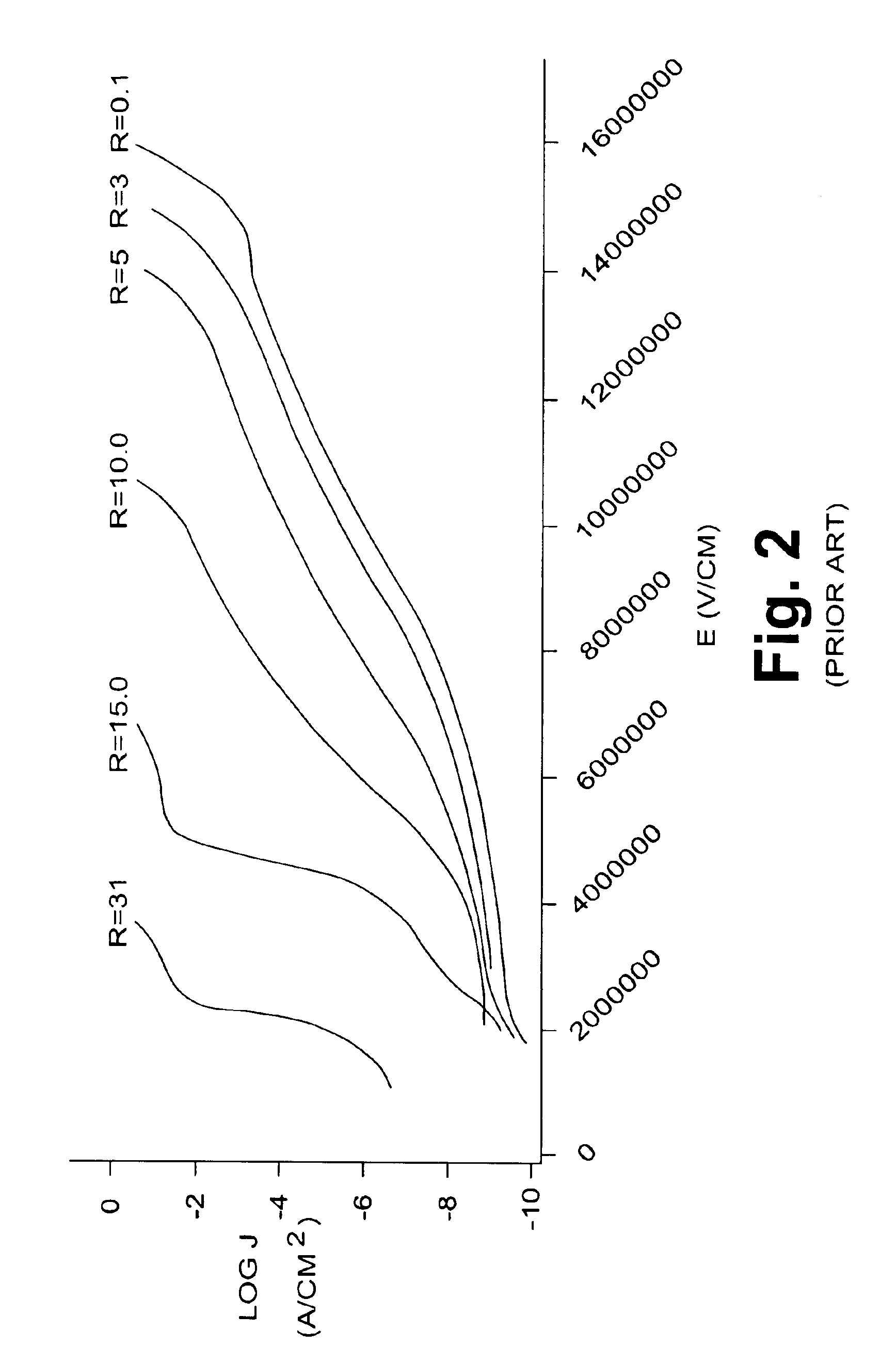
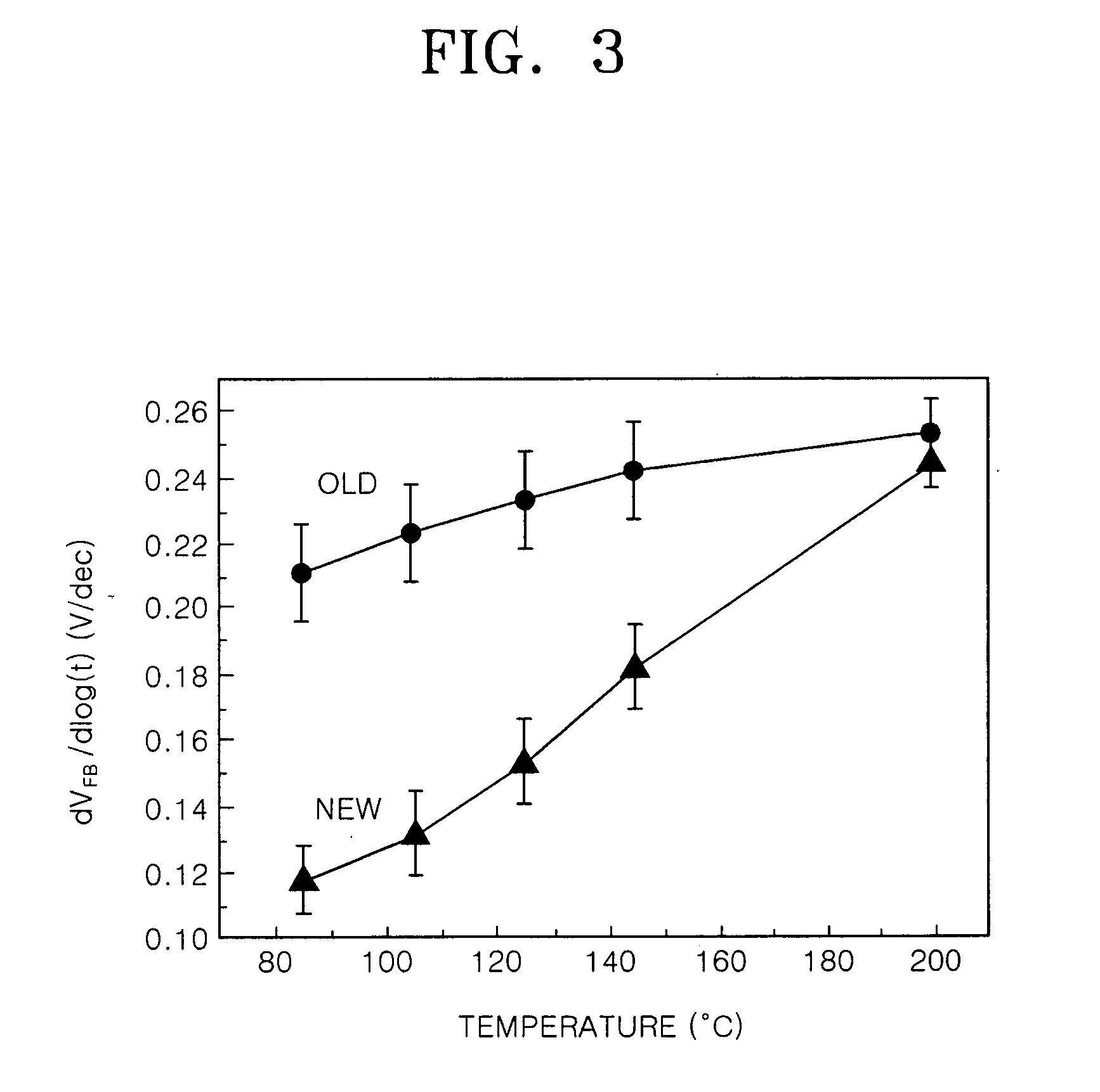
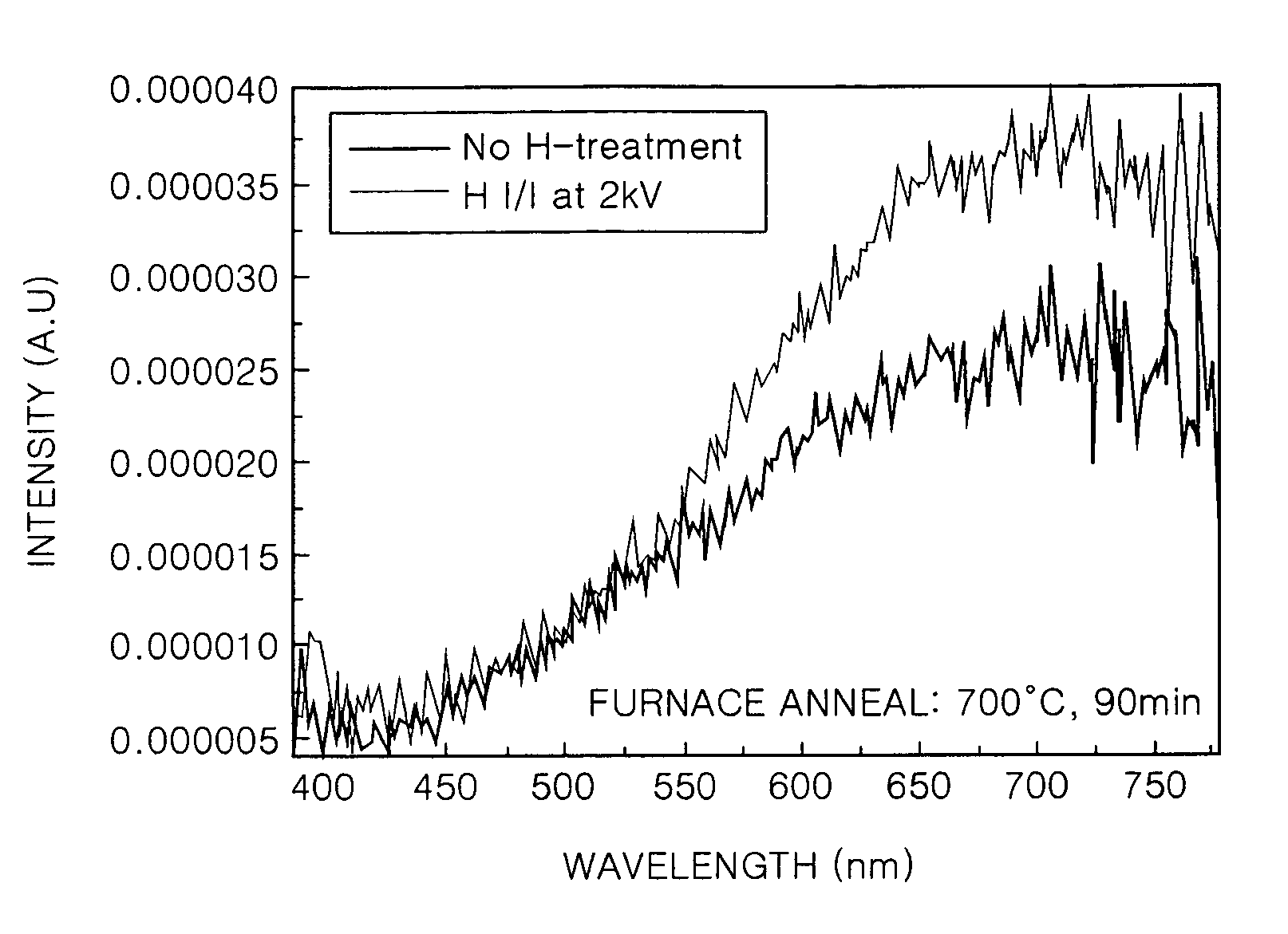
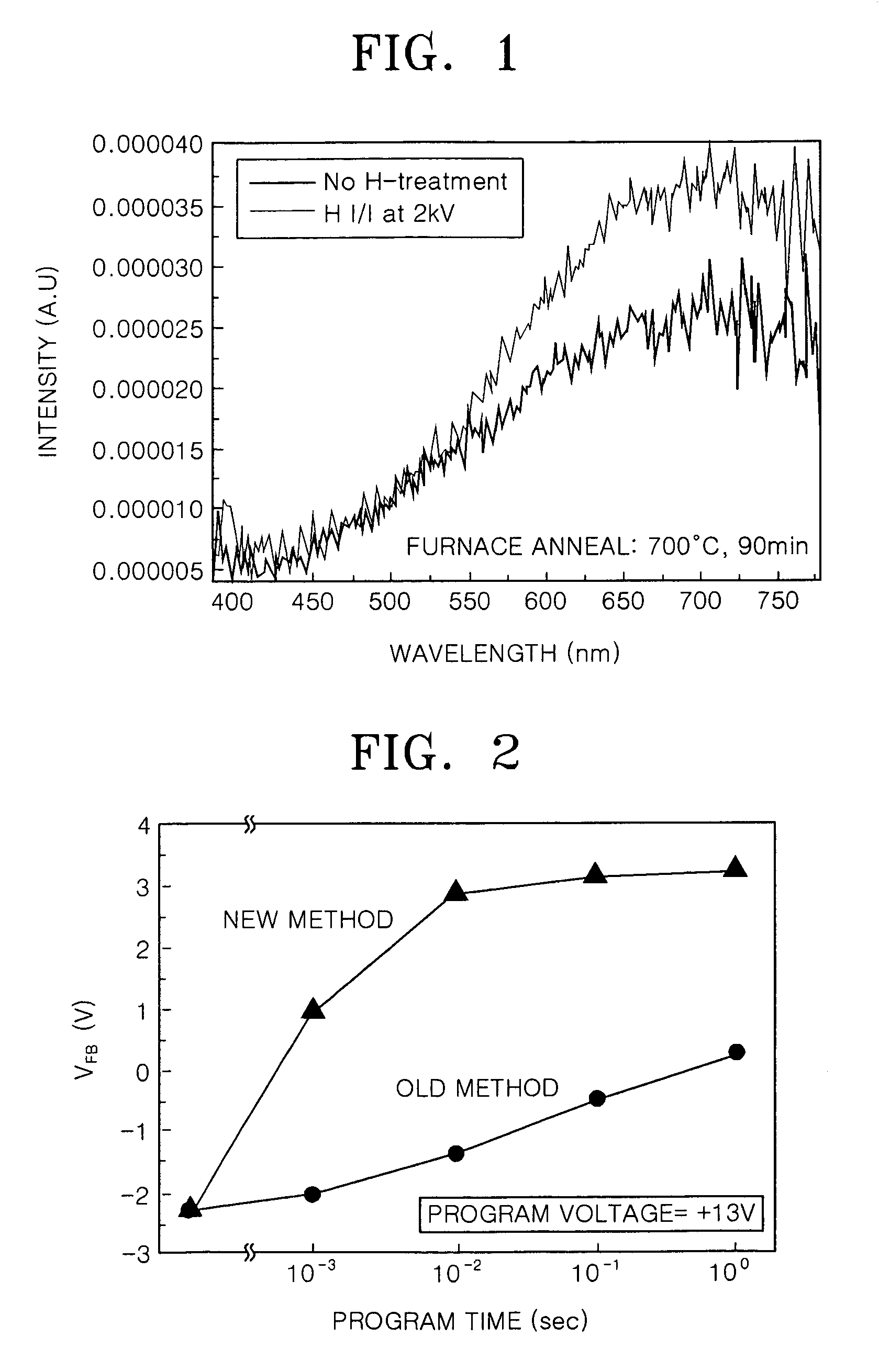
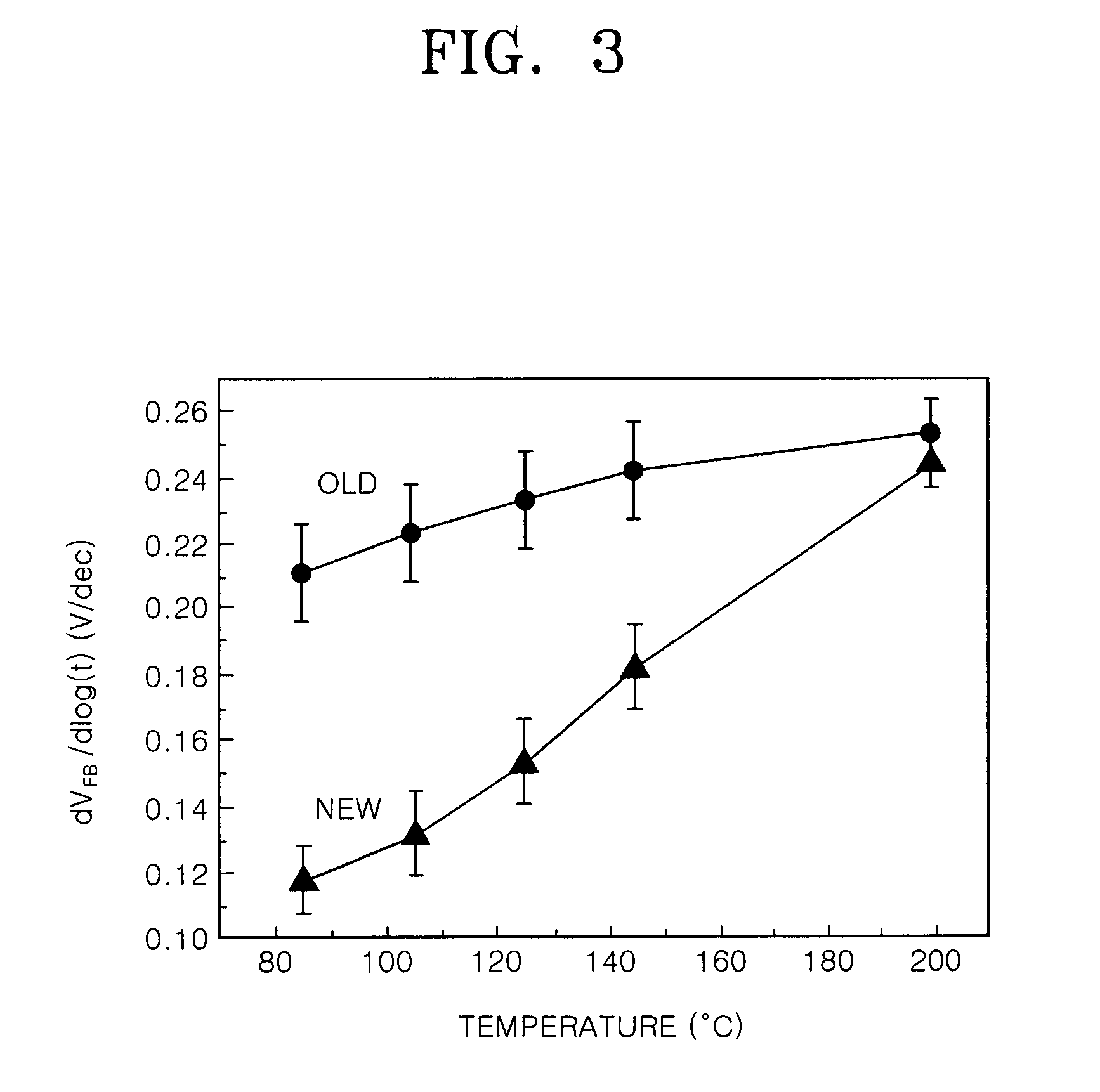
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Silicon nanocrystals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
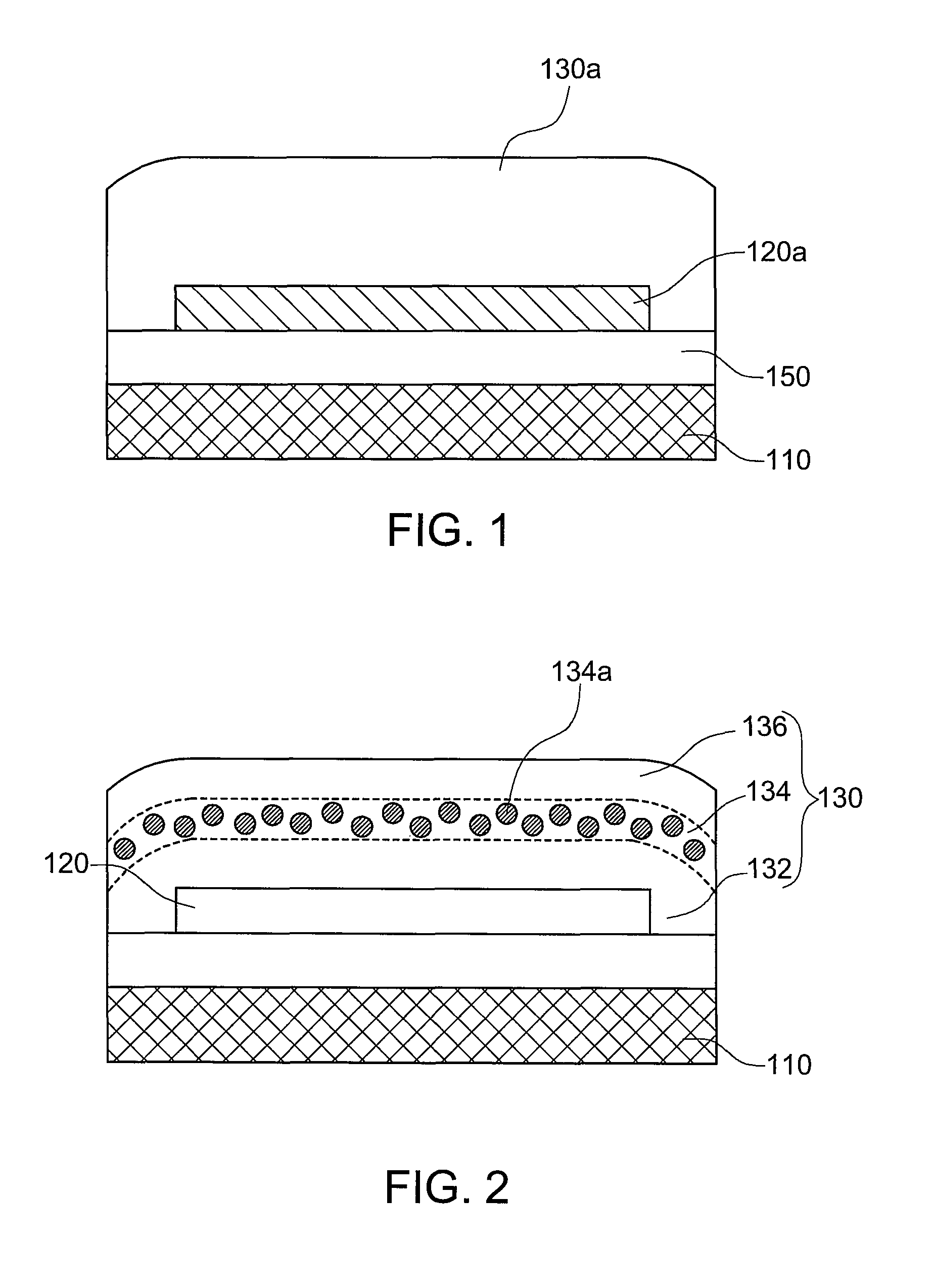
Organic solar cells including group IV nanocrystals and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050061363A1Promote absorptionEasy to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureHeterojunctionOrganic solar cell
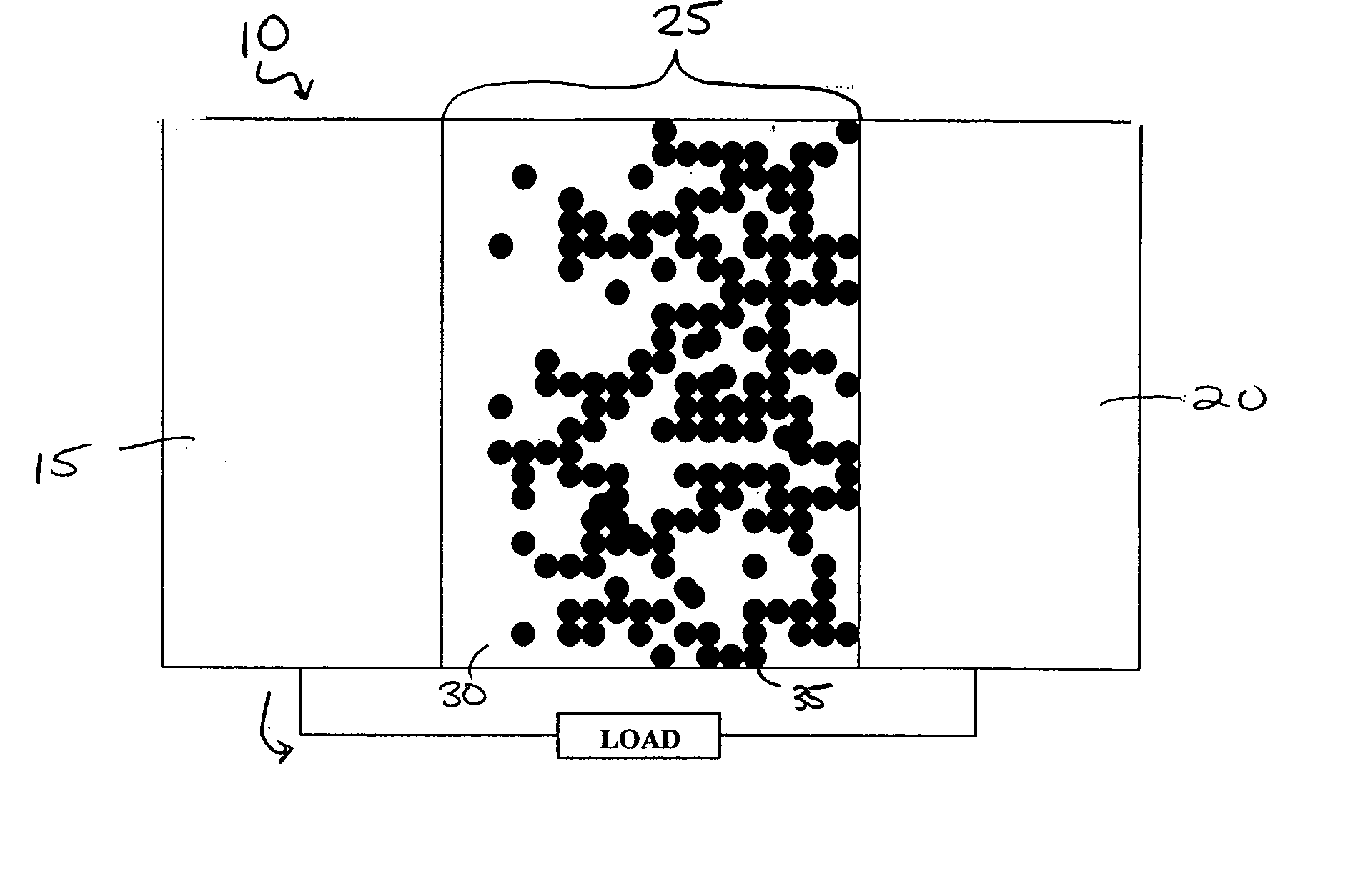
An improved organic solar cell converts light into electricity. The organic solar cell includes a cathode, an anode, and a bulk heterojunction material disposed therebetween. The bulk heterojunction material includes a plurality of group IV nanocrystals (e.g., silicon nanocrystals) disposed within an organic absorber (e.g., an organic polymer).
