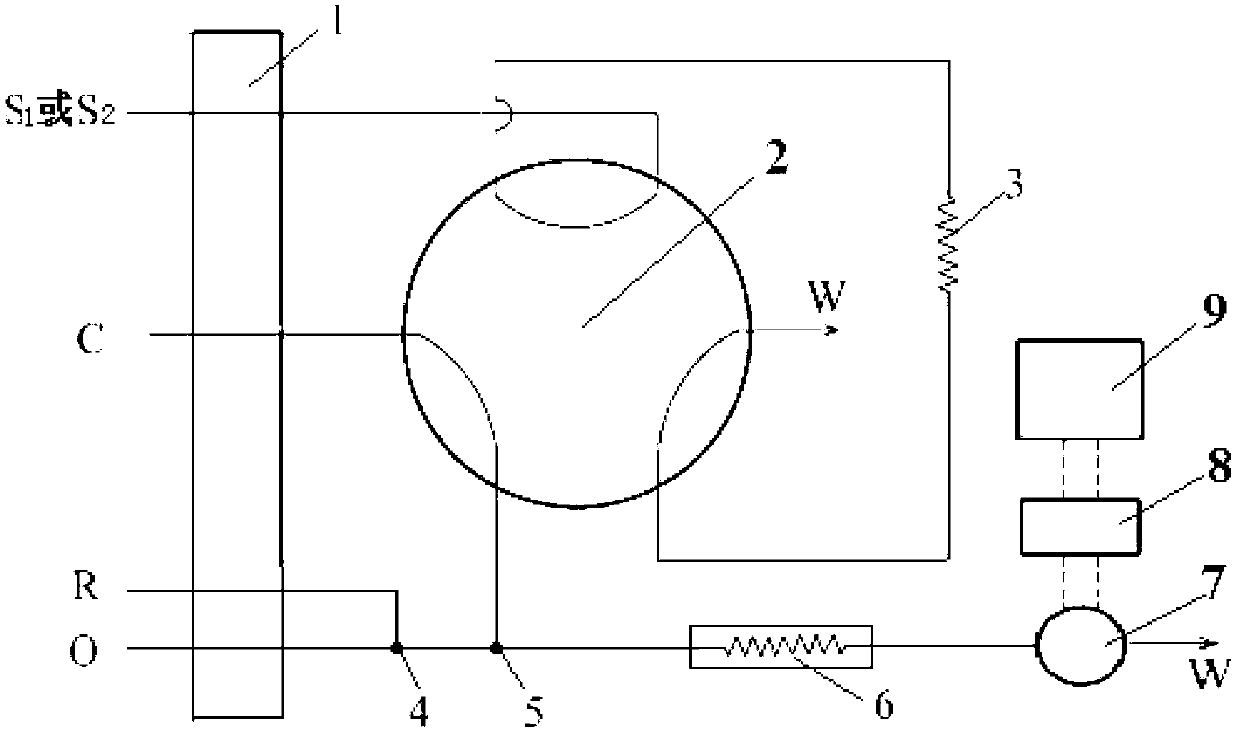
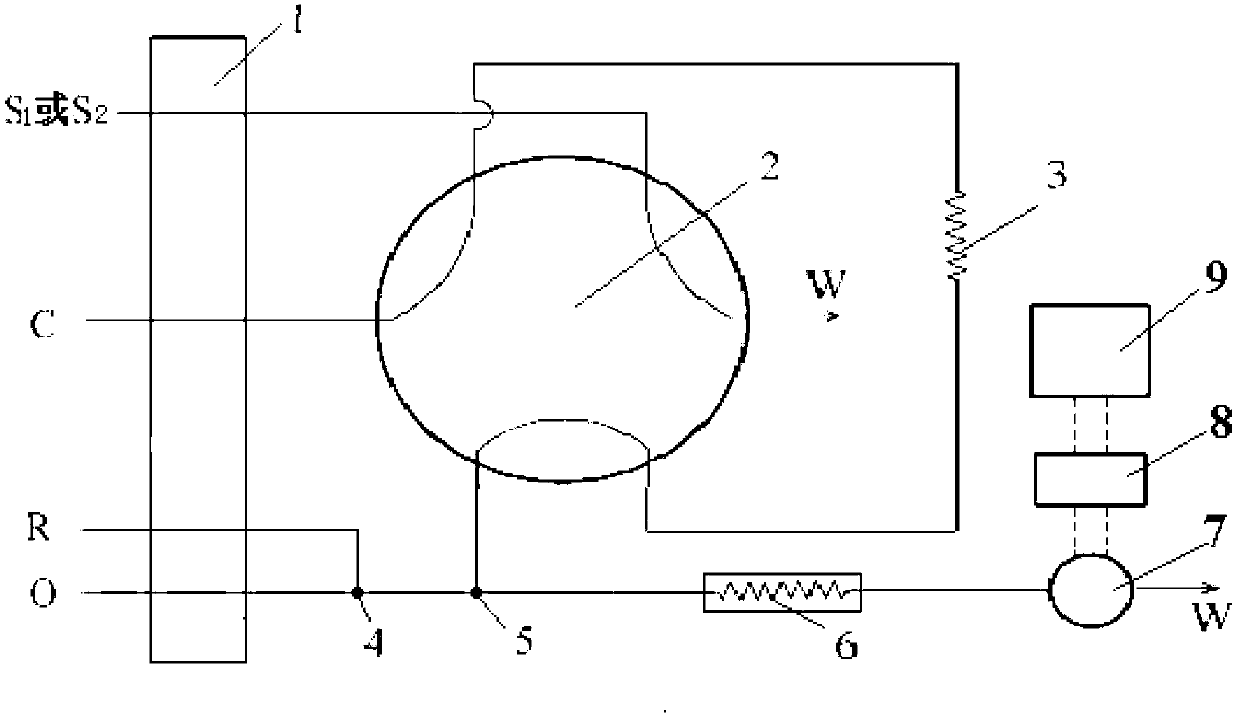
Autoanalysis method of iron content in water sample
An automatic analysis and iron content technology, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions, can solve problems such as slow analysis speed, poor precision, and weak oxidation , to achieve rapid detection, easy on-line monitoring, and high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
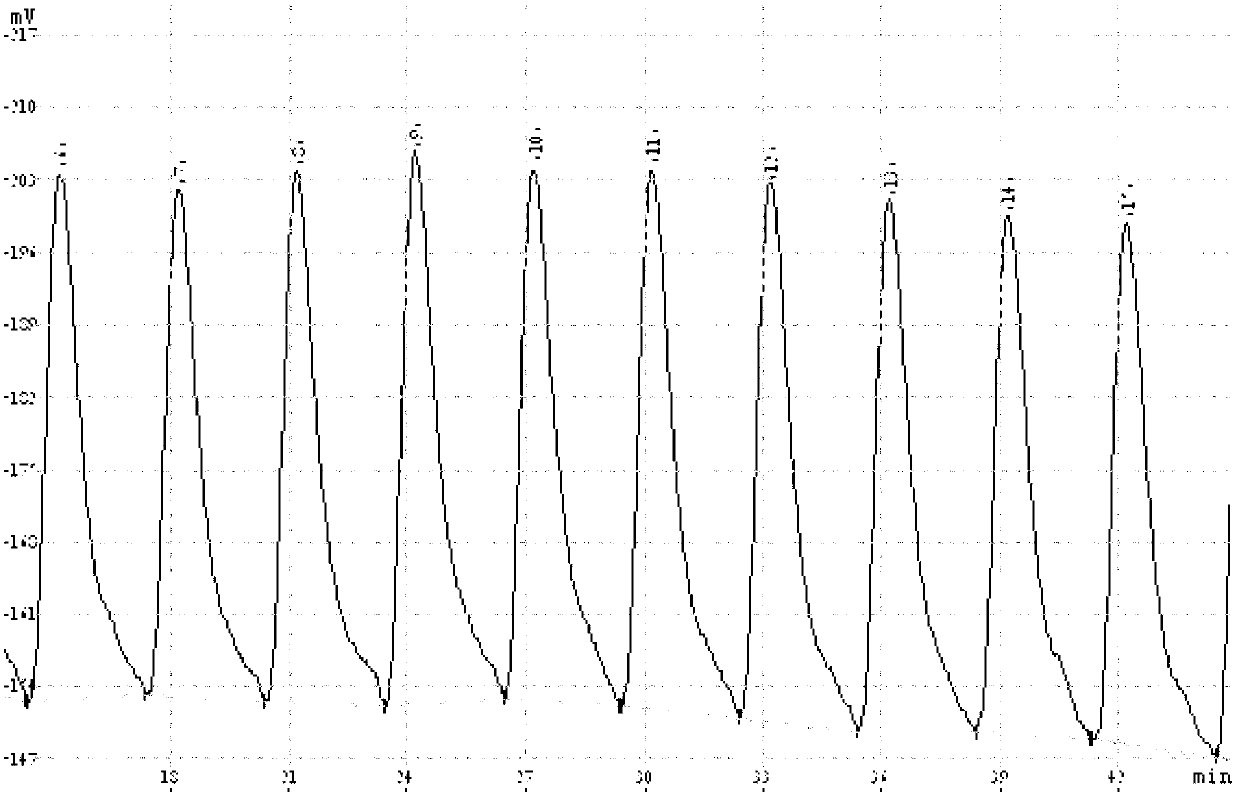
[0029] In this embodiment, the standard sample is tested, and the precision of the method of the present invention is investigated by using a standard sample with a known ferrous ion concentration. The steps are as follows:
[0030] 1. Preparation of standard samples
[0031] (1) Prepare a standard stock solution of ferrous ion Fe(II) with a concentration of 1000 mg / L: weigh 0.4975 g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O in a beaker, add 0.5mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, then add distilled water to dissolve, transfer all to a 100mL volumetric flask with distilled water to make up the volume, the concentration of ferrous ion Fe(II) is 1.0 g / L.
