Random positioning super-resolution microscopy method and device based on fluorescence emission suppression mechanism
A fluorescence emission and super-resolution technology, used in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., which can solve problems such as imperfection, damage to observed samples, and cumbersome sample processing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0063] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
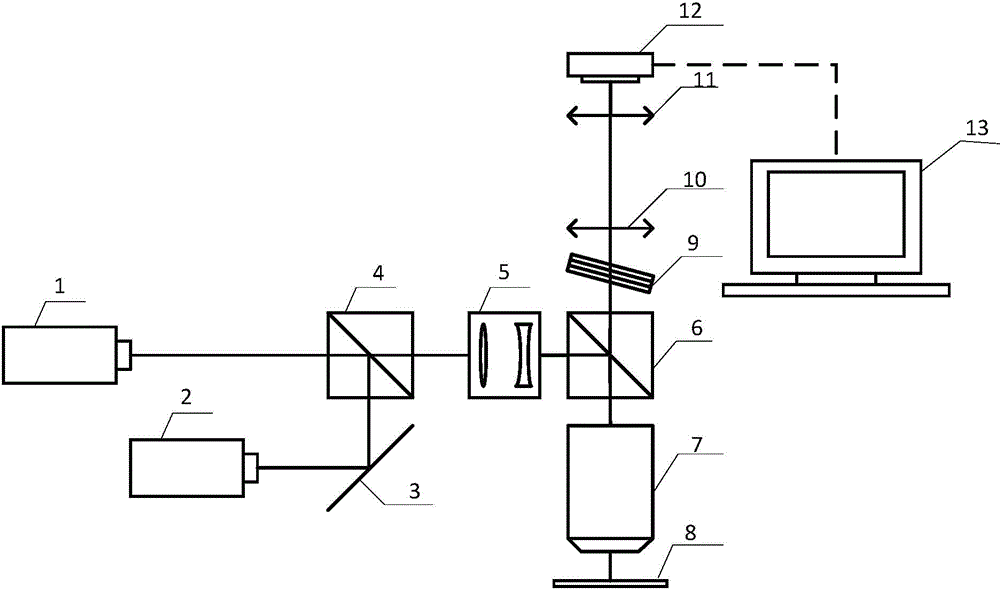
[0064] Such as figure 1 As shown, the randomly positioned super-resolution microscopy device based on the fluorescence emission suppression mechanism includes: a first laser light source 1, a second laser light source 2, a mirror 3, a first dichromatic mirror 4, a Kohler mirror group 5, a second two Color mirror 6, microscope objective lens 7, sample 8, optical filter 9, field lens 10, eyepiece 11, wide field photosensitive element 12 and computer 13.
[0065] In addition to the computer 13, the optical elements are arranged along the optical path direction, the first laser light source 1 and the first dichromatic mirror 4 are all located on the main axis optical path, and the second laser light source 2 converges with the first laser light source 1 on the first two through the reflector 3. On the color mirror 4 , th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com