Owner:EVERGREEN SOLAR
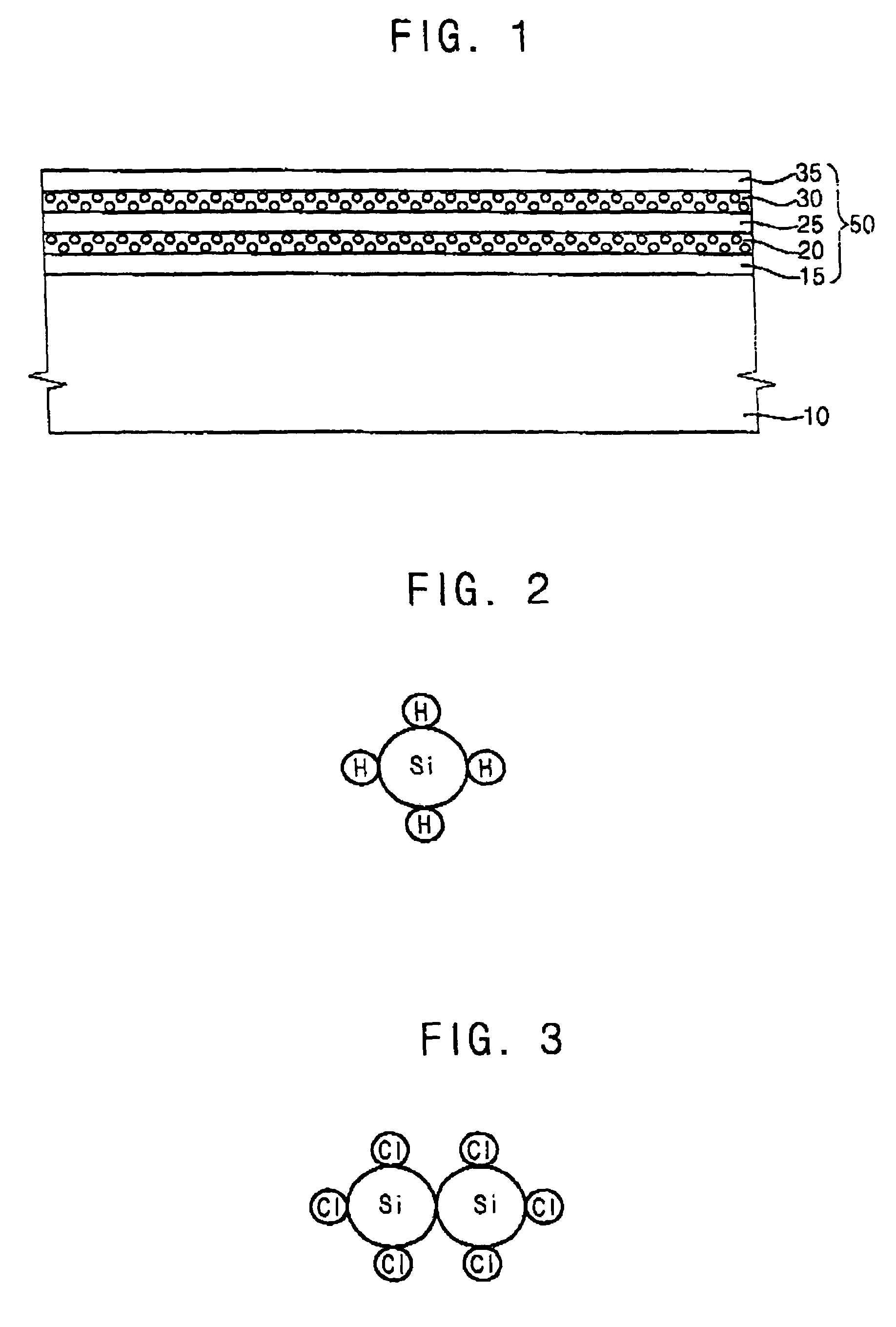
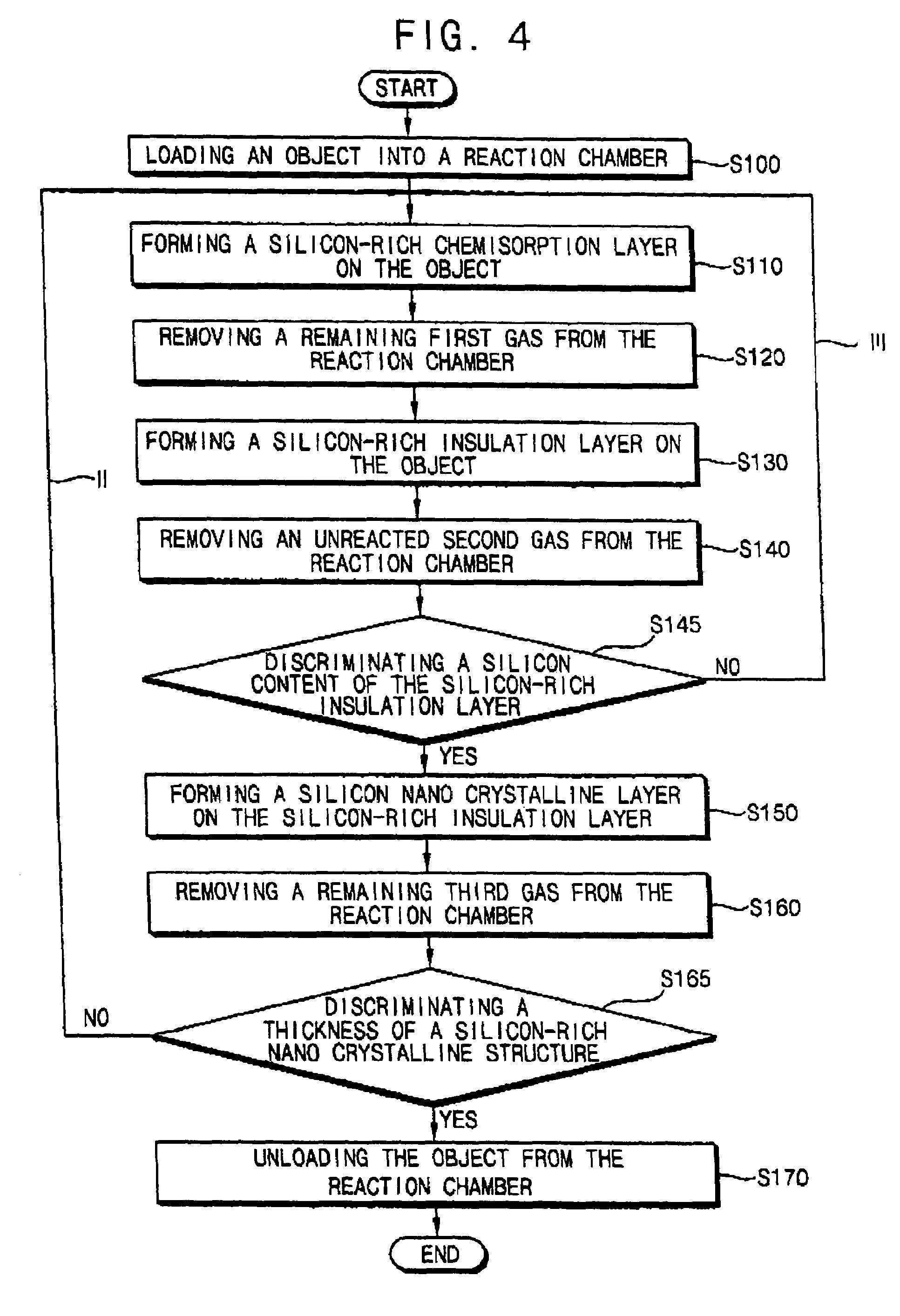
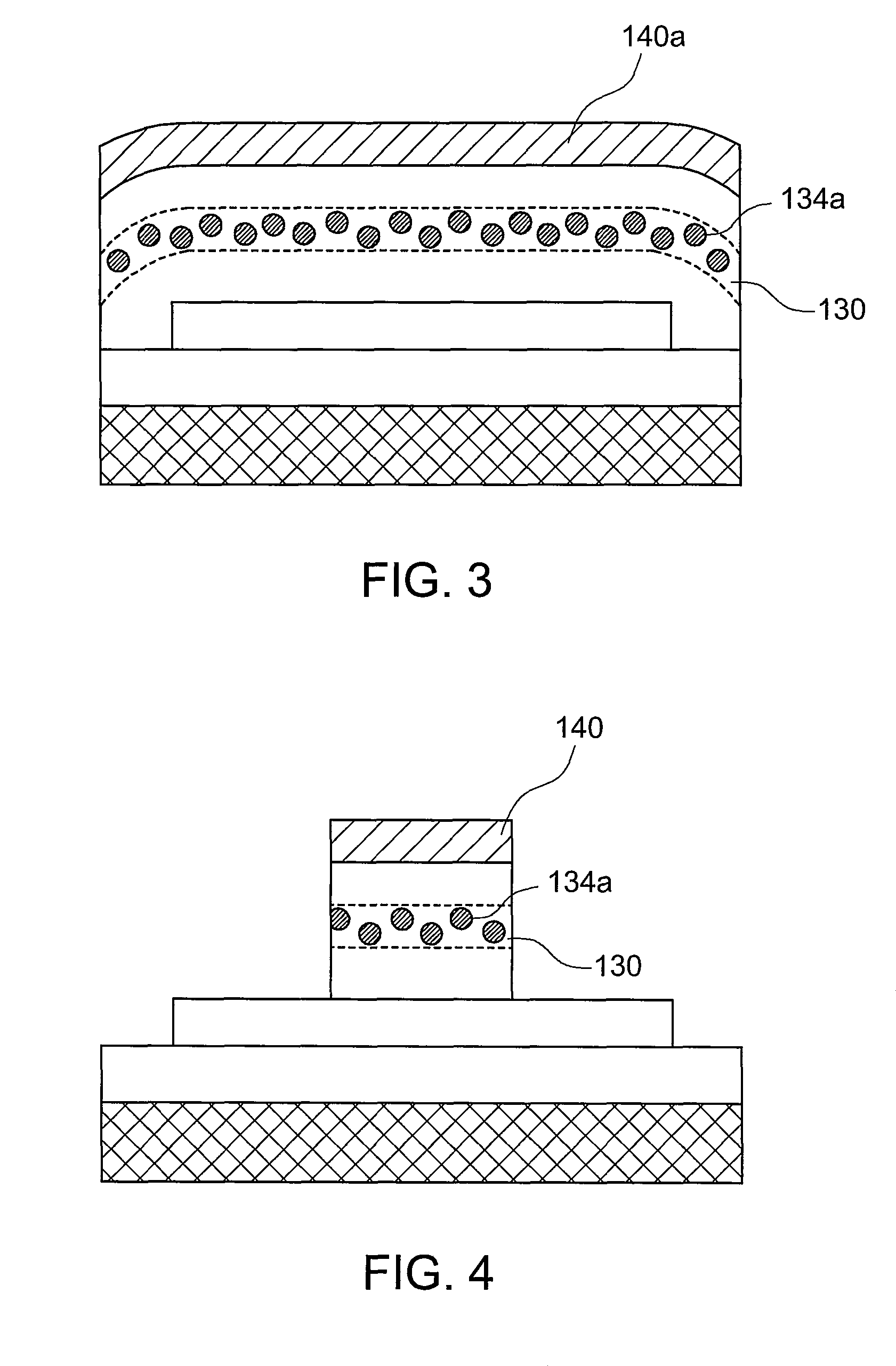
Method of forming a silicon-rich nanocrystalline structure by an atomic layer deposition process and method of manufacturing a non-volatile semiconductor device using the same
ActiveUS7419888B2Good step coverageImprove variationPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsSilicon nanocrystalsInsulation layer
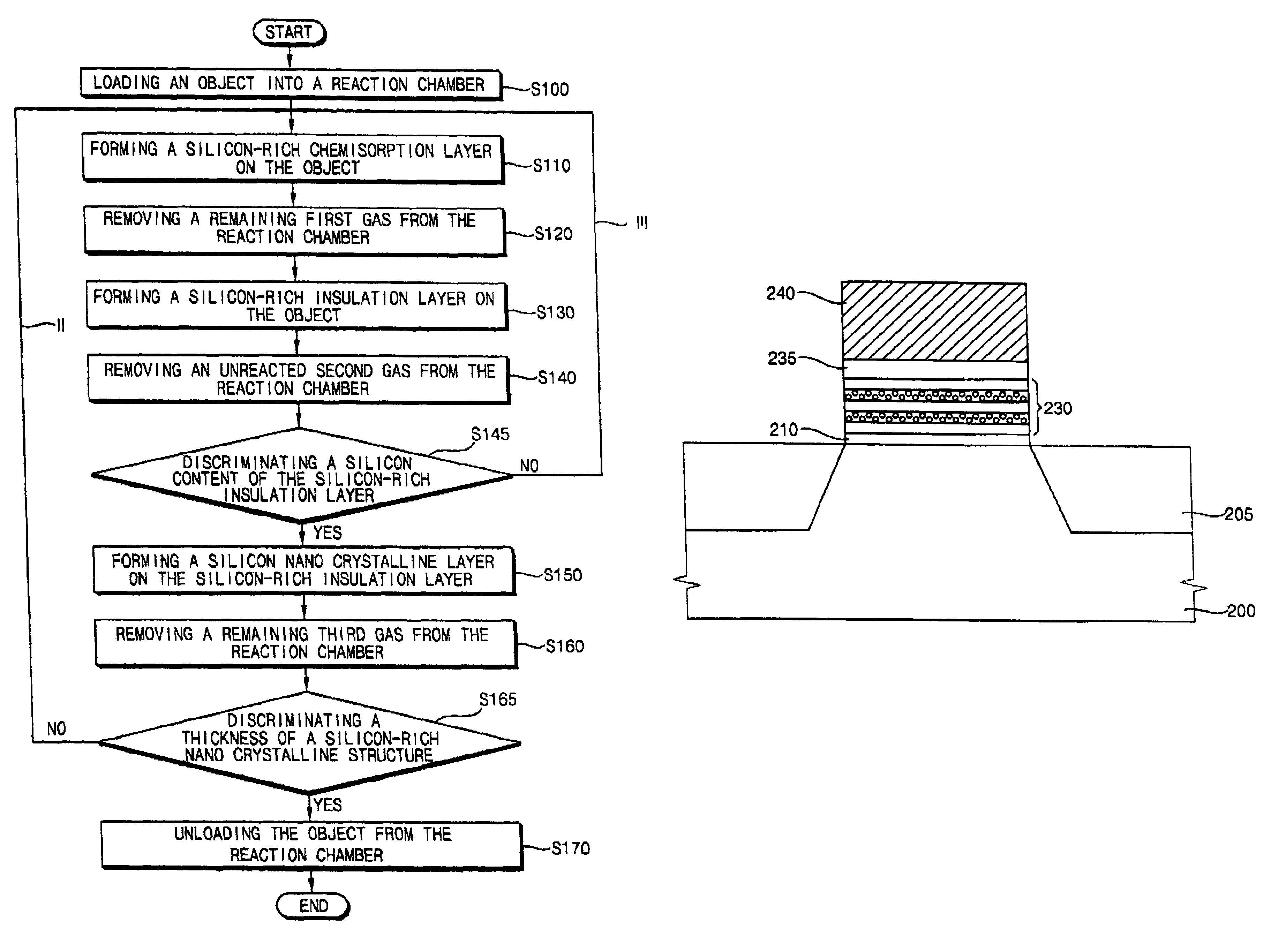
In a method of forming a silicon-rich nanocrystalline structure by an ALD process, a first gas including a first silicon compound is provided onto an object to form a silicon-rich chemisorption layer on the object. A second gas including oxygen is provided onto the silicon-rich chemisorption layer to form a silicon-rich insulation layer on the object. A third gas including a second silicon compound is provided onto the silicon-rich insulation layer to form a silicon nanocrystalline layer on the silicon-rich insulation layer. The first gas, the second gas and the third gas may be repeatedly provided to alternately form the silicon-rich nanocrystalline structure having a plurality of silicon-rich insulation layers and a plurality of silicon nanocrystalline layers on the object.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device with nanoclusters
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
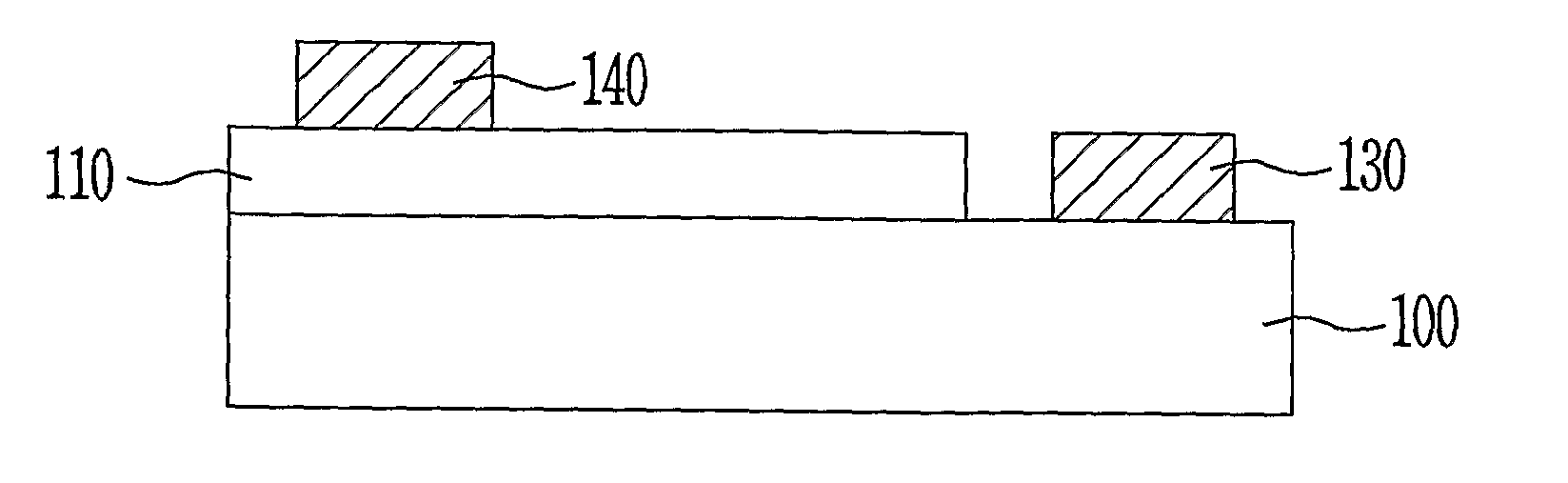
Methods of forming silicon nanocrystals by laser annealing
ActiveUS20080178794A1Enhanced vapor depositionPolycrystalline material growthNanotechSilicon nanocrystalsPhotodetector
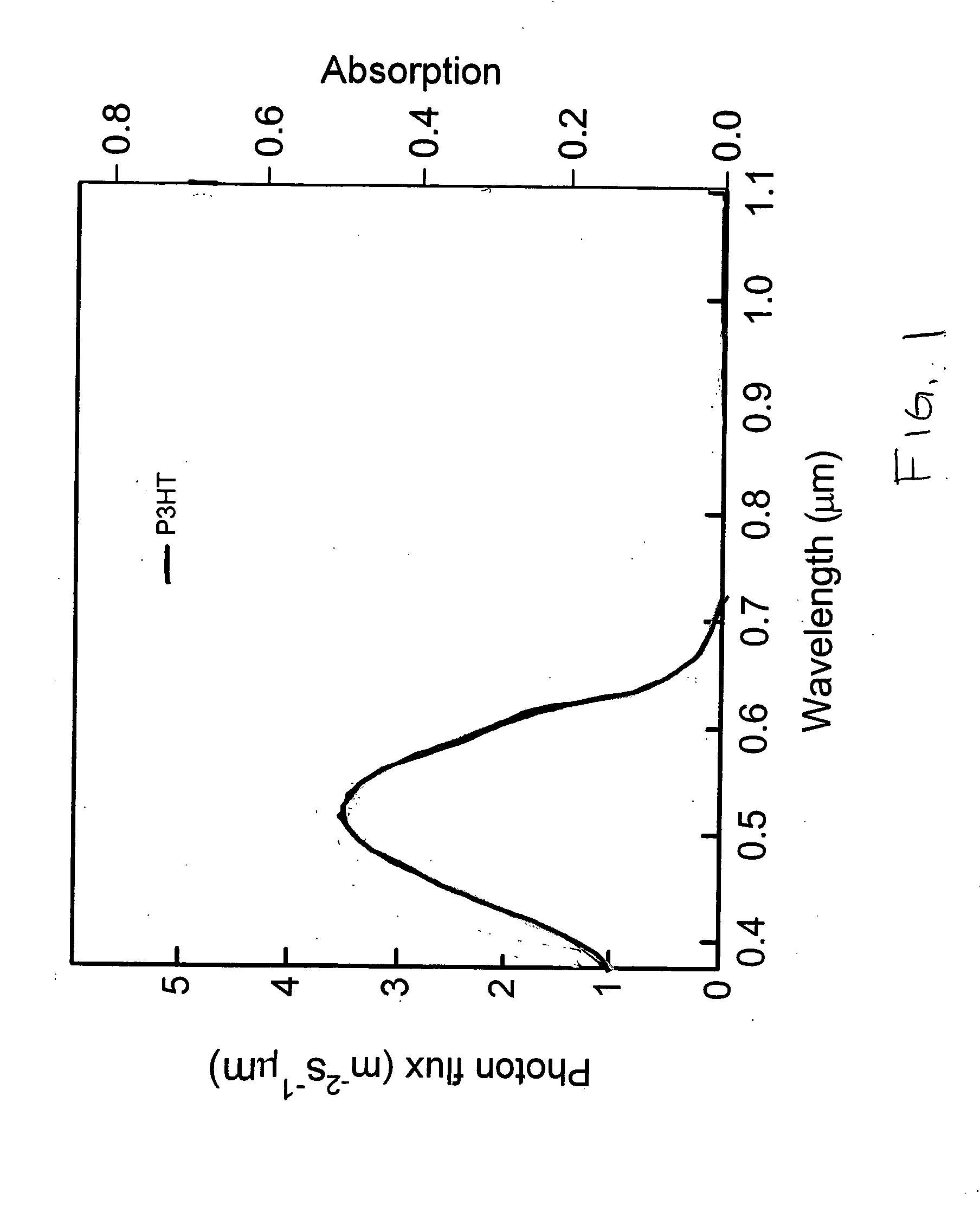
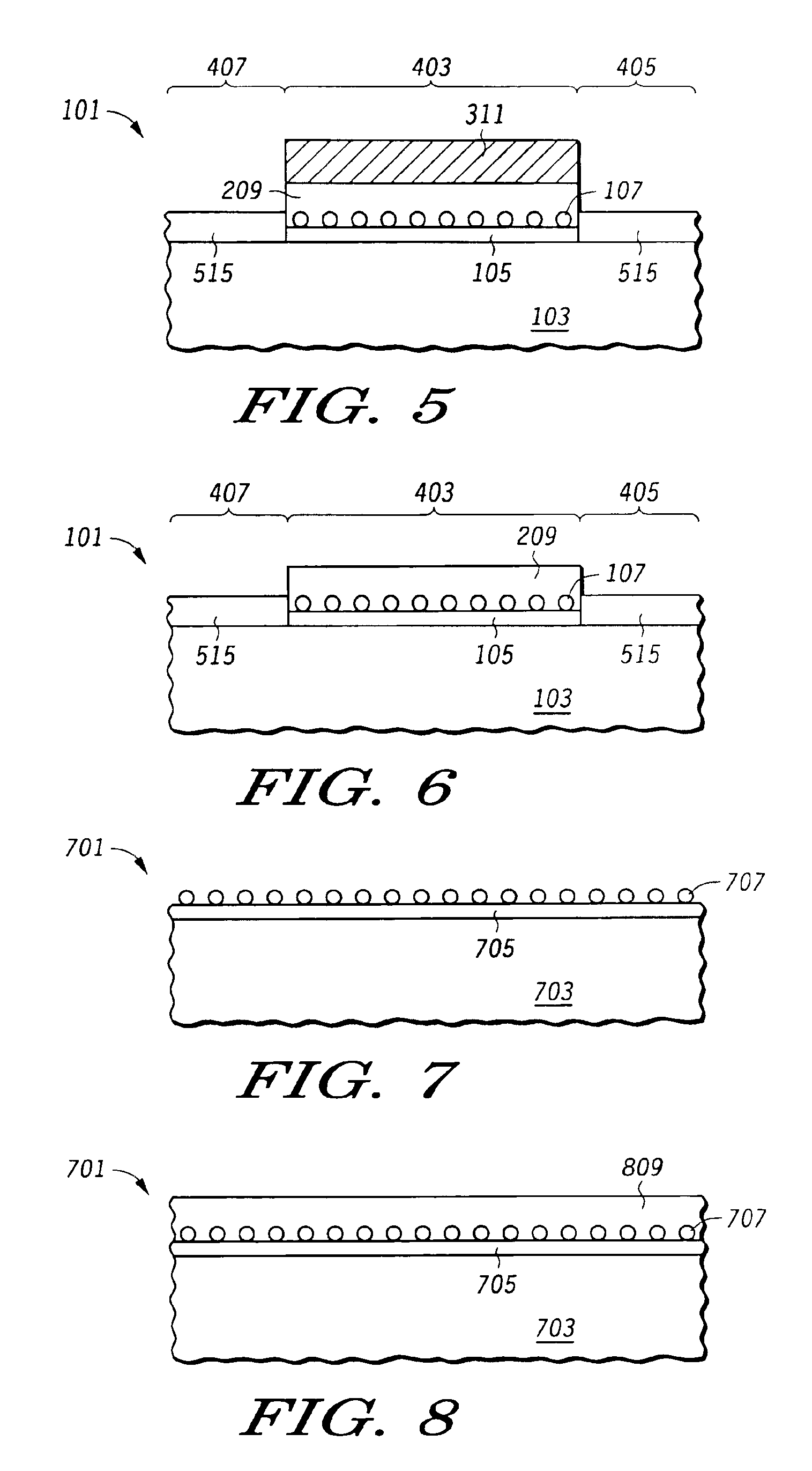
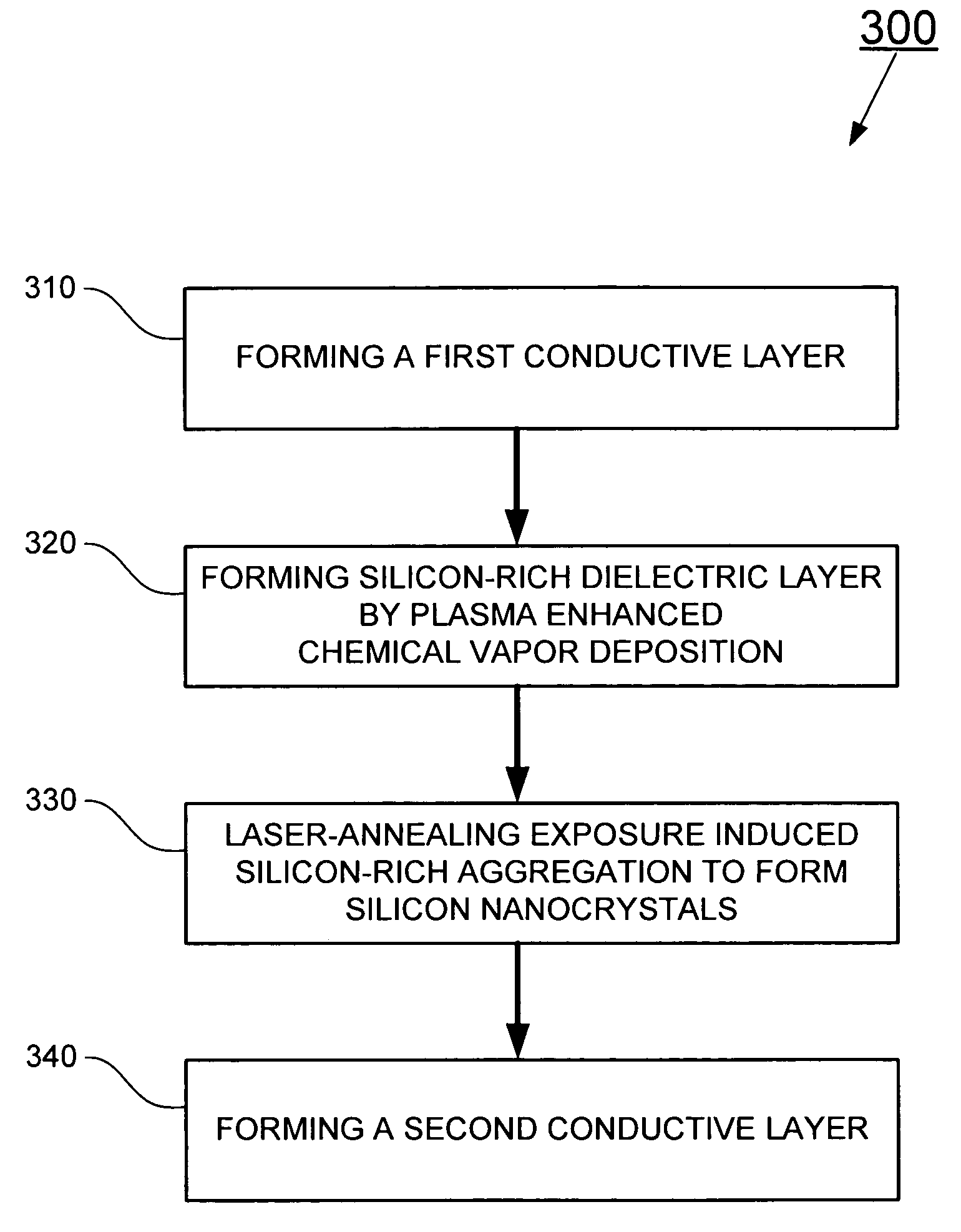
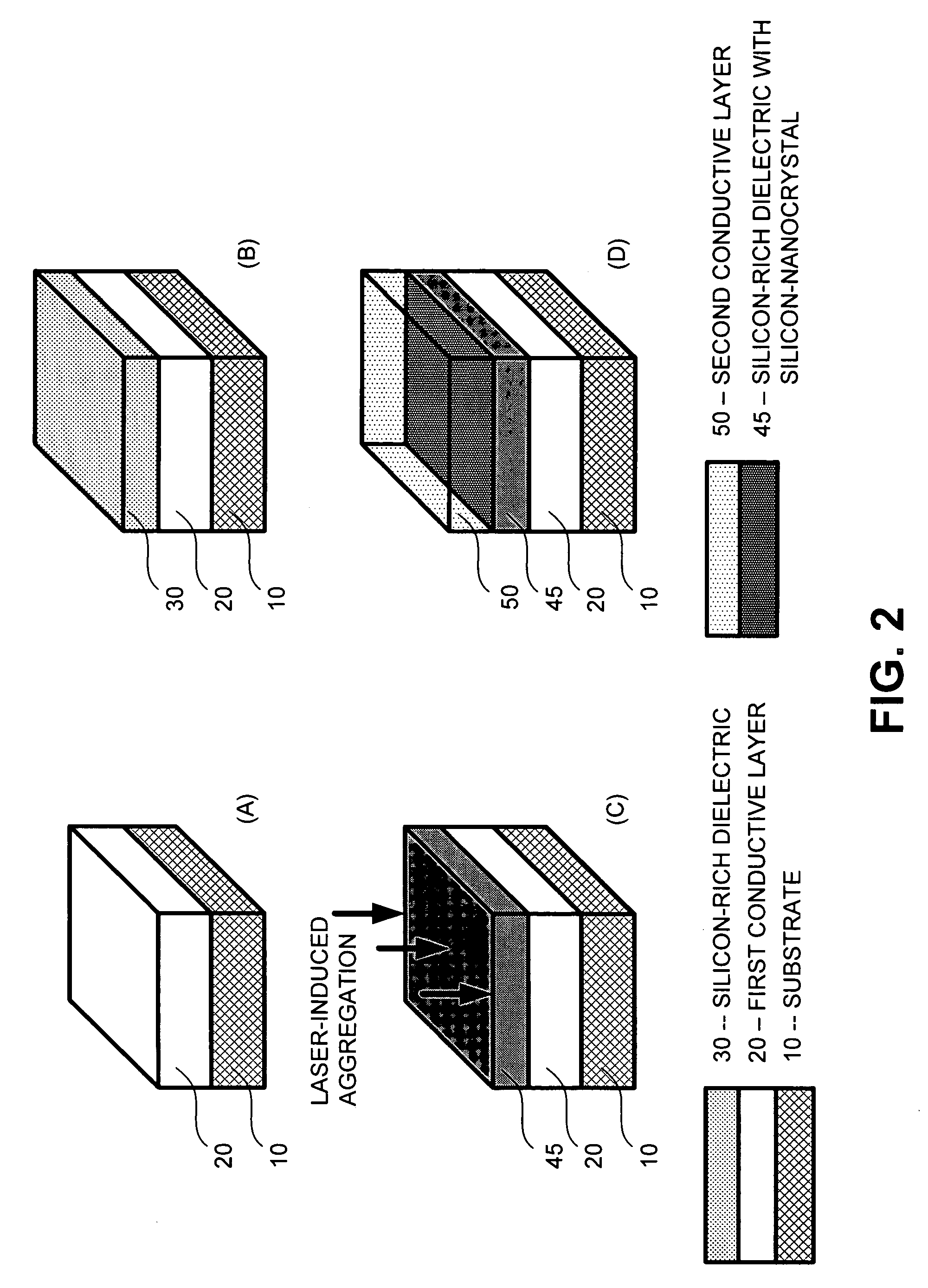
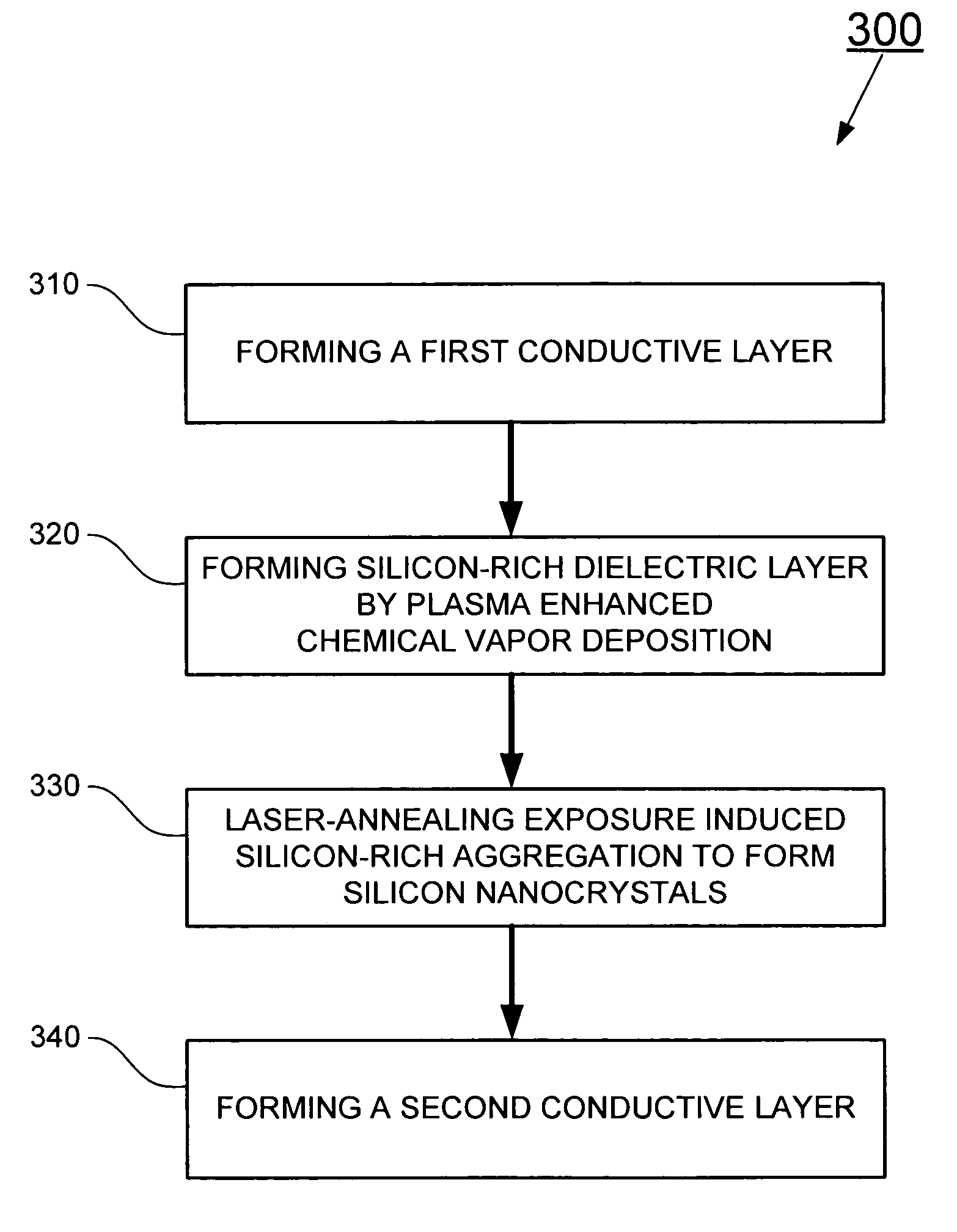
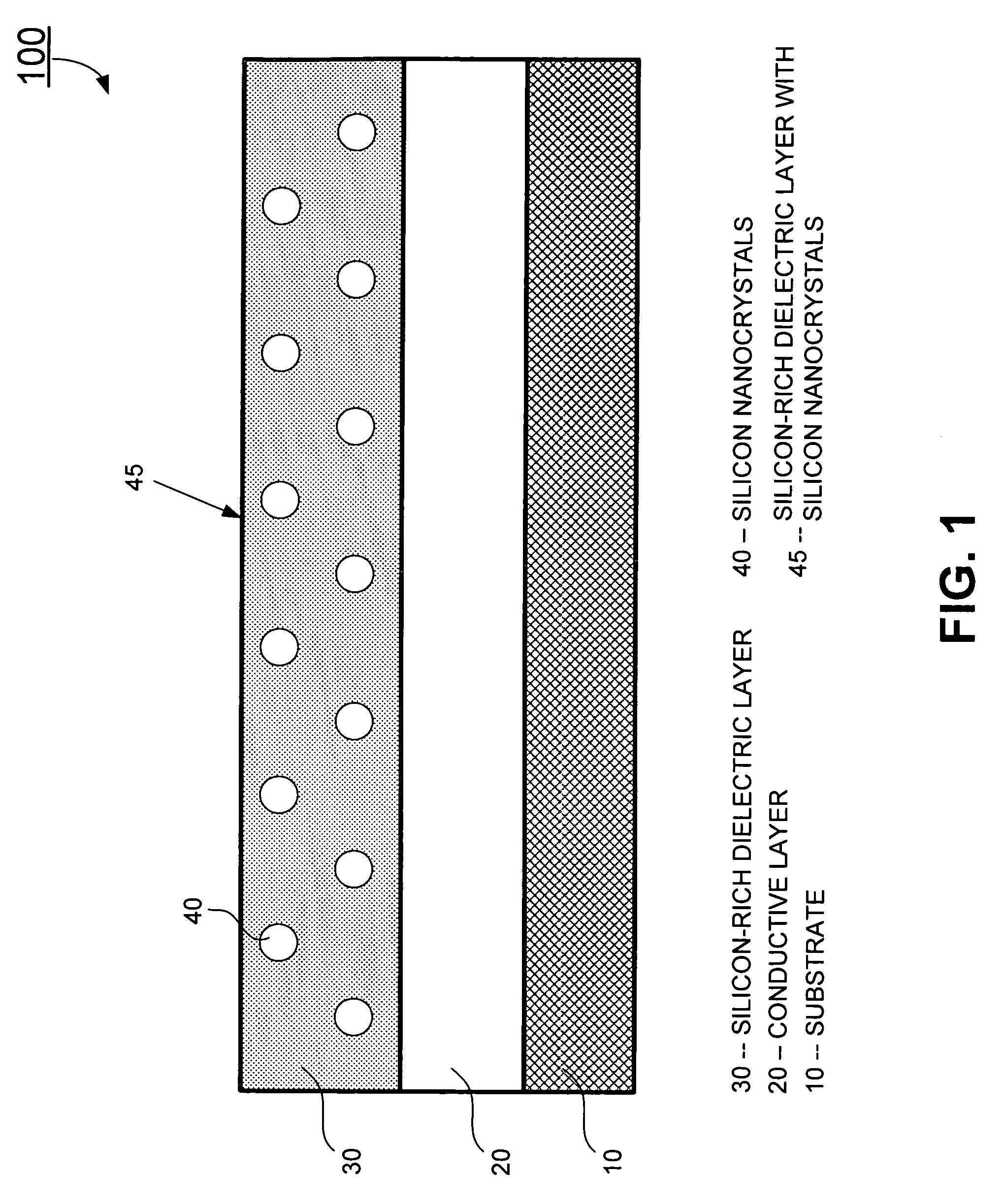
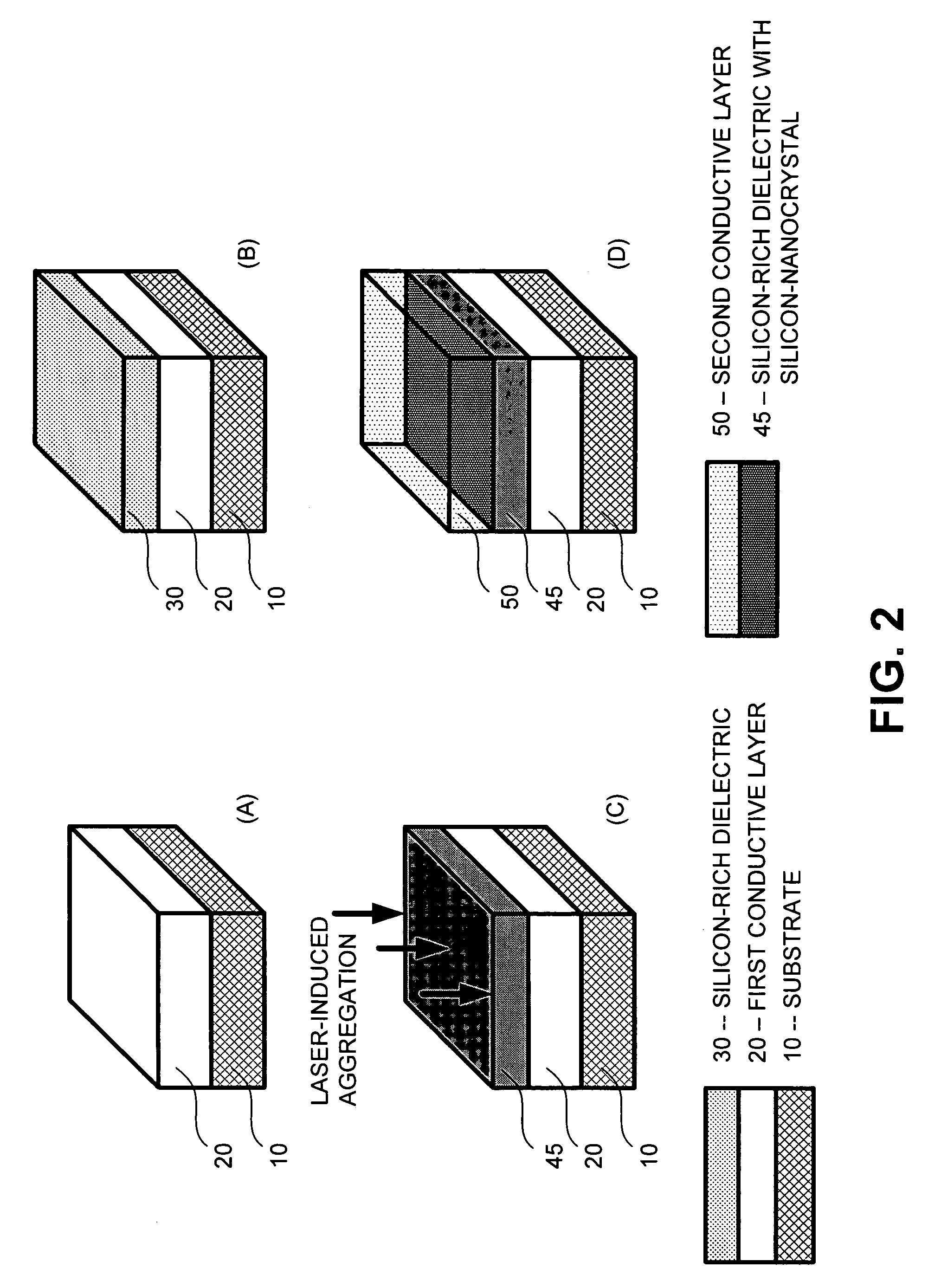
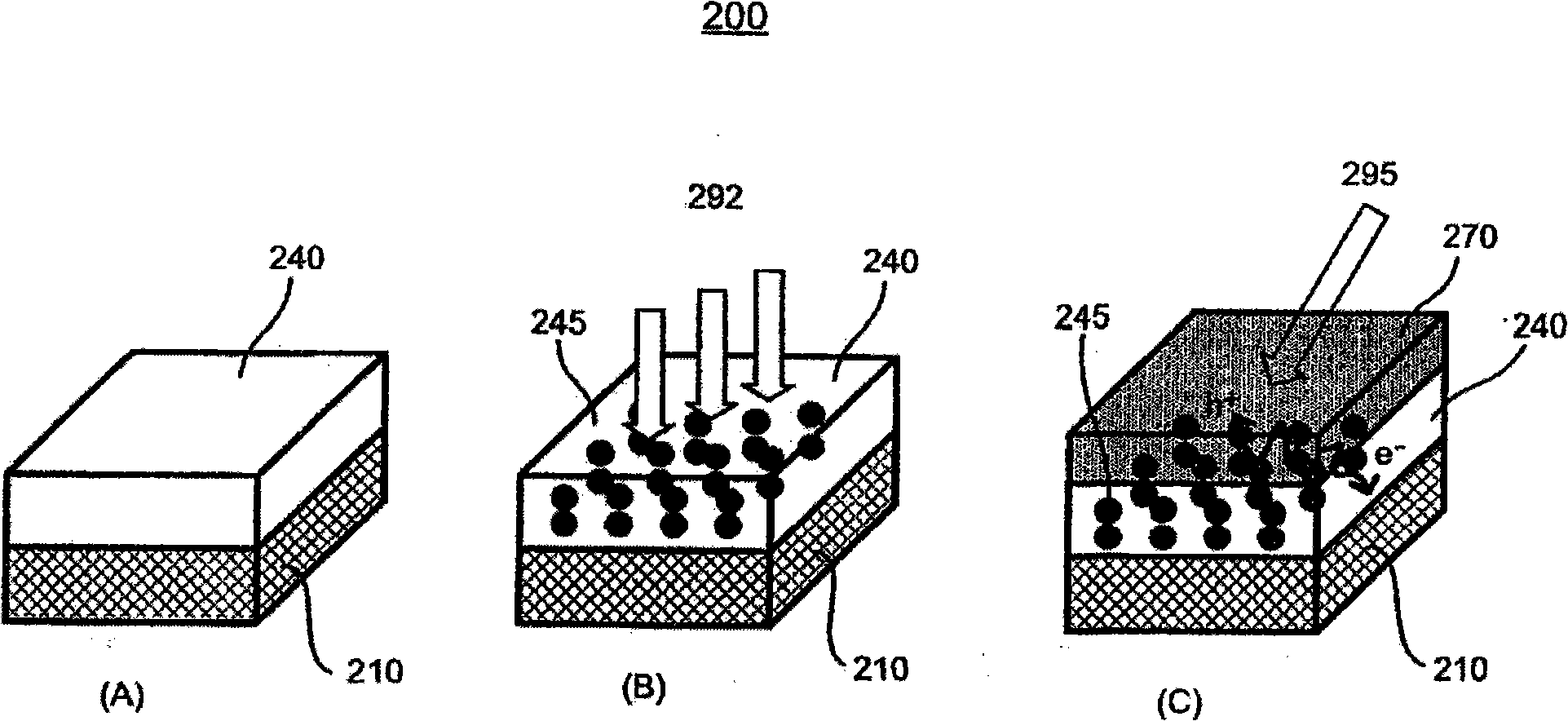
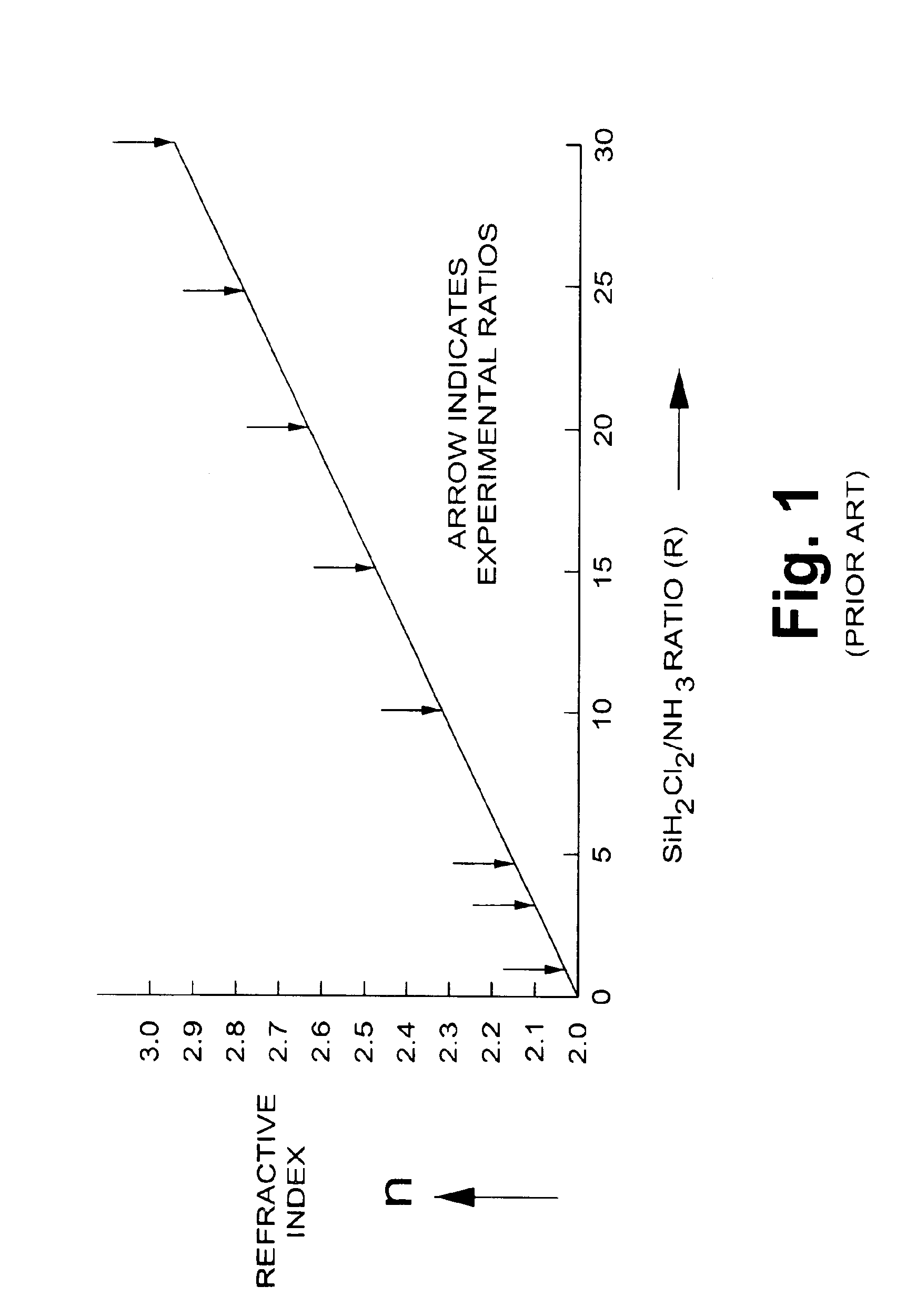
The present invention relates to a method for forming a layered structure with silicon nanocrystals. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: (i) forming a first conductive layer on a substrate, (ii) forming a silicon-rich dielectric layer on the first conductive layer, and (iii) laser-annealing at least the silicon-rich dielectric layer to induce silicon-rich aggregation to form a plurality of silicon nanocrystals in the silicon-rich dielectric layer. The silicon-rich dielectric layer is one of a silicon-rich