Molecular mark for detection of Zea mays L. opaque mutant 5512G, and applications of same
A molecular marker and mutant technology, which can be used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc. High accuracy and simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Using 5512G Mutant (5512G / 5512G) to Cultivate Dominant High Lysine Maize
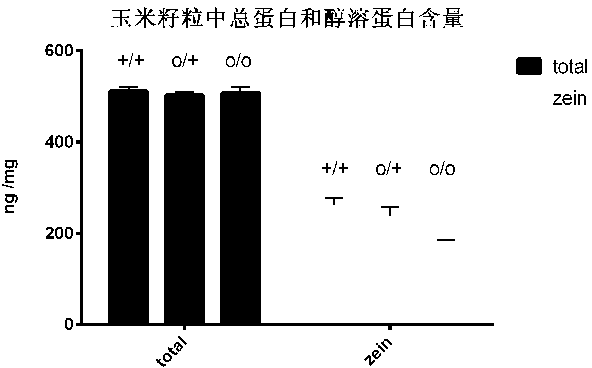
[0034] Since the 5512G mutant has a 45.70% increase in lysine (lys) content compared to its corresponding wild type, see Figure 4 , so high-lysine maize can be bred by crossing this gene with other elite varieties. By crossing the 5512G mutation homozygote (5512G / 5512G) with other corns with excellent production traits, a semi-dominant high-lysine heterozygote can be obtained, and high-lysine commercial corn can be obtained directly. Recessive homozygotes for dominant high lysine corn kernels can also be isolated in the F2 generation. Recessive homozygous through multi-generation selfing, recurrent selection, selection of seeds with good grain development and high lysine content generation by generation, and finally obtain stable recessive homozygous, high lysine inbred lines or populations, that is, high Lysine corn varieties.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Obtaining co-dominant molecular markers and determining the linkage relationship with the 5512G gene
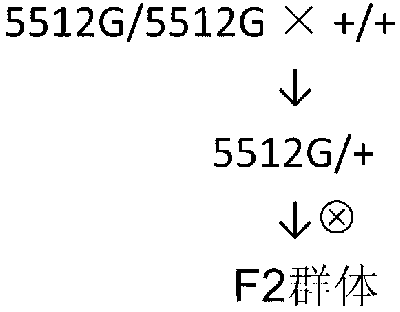
[0036] See the phenotype map of maize kernel homozygous mutant (5512G / 5512G), heterozygous (5512G / +) and wild type (+ / +) figure 1 . F1 (5512G / +) was obtained by crossing homozygous mutant (5512G / 5512G) with homozygous wild type (+ / +), and then selfing to obtain F2 population, see figure 2 . Genotype segregation appeared in the F2 population, including + / +, 5512G / + and 5512G / 5512G three genotypes, and the grains with + / + genotype were all non-Opaque wild type grains, with 5512G / + genotype The grains are all semi-Opaque heterozygous grains, and the grains with 5512G / 5512G genotype are Opaque mutant types.
[0037] The present invention extracts the genomic DNA of homozygous mutants, wild-types and individual plants of the F2 population through the constructed F2 population, uses the method of map-based cloning, and obtains the polymorphism and compares it ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Polymorphism identification of molecular markers among different parents
[0046] Genomic DNA of 5512G / 5512G mutant, wild type and inbred lines widely used in various breedings was extracted, and the polymorphism among different varieties was analyzed by PCR reaction. The results show that 4.9 has polymorphisms in 5512G and CIMBL62, CIMBL146, By807, Ry732, P178, B73, SC55, JY01, Liao5263, TY5, 7327, GEMS14 (see attached Figure 8 ), 5.7 has polymorphisms in 5512G with CIMBL1, CIMBL62, CIMBL146, Zi330, S22, chuan48-2, CA47, Z2018F, 05WN230, JY01, XZ698, Liao5263, TY5, Zheng28, DH29, B77, GEMS53 (see attached Figure 9 ). This result proves that molecular markers 4.9 and 5.7 can accurately detect the existence of 5512G gene in common populations with multiple breeding backgrounds.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com