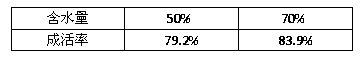Method for vegetative propagation of vaccinium plants through fresh sphagnum
A technique of asexual reproduction and sphagnum moss, which is applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, applications, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of low survival rate of seedling breeding and unsatisfactory cutting effect, and achieve the effect of improving the survival rate of seedling raising
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
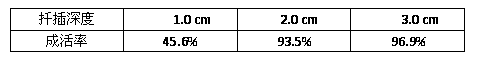
[0016] (1) Selection and treatment of cuttings: Select the branches that are semi-lignified in the current year, thick and straight, full of leaf buds, and free from diseases and insect pests to make cuttings. The degree of lignification of the cuttings is low, which is conducive to the formation of callus. Then form young roots, the cuttings are 6cm long, quickly dip the cuttings with indole butyric acid or soak the base of the cuttings with naphthalene acetic acid for 2 hours.
[0017] (2) Substrate preparation: firstly, the mycorrhizal spores extracted from Vaccinium cranium were prepared into a mycorrhizal suspension and inoculated into a small amount of fresh sphagnum moss plants cultivated in the experimental facility, so that the endophytic mycorrhizae were in it. A large number of proliferation; then, use the moss that has been inoculated as the mother plant of endomycorrhizae to inoculate in the fresh peat moss culture substrate. The fresh peat moss substrate must mee...
Embodiment 2
[0022] (1) Selection and treatment of cuttings: Select the branches that are semi-lignified in the current year, thick and straight, full of leaf buds, and free from diseases and insect pests to make cuttings. The degree of lignification of the cuttings is low, which is conducive to the formation of callus. Then form young roots, the cuttings are 8cm long, quickly dip the cuttings with indole butyric acid or soak the base of the cuttings with naphthalene acetic acid for 2 hours.
[0023] (2) Substrate preparation: firstly, the mycorrhizal spores extracted from Vaccinium cranium were prepared into a mycorrhizal suspension and inoculated into a small amount of fresh sphagnum moss plants cultivated in the experimental facility, so that the endophytic mycorrhizae were in it. A large number of proliferation; then, use the moss that has been inoculated as the mother plant of endomycorrhizae to inoculate in the fresh peat moss culture substrate. The fresh peat moss substrate must mee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com