Method for identifying true and false beef and mutton
A beef and mutton, genuine and fake technology, applied in the field of identifying genuine and fake beef and mutton, can solve the problems of missed DNA detection, consumer troubles, and the impact of sampling part identification, achieving good repeatability and stability, wide application prospects, Simple and fast effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1. Experimental samples
[0036] Beef, Lamb, Pork, Duck
[0037] 2. Experimental equipment and sample preparation
[0038] Bruker AVANCEIII600 Superconducting NMR Spectrometer
[0039] Preparation of test samples: take 500mg meat sample, add 1mL deuterated chloroform, soak and stir for 5-10min, and centrifuge. Add water in anhydrous sodium sulfate drying solvent to the separated deuterated chloroform layer, and shake until the solution becomes clear. Transfer the dried chloroform layer to a 5mm diameter NMR tube, and mix well for testing.
[0040] Treat beef, lamb, pork, duck according to the above method.
[0041] 3. NMR spectrum detection:
[0042] Measuring conditions: temperature 20°C, CDCl3 as internal lock, scanning times 200 times, spectral width 210ppm, sampling time AQ 0.9s; pulse sequence: zgdc30.
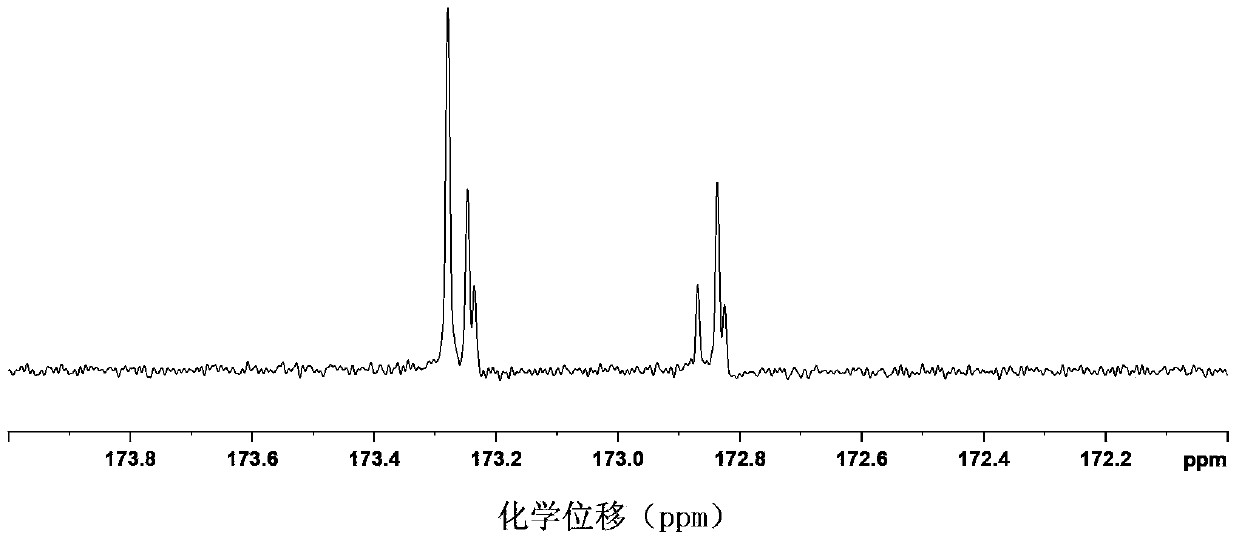