oxide film having a refractive index in the range of about 1.4 to 2.3, or a silicon-rich nitride film having a refractive index in the range of about 1.7 to 2.3. The layered structure with silicon nanocrystals in a silicon-rich dielectric layer is usable in a solar cell, a photodetector, a touch panel, a non-volatile memory device as storage node, and a liquid crystal display.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
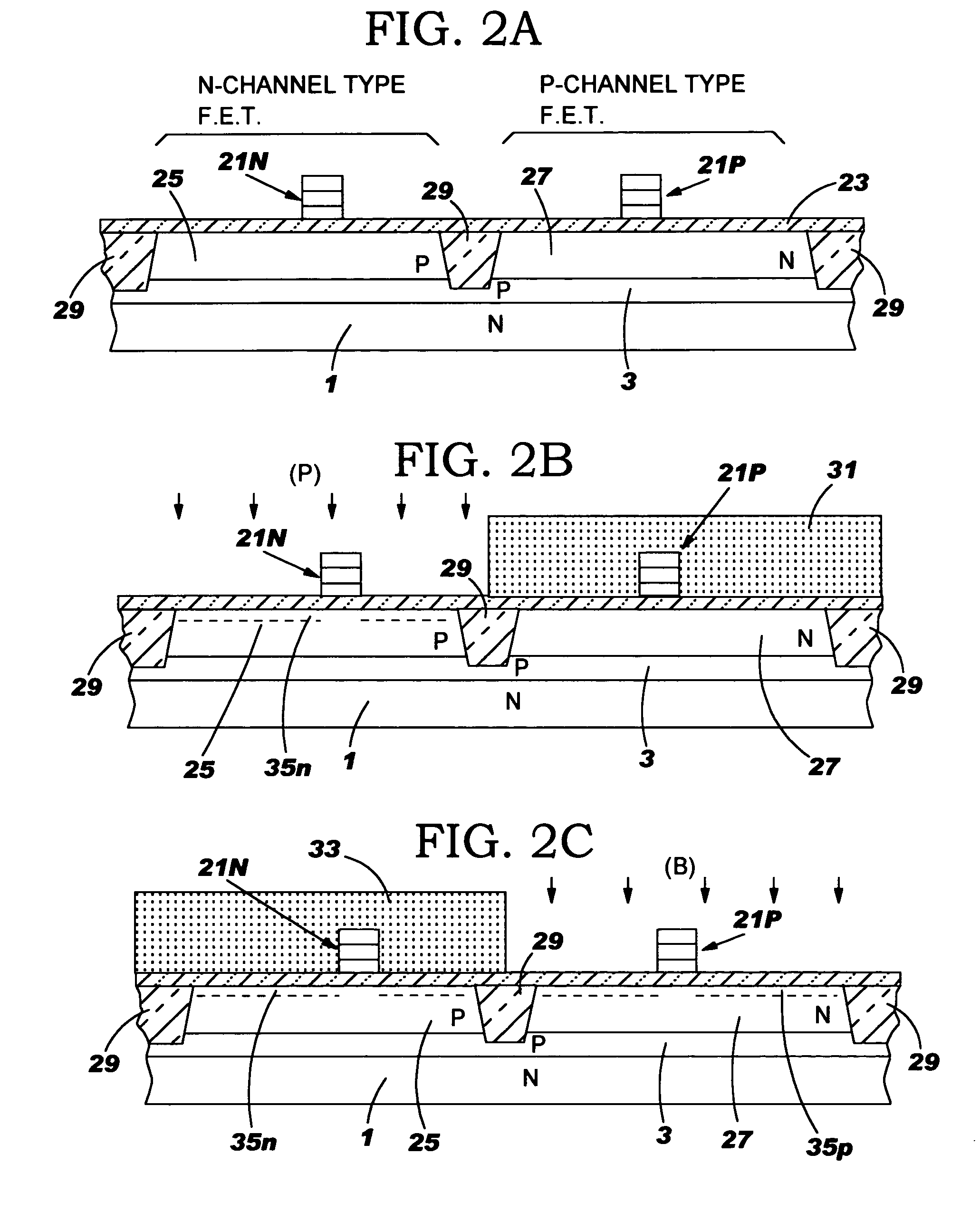
Split poly-SiGe/poly-Si alloy gate stack
InactiveUS6927454B2Simple processSimple structureTransistorSolid-state devicesSilicon nanocrystalsGate dielectric
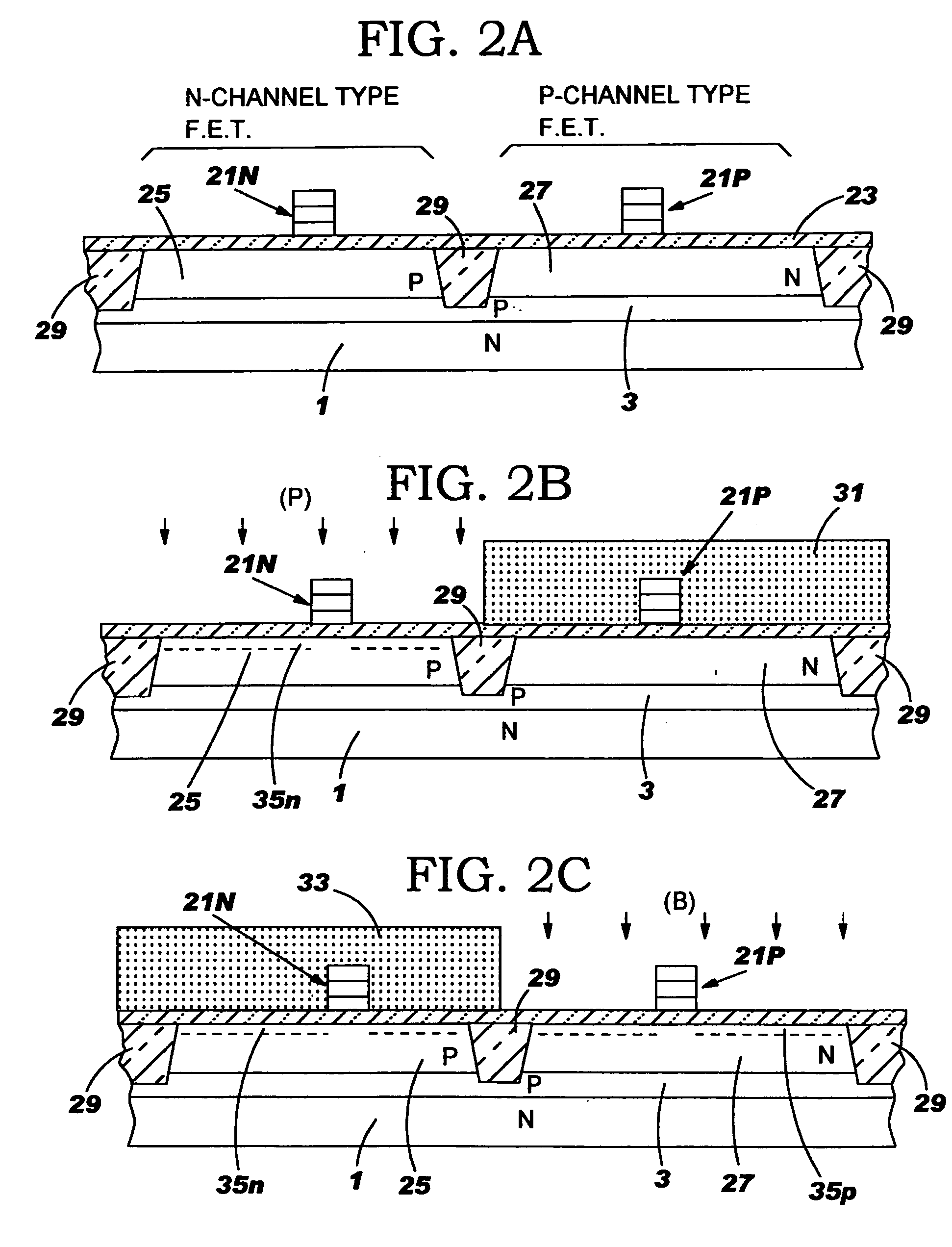
A multi-layered gate electrode stack structure of a field effect transistor device is formed on a silicon nano crystal seed layer on the gate dielectric. The small grain size of the silicon nano crystal layer allows for deposition of a uniform and continuous layer of poly-SiGe with a [Ge] of up to at least 70% using in situ rapid thermal chemical vapor deposition (RTCVD). An in-situ purge of the deposition chamber in a oxygen ambient at rapidly reduced temperatures results in a thin SiO2 or SixGeyOz interfacial layer of 3 to 4A thick. The thin SiO2 or SixGeyOz interfacial layer is sufficiently thin and discontinuous to offer little resistance to gate current flow yet has sufficient [O] to effectively block upward Ge diffusion during heat treatment to thereby allow silicidation of the subsequently deposited layer of cobalt. The gate electrode stack structure is used for both nFETs and pFETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
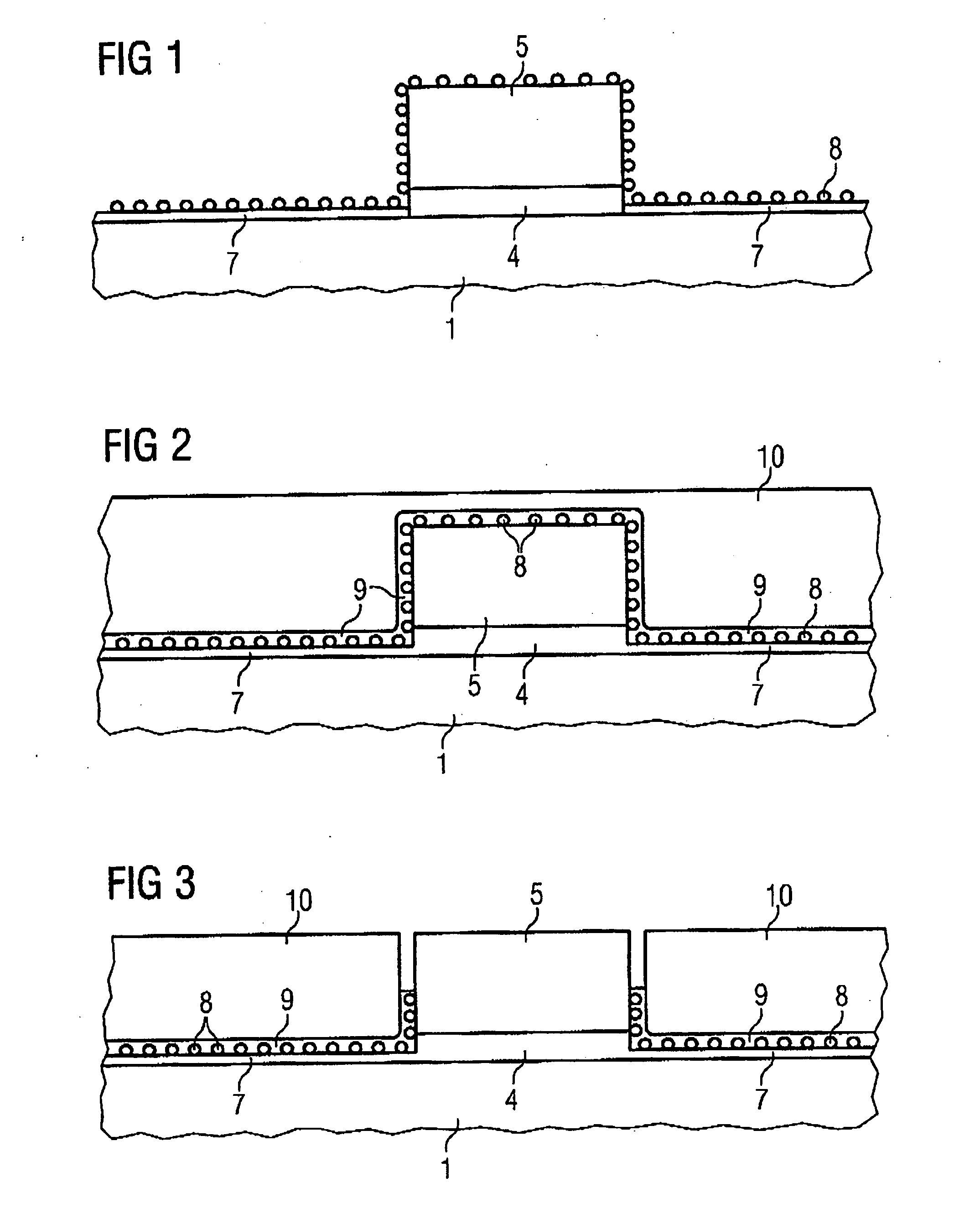
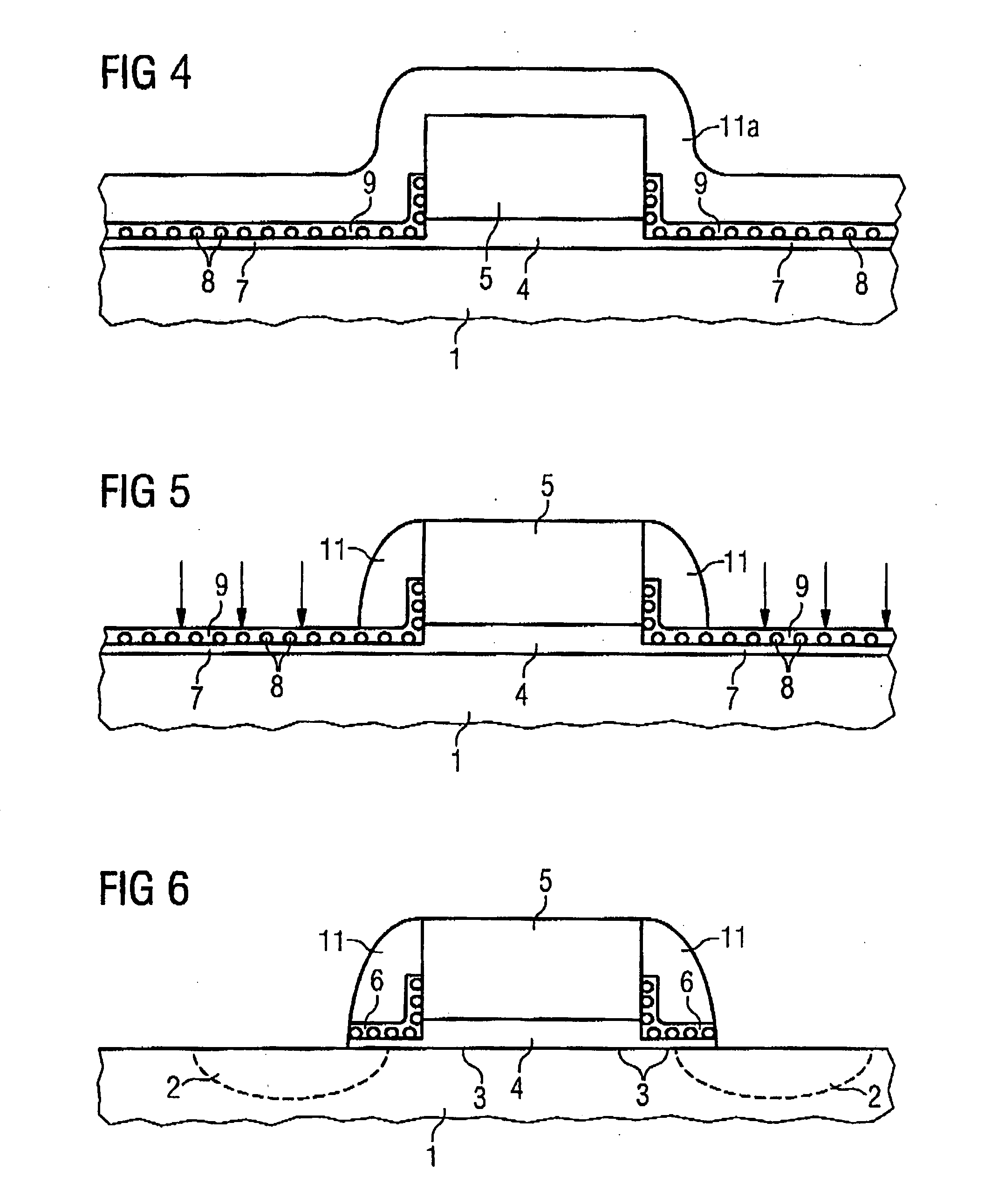
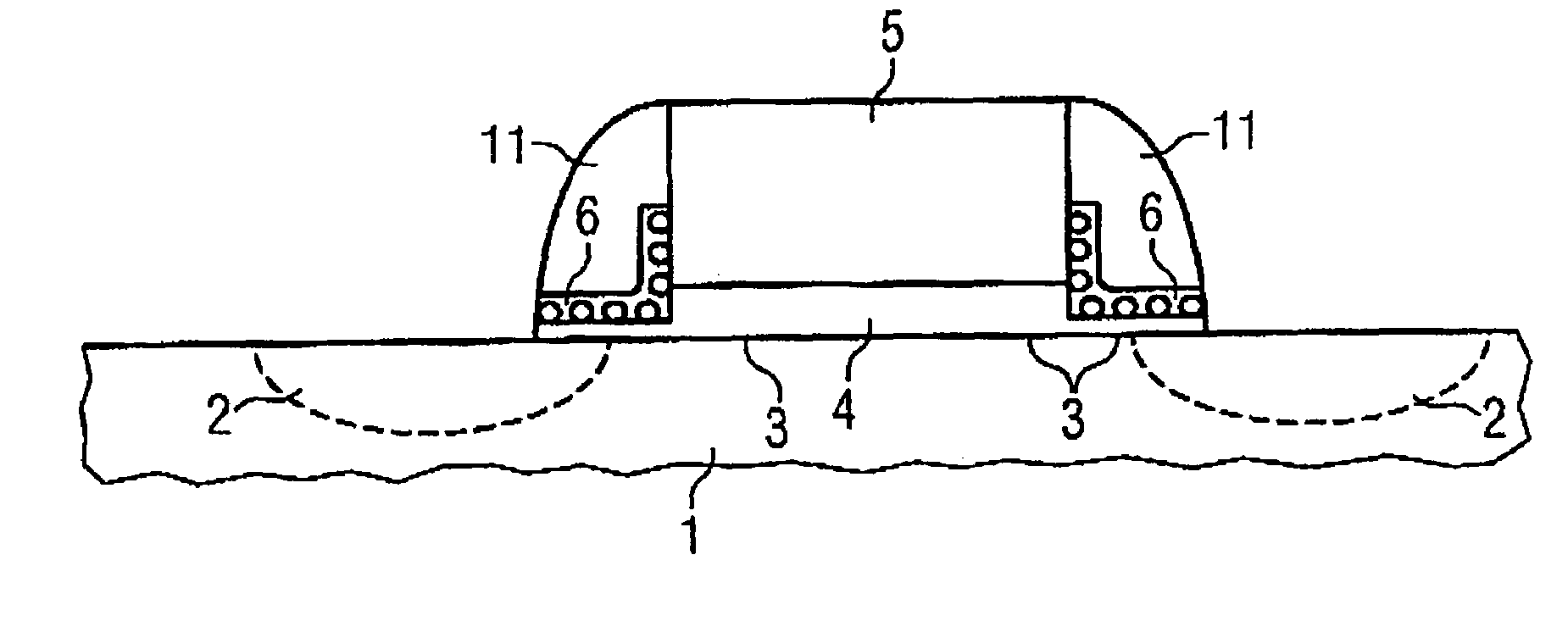
Method for fabricating a memory cell
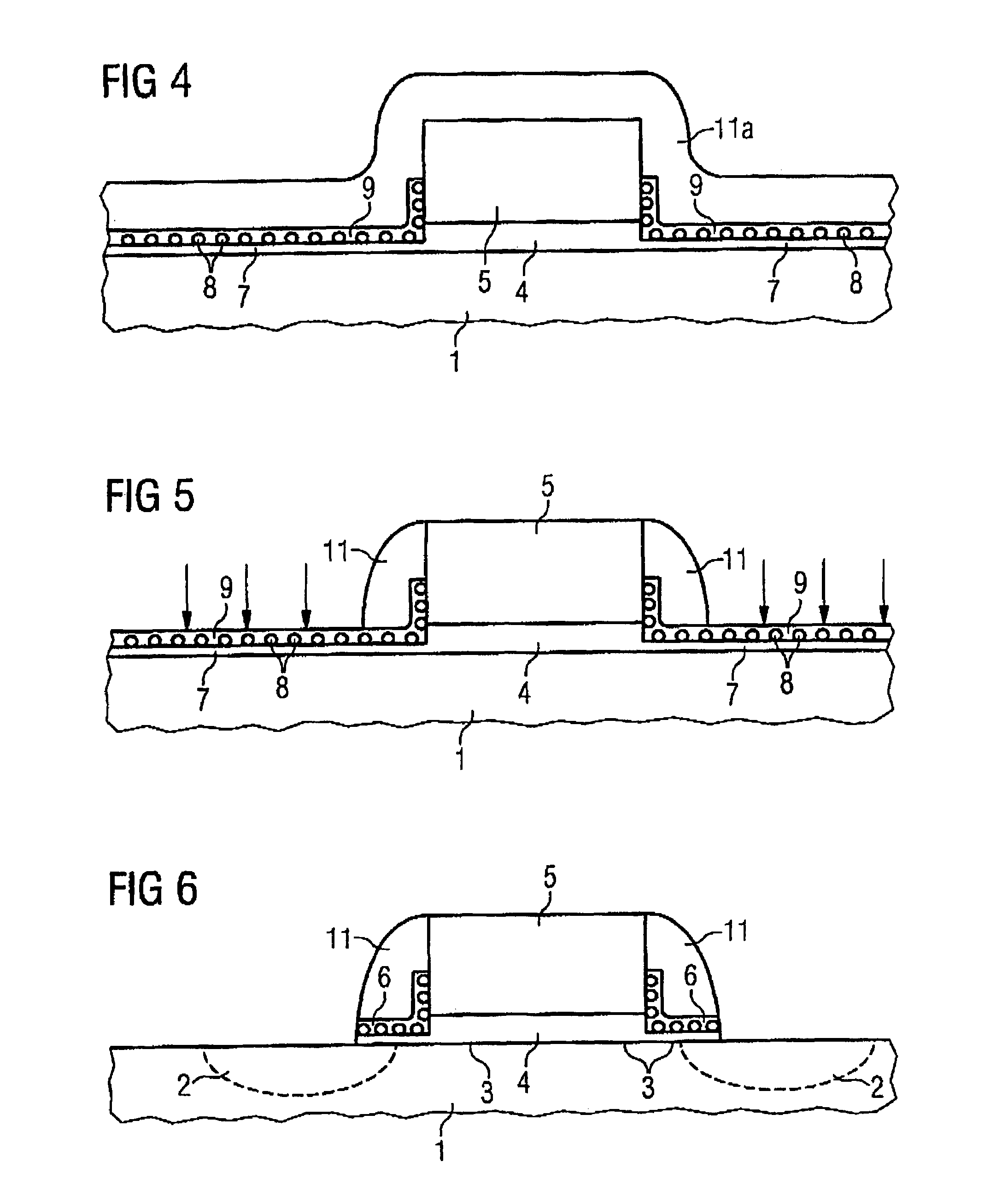
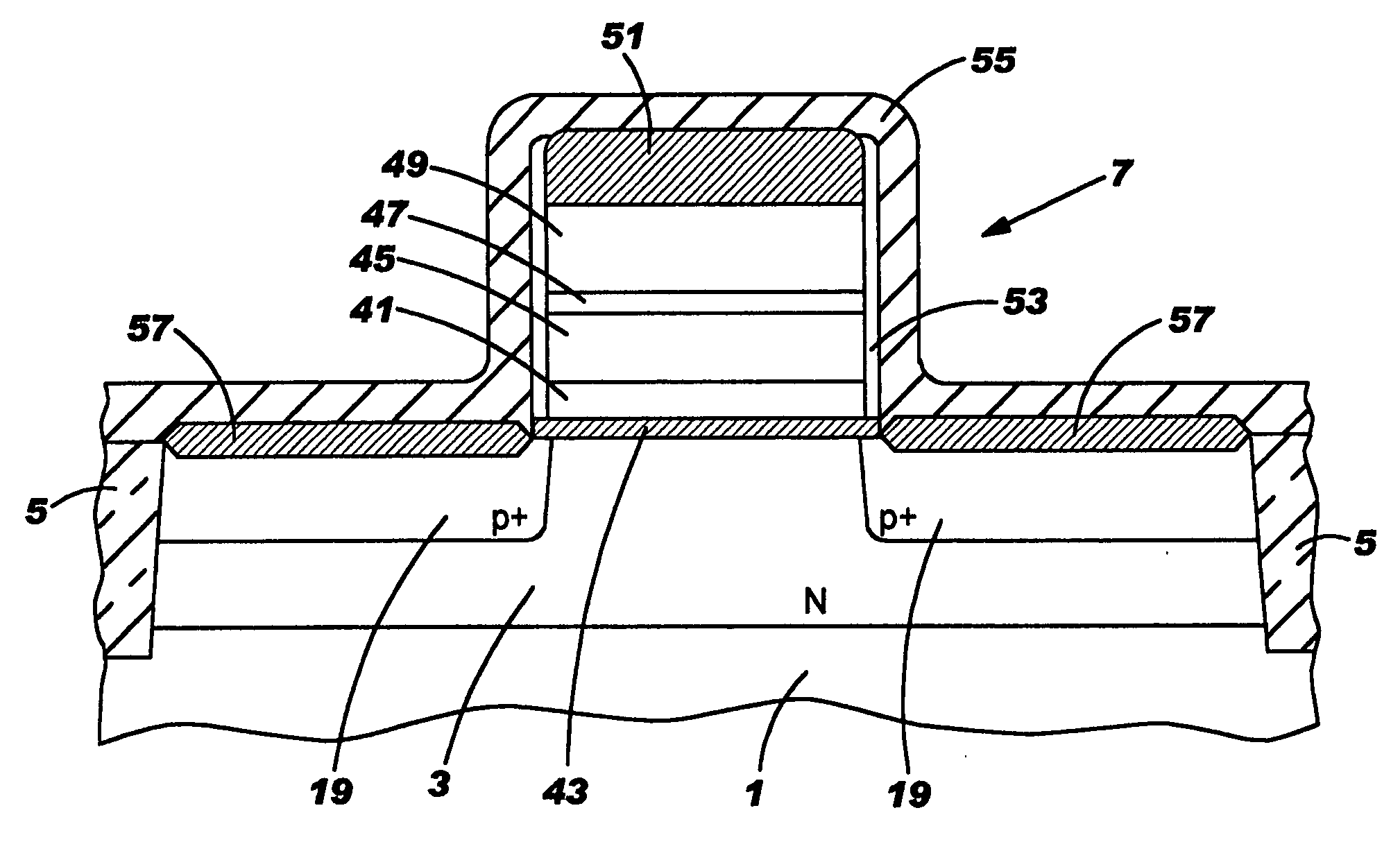
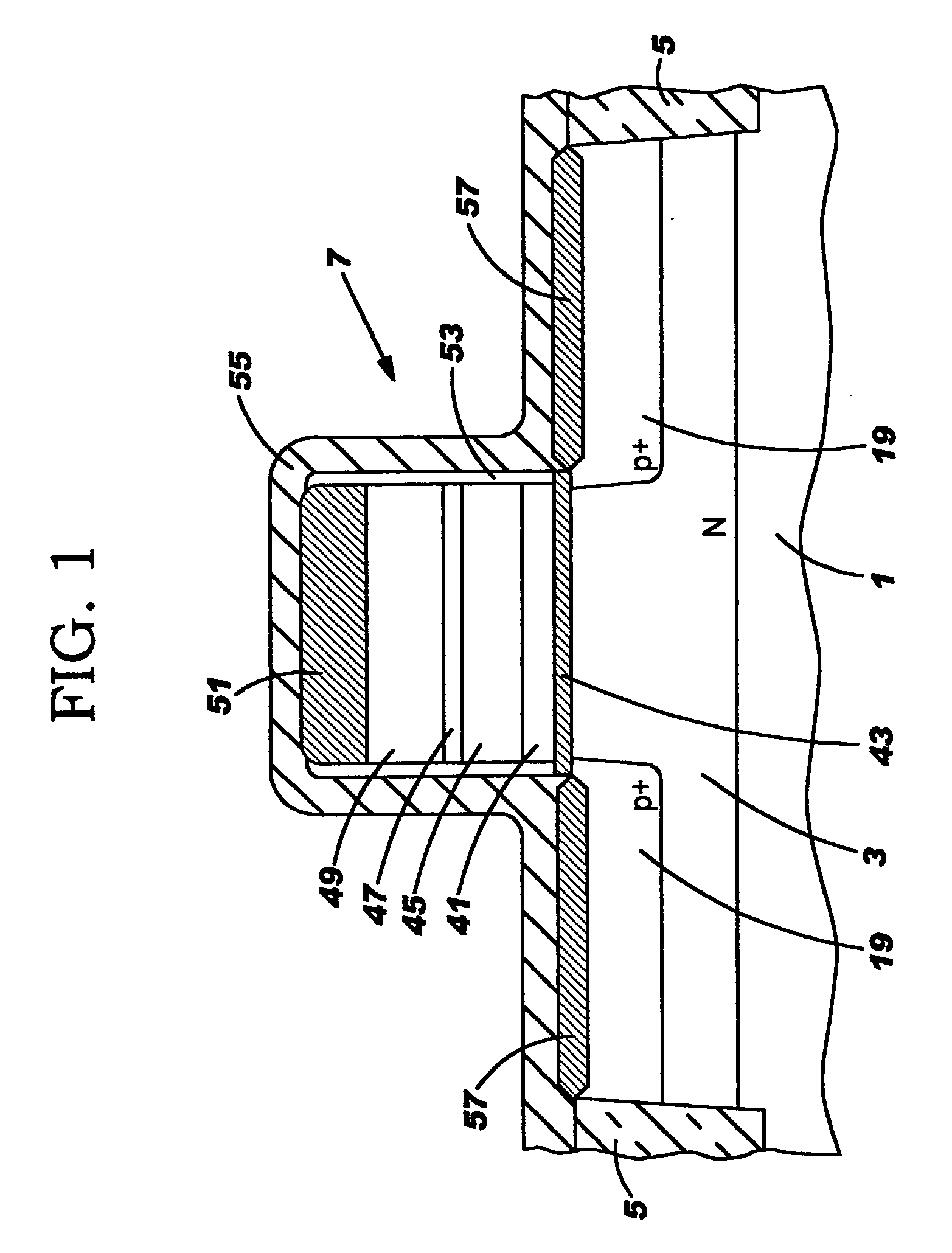
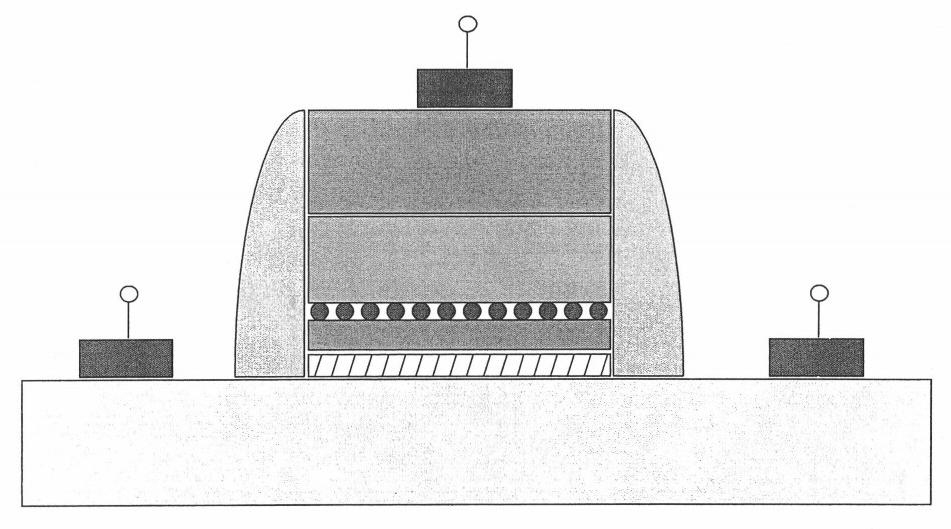
Silicon nanocrystals are applied as storage layer (6) and removed using spacer elements (11) laterally with respect to the gate electrode (5). By means of an implantation of dopant, source / drain regions (2) are fabricated in a self-aligned manner with respect to the storage layer (6). The portions of the storage layer (6) are interrupted by the gate electrode (5) and the gate dielectric (4), so that a central portion of the channel region (3) is not covered by the storage layer (6). This memory cell is suitable as a multi-bit flash memory cell in a virtual ground architecture.
