Method for writing data in nonvolatile storage element, and nonvolatile storage device
A non-volatile storage and data writing technology, applied in the direction of information storage, static memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve large capacity, achieve the effect of suppressing swing and improving retention characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0058] [Structure of nonvolatile memory element]
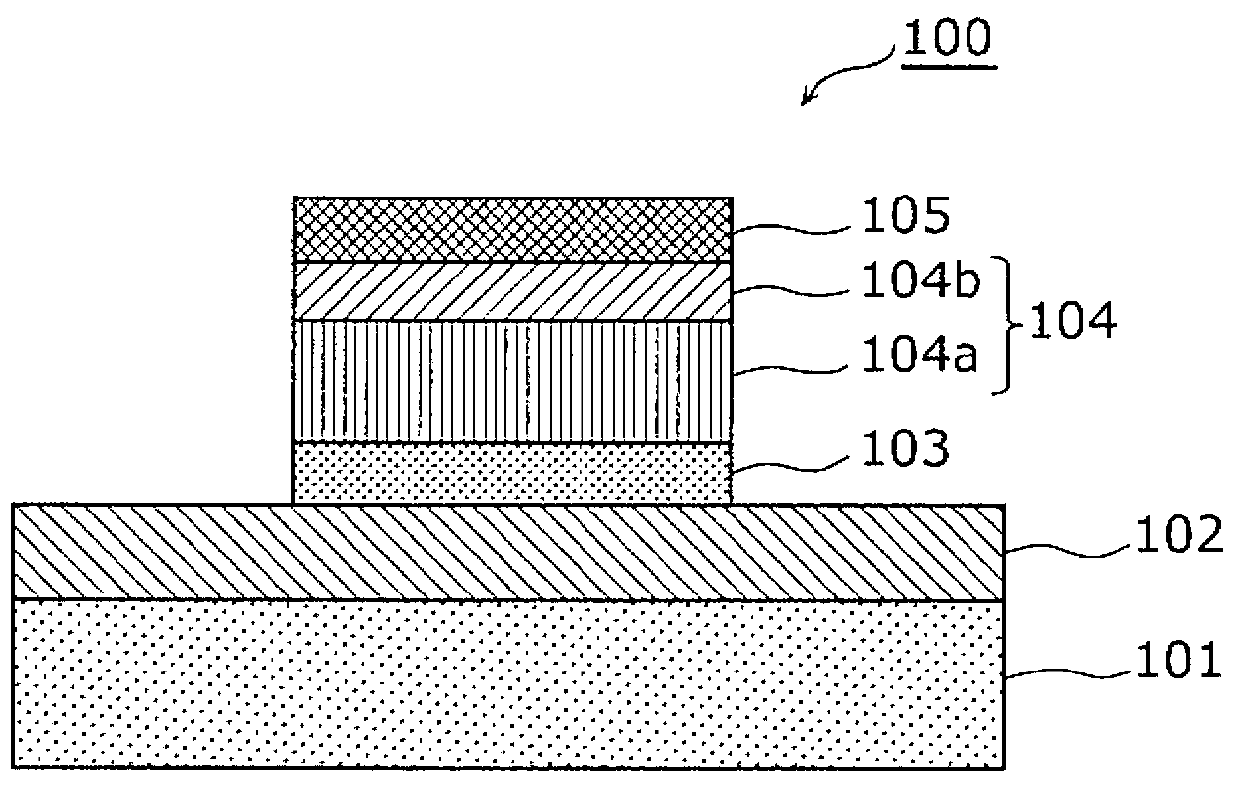
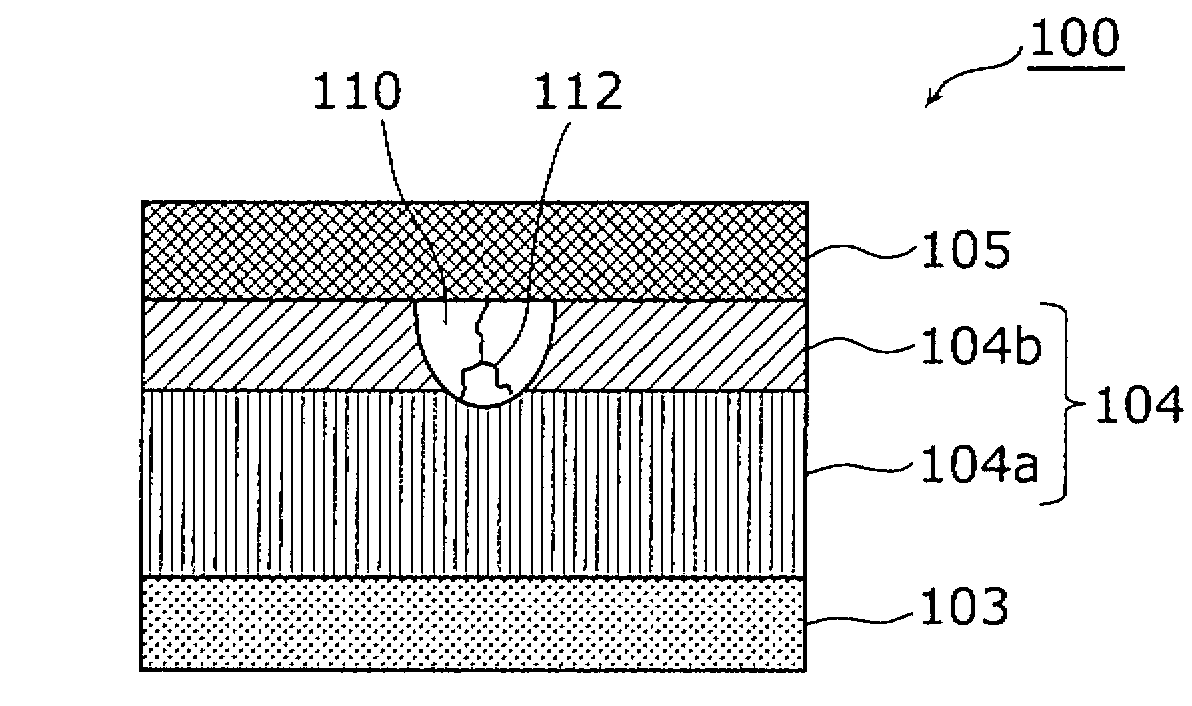
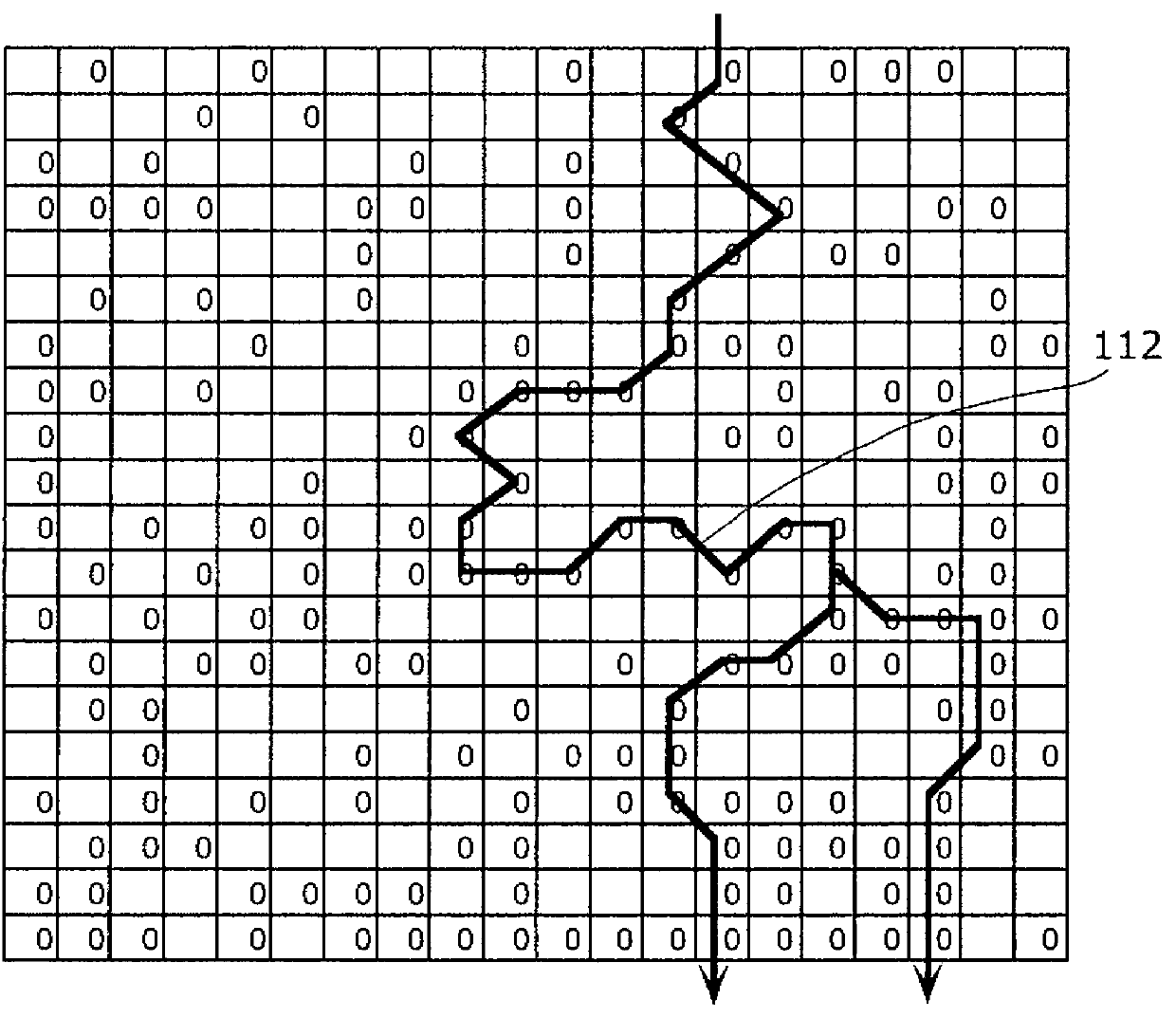
[0059] Figure 1A It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the nonvolatile memory element according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0060] Such as Figure 1A As shown, the nonvolatile memory element 100 of this embodiment includes a substrate 101, an interlayer insulating film 102 formed on the substrate 101, a first electrode 103 and a second electrode 105 formed on the interlayer insulating film 102. , the variable resistance layer 104 sandwiched between the first electrode 103 and the second electrode 105 . In addition, in this figure, the nonvolatile memory element 100 has the substrate 101 and the interlayer insulating film 102, but these constituent elements are not essential.