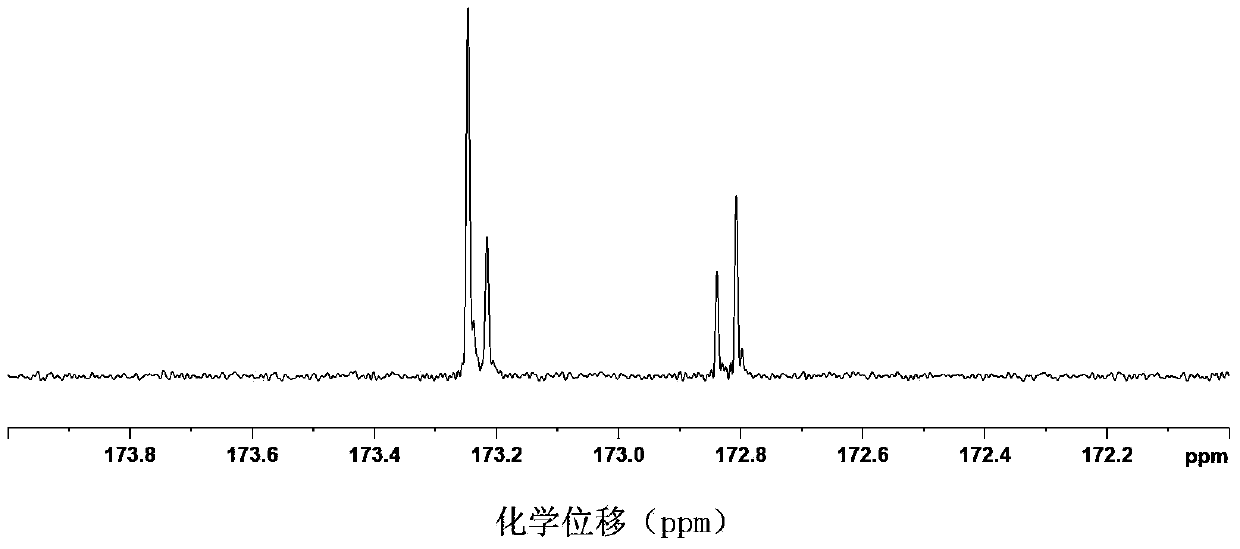
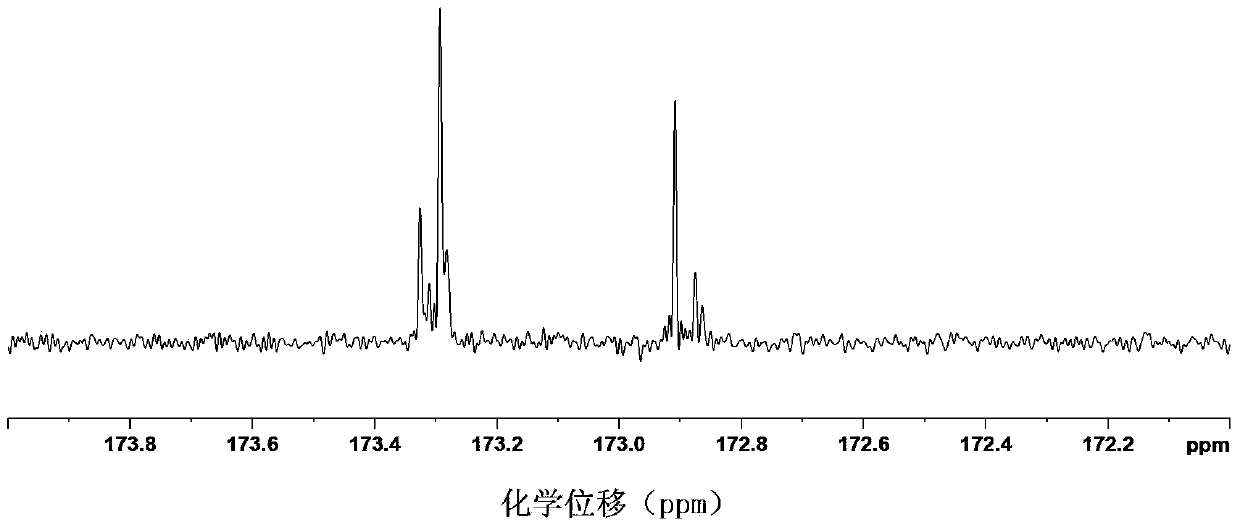
[0043] The chloroform solution NMR tubes extracted from different meat samples were put into the NMR spectrometer, and the carbon spectrum data of the sample...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 1. Experimental samples
[0050] Buy mutton 1, mutton 2, mutton 3, mutton 4, mutton 5 in the market.
[0051] Two. Experimental apparatus and test method are with embodiment 1
[0052] 3. Data analysis
[0053] pass Figure 5and Figure 1~4 The contrast of different fingerprint peaks can be observed. according to Figure 5 Comparison of the intensity and peak shape of the fingerprint peaks in the middle, Figures c, d, e and figure 2 The fingerprint spectrum of mutton is consistent, and the peak shape of the carbon spectrum of the fingerprint and the intensity of different peaks are consistent with the figure 2 The mutton map is consistent, and the X value is close to the mutton index, so it can be determined that it is mutton. a with image 3 The fingerprints are consistent, and the X value is close to the pork index, so it can be determined that it is pork. b with Figure 4 The fingerprints are consistent, and the X value is close to the duck meat index, so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com