Owner:QIMONDA
Method for fabricating a memory cell
Silicon nanocrystals are applied as storage layer (6) and removed using spacer elements (11) laterally with respect to the gate electrode (5). By means of an implantation of dopant, source / drain regions (2) are fabricated in a self-aligned manner with respect to the storage layer (6). The portions of the storage layer (6) are interrupted by the gate electrode (5) and the gate dielectric (4), so that a central portion of the channel region (3) is not covered by the storage layer (6). This memory cell is suitable as a multi-bit flash memory cell in a virtual ground architecture.
Owner:QIMONDA
Methods of forming silicon nanocrystals by laser annealing
The present invention relates to a method for forming a layered structure with silicon nanocrystals. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: (i) forming a first conductive layer on a substrate, (ii) forming a silicon-rich dielectric layer on the first conductive layer, and (iii) laser-annealing at least the silicon-rich dielectric layer to induce silicon-rich aggregation to form a plurality of silicon nanocrystals in the silicon-rich dielectric layer. The silicon-rich dielectric layer is one of a silicon-rich oxide film having a refractive index in the range of about 1.4 to 2.3, or a silicon-rich nitride film having a refractive index in the range of about 1.7 to 2.3. The layered structure with silicon nanocrystals in a silicon-rich dielectric layer is usable in a solar cell, a photodetector, a touch panel, a non-volatile memory device as storage node, and a liquid crystal display.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
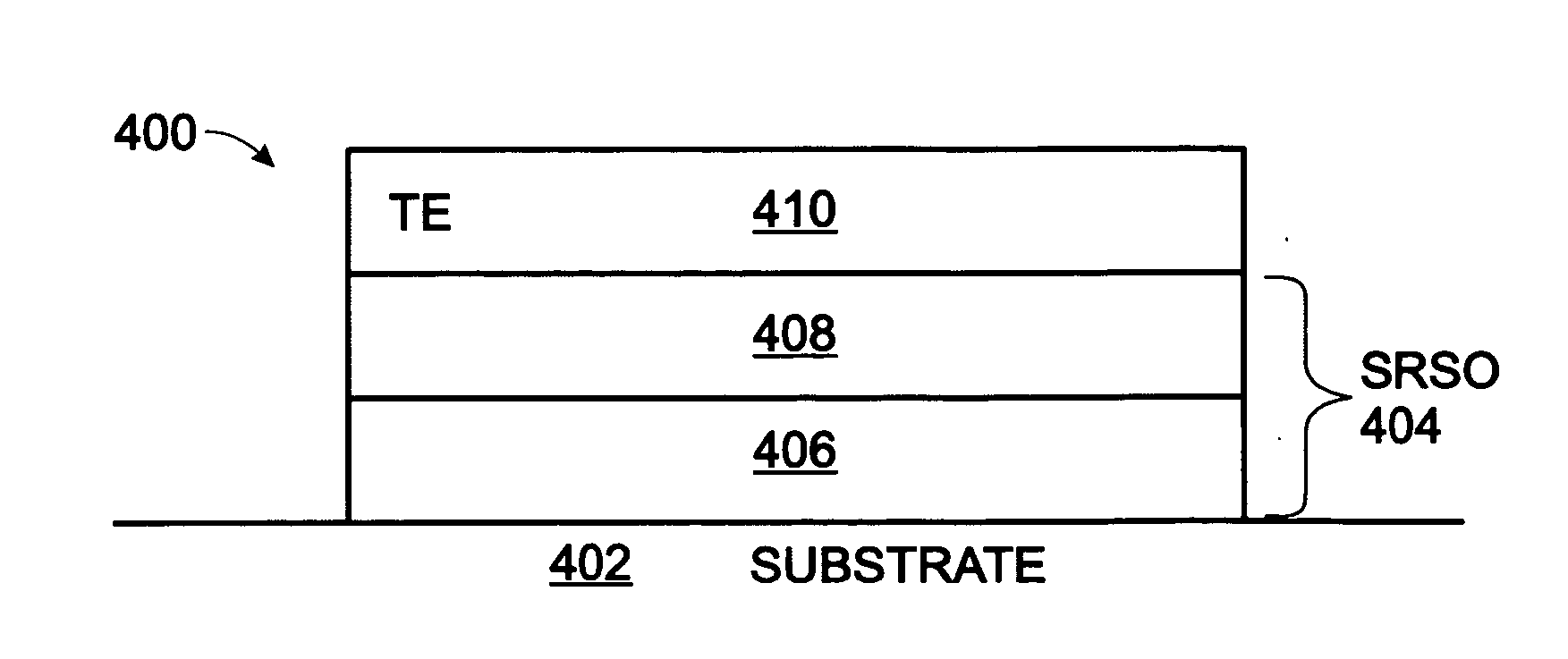
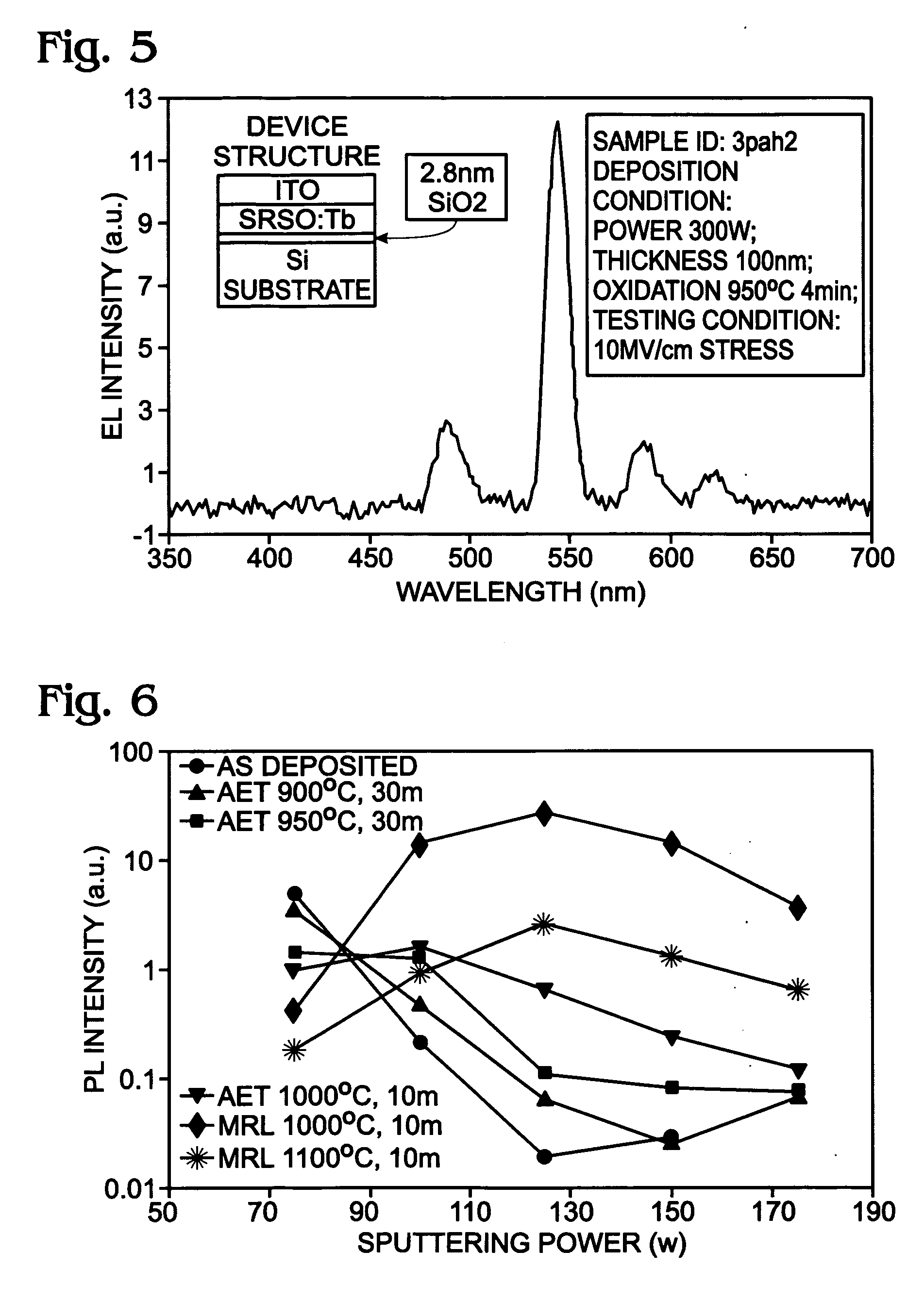
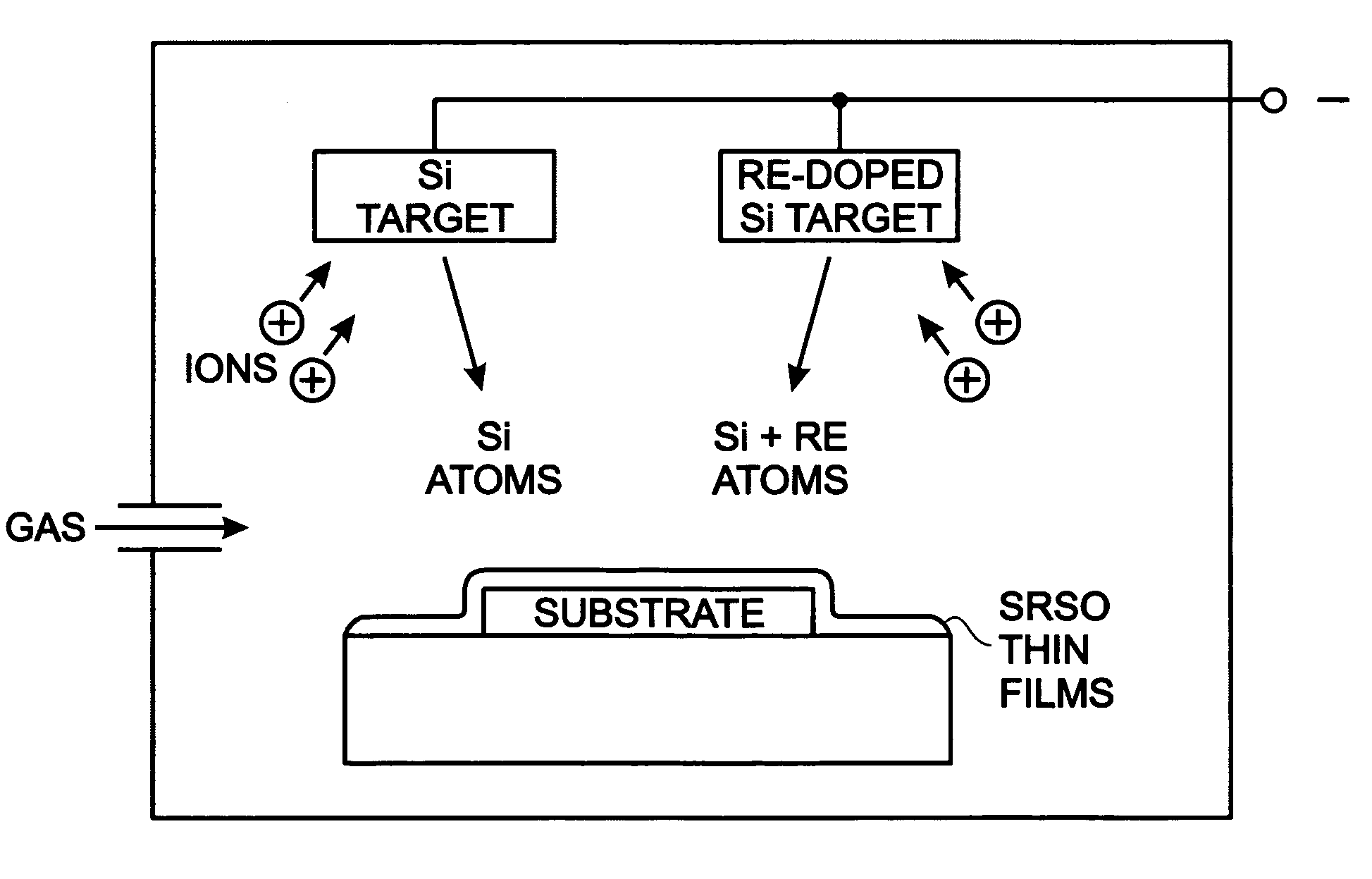
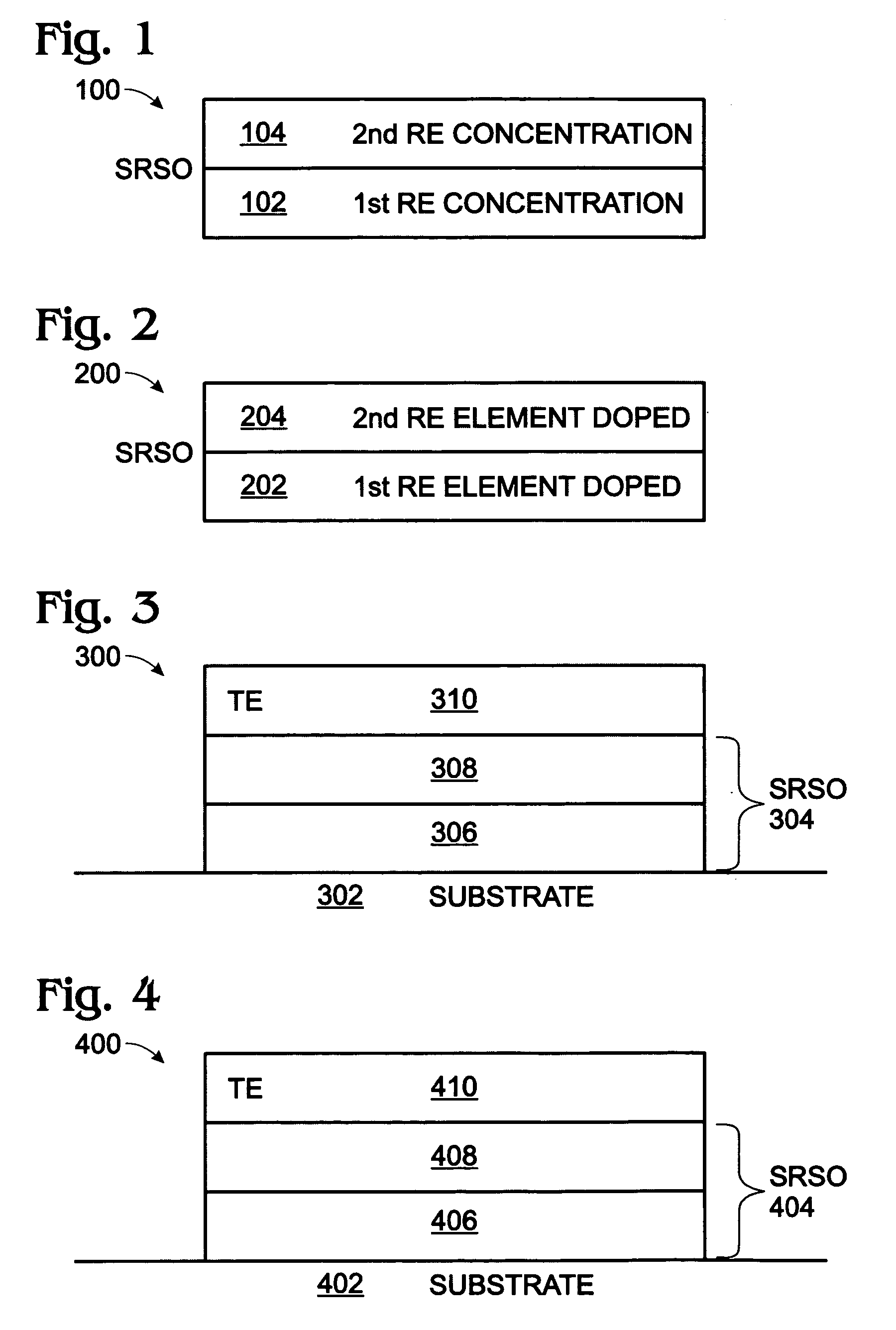
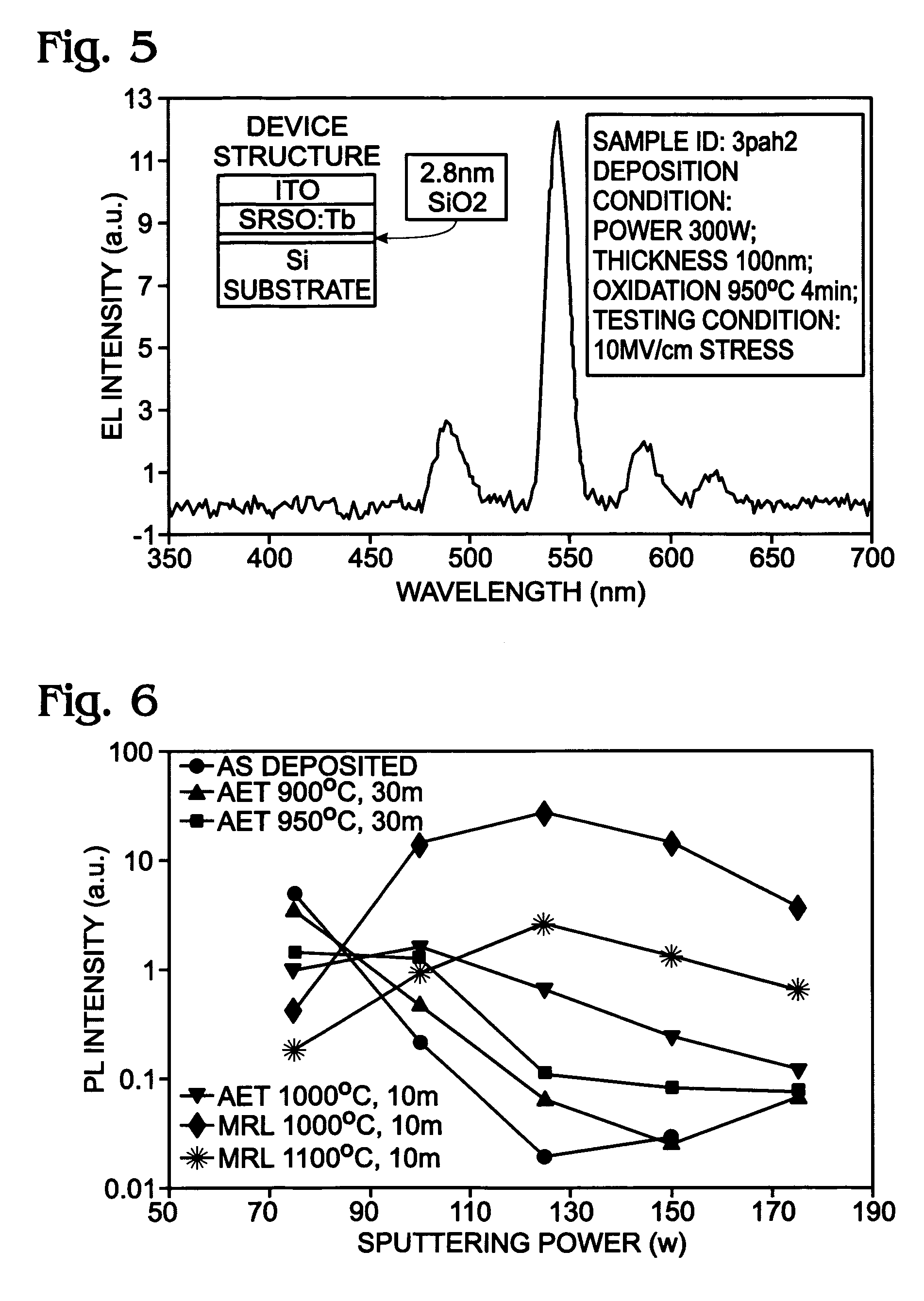
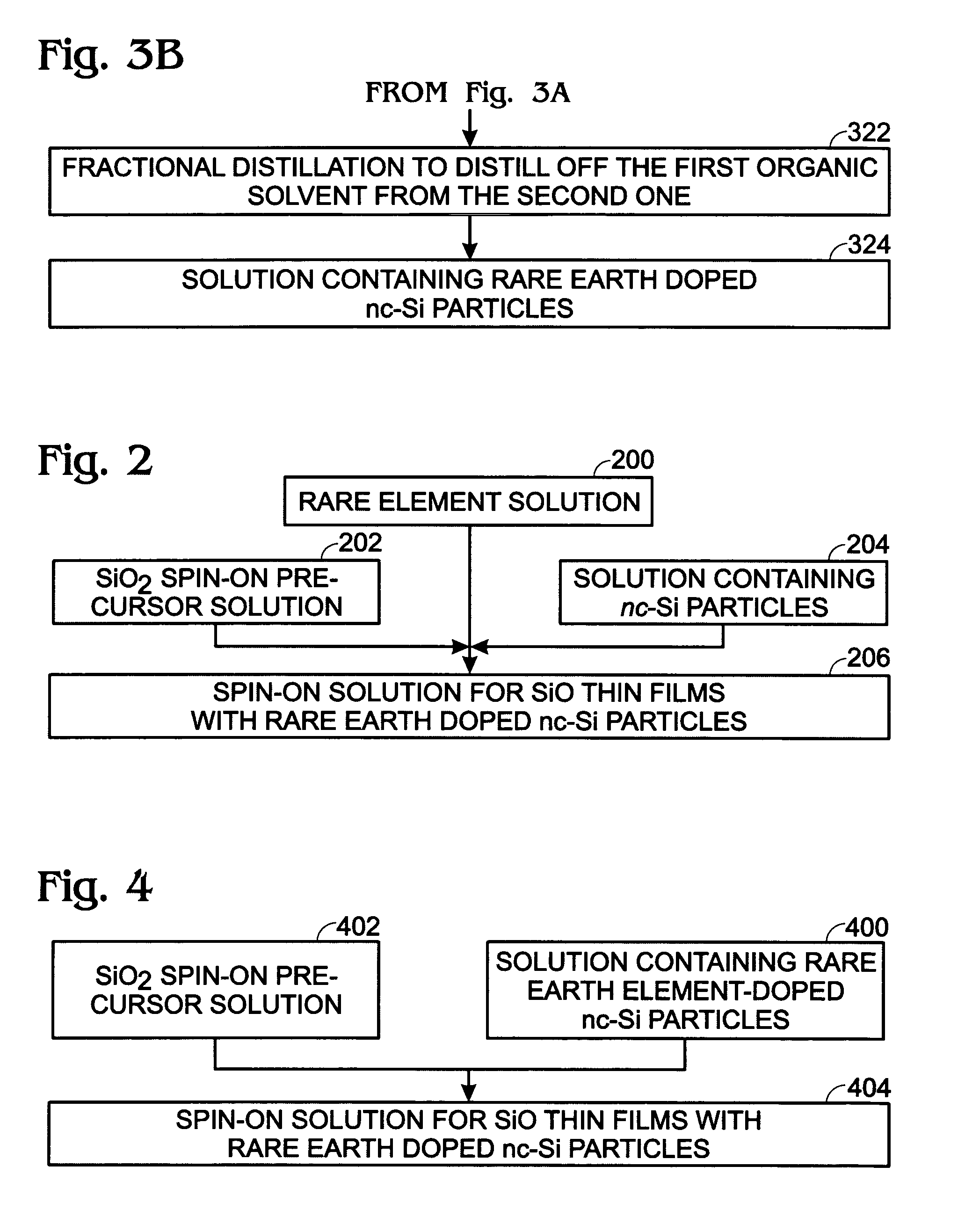
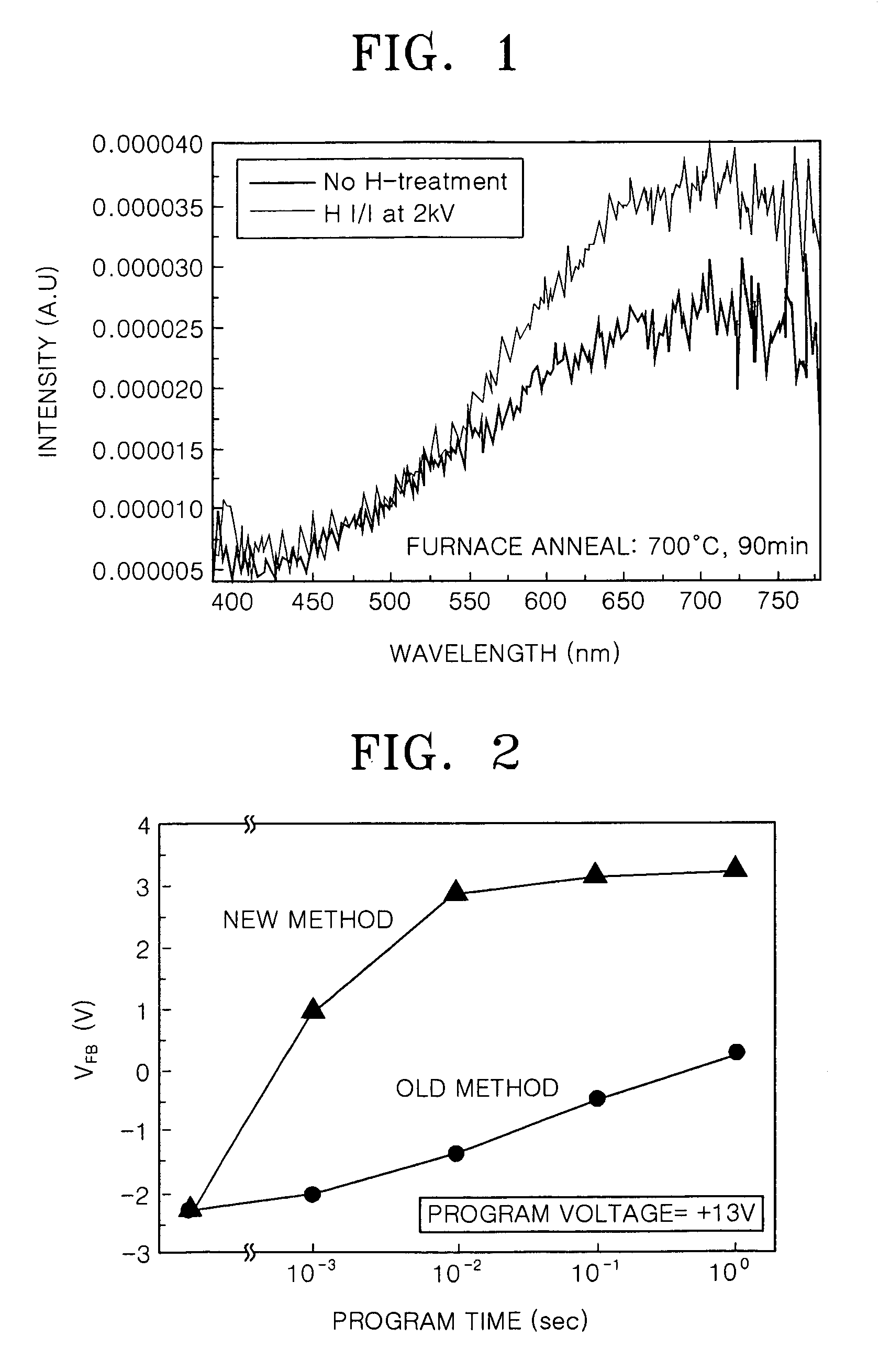
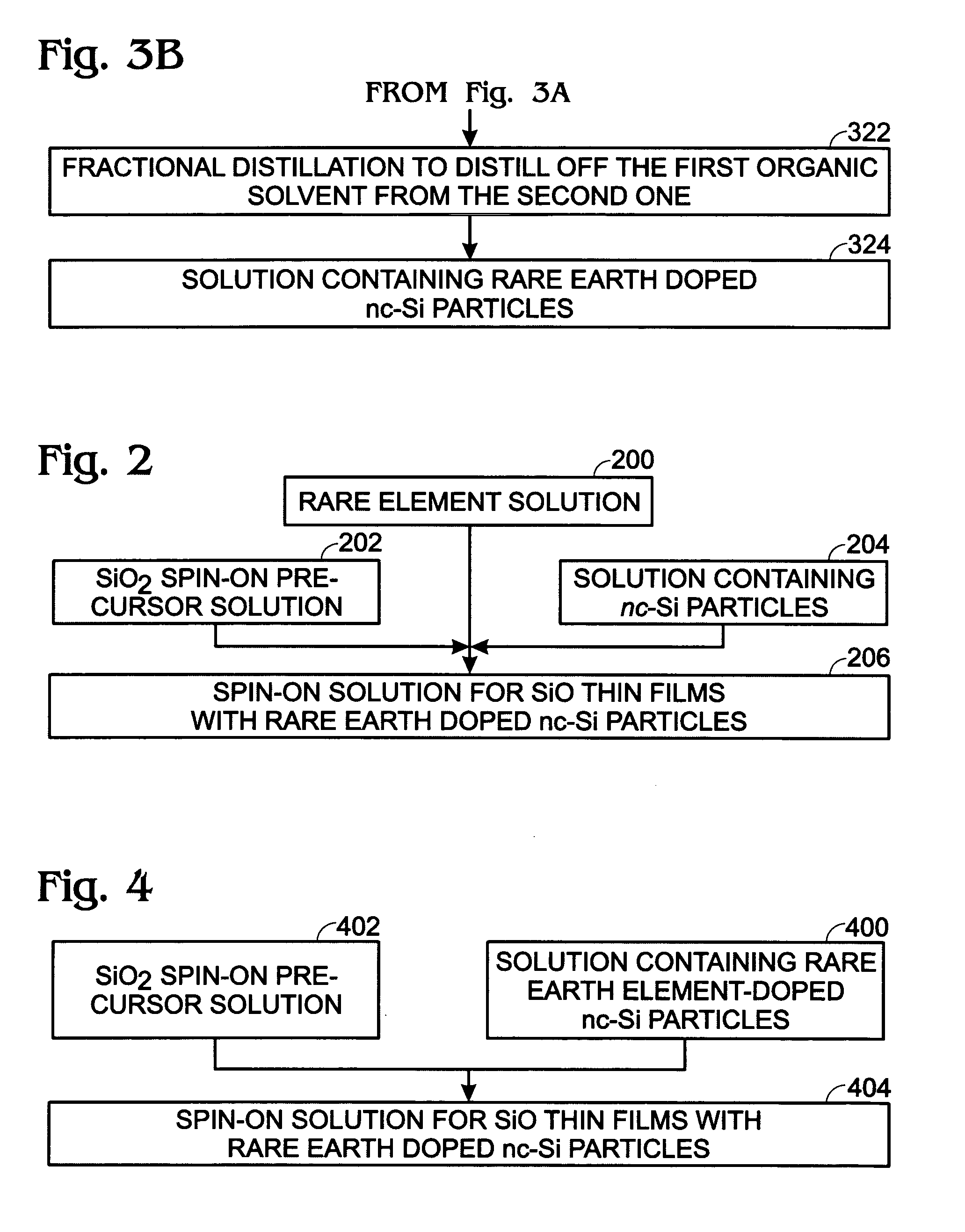
Sputter-deposited rare earth element-doped silicon oxide film with silicon nanocrystals for electroluminescence applications
InactiveUS20060183305A1Electroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nanocrystalsCerium
A method is provided for forming a rare earth (RE) element-doped silicon (Si) oxide film with nanocrystalline (nc) Si particles. The method comprises: providing a first target of Si, embedded with a first rare earth element; providing a second target of Si; co-sputtering the first and second targets; forming a Si-rich Si oxide (SRSO) film on a substrate, doped with the first rare earth element; and, annealing the rare earth element-doped SRSO film. The first target is doped with a rare earth element such as erbium (Er), ytterbium (Yb), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), or terbium (Tb). The sputtering power is in the range of about 75 to 300 watts (W). Different sputtering powers are applied to the two targets. Also, deposition can be controlled by varying the effective areas of the two targets. For example, one of the targets can be partially covered.
