Laser device
A laser and grating technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of limited speed and energy consumption, insufficient, and inability to significantly reduce the length of the effective cavity, and achieve the effect of excellent single-mode properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
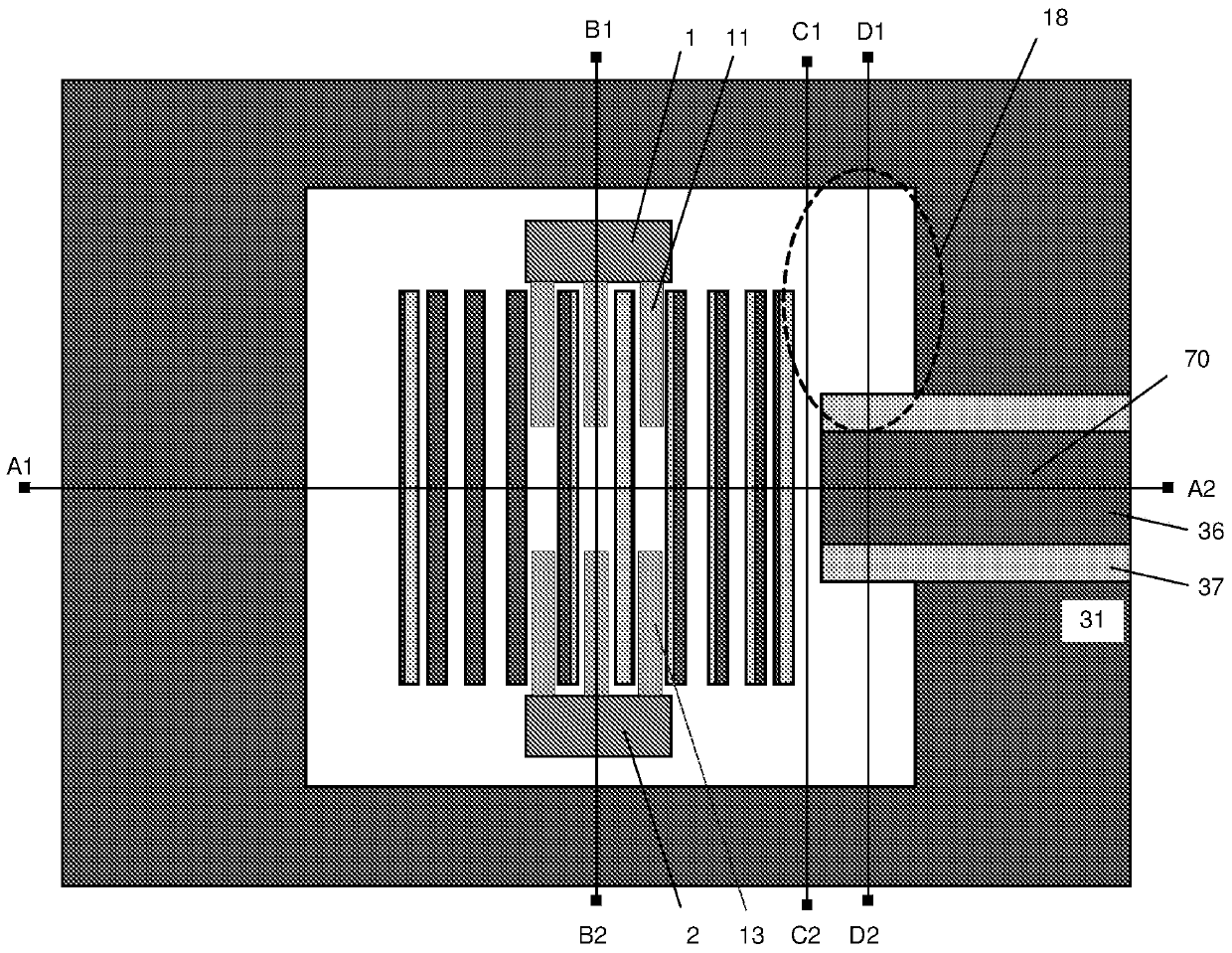
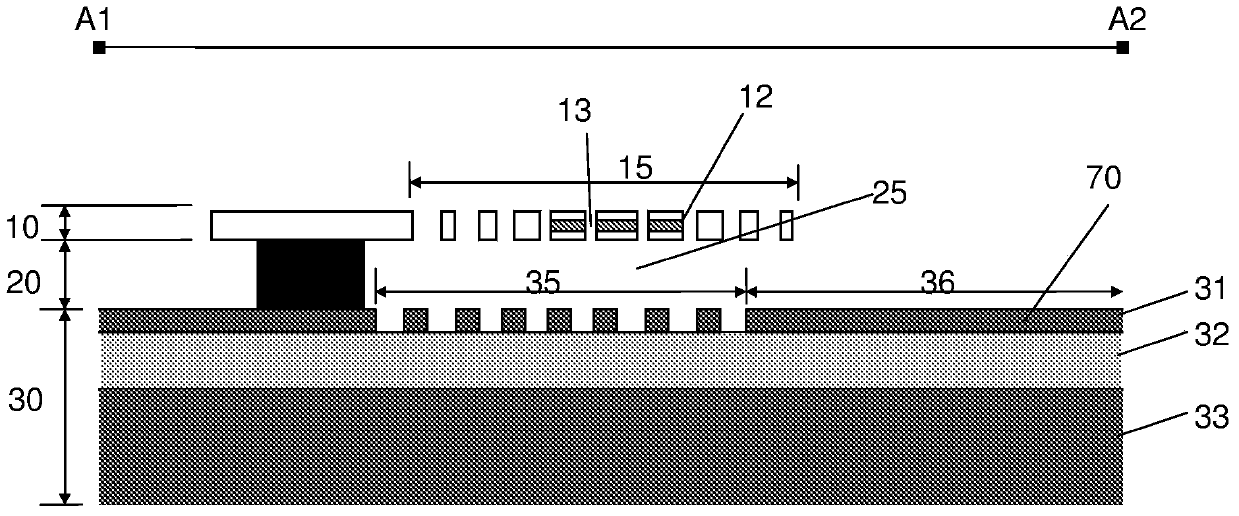
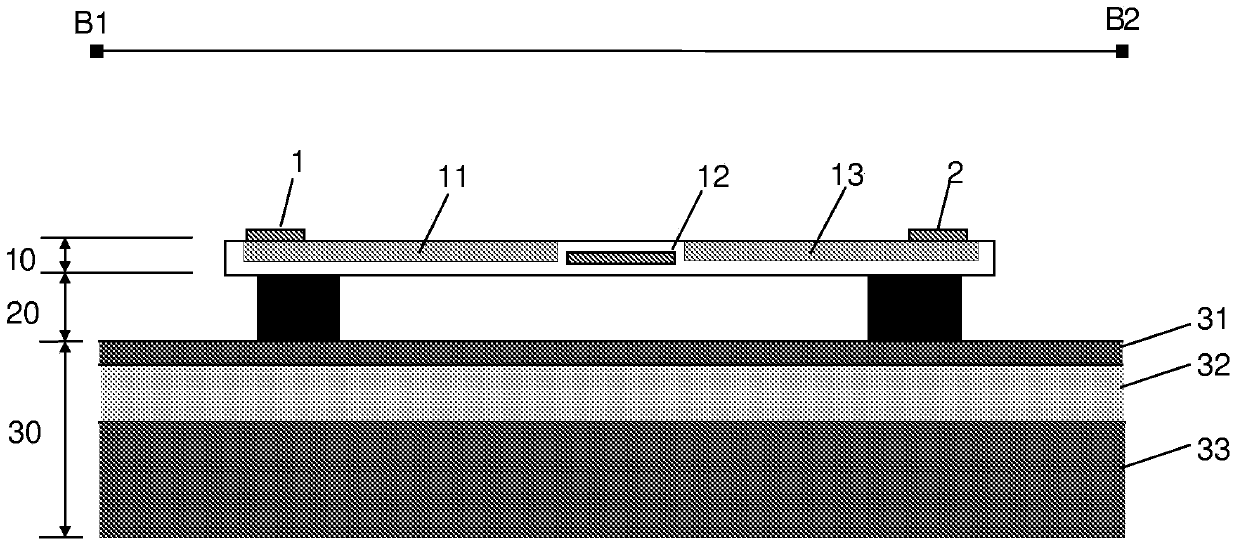
[0078] exist Figures 1A-1E The middle diagram shows an exemplary embodiment of a laser according to the invention. exist Figure 1B is shown along the Figure 1A Cross-sectional device structure of lines A1-A2.
[0079] by first thinking together Figure 1A and 1B , the basic structure of the invention will be best understood. The laser structure includes an active grating region 15 , an air cavity 25 and a passive grating region 35 . An active grating region 15 and a passive grating region 35 are typically placed on each side of the air cavity 25 to form a resonant structure, which forms the laser cavity. Both the active grating 15 and the passive grating 35 may be periodic gratings and act as highly reflective mirrors. The grating 15, 35 is generally periodic in a direction parallel to the plane of the semiconductor structure.
[0080] The periodicity of the active grating 15 can be spatially modulated to focus the reflected light. This results in lateral optical co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com