Infectious cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) clone, construction method and application of recombinant subgroup J avian leucosis virus capable of expressing EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein)
An avian leukemia virus and an infectious technology are applied in the preparation method and application field of the virus to achieve the effect of simple and effective large-scale detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1 Construction of recombinant J subgroup avian leukosis virus infectious clone capable of expressing EGFP
[0025] method:
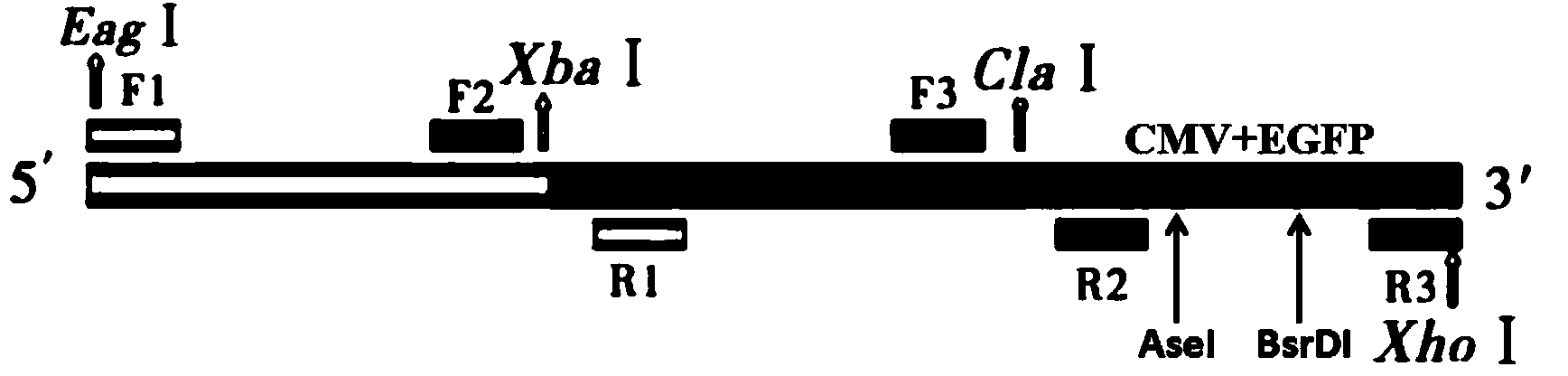
[0026] 1. According to the completed ALV-J HPRS-103 proviral genome sequence (GenBank: Z46390.1), the spliced sequence was analyzed by MapDraw software, and it was found that XBaI and ClaI had only one site in the whole genome, The location exactly divides the whole genome into 3 segments that are close in length ( figure 1 ). Although the synthetic primers R1, F2, R2, and F3 did not introduce restriction sites, the PCR products all spanned these two single restriction sites, that is, the amplified fragments of primers F1 and R1 and the amplified fragments of F2 and R2 There are XBaI sites between the overlapping sequences. Similarly, there is a ClaI site between the overlapping sequences of the amplified fragments of primers F2 and R2 and the amplified fragments of F3 and R3. To facilitate cloning into the pBluescript II KS(+) ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 Construction of the recombinant J subgroup avian leukosis virus capable of expressing EGFP with CMV promoter
[0035] method:
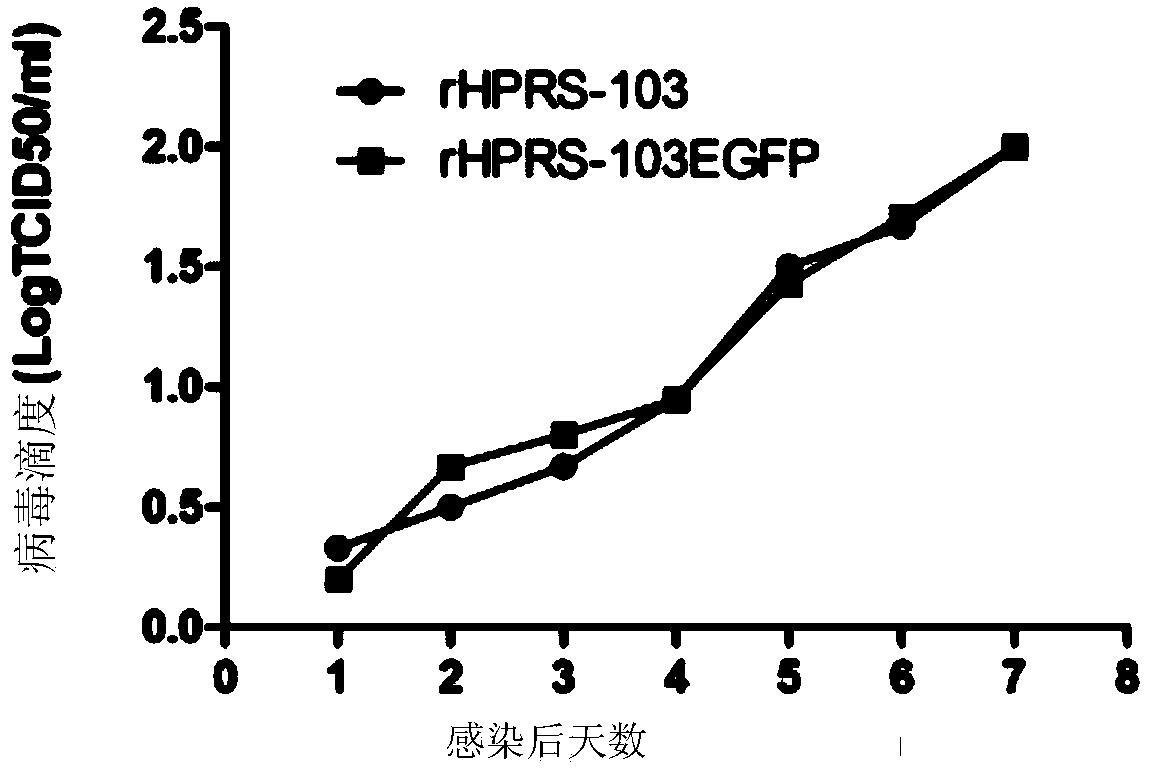
