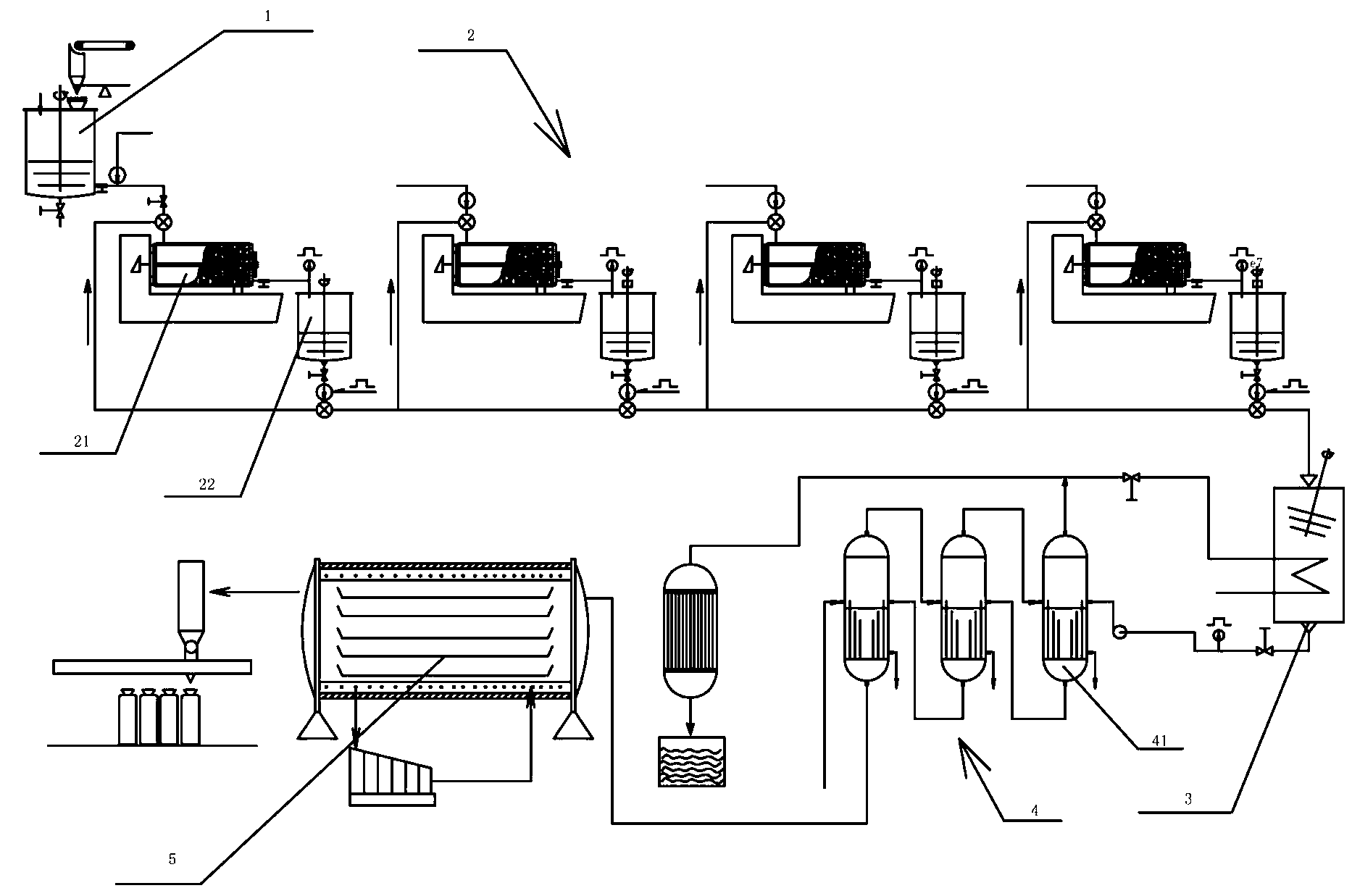
Wet-to-dry dispersant-free method for producing ultrafine nanoscale dry powder and involved device
An ultra-fine nanotechnology, production method, applied in the fields of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, which can solve the problem of equipment energy consumption and parts loss, high temperature caused by equipment grinding, and increased maintenance costs. and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving quality, improving operation speed, and improving product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Include the following steps:
[0045] 1) Ingredients: mix the barite ore with water evenly, and the solid weight accounts for 30%-40% of the total weight; the BaSO of the barite ore used 4 ≥98%, particle size 80-100 mesh;
[0046] 2) Grinding: Grinding the material obtained in step 1) through a four-stage circulating grinding system until the D90 is 100nm. The grinding medium used in the grinding process is yttrium-stabilized zirconia beads, and then heated and concentrated until the solid content of the material is ≥ 60%;
[0047] 3) The material obtained in step 2) is dried by ultra-low temperature vacuum sublimation to obtain ultrafine nano-dry powder with a particle size of D90-100nm, and finally packed.
Embodiment 2
[0049] A method for producing ultrafine nano-dry powder without dispersant and wet-to-dry method, comprising the following steps:
[0050] 1) Ingredients: mix the quartz stone ore with water evenly, and the solid weight accounts for 30%-40% of the total weight; the quartz stone ore used is SiO 2 ≥99.99%, particle size 80-100 mesh.
[0051] 2) Grinding: The material obtained in step 1) is ground through a three-stage circulating grinding system until the D90 is 100-300nm. The grinding medium used in the grinding process is yttrium-stabilized zirconia beads, and then heated and concentrated until the solid content of the material is ≥60 %;
[0052] 3) The material obtained in step 2) is vacuum-dried at ultra-low temperature to obtain an ultrafine nano-dry powder with a particle size D90 of 100-300nm, and finally packed.
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for producing ultrafine nano-dry powder without dispersant and wet-to-dry method, comprising the following steps:
[0055] 1) Ingredients: mix the quartz stone ore with water evenly, and the solid weight accounts for 35% of the total weight; the quartz stone ore used is SiO 2 ≥99.99%, particle size 80-100 mesh.
[0056] 2) Grinding: The material obtained in step 1) is ground through a four-stage circulating grinding system until the D90 is 100nm. The grinding medium used in the grinding process is yttrium-stabilized zirconia beads, and then heated and concentrated until the solid content of the material is ≥ 60%;
[0057] 3) The material obtained in step 2) is vacuum-dried at ultra-low temperature to obtain ultrafine nano-dry powder with a particle size of D90 30-100nm, and finally packed.
[0058] In addition, the method and device provided by the present invention are not only suitable for barite or quartz stone, other water-insoluble inorganic materials or...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com