Owner:SHARP KK
Sputter-deposited rare earth element-doped silicon oxide film with silicon nanocrystals for electroluminescence applications
InactiveUS7297642B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare-earth elementSilicon nanocrystals
A method is provided for forming a rare earth (RE) element-doped silicon (Si) oxide film with nanocrystalline (nc) Si particles. The method comprises: providing a first target of Si, embedded with a first rare earth element; providing a second target of Si; co-sputtering the first and second targets; forming a Si-rich Si oxide (SRSO) film on a substrate, doped with the first rare earth element; and, annealing the rare earth element-doped SRSO film. The first target is doped with a rare earth element such as erbium (Er), ytterbium (Yb), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), or terbium (Tb). The sputtering power is in the range of about 75 to 300 watts (W). Different sputtering powers are applied to the two targets. Also, deposition can be controlled by varying the effective areas of the two targets. For example, one of the targets can be partially covered.
Owner:SHARP KK
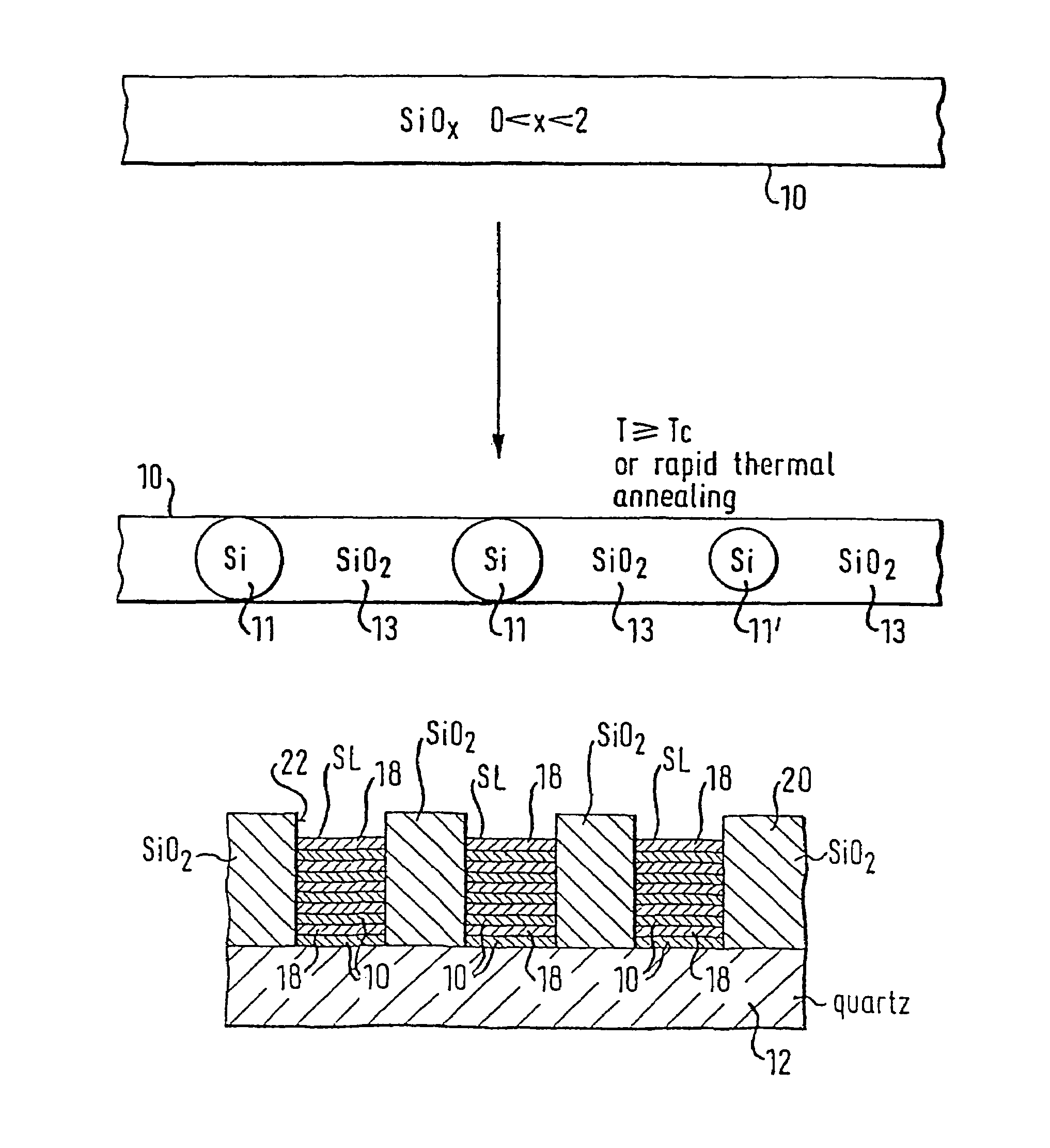
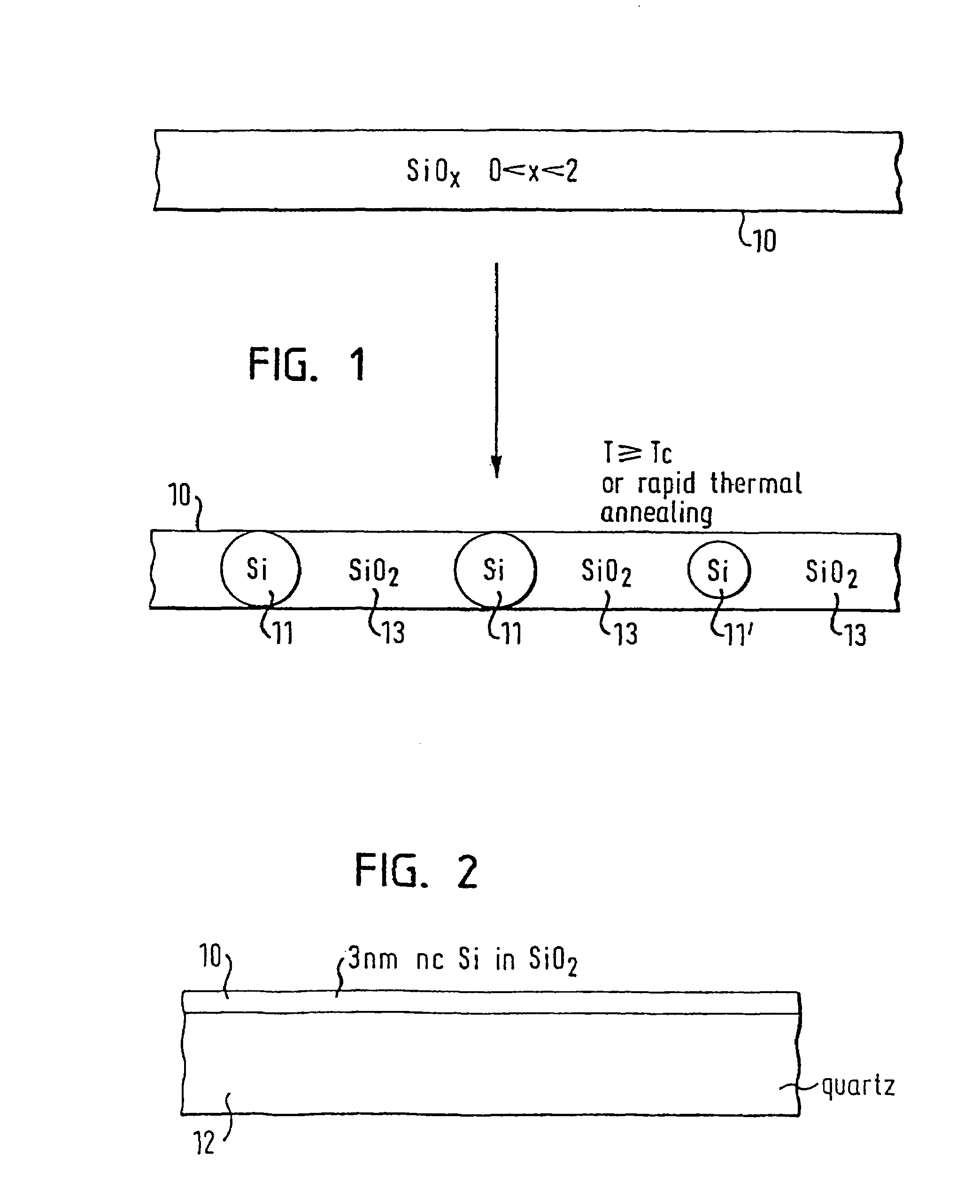
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor structure comprising clusters and/or nanocrystal of silicon and a semiconductor structure of this kind
InactiveUS7220609B2High densityCarry-out economicallyNanotechLaser detailsSilicon nanocrystalsHigh density
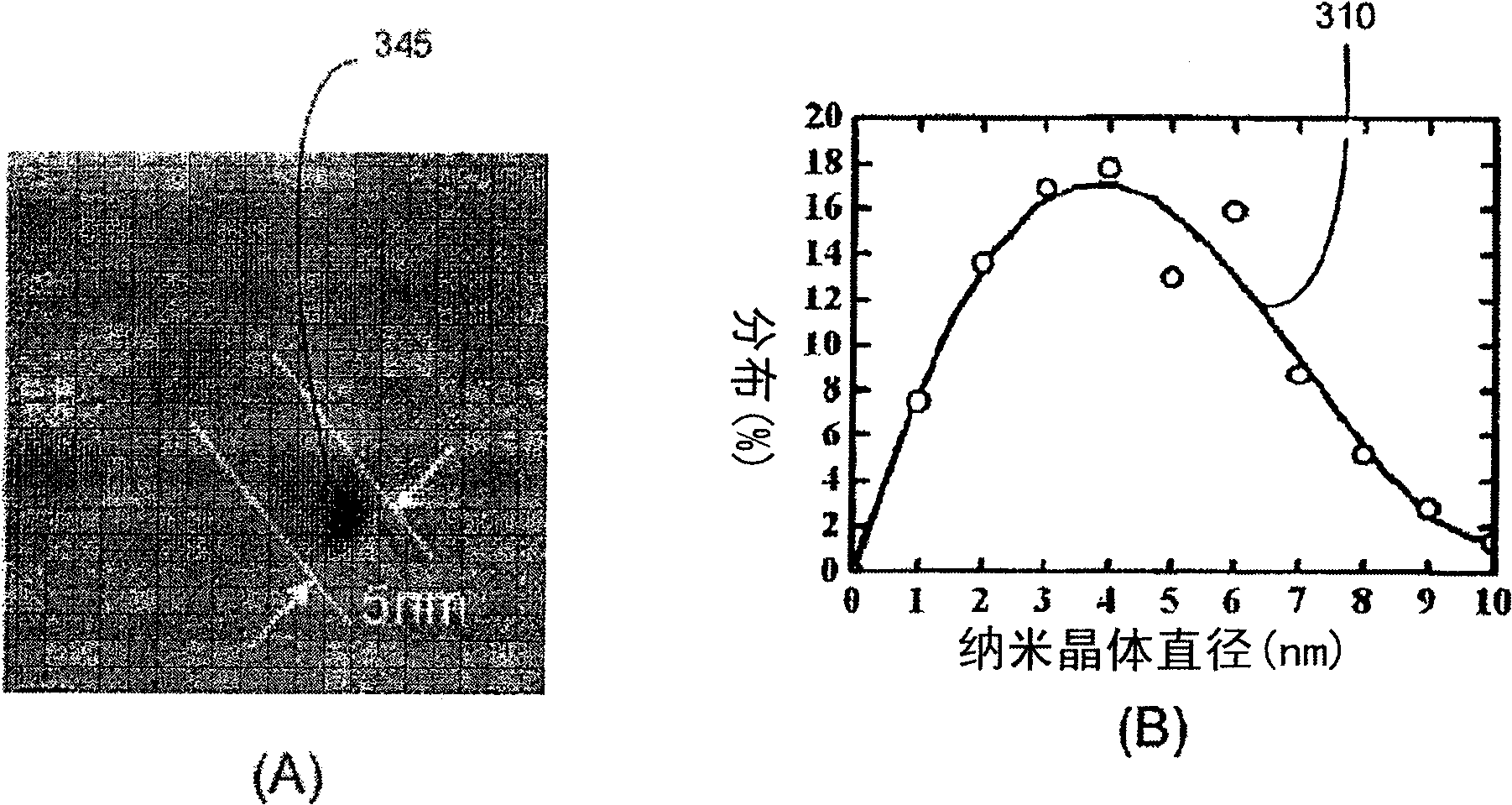
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor structure comprising clusters and / or nanocrystals of silicon described which are present in distributed form in a matrix of silicon compound. The method comprises the steps of depositing a layer of thermally nonstable silicon compound having a layer thickness in the range between 0.5 nm and 20 nm especially between 1 nm and 10 nm and in particular between 1 nm and 7 nm on a support and thermal treatment at a temperature sufficient to carry out a phase separation to obtain clusters or nanocrystals of silicon in a matrix of thermally stable silicon compound. The claims also cover semiconductor structures having such distributed clusters or nanocrystals of silicon The method described enables the economic production of high density arrays of silicon clusters or nanocrystals with a narrow size distribution.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
