Technological method for reducing defect of extrusion rod
A process method and technology of extruding rods, which are applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, welding media, etc., can solve problems such as increasing defects in final products, affecting wire drawing production efficiency, and wire breakage, so as to reduce product defects and avoid Slag inclusion phenomenon, the effect of avoiding oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
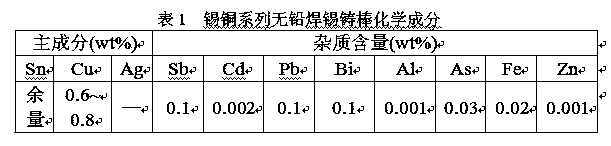
[0033] The invention is used in the field of solder production, especially for tin-copper series lead-free solder products. Refined tin raw materials and electrolytic copper (Yunnan Tin Industry, Yunnan Copper Industry) are used, and the proportion of raw materials is carried out according to the requirements of the chemical composition of the product in the implementation of technical standards for production products.
[0034]
[0035] A process for reducing defects in extruded rods, comprising the following steps:
[0036] 1. Smelting tin and copper in a smelting furnace to form a molten metal, and then adding a refining agent to the molten metal at a temperature range of 240-300°C to refine the molten metal;
[0037] 2. Add 100ppm anti-oxidation master alloy to the refined metal melt, press the antioxidant master alloy into the metal melt, and slowly move the anti-oxidation master alloy until it is completely melted into a casting melt, and control the temperature rise ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A process for reducing defects in extruded rods, comprising the following steps:
[0045] 1. Smelting tin-copper into molten metal in a smelting furnace: first put part of the tin raw material into the smelting furnace, raise the temperature of the smelting furnace, and the temperature of the furnace is 520-580°C. After the tin raw material is completely melted, put in the impurity-removed Copper block / shavings, fully stirred for 3-5 minutes to completely melt the copper block / swarf; finally put in the remaining tin raw material, and after it is completely melted, cool down the entire molten metal to 240-300°C; 240°C, 250°C can be selected °C, 255 °C, 260 °C, 270 °C, 280 °C, 290 °C, 300 °C and other temperatures to cool down the molten metal to reduce the burning loss of metal elements.
[0046] 2. Then add refining agent to the molten metal in the temperature range of 240-300°C to refine the molten metal;
[0047] 3. Add the anti-oxidation gallium phosphorus master...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A process for reducing defects in extruded rods, comprising the following steps:
[0053] 1. Smelting tin-copper into molten metal in a smelting furnace: first put part of the tin raw material into the smelting furnace, raise the temperature of the smelting furnace, and the temperature of the furnace is 520-580°C. After the tin raw material is completely melted, put in the impurity-removed Copper block / shavings, fully stirred for 3-5 minutes to completely melt the copper block / shavings; finally put in the remaining tin raw material, and after it is completely melted, cool the entire molten metal to 240-300°C; the melting furnace is a titanium alloy electric Magnetic induction tin melting furnace; the outer layer of the lead-free titanium alloy electromagnetic induction melting furnace is cast iron, and the inner layer is titanium alloy, which can effectively prevent the crucible material from being corroded and dissolved into the molten liquid, so as to ensure that ther...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com