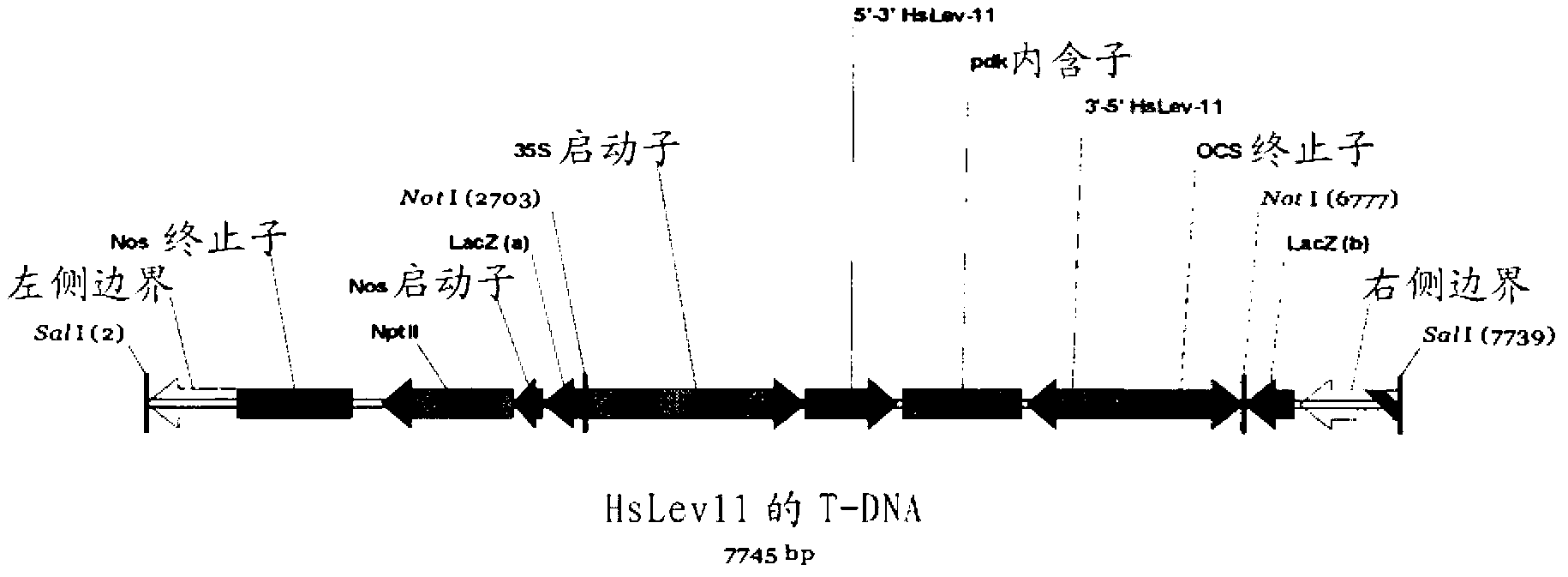
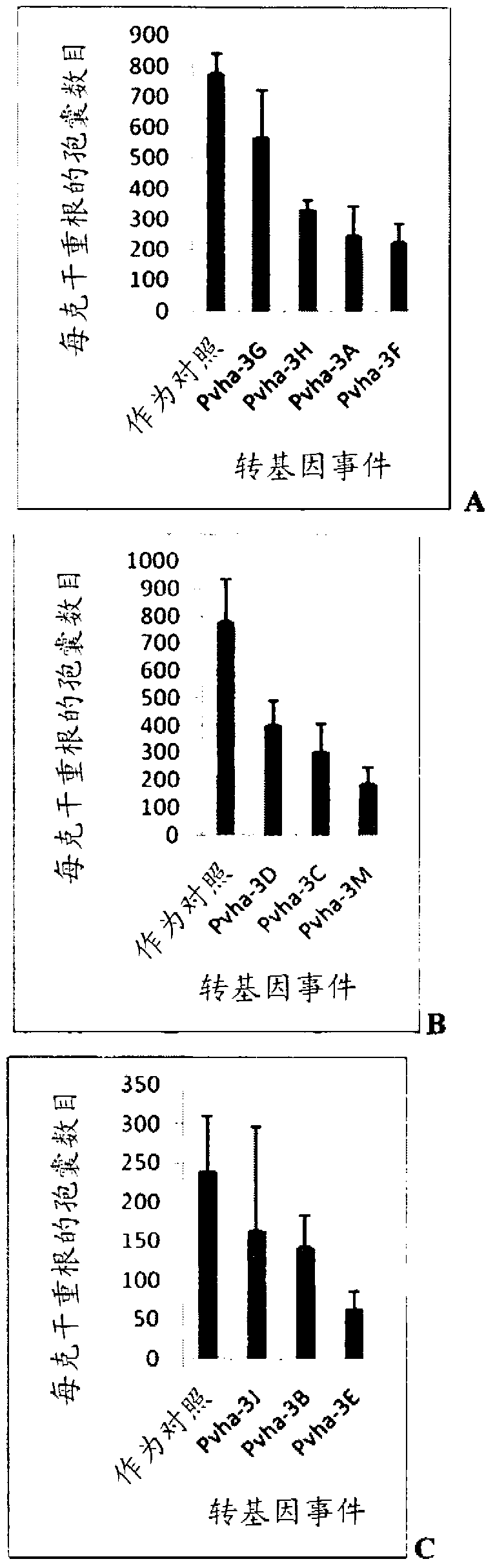
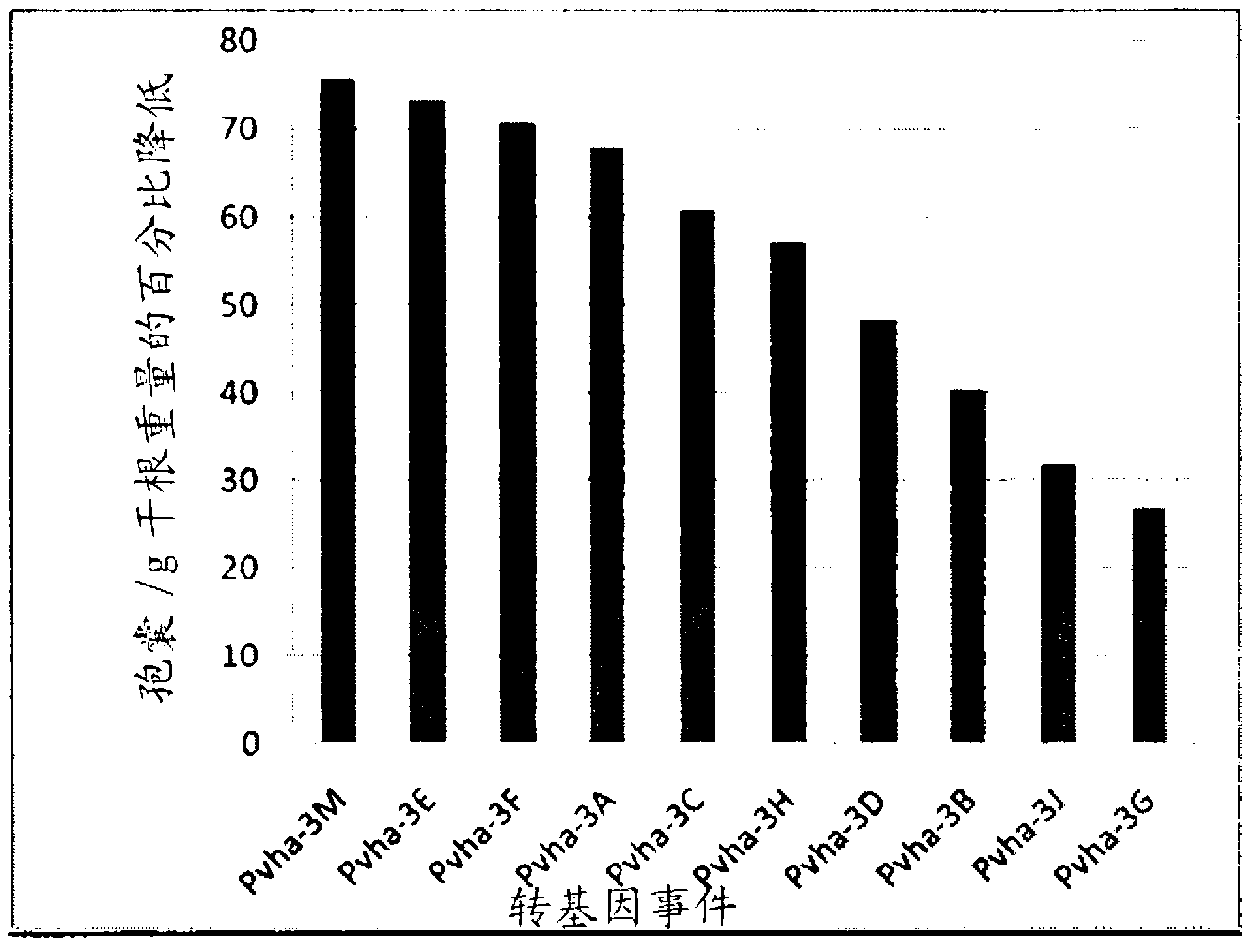
Target genes for control of plant parasitic nematodes and use of same
A technology for parasitic nematodes and plants, applied in the field of target genes and their applications for controlling plant parasitic nematodes, capable of solving problems such as systematic methods for identifying target nematode genes that have not yet been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Identification of target genes
[0117] To identify the target genes of the present invention, RNAi of genes in Wormbase, a comprehensive database of information on C. elegans, was carefully studied. The C. elegans genes identified for the present invention are known to be critical genes for which RNAi disrupts development, growth and viability at different life cycle stages of the nematode. The functions of these genes are expected to be conserved among diverse organisms and especially among nematodes. Bioinformatic studies of the genes indicate that they are specific enough to avoid off-target effects; more specifically, their sequences differ from those of plants, humans