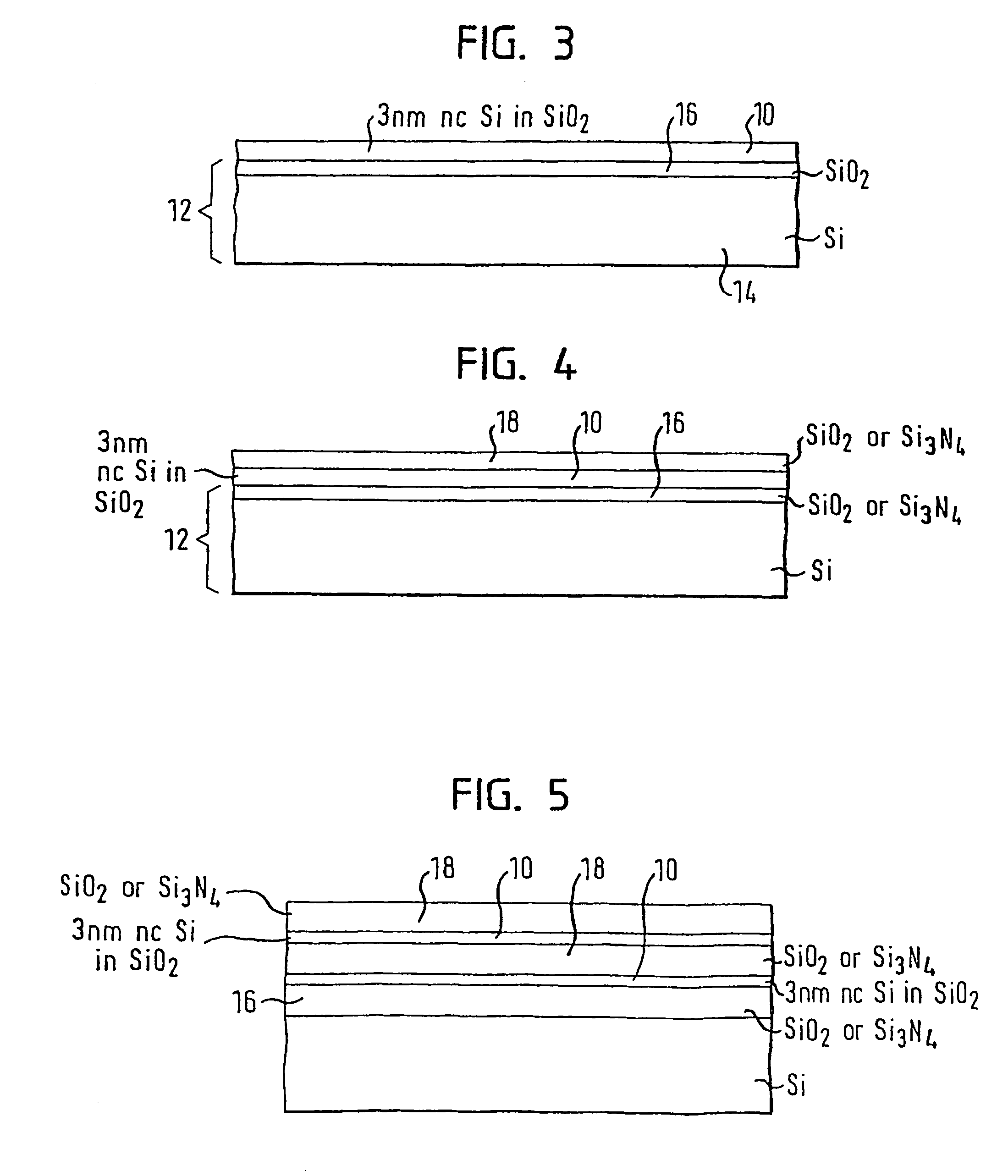
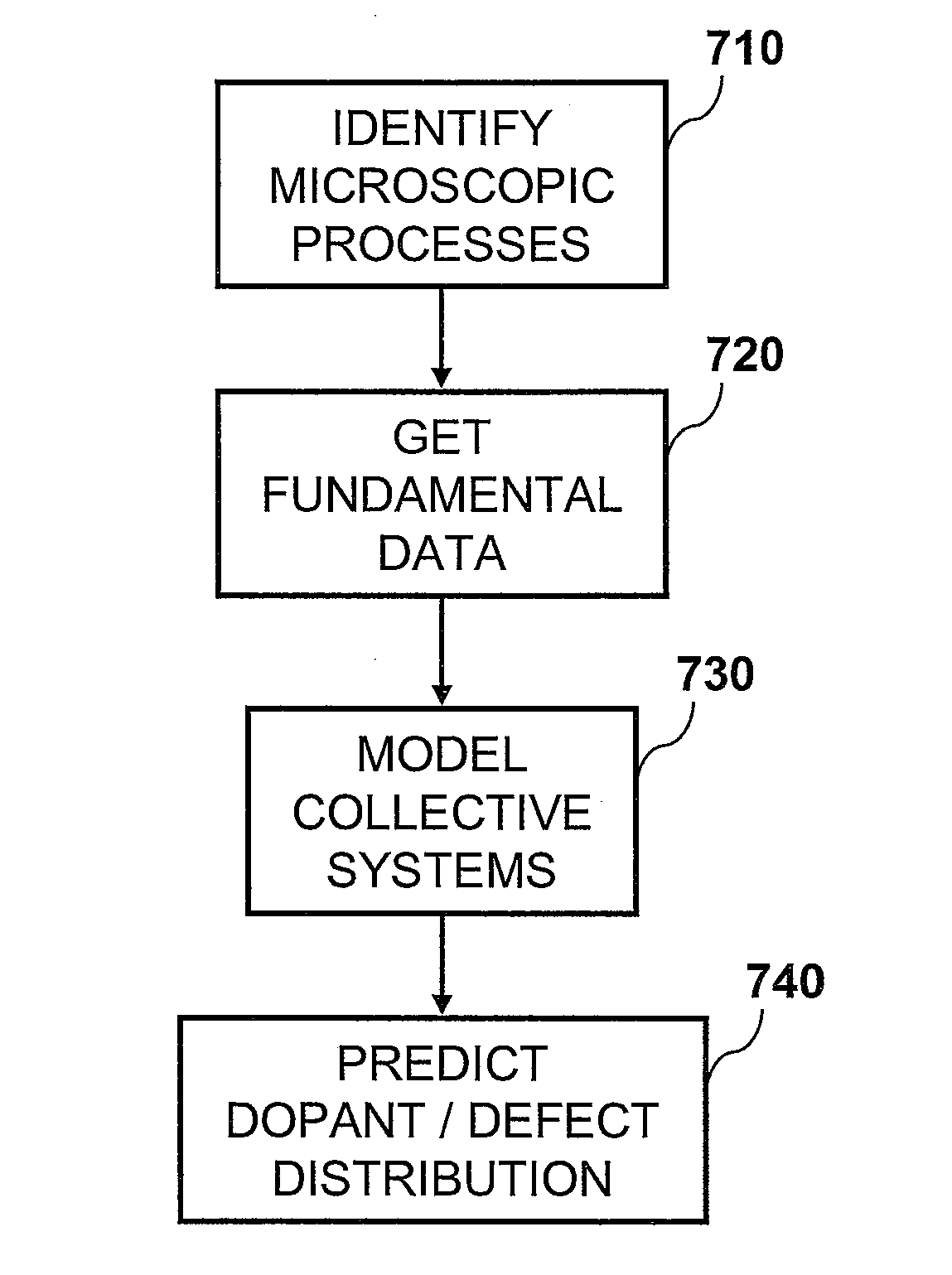
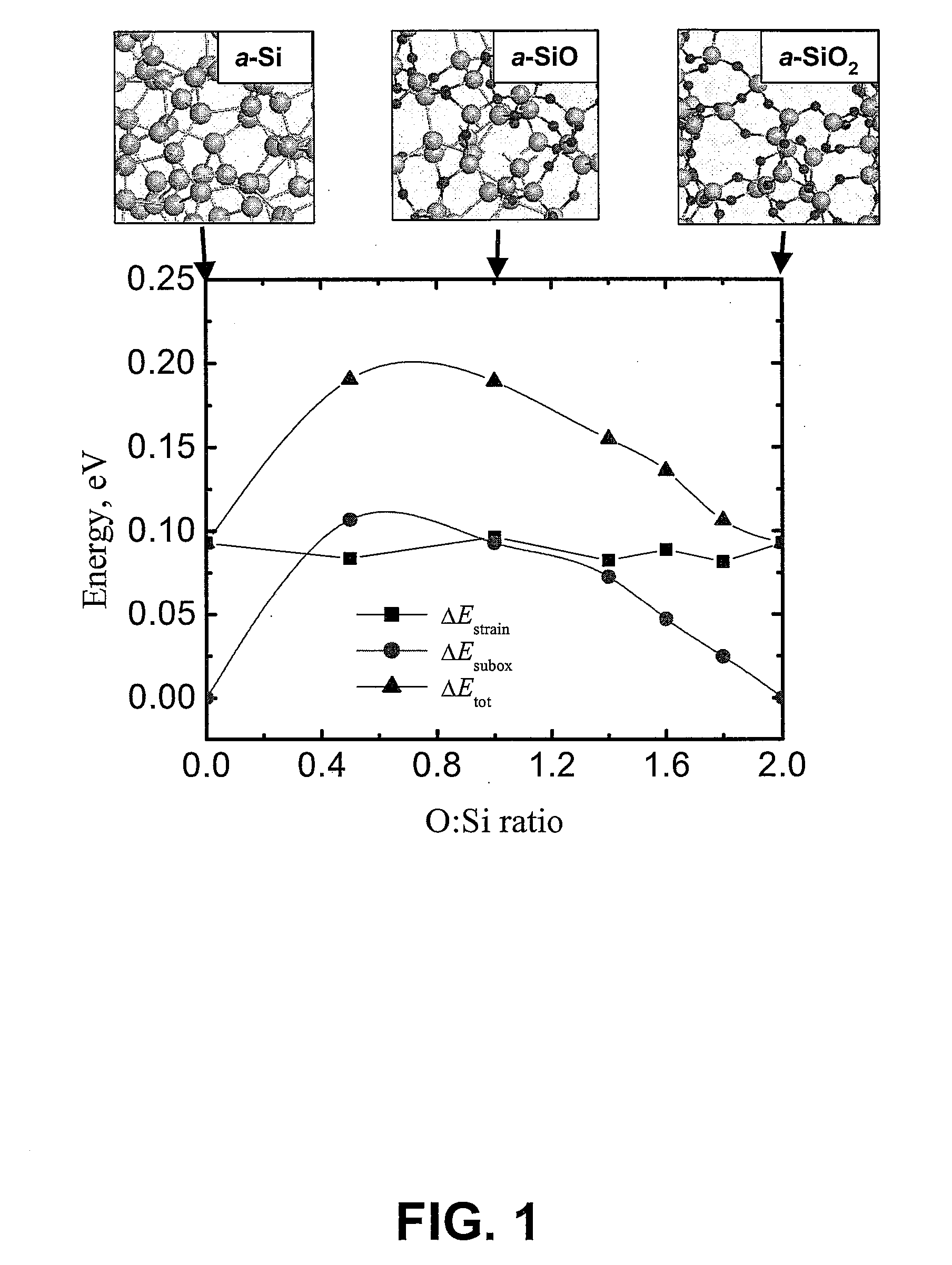
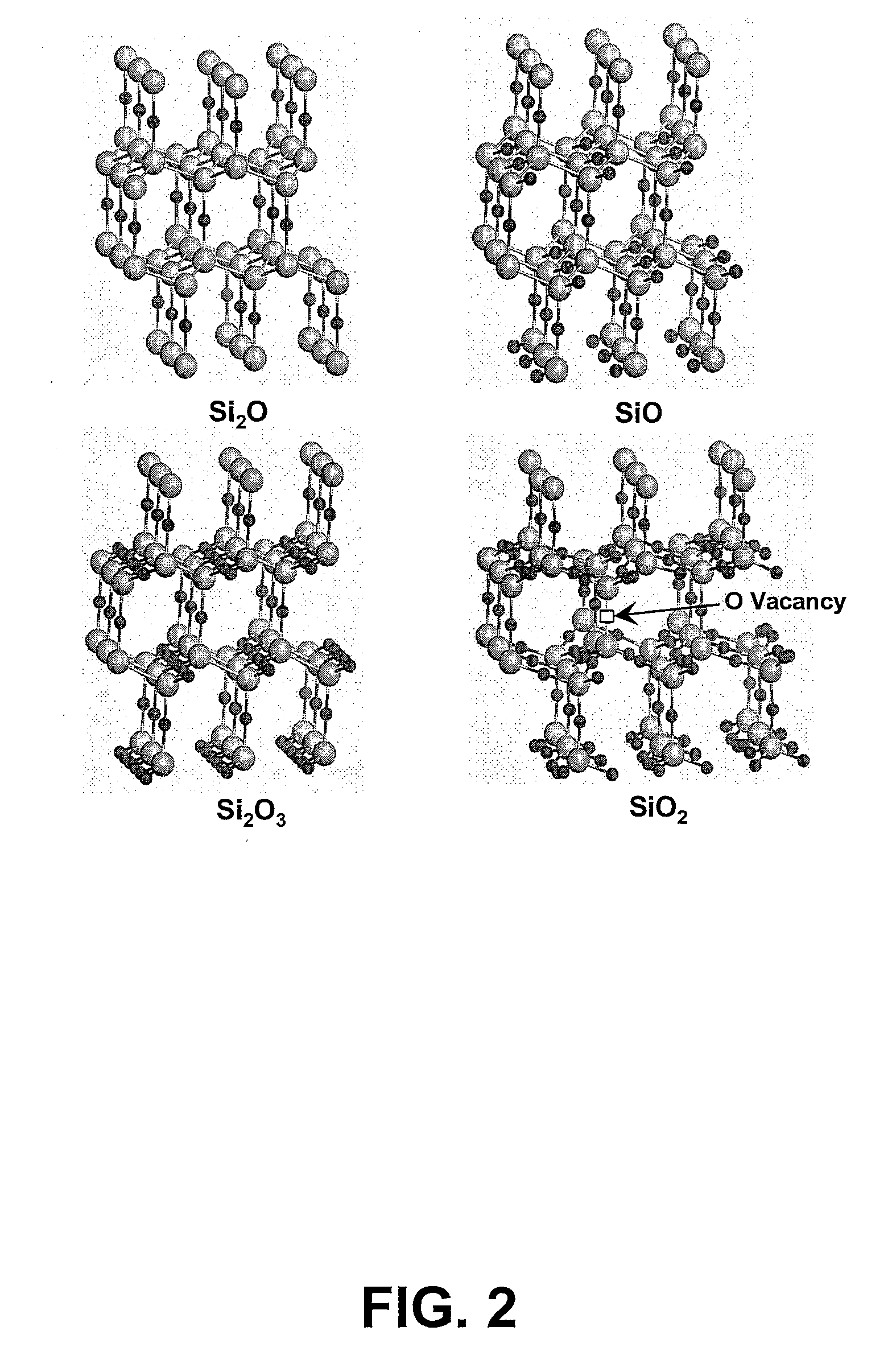
Method For Predicting The Formation Of Silicon Nanocrystals In Embedded Oxide Matrices
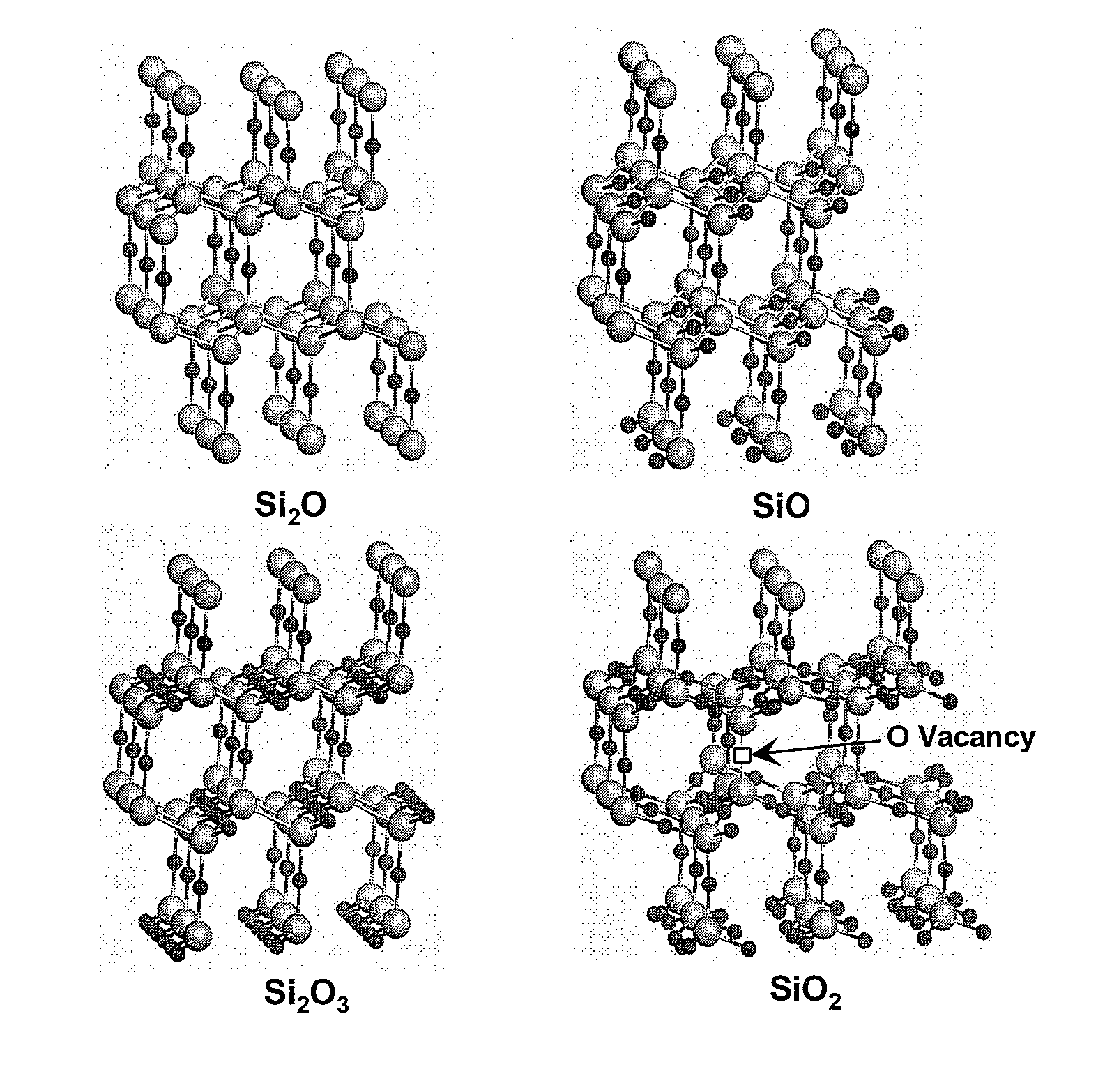
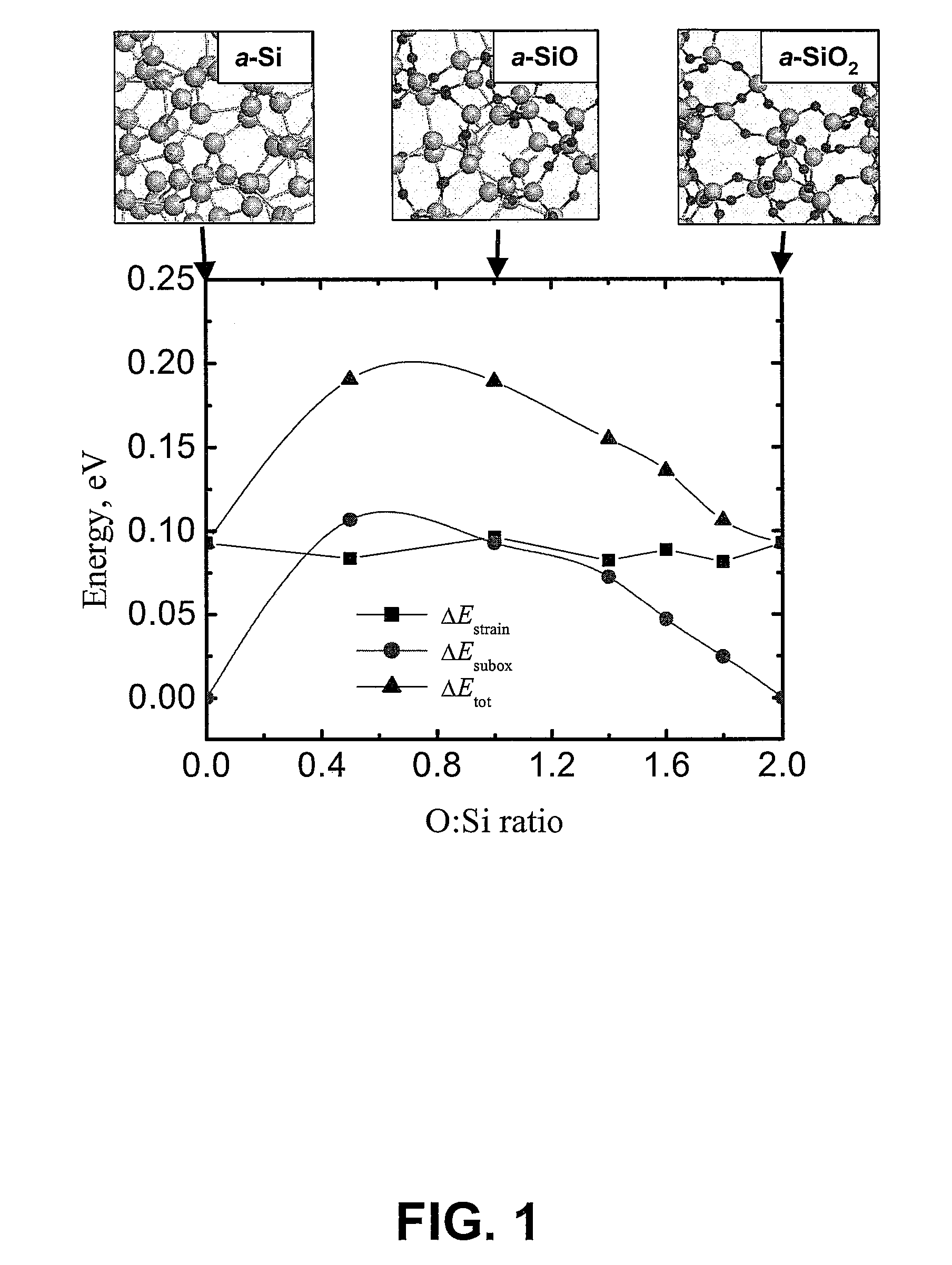
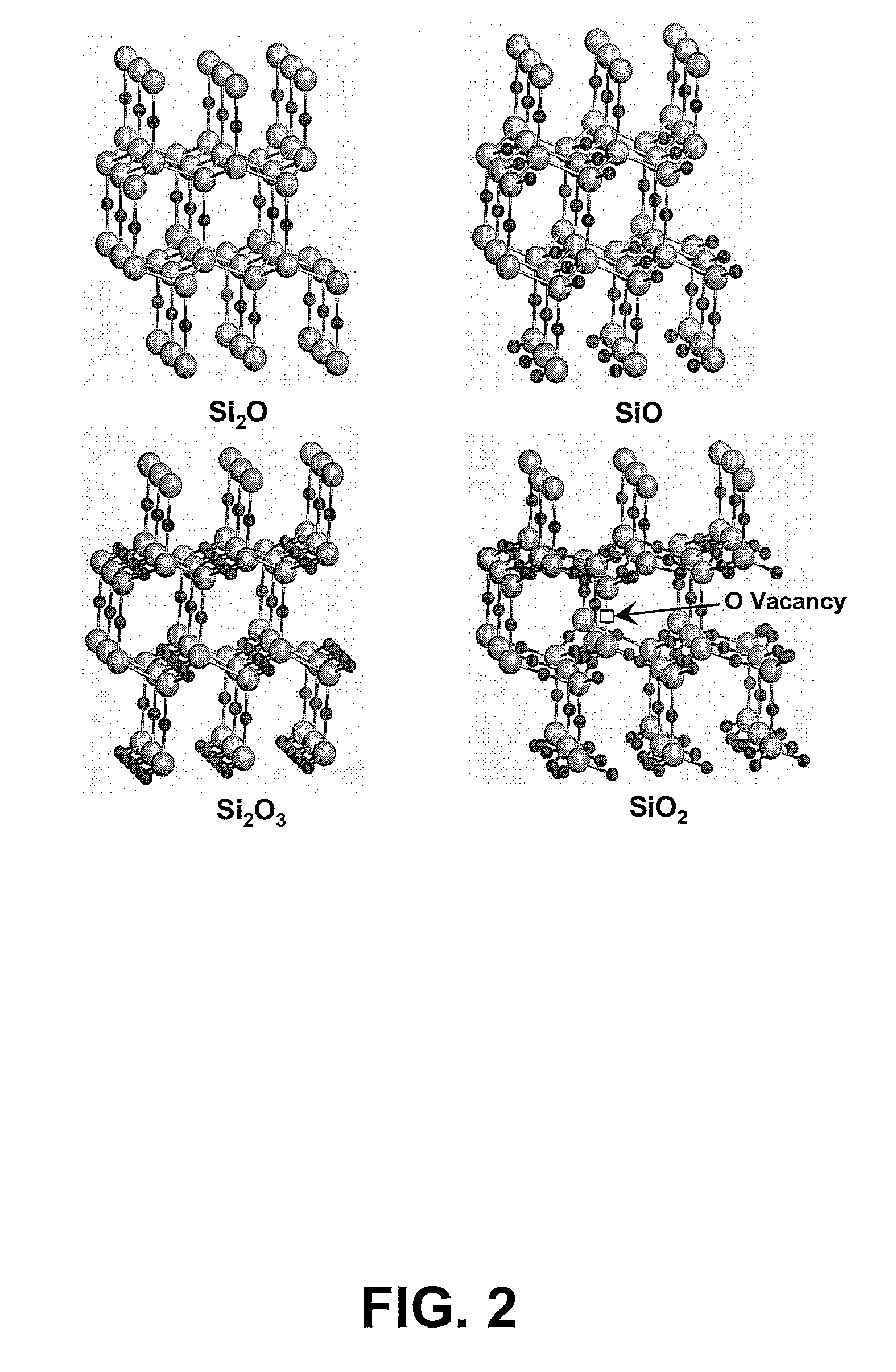
ActiveUS20070072318A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesSilicon nanocrystalsOxide matrix
A method for predicting the formation of silicon nanocrystals in an oxide matrix is disclosed. Initially, fundamental data for a set of microscopic processes that can occur during one or more material processing operations are obtained. Kinetic models are then built by utilizing the fundamental data for a set of reactions that can contribute substantially to the formation of silicon nanocrystals in a silicon oxide matrix. Finally, the kinetic models are applied to predict shape, size distribution, spatial arrangements of silicon nanocrystals.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 40
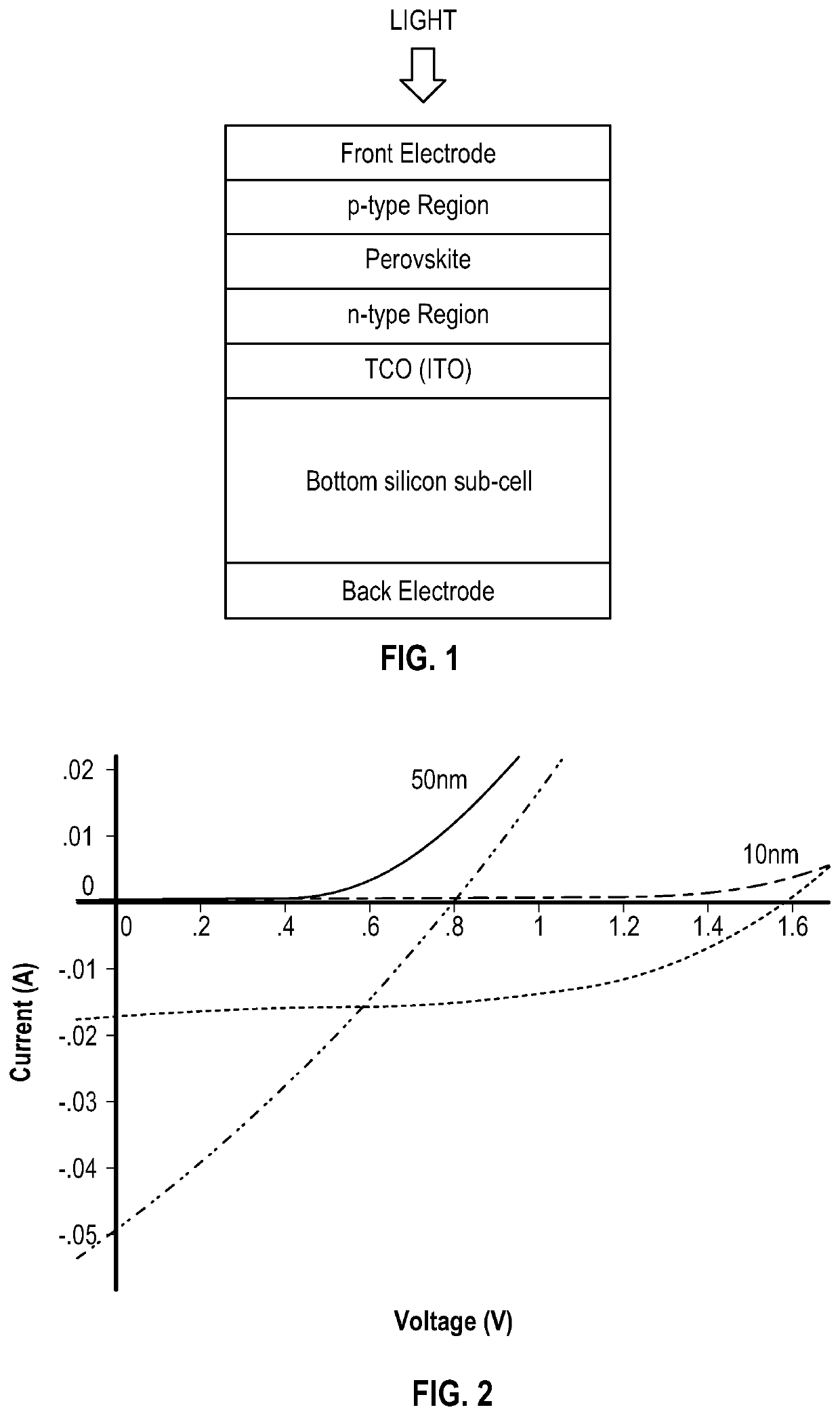
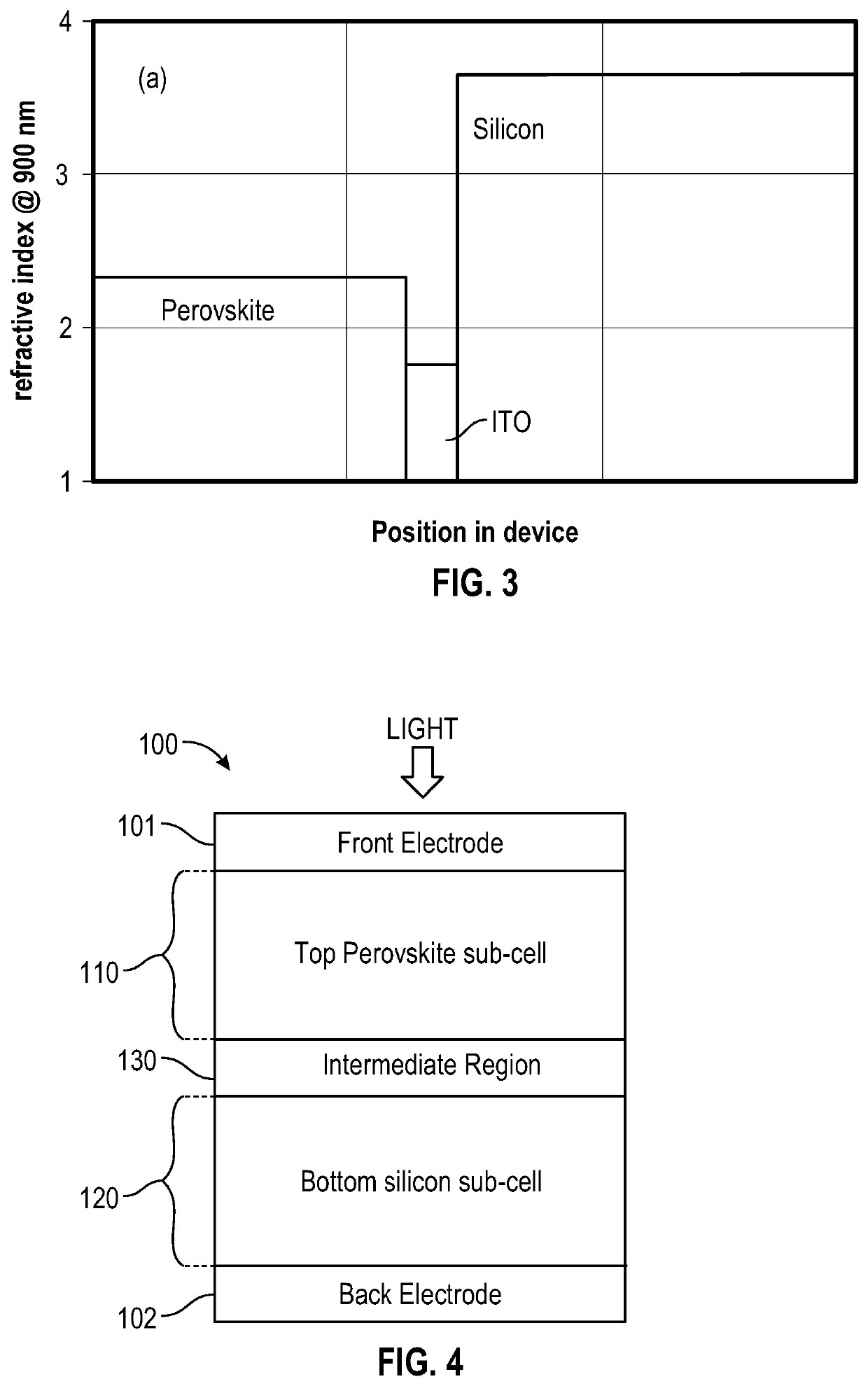
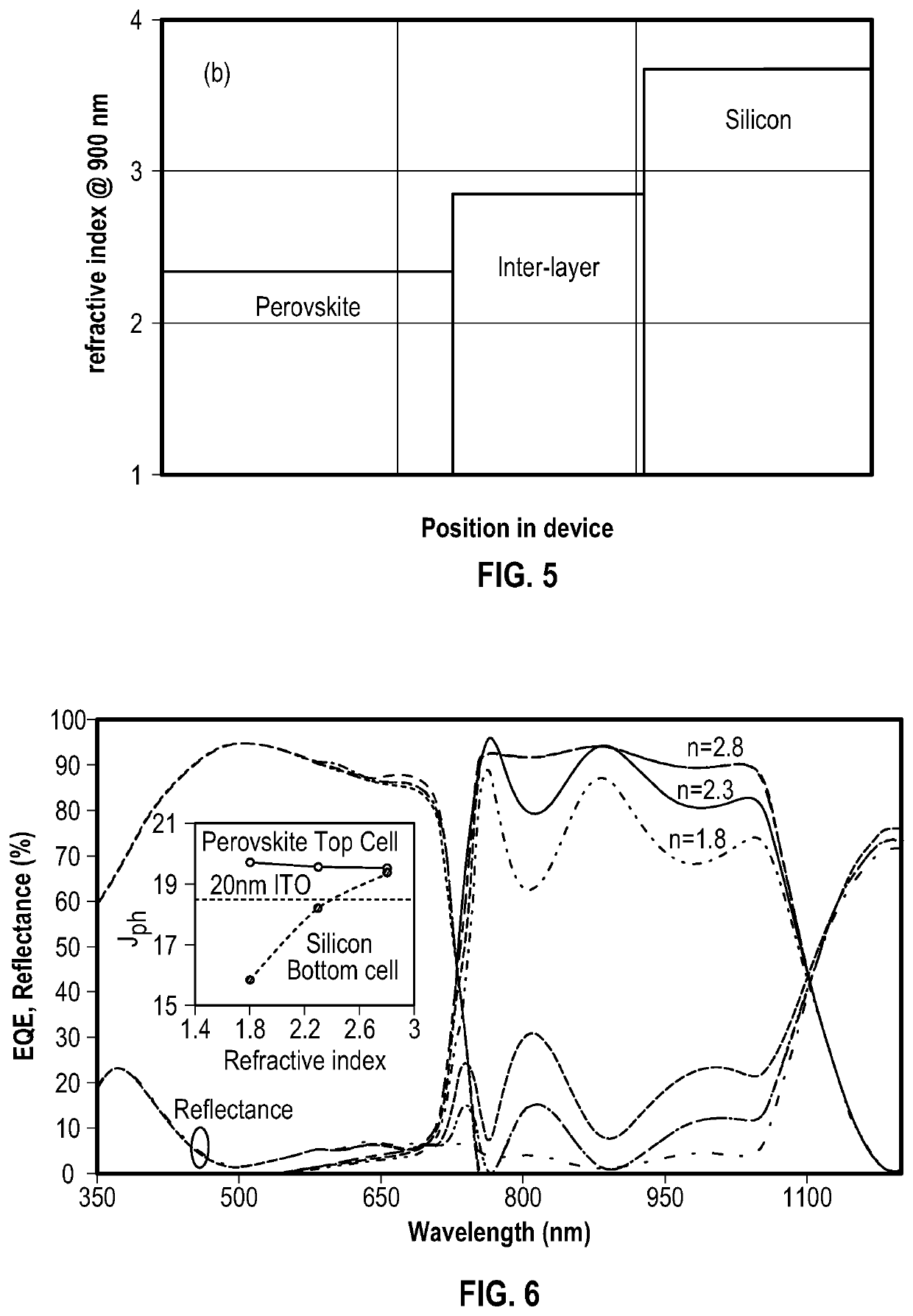
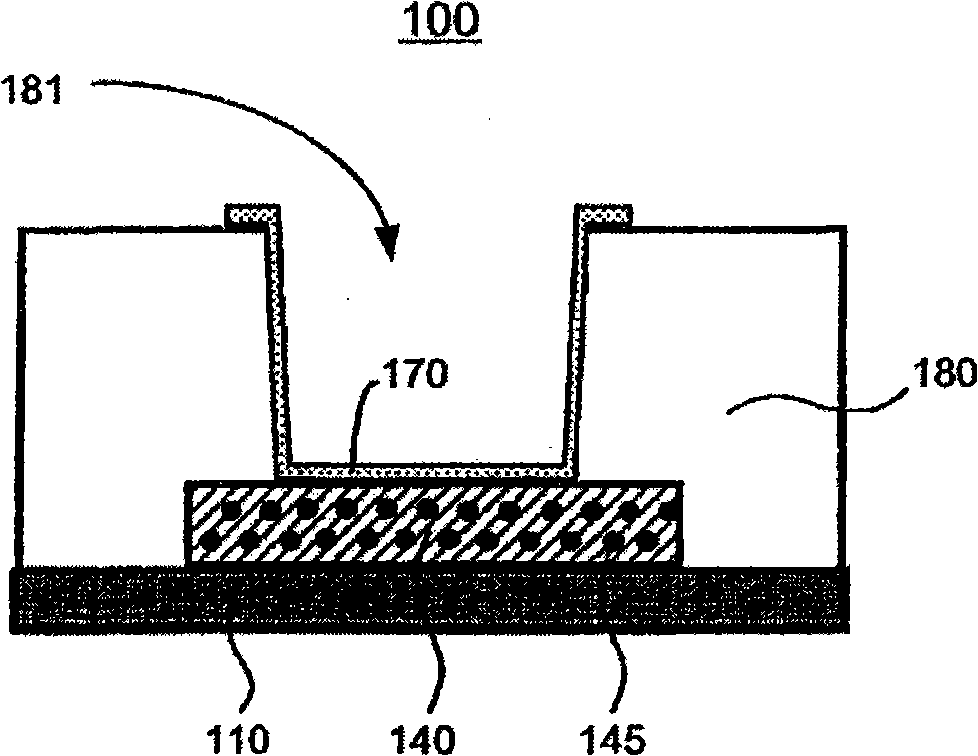
Multijunction photovoltaic device
ActiveUS20200058819A1Reduce reflection lossOvercome lack of conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon matrixSilicon nanocrystals
There is provided a multi junction photovoltaic device comprising a first sub-cell comprising a photoactive region comprising a layer of perovskite material, a second sub-cell comprising a photoactive silicon absorber. and an intermediate region disposed between and connecting the first sub-cell and the second sub-cell. The intermediate region comprises an interconnect layer, the interconnect layer comprising a two-phase material comprising elongate (i.e. filament like) silicon nanocrystals embedded in a silicon oxide matrix.
