Artificial breeding method of southward stichopus japonicus
An artificial breeding, sea cucumber technology, applied in the direction of climate change adaptation, animal feed, animal feed, etc., can solve the problems that limit the progress of sea cucumber southward migration seed breeding, low planktonic larvae survival rate and metamorphic attachment rate, fertilized eggs Problems such as low hatching rate, to achieve the effect of improving immunity and survival rate, improving feed utilization rate, high hatching rate and survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
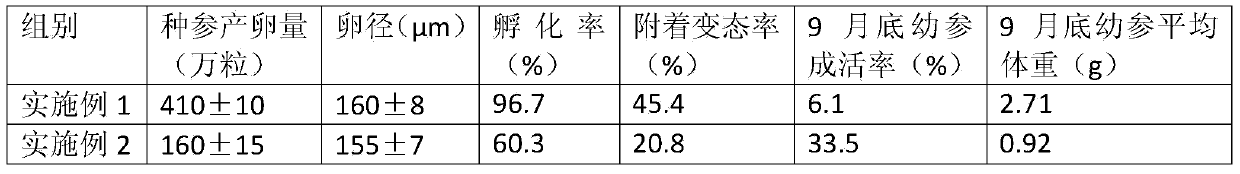
[0022] This embodiment achieved good results through the following work in Guanwu Ocean Development Co., Ltd.:
[0023] An artificial breeding method for moving sea cucumbers to the south. In the north in autumn, when the seawater temperature in the natural sea area reaches 10-15°C, the seed ginseng is collected and stored at low temperature. The water temperature for storage is the natural water temperature. When the natural water temperature drops to 4-6°C At this time, the water temperature is maintained for 10 days, and then transported by water to the south for sea cage culture. When the natural water temperature rises to 17°C, the ginseng is moved from the sea to the workshop for spawning, fertilization, hatching, and planktonic larvae. Cultivation, placement of attachment base, and young ginseng cultivation; when the natural water temperature in the south gradually exceeds 28°C, use the cooling water from kelp seedling cultivation to cool down the water for young ginseng...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The ginseng species of the same specification as those collected in the same batch in Example 1 were transported by water transport to Guanwu Ocean Co., Ltd. for storage in the workshop. , Change the water every morning, the influent water is natural sea water, the amount of water changed is half of the pool water, and the pool is poured every 3 to 5 days to completely remove the feces and residual bait in the storage pool.
[0046] The compound feed and sea mud were fed when stocking, and the composition and feeding method of the compound feed were the same as in Example 1.
[0047] When the natural water temperature rises to 17°C, oviposition, fertilization, hatching, planktonic larvae cultivation, attachment base feeding and juvenile ginseng cultivation are carried out; marine red yeast and fresh yeast are fed during the planktonic period, and the daily feeding amount is marine red yeast and 10,000 cells / mL each for fresh yeast. From the cultivation of planktonic la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com