Method for evaluating potential of complexation of water-soluble humus matter with heavy metals
A technology for water-soluble organics and humic substances, which can be used in material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., to solve the problems of low fluorescence intensity, few heavy metal binding sites, and high complexation potential, achieving high sensitivity, fast detection speed, and pre-sample. Handling simple effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
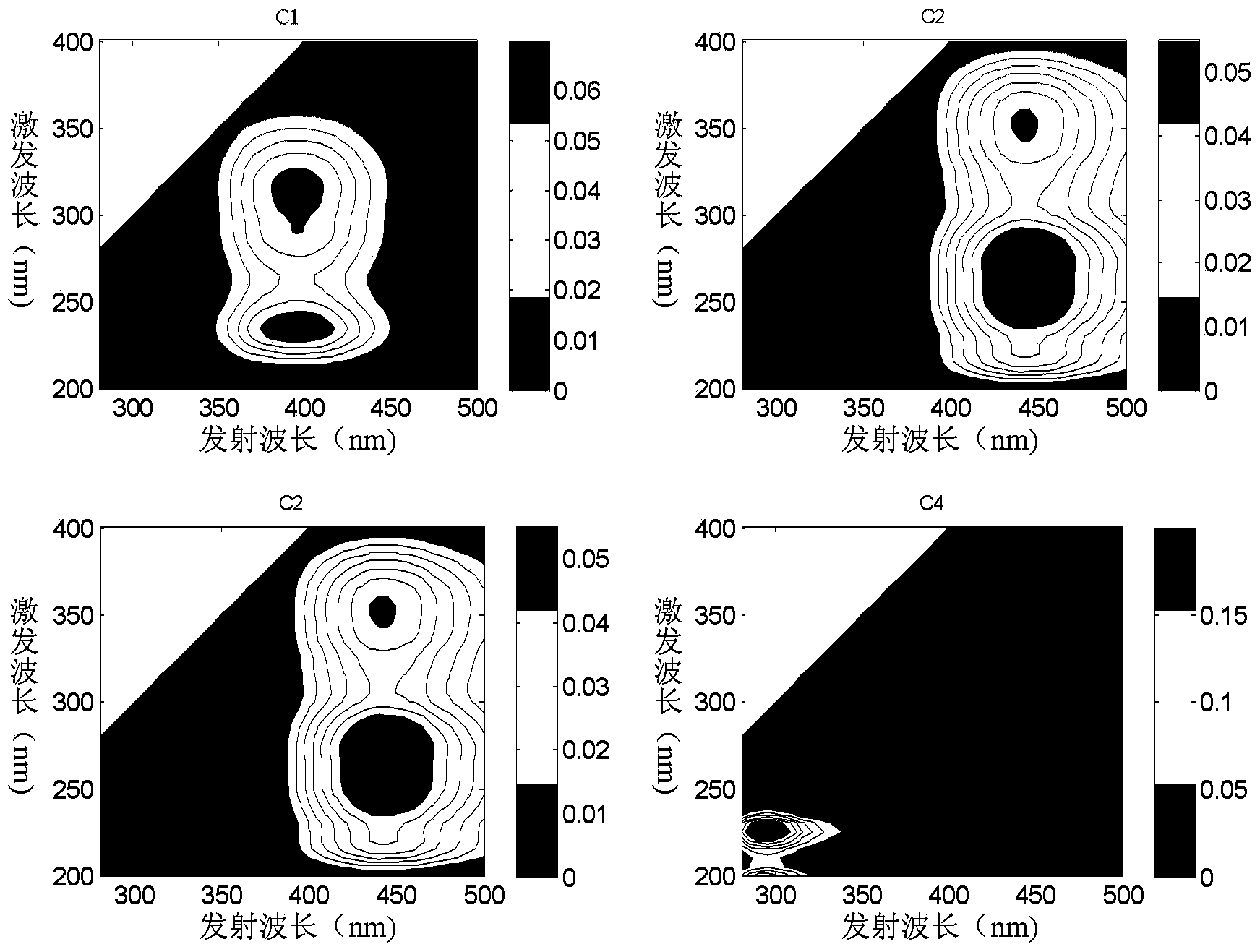
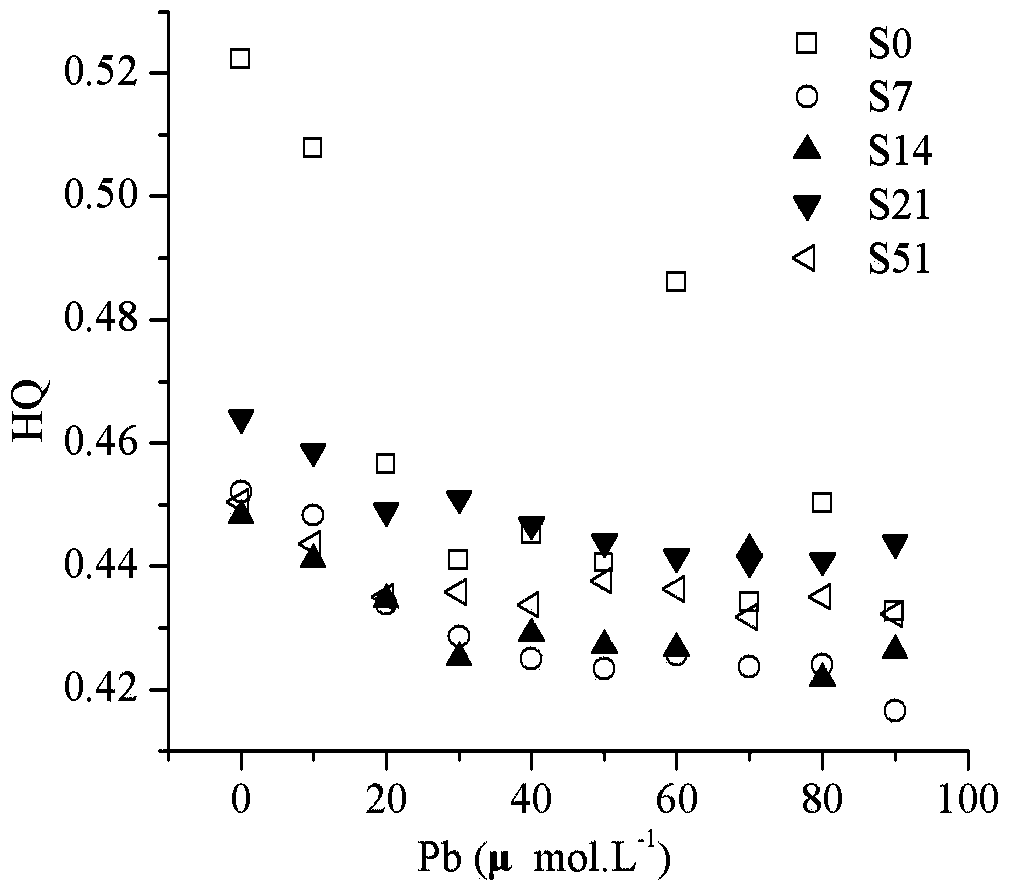
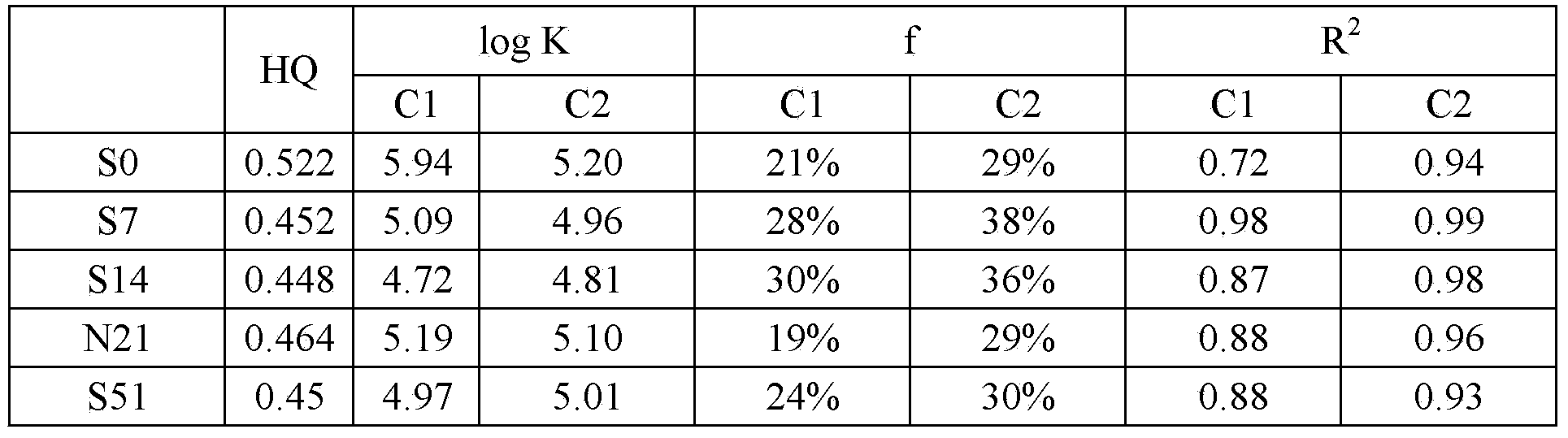
[0025] Collect samples of 0, 7, 14, 21 and 51 days of domestic waste composting, add double distilled water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1 (g): 10 (ml), and shake at 20°C for 16 hours to obtain an extract; Centrifuge at 4°C and above 10,000 rpm for 15 minutes, collect the supernatant, pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and collect the filtrate; divide each filtrate into 11 parts, and each part is divided into 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100 μmol L -1 After adding the heavy metal Pb at a concentration of 24 h at room temperature, 55 samples were collected, and the three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of the sample was scanned. The excitation wavelength range was 200-400nm, the emission wavelength range was 280-500nm, and the excitation and emission wavelength slit width Equal to 5nm, scan speed is less than 2400nmmin -1 After the scanning is completed, the fluorescence data is exported after deducting the three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of double di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com