Optical fiber for increasing spatial divergence angle of outputted light beam and homogenizing light spot and application thereof
A divergence angle, optical fiber technology, applied in the direction of coupling of optical waveguides, can solve problems such as reducing the flexibility of laser placement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
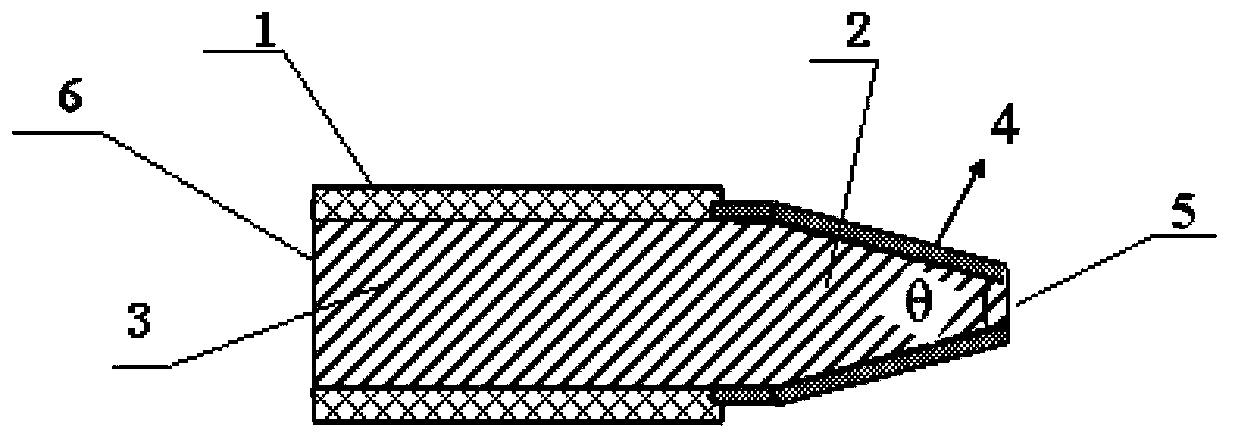
[0032] An optical fiber for increasing the spatial divergence angle of the output beam and homogenizing the spot, comprising a cylindrical optical fiber main body 3, an optical fiber coating layer 1 is arranged on the surface of the cylindrical optical fiber main body 3, and one end of the optical fiber main body 3 has a tapered optical fiber structure 2. The ratio of the area of the end face 5 of the tapered optical fiber structure to the area of the cross section 6 of the cylindrical optical fiber body is 1:1.5, and a layer of high reflection film 4 is plated on the sector surface of the tapered optical fiber structure 2. The high reflection film 4 is a 650 nm high reflection film.
[0033] The taper angle θ of the tapered fiber structure 2 is 20°. The diameter of the cylindrical optical fiber body 3: 308 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0035] A method for homogenizing a spot of a light beam by using the optical fiber described in embodiment 1, including the following steps:
[0036] (1) Pass the optical fiber into the protective tube, expose the tapered optical fiber structure 2 at one end of the protective tube, and expose a section of cylindrical optical fiber body 3 at the other end of the protective tube;
[0037] (2) Pass the exposed cylindrical optical fiber body 3 through the glue-filled connector to expose the part;
[0038] (3) Curing the glue in the connector;
[0039] (4) After curing, the cylindrical fiber body 3 exposed outside the connector is removed to form the fiber end face, and the fiber end face is polished to obtain an optical plane perpendicular to the central axis of the fiber to make an optical fiber jumper. Structure 2 is the output end of the optical fiber jumper, and the connector is the connection end of the optical fiber jumper;
[0040] (5) When in use, connect the connector of the above...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The optical fiber for increasing the spatial divergence angle of the output beam and homogenizing the spot as described in embodiment 1, the difference is that the area ratio of the end surface 5 of the tapered optical fiber structure to the cross section 6 of the cylindrical optical fiber body is: 1:2, a high-reflection film 4 is plated on the sector surface of the tapered optical fiber structure. The high reflective film is a 808 nm high reflective film 4.
[0050] The tapered angle θ of the tapered optical fiber structure 2 is 35°. The diameter of the cylindrical optical fiber body 3: 440 μm.
[0051] The optical fiber jumper prepared by this embodiment transmits light beams compared to ordinary optical fibers, and its beam quality factor is M 2 Decrease by 71%, increase brightness by 6 times, and homogenize light spots.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com