Owner:OXFORD PHOTOVOLTAICS
Photovoltaic cells of si-nanocrystals and applications in thin film transistor panel
ActiveCN101515608AStatic indicating devicesFinal product manufactureSilicon nanocrystalsNanocrystalline silicon
The present invention relates to a photovoltaic cell. In one embodiment, the photovoltaic cell includes a first conductive layer, an N-doped semiconductor layer formed on the first conductive layer, a first silicon layer formed on the N-doped semiconductor layer, a nanocrystalline silicon (nc-Si) layer formed on a first silicon layer, a second silicon layer formed on the nc-Si layer, a P-doped semiconductor layer on the second silicon layer, and a second conductive layer formed on the P-doped semiconductor layer, where one of the first silicon layer and the second silicon layer is formed of amorphous silicon, and the other of the first silicon layer and the second silicon layer formed of polycrystalline silicon.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Decoupling capacitor for high frequency noise immunity
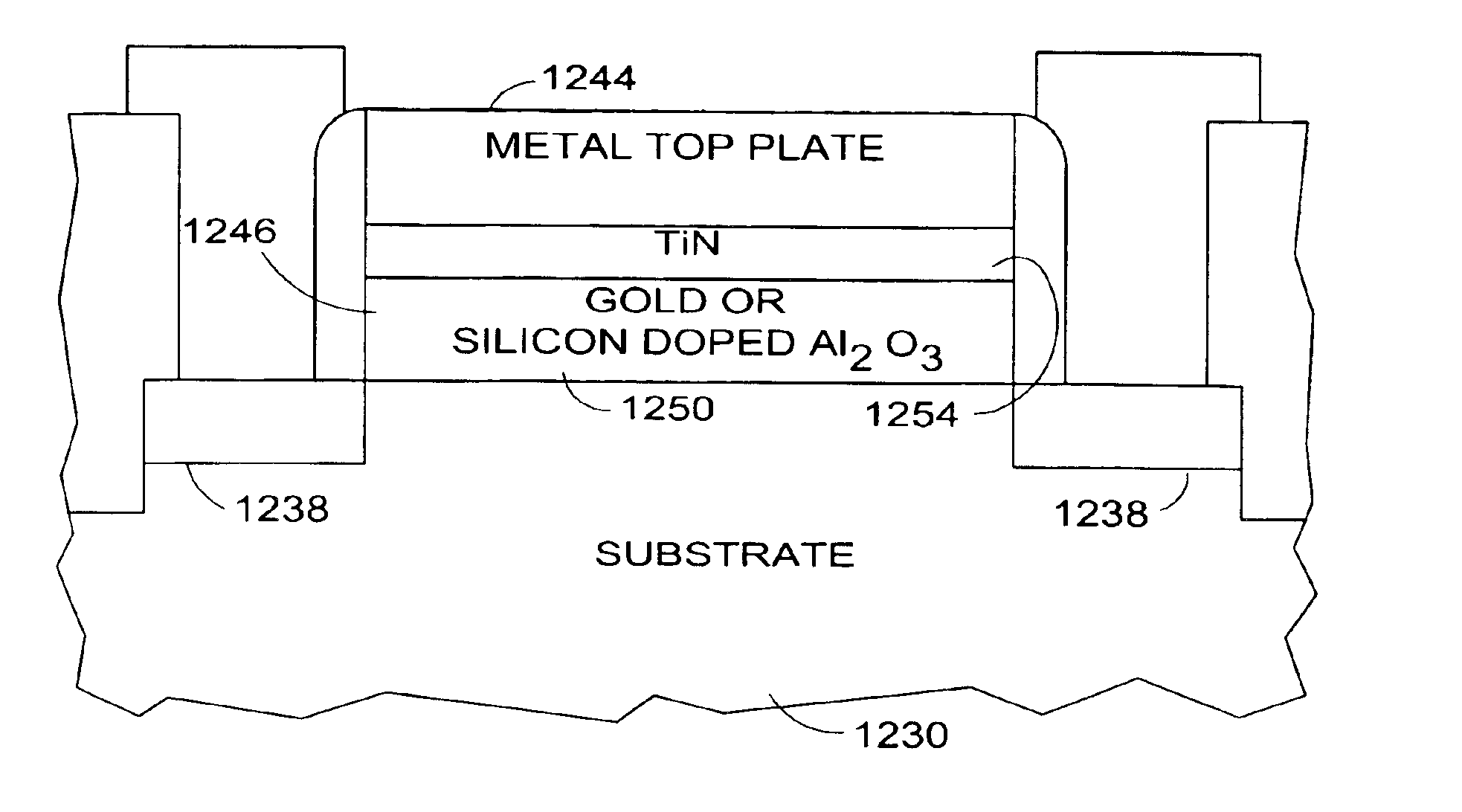
InactiveUS6955960B2Few process stepsIncrease the areaNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal-insulator-metalSilicon nanocrystals
Systems and methods are provided for an on-chip decoupling device and method. One aspect of the present subject matter is a capacitor. One embodiment of the capacitor includes a substrate, a high K dielectric layer doped with nano crystals disposed on the substrate, and a top plate layer disposed on the high K dielectric layer. According to one embodiment, the high K dielectric layer includes Al2O3. According to other embodiments, the nano crystals include gold nano crystals and silicon nano crystals. One capacitor embodiment includes a MIS (metal-insulator-silicon) capacitor fabricated on silicon substrate, and another capacitor embodiment includes a MIM (metal-insulator-metal) capacitor fabricated between the interconnect layers above silicon substrate. The structure of the capacitor is useful for reducing a resonance impedance and a resonance frequency for an integrated circuit chip. Other aspects are provided herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Cuprous oxide-zinc oxide heterojunction solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110112225AImprove efficiencyReduce defect densityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureHeterojunctionSilicon nanocrystals
The invention discloses a cuprous oxide-zinc oxide heterojunction solar cell and a preparation method thereof. Corning glass is used as a substrate, metal titanium is grown by a magnetron sputtering method, and then a silver electrode is sputtered on a titanium thin film; a nitrogen-doped Cu2O thin film is grown by using a reactive magnetron sputtering method; a microcrystalline silicon oxide thinfilm is grown on the surface of the nitrogen-doped Cu2O thin films by using an isotopic chemical vapor deposition method; a Al-doped ZnO thin film is grown by using the magnetron sputtering method; and a layer of Ag electrode is deposited on the ZnO thin film by using the magnetron sputtering method through a mask plate. The amorphous silicon oxide in microcrystalline silicon oxide is applied topassivate CuO deep level defect on the Cu2O surface, the doped silicon nanocrystals transport photogenerated carriers, and the hydrogen introduced in the growth process is diffused into Cu2O at subsequent annealing temperatures so as to reduce the defect density and improve the efficiency of the Cu2O solar cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
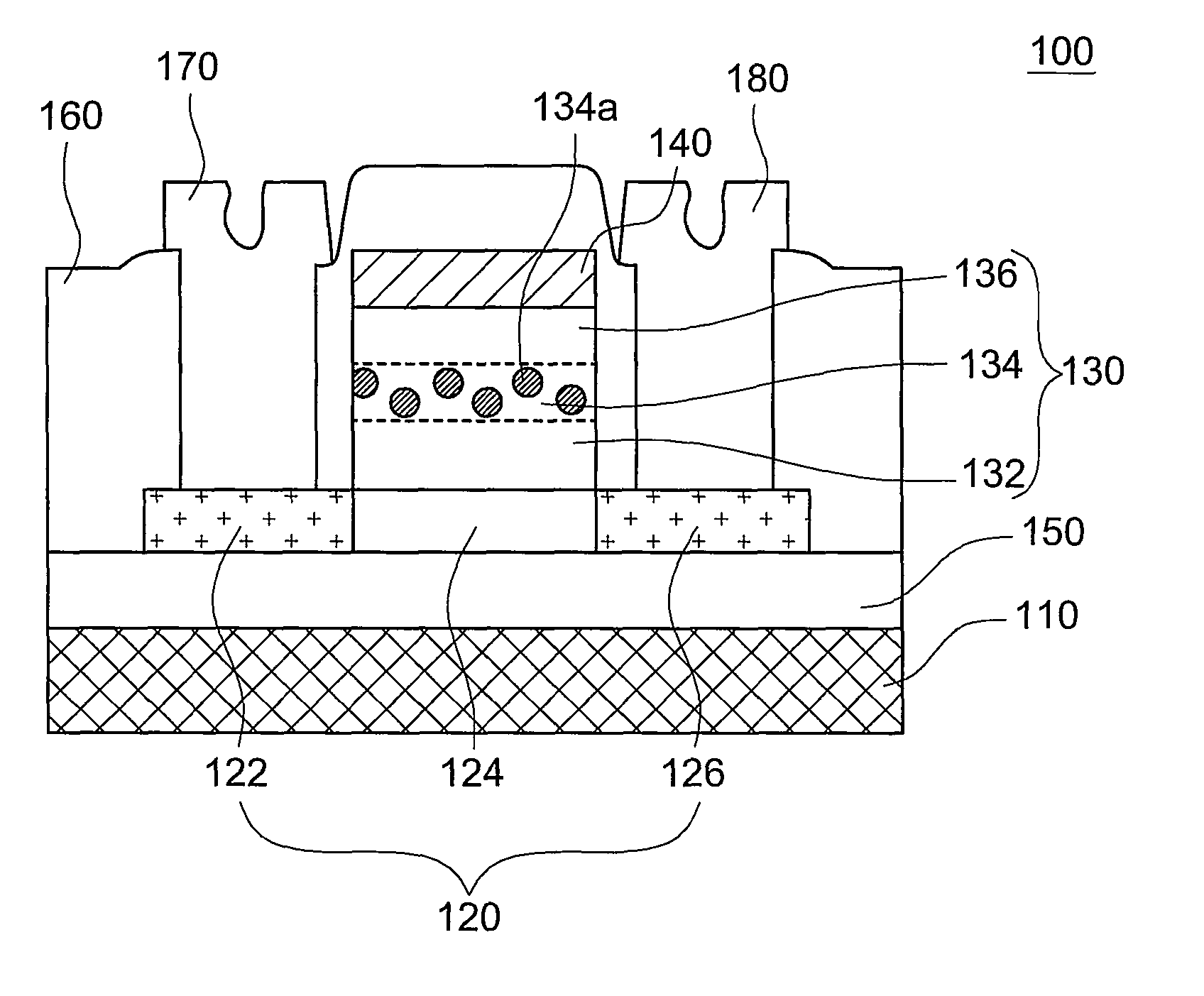
Multi-layer floating gate nonvolatile memory structure and production method thereof
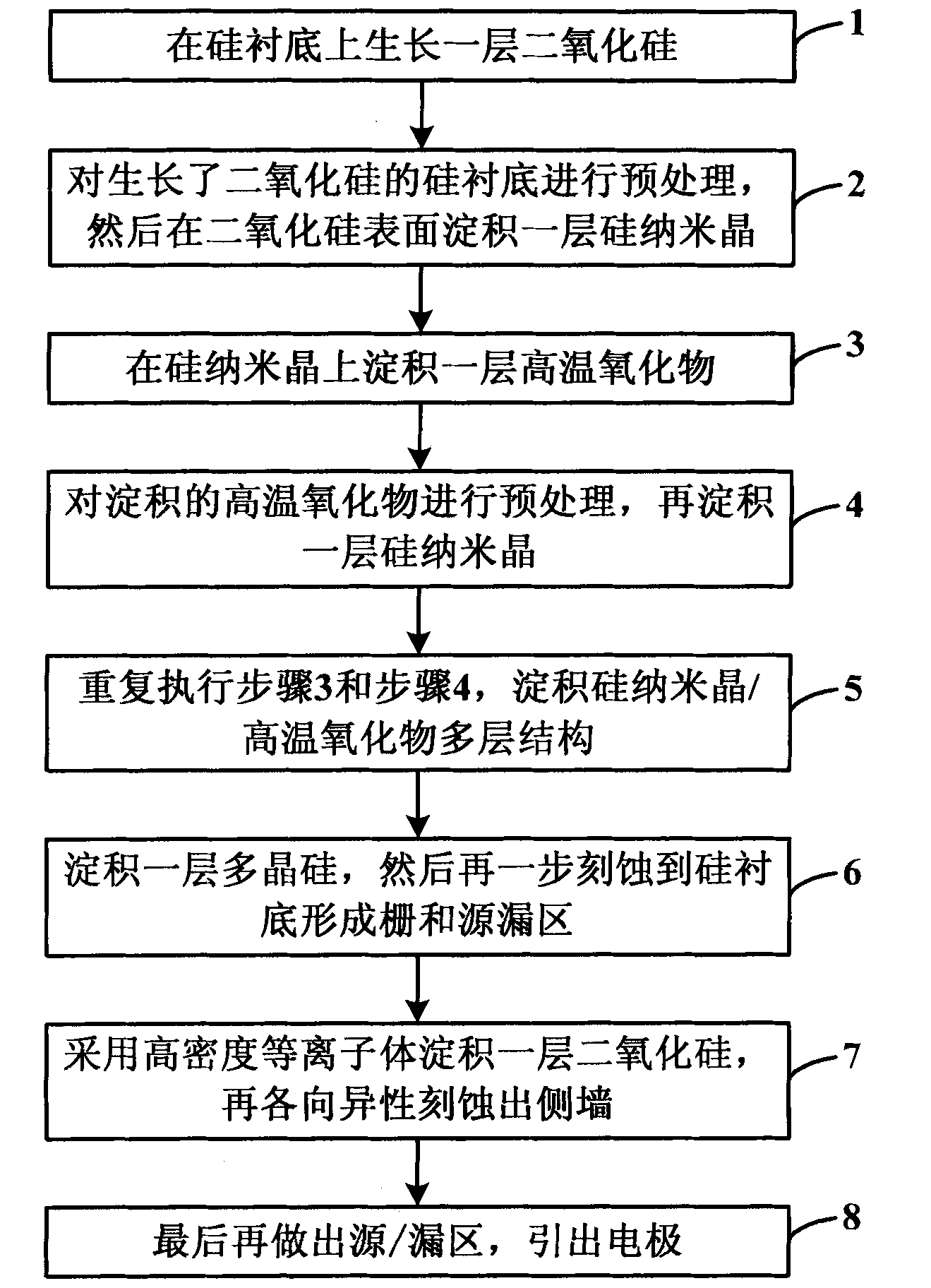
InactiveCN101814505AHigh densityIncrease storage windowSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nanocrystalsSilicon dioxide
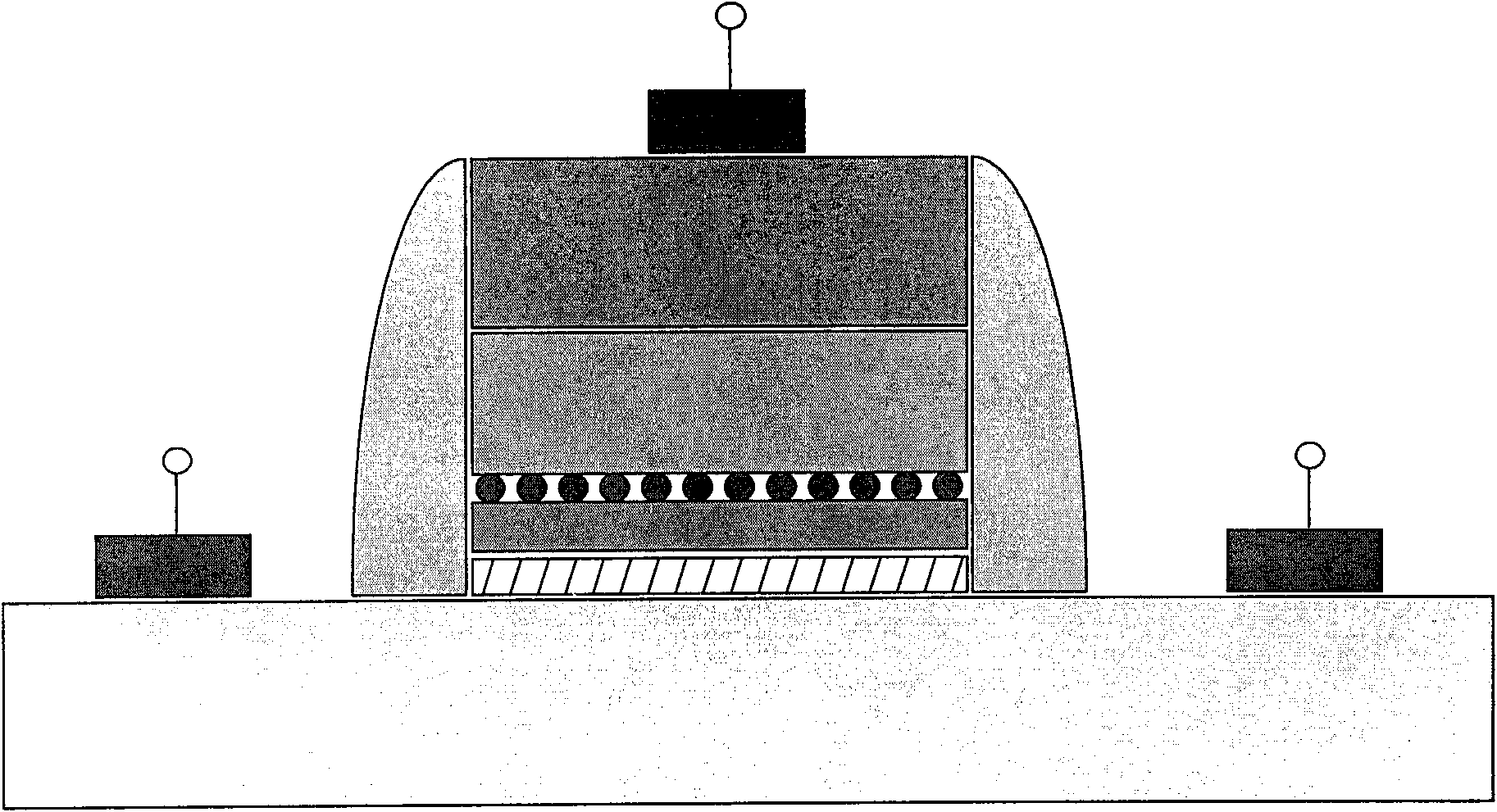
The invention discloses a multi-layer floating gate nonvolatile memory structure and a production method thereof, wherein the multi-layer floating gate nonvolatile memory structure comprises a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide layer, a silicon nanocrystals / high temperature oxide multilayer structure, a polysilicon layer, a silicon dioxide layer, grid and source / drain region formed by sculpturing on the silicon substrate, and a side wall formed by sculpturing on the silicon dioxide layer. The invention solves the defects because the traditional Flash technology node can downsized, utilizes the multi-layer floating gate to storage charge to enhance a storage window, so that the reliability of the floating grid for storing charge can be increased and the retention performance of a floating device can be improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photo detectors
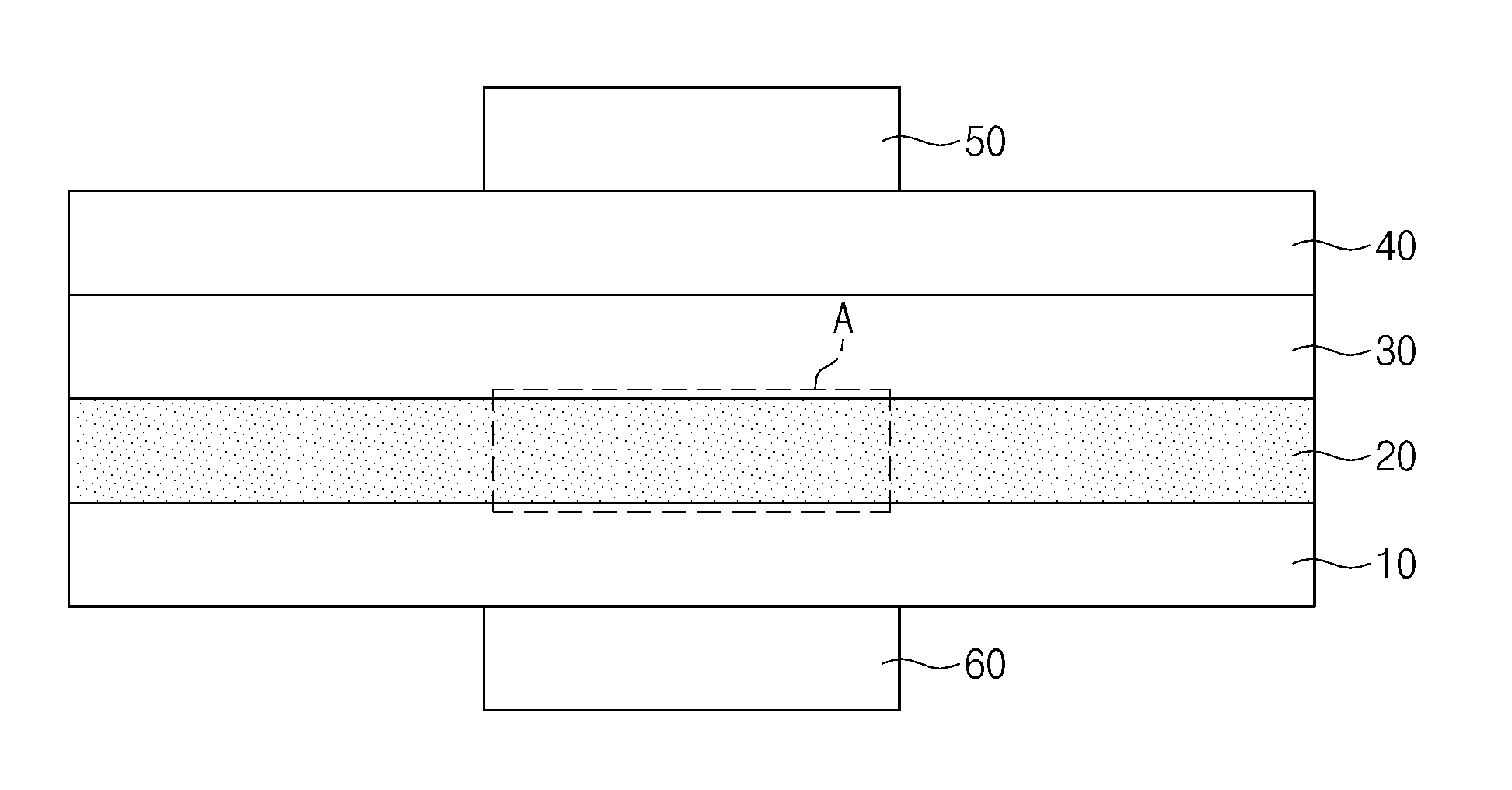
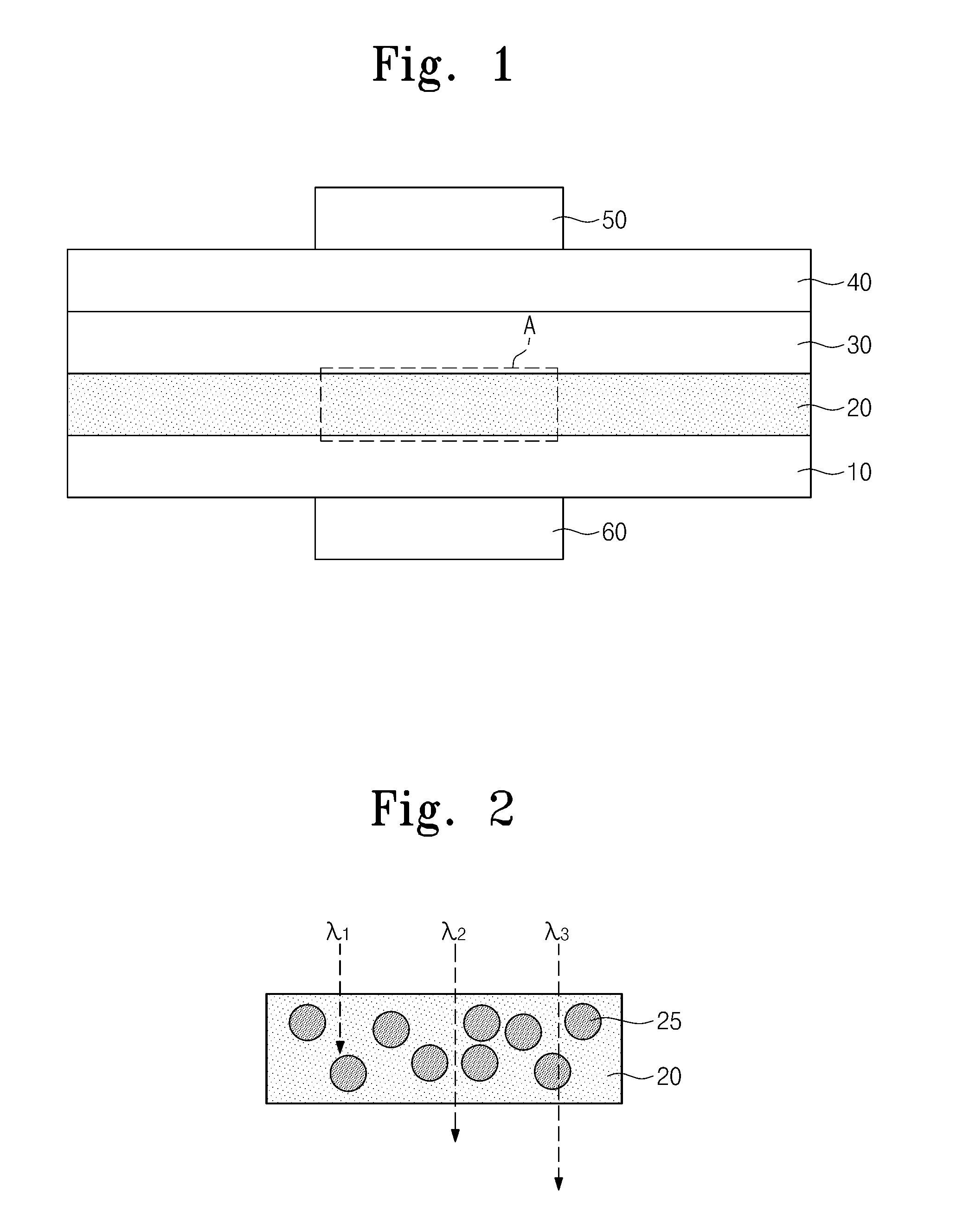
InactiveUS20130154040A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight absorption efficiencySolid-state devicesNanoopticsSilicon nanocrystalsPhotovoltaic detectors
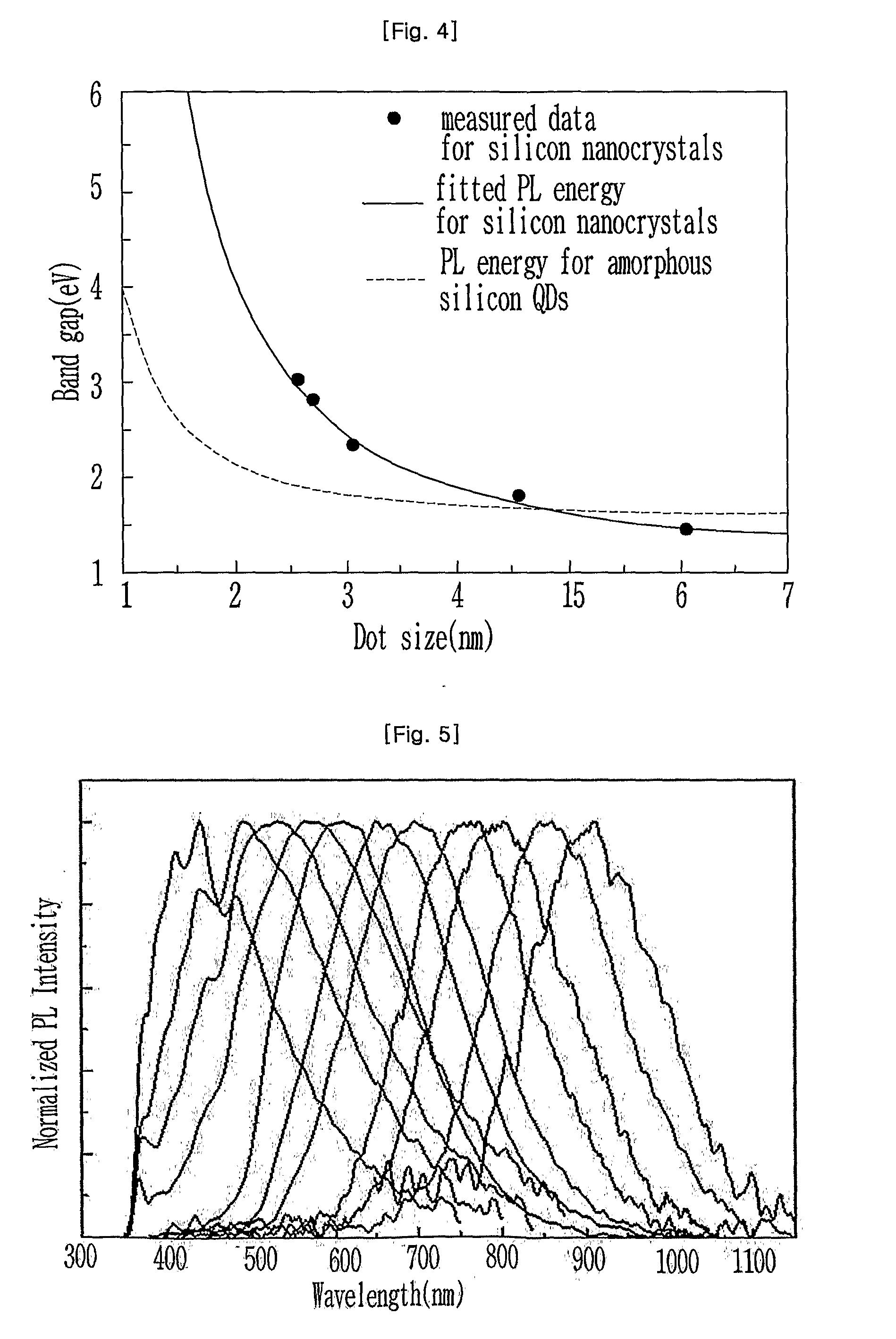
Photo detectors are provided. The photo detector includes a photoelectric conversion layer between a lower carrier transportation layer and an upper carrier transportation layer, and a common electrode on the upper carrier transportation layer opposite to the photoelectric conversion layer. The photoelectric conversion layer includes a plurality of light absorption layers and each of the light absorption layers contains silicon nanocrystals. The silicon nanocrystals in respective ones of the light absorption layers have different sizes from each other.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Split poly-SiGe/poly-Si alloy gate stack
InactiveUS20050199906A1Simple processSimple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricSilicon nanocrystals
A multi-layered gate electrode stack structure of a field effect transistor device is formed on a silicon nano crystal seed layer on the gate dielectric. The small grain size of the silicon nano crystal layer allows for deposition of a uniform and continuous layer of poly-SiGe with a [Ge] of up to at least 70% using in situ rapid thermal chemical vapor deposition (RTCVD). An in-situ purge of the deposition chamber in a oxygen ambient at rapidly reduced temperatures results in a thin SiO2 or SixGeyOz interfacial layer of 3 to 4 A thick. The thin SiO2 or SixGeyOz interfacial layer is sufficiently thin and discontinuous to offer little resistance to gate current flow yet has sufficient [O] to effectively block upward Ge diffusion during heat treatment to thereby allow silicidation of the subsequently deposited layer of cobalt. The gate electrode stack structure is used for both nFETs and pFETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Silicon nitride layer for light emitting device, light emitting device using the same, and method of forming silicon nitride layer for light emitting device
ActiveUS20100048002A1NanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nanocrystalsLength wave
Provided are a silicon nitride layer for a light emitting device, light emitting device using the same, and method of forming the silicon nitride layer for the light emitting device. The silicon nitride layer of the light emitting device includes a silicon nitride matrix and silicon nanocrystals formed in the silicon nitride matrix. A light emitting device manufactured by the silicon nitride layer has a good luminous efficiency and emits light in the visible region including the short-wavelength blue / violet region and the near infrared region.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Split poly-SiGe/poly-Si alloy gate stack
ActiveUS20050073014A1Simple processSimple structureTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricSilicon nanocrystals
A multi-layered gate electrode stack structure of a field effect transistor device is formed on a silicon nano crystal seed layer on the gate dielectric. The small grain size of the silicon nano crystal layer allows for deposition of a uniform and continuous layer of poly-SiGe with a [Ge] of up to at least 70% using in situ rapid thermal chemical vapor deposition (RTCVD). An in-situ purge of the deposition chamber in a oxygen ambient at rapidly reduced temperatures results in a thin SiO2 or SixGeyOz interfacial layer of 3 to 4 A thick. The thin SiO2 or SixGeyOz interfacial layer is sufficiently thin and discontinuous to offer little resistance to gate current flow yet has sufficient [O] to effectively block upward Ge diffusion during heat treatment to thereby allow silicidation of the subsequently deposited layer of cobalt. The gate electrode stack structure is used for both nFETs and pFETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
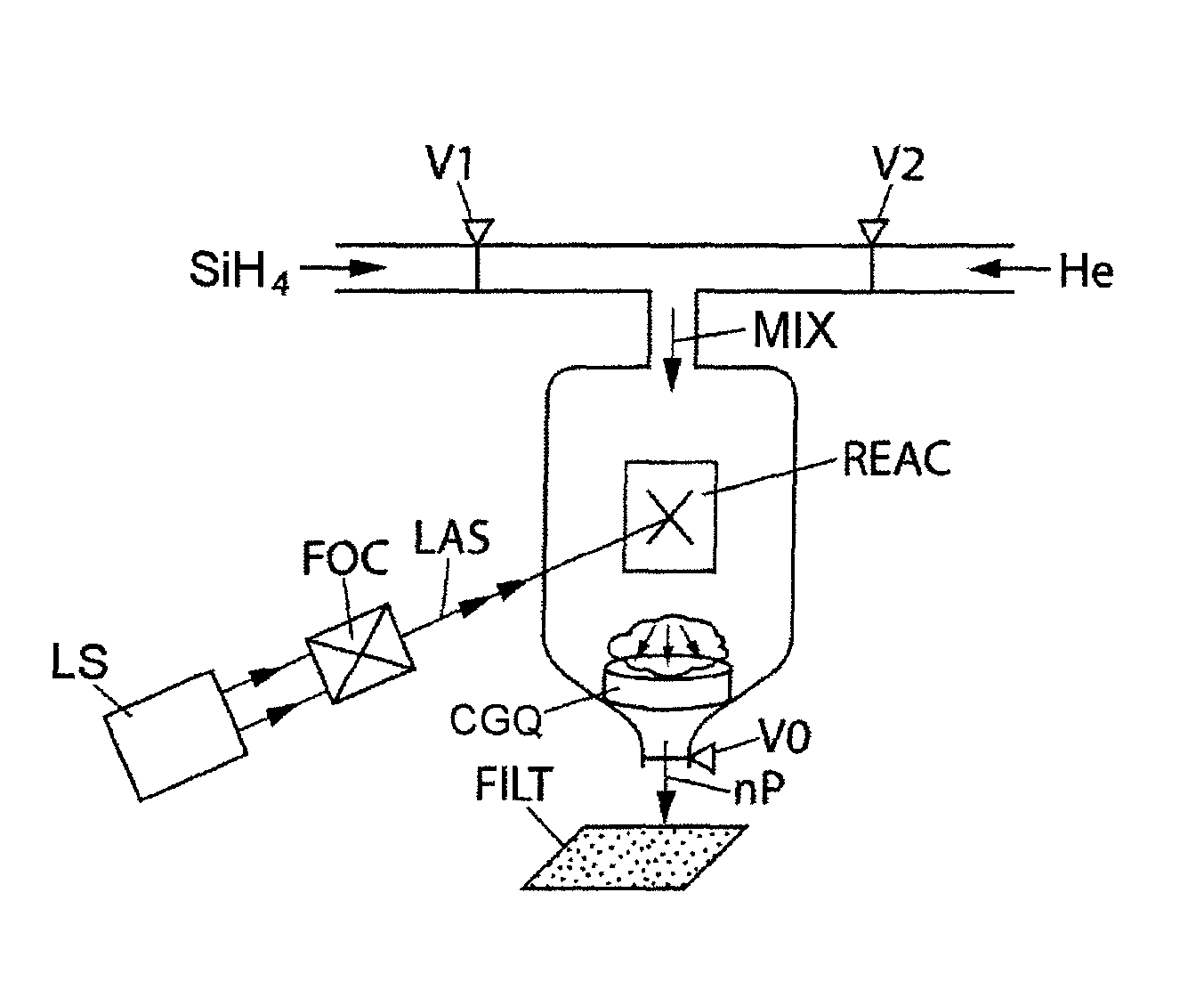