[0032] (2) Prepare 40 μg / L ferrous ion Fe(II) ion standard sample: pipette 10 μL of 1.0 g / L ferrous ion Fe(II) standard stock solution into a 250 mL volumetric flask, and use a deionized Dilute to the mark with water.
[0033] 2. Preparation of chromogenic solution R
[0034] (1) Add 0.1 g of neutral red into a 100 mL volumetric flask, and prepare a n...
Embodiment 2
[0046] In this embodiment, there are three kinds of samples to be tested, wherein, 1# sample is Funan River water in Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, China, 2# sample is A1 pond water in Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, China, and 3# sample is Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, China City B1 pond water. The sample to be tested was diluted 5 times and then injected for analysis.
[0047] The analysis steps are as follows:
[0048] 1. Preparation of standard samples
[0049] (1) Prepare a standard stock solution of ferrous ion Fe(II) with a concentration of 1000 mg / L: weigh 0.4975 g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O in a beaker, add 0.5mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, then add distilled water to dissolve, transfer all to a 100mL volumetric flask with distilled water to make up the volume, the concentration of ferrous ion Fe(II) is 1.0 g / L.
[0050] (2) Dilute the standard stock solution prepared in step (1) with deionized water to prepare a series of standard samples. The concentrations of ferrous...
Embodiment 3
[0070] In the present embodiment, there are three kinds of tested samples, wherein, 1# sample is Funan River water in Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China, 2# sample is A2 pond water in Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China, and 3# sample is Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China City B2 pond water. The sample to be tested was diluted 5 times and then injected for analysis.
[0071] 1. Preparation of standard samples
[0072] The preparation of the standard sample is the same as in Example 2, and the concentrations of ferrous ion Fe(II) in each standard sample are: 5 μg / L, 10 μg / L, 20 μg / L, 40 μg / L, 60 μg / L , 70 μg / L.
[0073] 2. Preparation of chromogenic solution R
[0074] (1) Add 0.1 g of neutral red into a 100 mL volumetric flask, and prepare a neutral red aqueous solution with a concentration of 1.0 g / L with deionized water;
[0075] (2) Take 0.3 mL of neutral red (NR) solution with a concentration of 1.0 g / L, 5 mL of H with a concentration of 0.01 mol / L 2 S0 4 In a 100 mL volume...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com