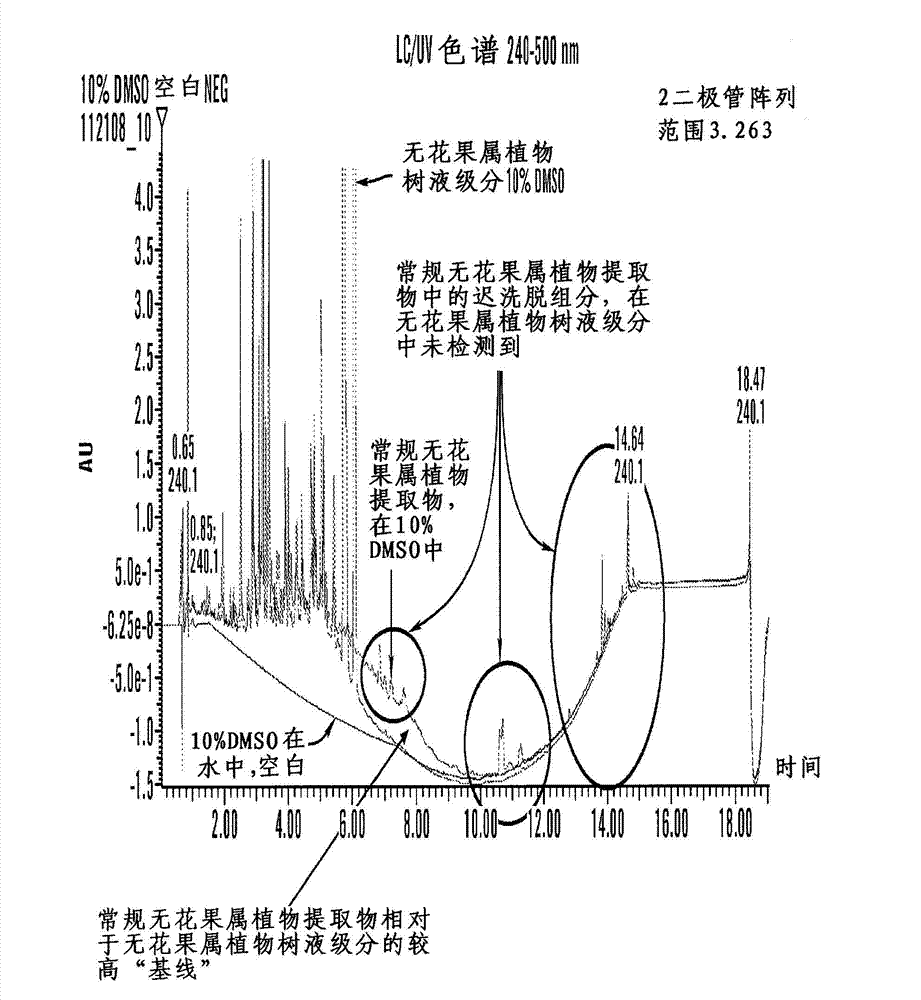
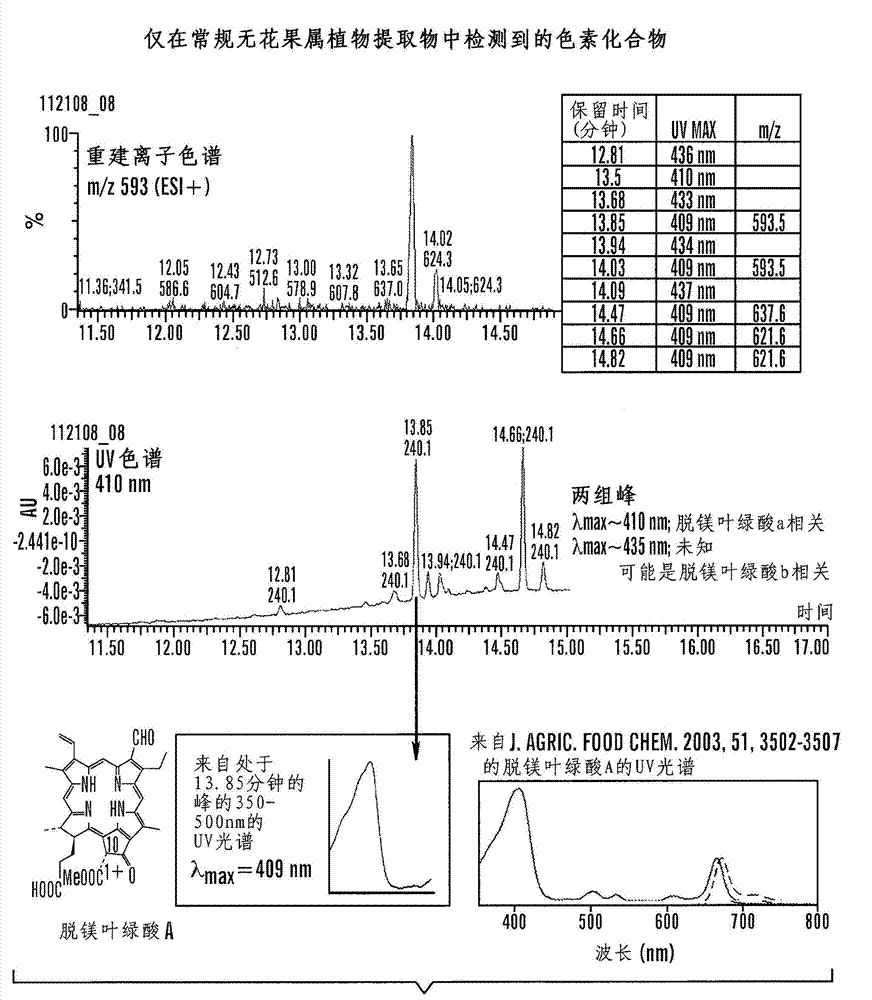
[0223] Obtained from the cell juice of Ficus benghalensis Comparison of properties and in vitro activities of serum fractions
[0224] Fresh Ficus leaves from various locations were collected and processed into cell juice as described in Example 1. The cell juice was frozen and stored at -30°C in airtight 15 liter rectangular HDPE containers. Using the same method as described in Example 1, one or more containers at a time were processed into serum fractions.
[0225] The data presented in Tables 6 and 7 show selected properties of the serum fractions obtained from multiple fractions of the same frozen cell juice source at different periods and from fractions from different frozen cell juice sources and changes in in vitro activity.
[0226] Table 6. Selected properties of sap fractions obtained from cell sap of Ficus bengal
[0227]
[0228] * ) dry matter (%) is reported for the product before the addition of stabilizers
[0229] ** ) in some samples can identif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com