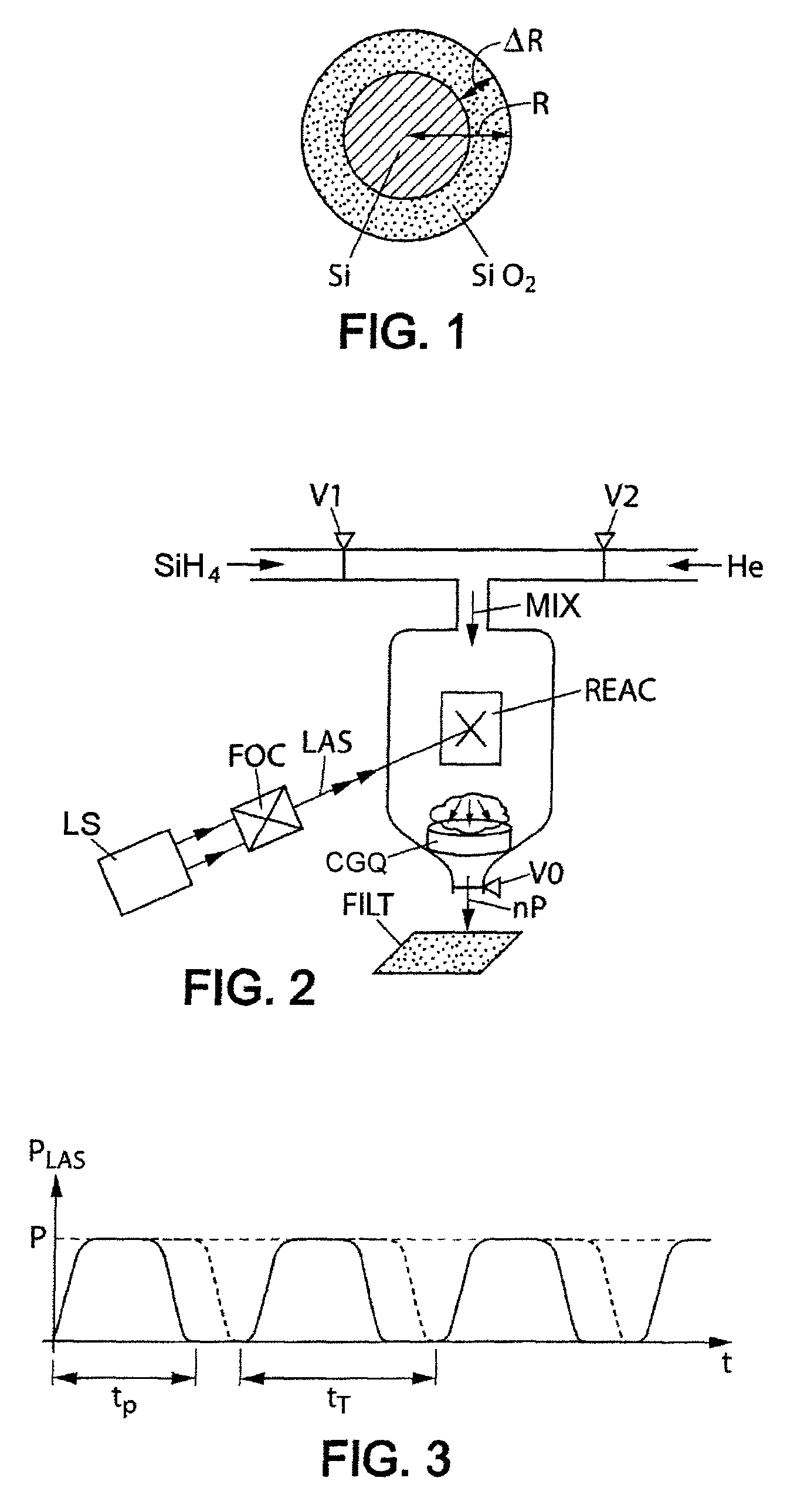
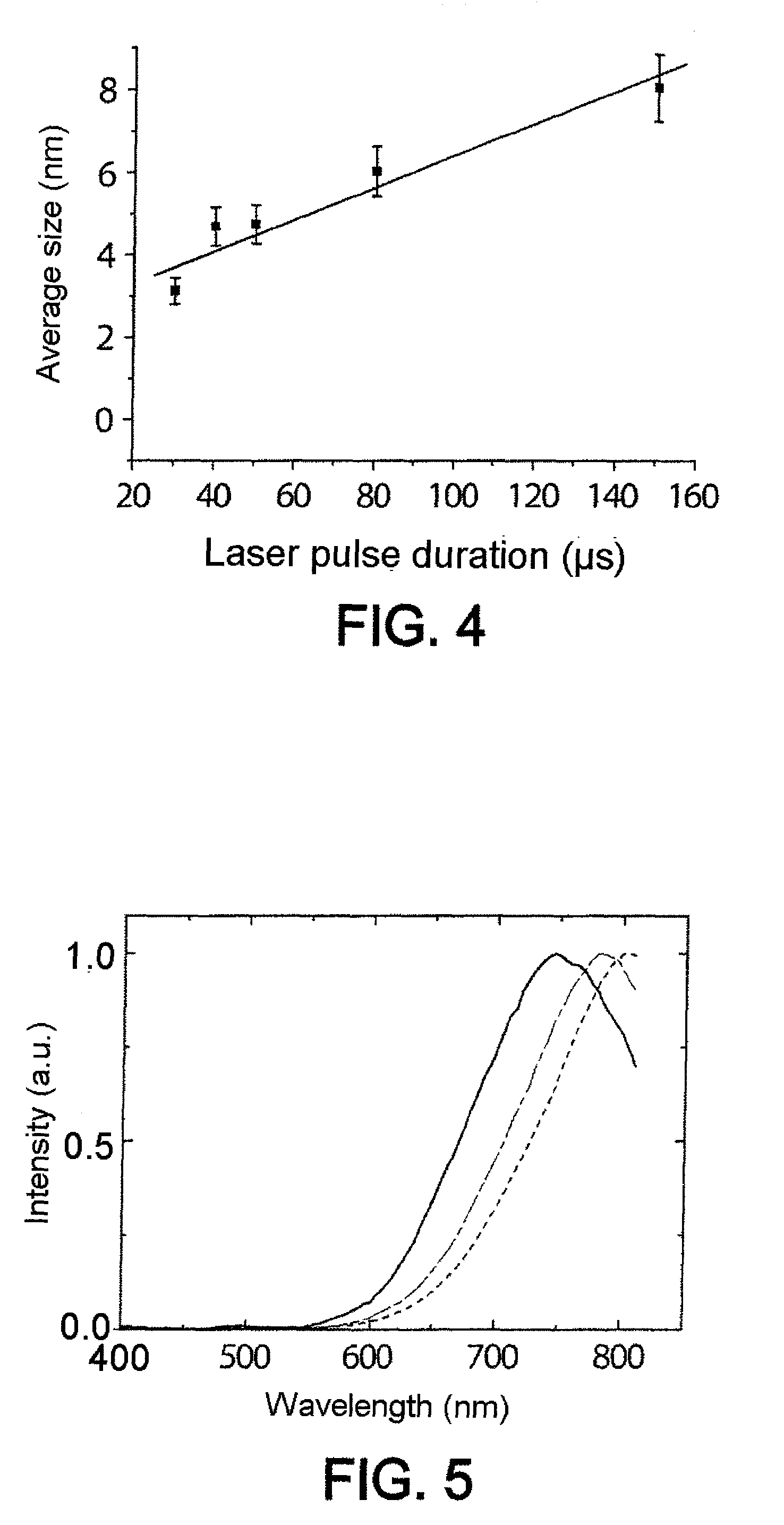
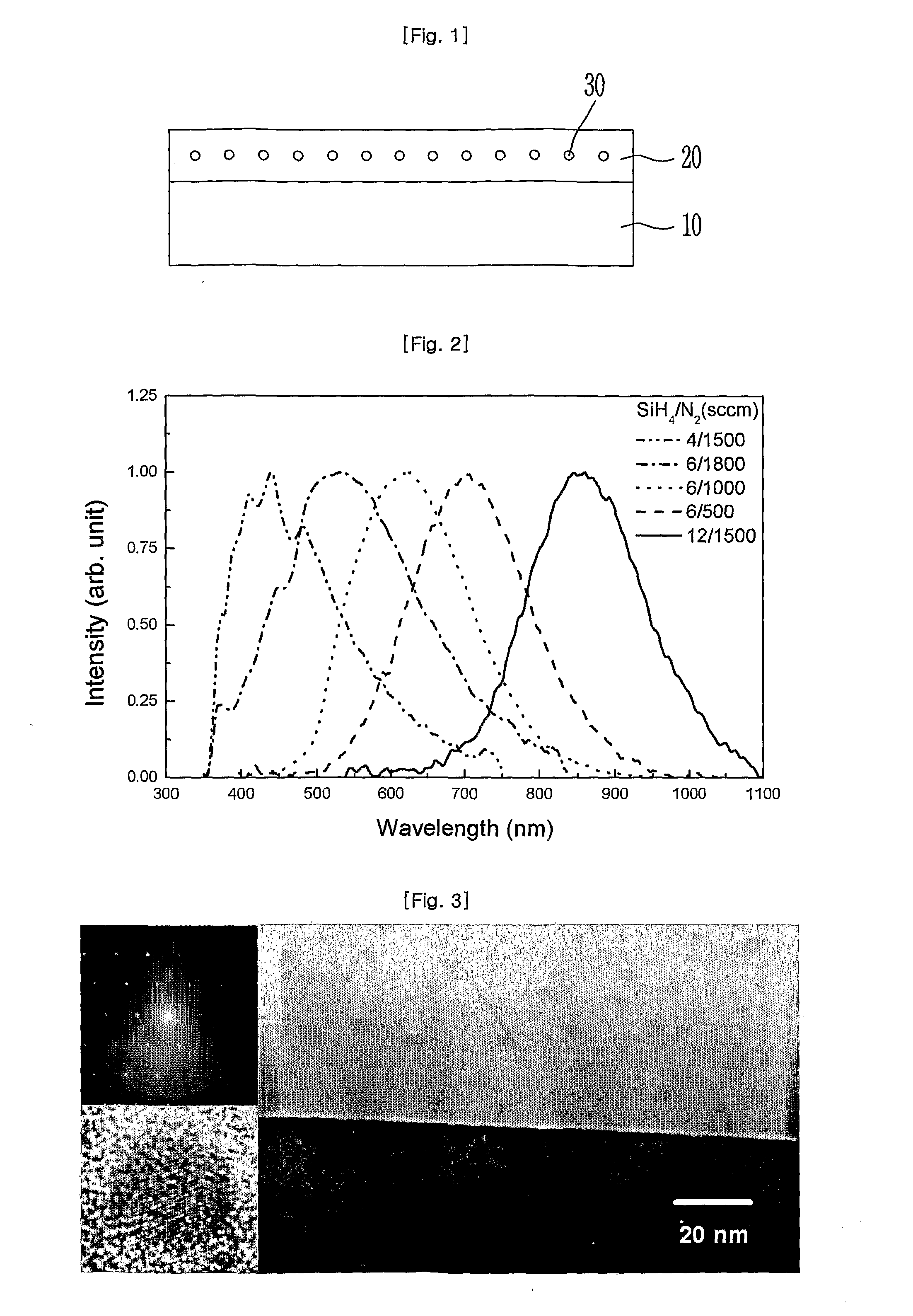
Synthesis of silicon nanocrystals by laser pyrolysis
ActiveUS8337673B2Improve productivityIncrease ratingsMaterial nanotechnologyEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSilicon nanocrystalsCrystal structure
The invention relates to the synthesis of silicon-containing nanoparticles by laser pyrolysis. For this purpose: a precursor (SiH4) containing the element silicon is conveyed, by a transport fluid (He), into a pyrolysis reactor (REAC); laser radiation (LAS) is applied, in the reactor, to a mixture that the transport fluid and the precursor form; and silicon-containing nanoparticles (nP) are recovered at the exit of the reactor. In particular, the power of the laser radiation is controlled. Furthermore, the effective pulse duration is controlled within a laser firing period. Typically, for a power greater than 500 watts and a pulse duration greater than 40% of a laser firing period, nanoparticles having a crystalline structure with a size of less than or of the order of one nanometer are obtained at a rate greater than or of the order of 80 milligrams per hour. Under optimum conditions, a record rate of greater than 740 milligrams per hour was able to be obtained.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
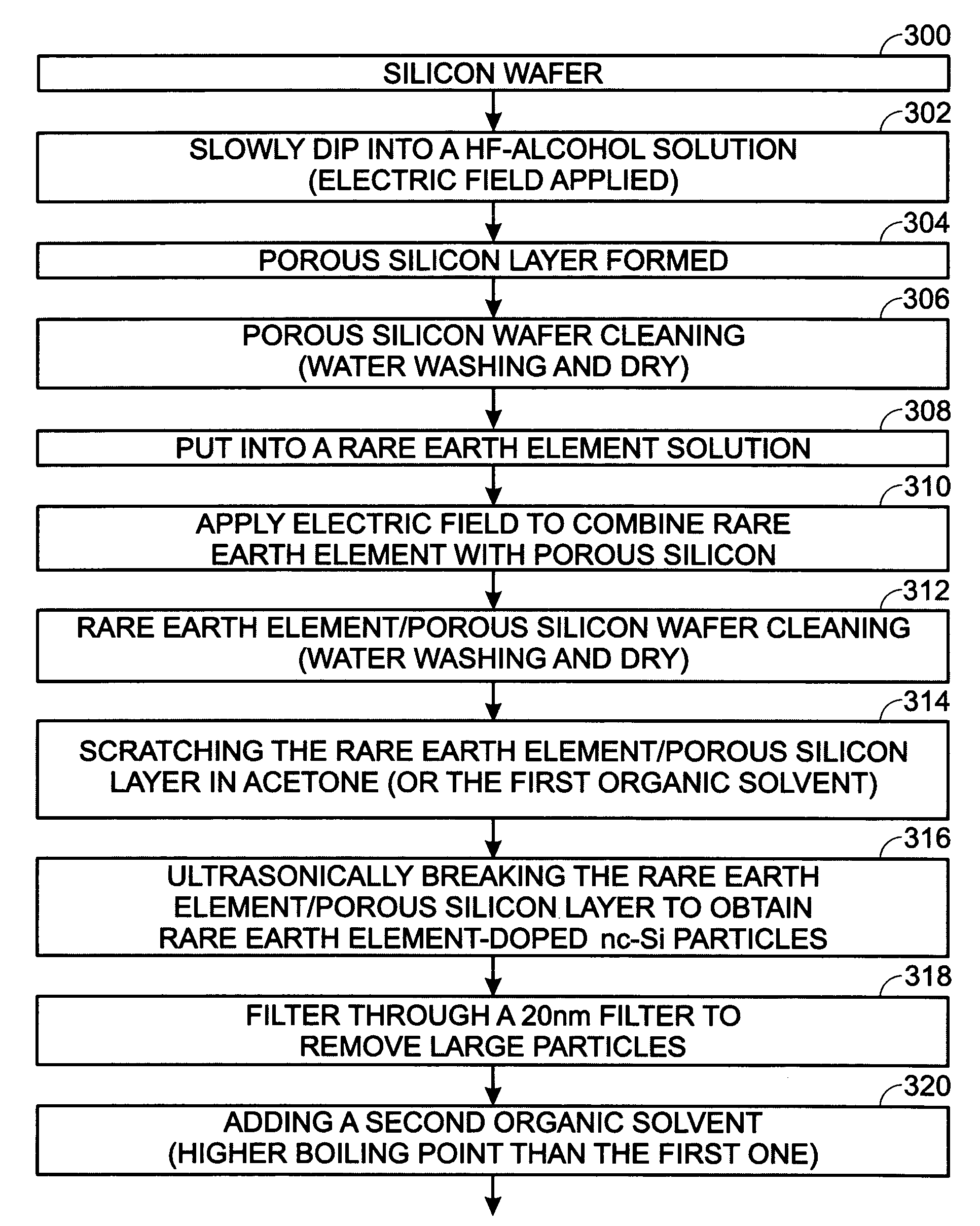
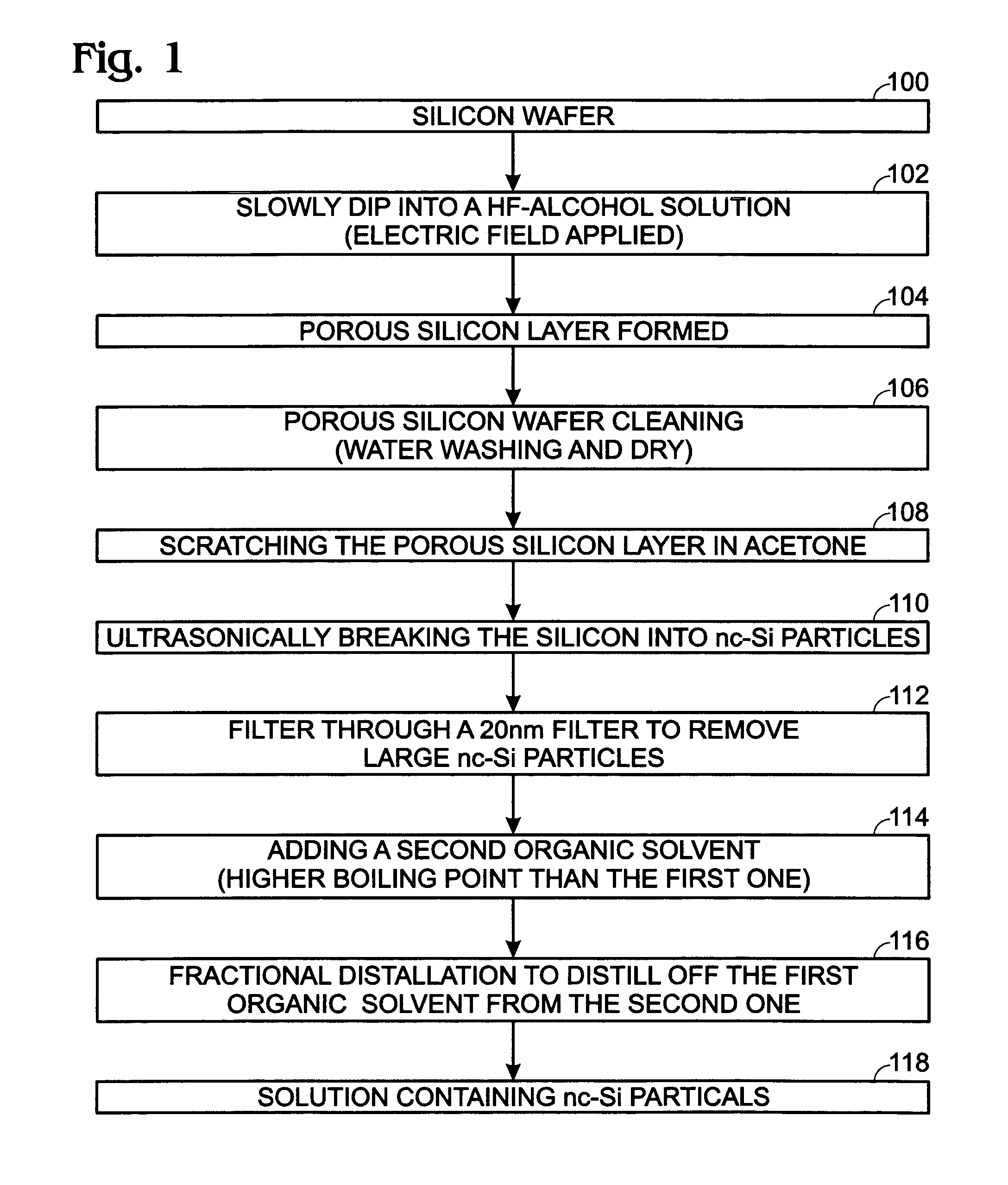
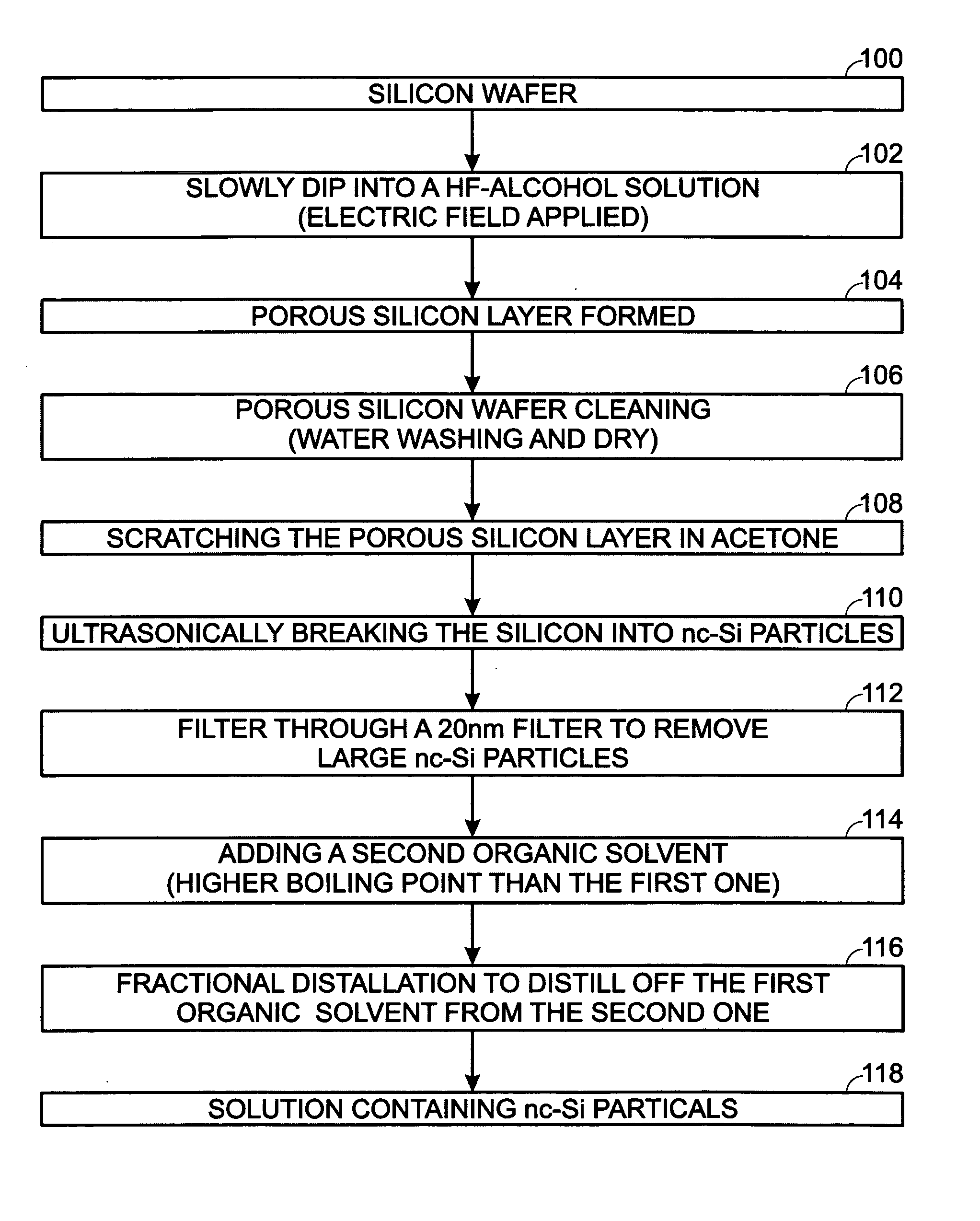
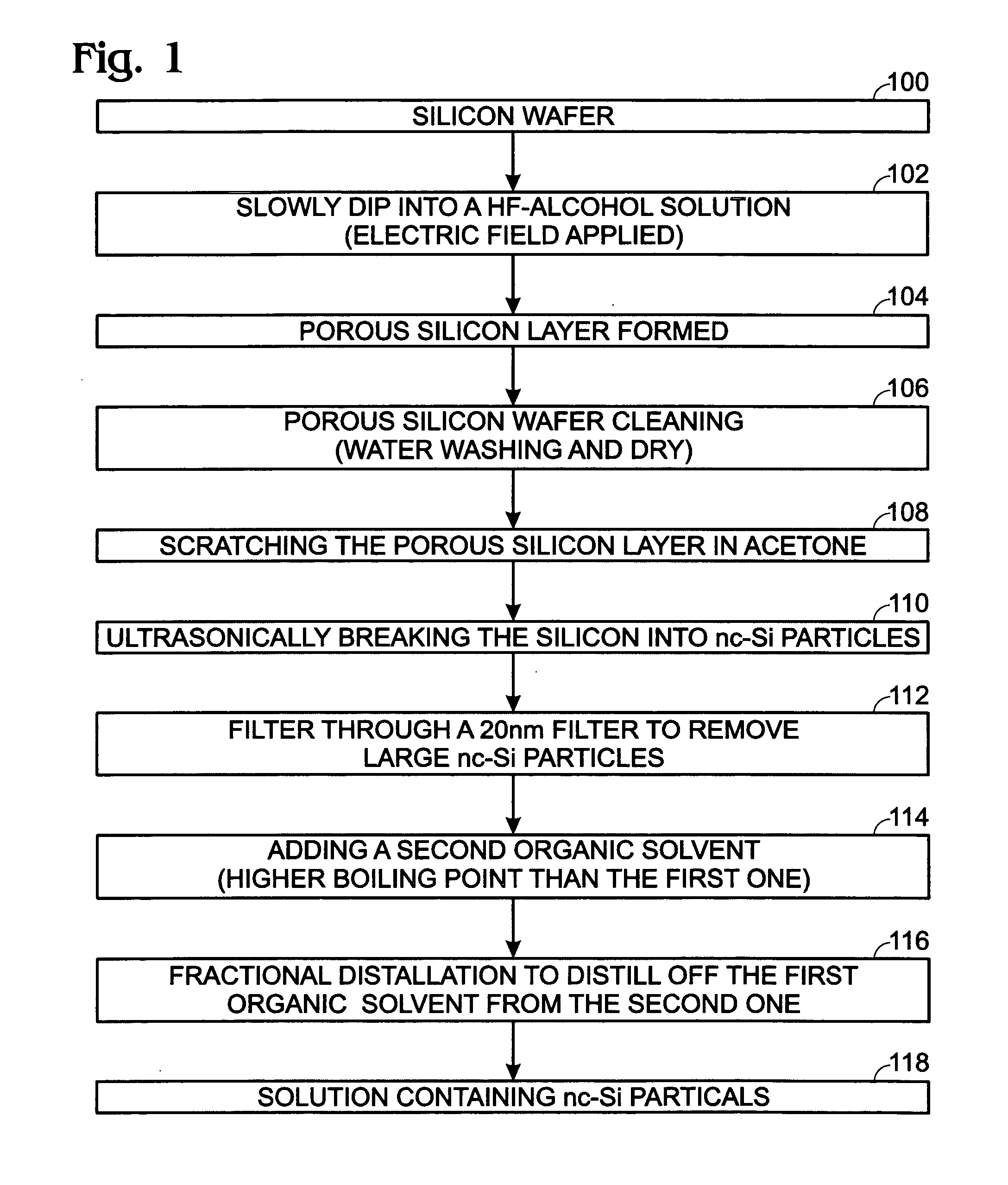
Rare earth element-doped oxide precursor with silicon nanocrystals
InactiveUS7585788B2Low production costInexpensively formedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare-earth elementSilicon nanocrystals
A method is provided for forming a rare earth element-doped silicon oxide (SiO2) precursor with nanocrystalline (nc) Si particles. In one aspect the method comprises: mixing Si particles into a first organic solvent, forming a first solution with a first boiling point; filtering the first solution to remove large Si particles; mixing a second organic solvent having a second boiling point, higher than the first boiling point, to the filtered first solution; and, fractionally distilling, forming a second solution of nc Si particles. The Si particles are formed by immersing a Si wafer into a third solution including hydrofluoric (HF) acid and alcohol, applying an electric bias, and forming a porous Si layer overlying the Si wafer. Then, the Si particles are mixed into the organic solvent by depositing the Si wafer into the first organic solvent, and ultrasonically removing the porous Si layer from the Si wafer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Methods of forming silicon nano-crystals using plasma ion implantation and semiconductor devices using the same
ActiveUS20070117402A1Improve featuresDensityPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsSilicon nanocrystalsHydrogen
In a method for forming silicon nano-crystals using plasma ion implantation and a semiconductor memory device using the same, silicon nano-crystals may be formed using plasma ion implantation. An insulating layer may be formed on a substrate, and ions may be implanted into the insulating layer using hydrogen and a gas including silicon. Silicon nano-crystals may be formed using a heat treatment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods of forming silicon nano-crystals using plasma ion implantation and semiconductor devices using the same
ActiveUS7449398B2Improve featuresDensityPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsSilicon nanocrystalsHydrogen
In a method for forming silicon nano-crystals using plasma ion implantation and a semiconductor memory device using the same, silicon nano-crystals may be formed using plasma ion implantation. An insulating layer may be formed on a substrate, and ions may be implanted into the insulating layer using hydrogen and a gas including silicon. Silicon nano-crystals may be formed using a heat treatment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rare earth element-doped oxide precursor with silicon nanocrystals
InactiveUS20070238239A1Low production costInexpensively formedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare-earth elementSilicon nanocrystals
A method is provided for forming a rare earth element-doped silicon oxide (SiO2) precursor with nanocrystalline (nc) Si particles. In one aspect the method comprises: mixing Si particles into a first organic solvent, forming a first solution with a first boiling point; filtering the first solution to remove large Si particles; mixing a second organic solvent having a second boiling point, higher than the first boiling point, to the filtered first solution; and, fractionally distilling, forming a second solution of nc Si particles. The Si particles are formed by immersing a Si wafer into a third solution including hydrofluoric (HF) acid and alcohol, applying an electric bias, and forming a porous Si layer overlying the Si wafer. Then, the Si particles are mixed into the organic solvent by depositing the Si wafer into the first organic solvent, and ultrasonically removing the porous Si layer from the Si wafer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for manufacturing non-volatile memory and structure thereof
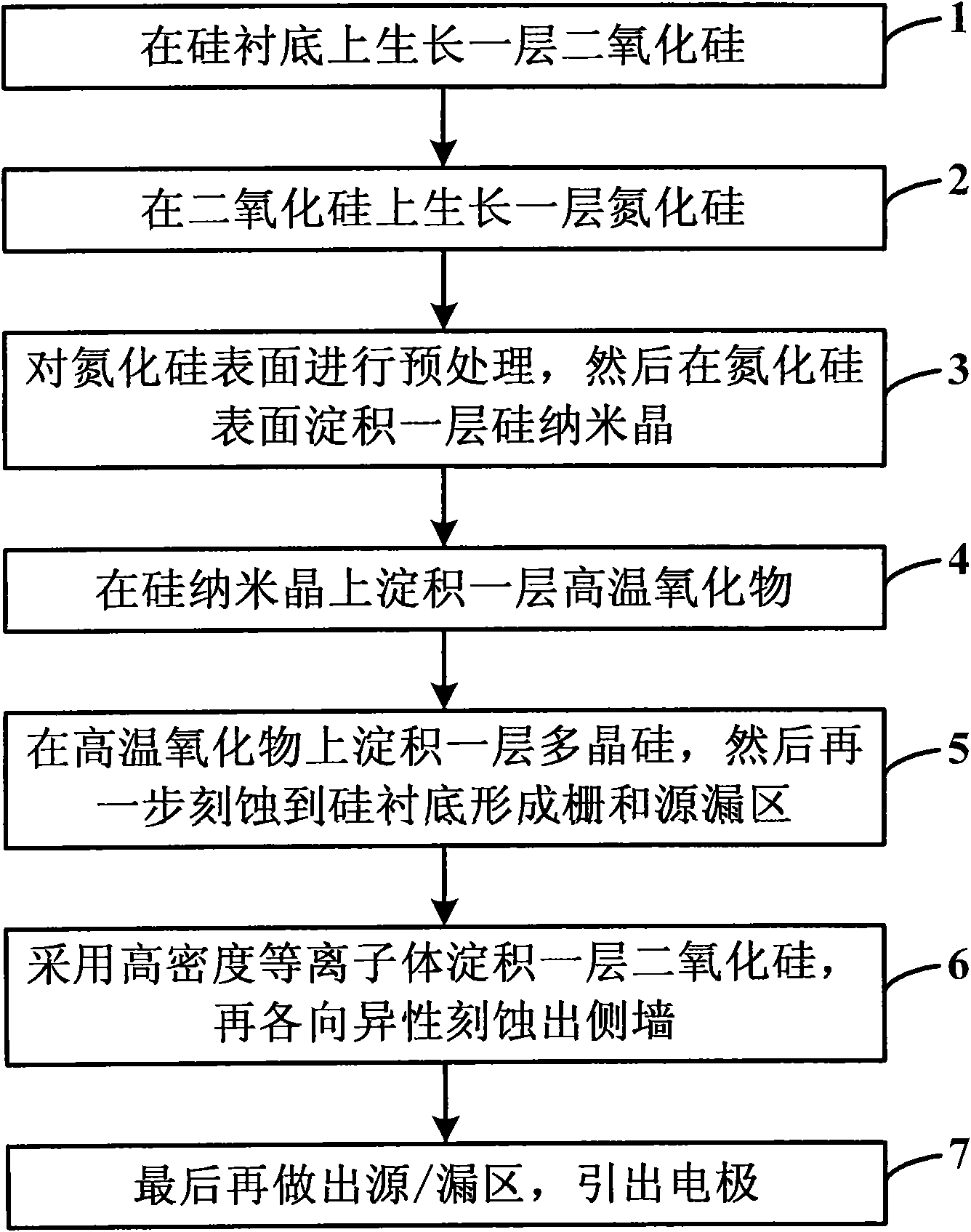
A method for manufacturing a non-volatile memory and a structure thereof are provided. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps. Firstly, a substrate is provided. Next, a semiconductor layer is formed on the substrate. Then, a Si-rich dielectric layer is formed on the semiconductor layer. After that, a plurality of silicon nanocrystals is formed in the Si-rich dielectric layer by a laser annealing process to form a charge-storing dielectric layer. Last, a gate electrode is formed on the charge-storing dielectric layer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Silicon Nitride Layer for Light Emitting Device, Light Emitting Device Using the Same, and Method of Forming Silicon Nitride Layer for Light Emitting Device
InactiveUS20080093609A1Simple wayNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nitrideSilicon nanocrystals
Provided are a silicon nitride layer for a light emitting device, light emitting device using the same, and method of forming the silicon nitride layer for the light emitting device. The silicon nitride layer of the light emitting device includes a silicon nitride matrix and silicon nanocrystals formed in the silicon nitride matrix. A light emitting device manufactured by the silicon nitride layer has a good luminous efficiency and emits light in the visible region including the short-wavelength blue / violet region and the near infrared region.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Composite storage medium floating-gate memory structure and manufacture method thereof
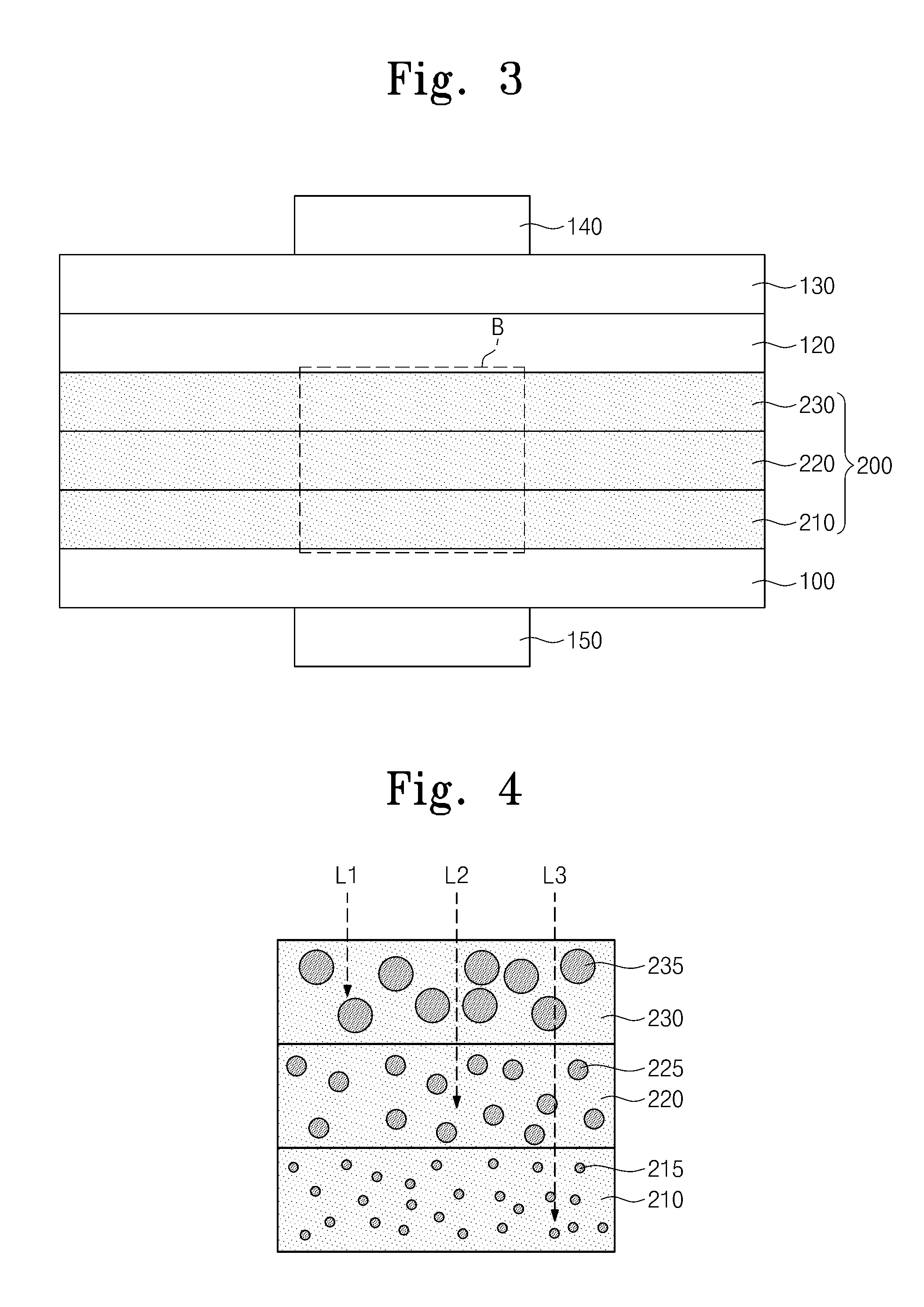
InactiveCN101814506AHigh densityIncrease storage windowTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationSilicon nanocrystalsOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a composite storage medium floating-gate memory structure and a manufacture method thereof. The composite storage medium floating-gate memory structure sequentially comprises the following structures from bottom to top: a silicon substrate, a tunneling medium layer, silicon nitride, silicon nanocrystals, high-temperature oxides, a polysilicon layer, a grid and source / drain region and a side wall, wherein the grid and source / drain region is formed on the silicon substrate through etching, and the side wall is etched on the silicon dioxide layer. When being used, the invention solves the problem of reducibility of nodes in the traditional Flash technology, two storage media are adopted for storing electric charges, and a storage window is enlarged, so the reliability of the floating-gate electric charge storage is improved, and the holding feature of a floating-grate device is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for predicting the formation of silicon nanocrystals in embedded oxide matrices
ActiveUS8036864B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesSilicon nanocrystalsOxide matrix
A method for predicting the formation of silicon nanocrystals in an oxide matrix is disclosed. Initially, fundamental data for a set of microscopic processes that can occur during one or more material processing operations are obtained. Kinetic models are then built by utilizing the fundamental data for a set of reactions that can contribute substantially to the formation of silicon nanocrystals in a silicon oxide matrix. Finally, the kinetic models are applied to predict shape, size distribution, spatial arrangements of silicon nanocrystals.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 40
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com