[0036] 1. Use QIAGEN Plasmid Midi Kits to prepare and purify the expression vector pHPRS-103-egfp prepared in Example 1, by Lipofectctamine TM 2000 respectively mediated the transfection of about 80% of monolayer DF1 cells, and normal DF1 was used as the control, discarded the supernatant of cells 6 hours after transfection, added 2ml DMEM (containing 10% PAA fetal bovine serum) and continued in a 37°C incubator After culture, the virus was harvested 72 hours after transfection, and after repeated freezing and thawing three times, it was continuously passaged on DF1. After identification, the rescued virus was named HPRS-103-egfp ( figure 2 B).
[0037] 2. Infect DF-1 cells with HPRS-103-egfp, and use HPRS-103 parental virus as a control, extract the supernatant and precipitated RNA of the infected cells, reverse transcription...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Application of J Subgroup Avian Leukemia Virus Expressing EGFP in Detection of Virus Neutralizing Antibodies
[0042] method:
[0043] The expression of EGFP is easy to observe under a fluorescent microscope. Taking advantage of this feature, the present invention uses the virus rescued by this invention to perform a neutralizing antibody detection test (NT-EGFP). In order to verify the feasibility, specificity and sensitivity of the method. The present invention uses 30 parts of ALV-J serum, 50 parts of field serum, 30 parts of SPF chicken serum and 3 parts of anti-IBDV, ARV, ALV-A, ALV-B and MDV serums from animal experiments. All sera were tested for immunofluorescence (NIT) using HPRS-103 in parallel while using fluorescent viruses to detect neutralizing antibodies as controls. The reciprocal of the serum dilution factor was used as the neutralization index. Use the MedCalc software to draw the curve. In the NT-EGFP test, when the neutralization index...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com