[0061] The variable resistance layer 104 has a stacked structure of a first metal oxide layer 104a including an oxide of a first metal and a second metal oxide layer 104b including an oxide of a second metal. In this em...
Embodiment approach 2
[0140] Embodiment 2 is a nonvolatile memory device of a 1-transistor / 1 nonvolatile memory unit type (so-called 1T1R type) configured using the nonvolatile memory element described in Embodiment 1. FIG.
[0141] [Structure of Nonvolatile Memory Device]
[0142] Figure 12 It is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the nonvolatile memory device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Such as Figure 12 As shown, the nonvolatile memory device 300 of this embodiment includes: a memory cell array 301 having nonvolatile memory elements R311 to R322, an address buffer 302, a control unit 303, a row decoder 304, a word line driver 305, Column decoder 306 , bitline / plateline driver 307 . Furthermore, the bit line / plate line driver 307 has a readout circuit (sense amplifier), and can measure the current flowing through the bit line or the plate line.
[0143] The memory cell array 301 has: two word lines W1, W2 extending parallel to each other; two ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0177] Embodiment 3 is a cross-point nonvolatile memory device configured using the nonvolatile memory element described in Embodiment 1. FIG. Here, the cross-point nonvolatile memory device is a memory device of a type in which an active layer exists at an intersection point (three-dimensional intersection point) between a word line and a bit line. Next, the configuration and operation of this nonvolatile memory device will be described.
[0178] [Structure of Nonvolatile Memory Device]
[0179] Figure 13 It is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the nonvolatile memory device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Such as Figure 13 As shown, the nonvolatile memory device 400 of this embodiment includes: a memory cell array 401 having nonvolatile memory elements R11 to R33, an address cache 402, a control unit 403, a row decoder 404, a word line driver 405, Column decoder 406, bit line driver 407. Furthermore, the bit line driver 407 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com