Method for realizing high-resolution incremental bus-based optical-electricity encoder
A photoelectric encoder, high-resolution technology, applied in the direction of using optical devices to transmit sensing components, can solve the problems of low precision, high cost, strict mechanical requirements, etc., and achieve high production efficiency, low manufacturing cost, and simple assembly. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
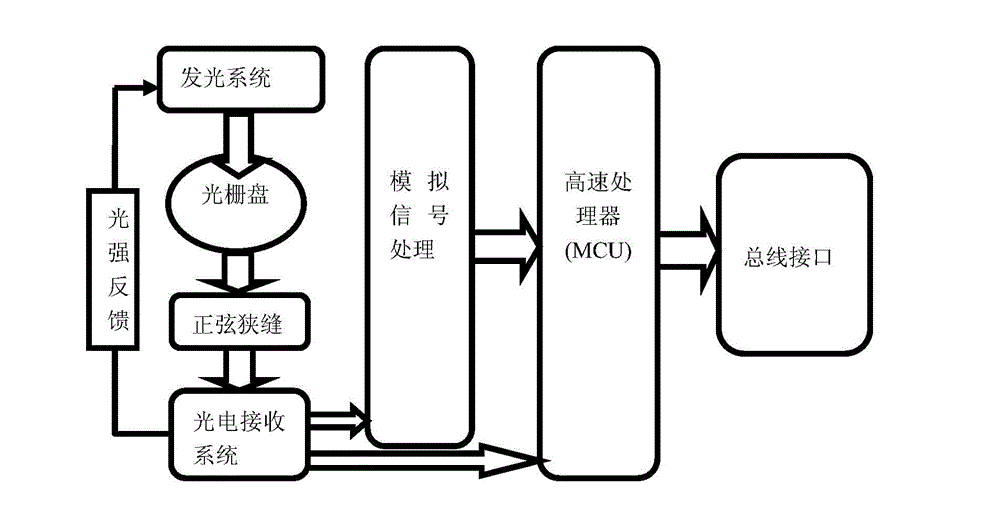
[0037] Include the following steps:
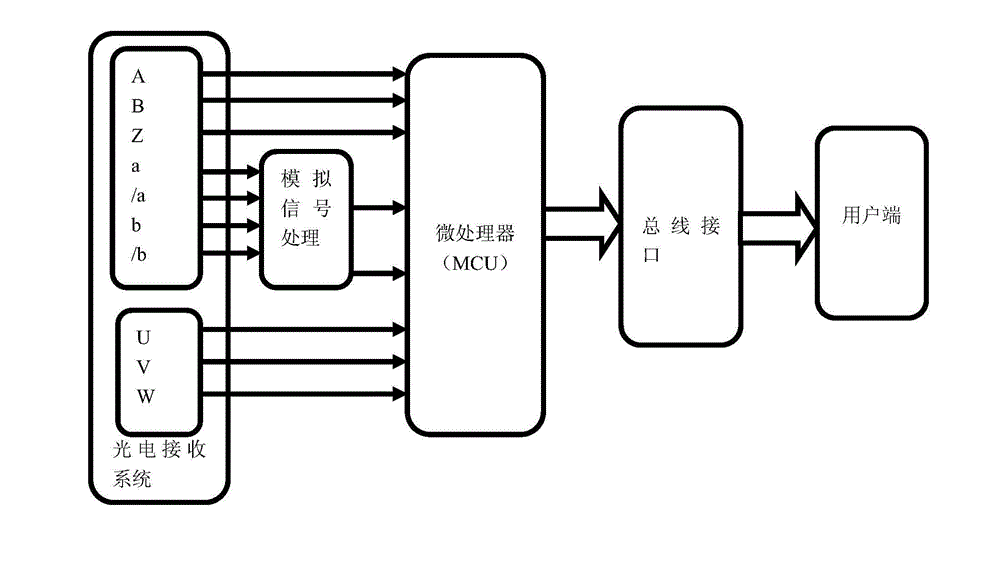
[0038] The light-emitting system outputs A, B, Z square wave digital signals through the slits on the grating disk, and simultaneously outputs differential analog signals a, / a, b, / b, and electrode control signals U, V, W;
[0039] Received by the photoelectric receiving system,
[0040] The analog signals a, / a, b, / b are processed by the analog signal processor and output two differential analog signals Va x , Vb x to the microprocessor MCU,
[0041] The photoelectric receiving system outputs A, B, Z square wave digital signals and electrode control signals U, V, W to the microprocessor MCU;
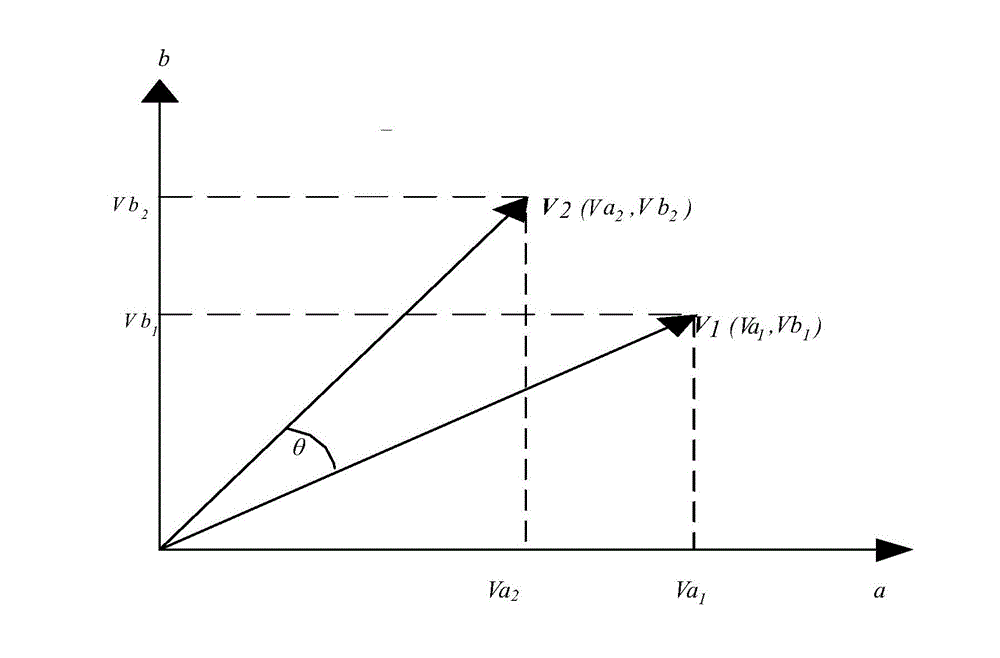
[0042] Microprocessor MCU subdivision method: two-way differential analog signal Va x , Vb x Input to the microprocessor MCU, the analog-to-digital converter AD inside the processor converts the analog signal into a digital signal, and the two converted digital signals are finely subdivided by the CORDIC algorithm, and the vector V 1 Get a n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com