and other mammals. Six genes involved in the growth and development of target nematodes were analyzed. They are involved in general metabolic processes, including embryogenesis, developing adults, such that their downregulation leads to RNAi phenotypes in C. elegans that affect growth and develop...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Structure and biology of target genes
[0120] vacuolar H ATPase subunit 3 (vha-3)
[0121] The vha-3 gene encodes an orthologue of subunit c of the membrane-binding domain of the vacuolar proton-translocating ATPase (V-ATPase), which is predicted to carry protons from the cytosol to vha-5, vha-6, vha-7, or unc-32 for transmembrane export (Oka et al., 1998; Oka and Futai 2000; Inoue et al., 2005). VHA-3 is functionally identical to VHA-2, but lacks an intron, and shares an operator with vha-11 (Oka and Futai 2000; Inoue et al., 2005). vha-3 is expressed predominantly in the gastrointestinal and subcutaneous cells of C. elegans and to a lesser extent in excretory cells (Oka and Futai 2000; Inoue et al., 2005). It is highly expressed during embryonic and developmental to adult stages, but much lower during the larval stage. RNAi of vha-3 in C. elegans affects molting, motility, and structure, and in some cases, leads to arrest of larval development and also embryon...
Embodiment 3
[0136] Amplification of target genes from H. beetle and H. soybean
[0137] Amino acid sequences derived from the C. elegans gene sequence were used to interrogate several databases, including the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), Nembase (www.nematode.org) and Nematode.net to obtain six H. beetleensis orthologs of the genes (SEQ ID NO: 1-9). Comparative analysis of the identified orthologs was then performed to confirm identity with genes from other parasitic nematodes, including plant and animal parasites such as B. malayi. The available sequences were further analyzed using ORFFinder after back-translation to identify coding regions. In cases where more than one EST was available, contigs were generated after multiple alignments to obtain the maximum possible length of the coding region. When no EST was available for H. beetleensis in the database, an EST for the closely related H. soybean was used to design primers. These genes are referred to as "...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com