Time-division frequency-division multiplexing rotor-type micro-gyroscope detection device
A technology of frequency division multiplexing and detection device, which is applied in the field of micro-gyroscope detection to achieve the effect of eliminating cross-sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
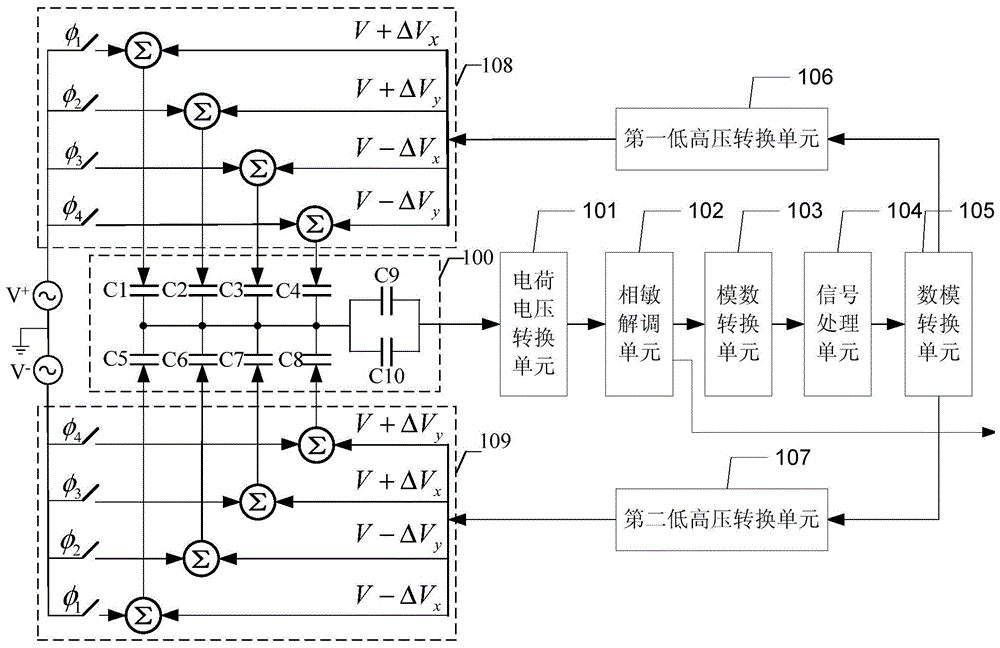
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment mode, the time-division-frequency-division-multiplexing rotor-type micro-gyroscope detection device described in this embodiment mode, which includes a rotor-type micro-gyroscope sensitive unit 100, a charge-voltage conversion unit 101, a phase-sensitive demodulation unit 102, and an analog-to-digital conversion unit 103 , a signal processing unit 104, a digital-to-analog conversion unit 105, a first low and high voltage conversion unit 106, a second low and high voltage conversion unit 107, a first time division frequency division multiplexing unit 108 and a second time division frequency division multiplexing unit 109;
[0020] The carrier excitation signal V of the first time division frequency division multiplexing unit 108 + Multiplexed with the feedback control signal and loaded to the first group of multiplexed signal input terminals of the rotor-type micro-gyroscope sen...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: This embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1. The rotor-type micro-gyroscope sensitive unit 100 includes four pairs of differential capacitors and a pair of pickup capacitors. The four pairs of differential capacitors are C1, C5; C2, C6; C3, C7 ; With C4, C8; the pair of pickup capacitors are C9, C10; pickup capacitors C9 and C10 are connected in parallel;
[0032] The multiplexing signal loaded by the differential capacitors C1, C2, C3 and C4 is the carrier excitation signal V + and feedback control signal; the multiplexing signal loaded by differential capacitors C5, C6, C7 and C8 is the carrier excitation signal V - and feedback control signals;
[0033] The differential capacitor C1 multiplexes and loads the carrier excitation signal V + and feedback control signal V+ΔV x ;
[0034] The differential capacitor C2 multiplexes and loads the carrier excitation signal V + and feedback control signal V+ΔV y ;
[0035] The differential capacitor C...
specific Embodiment approach 3
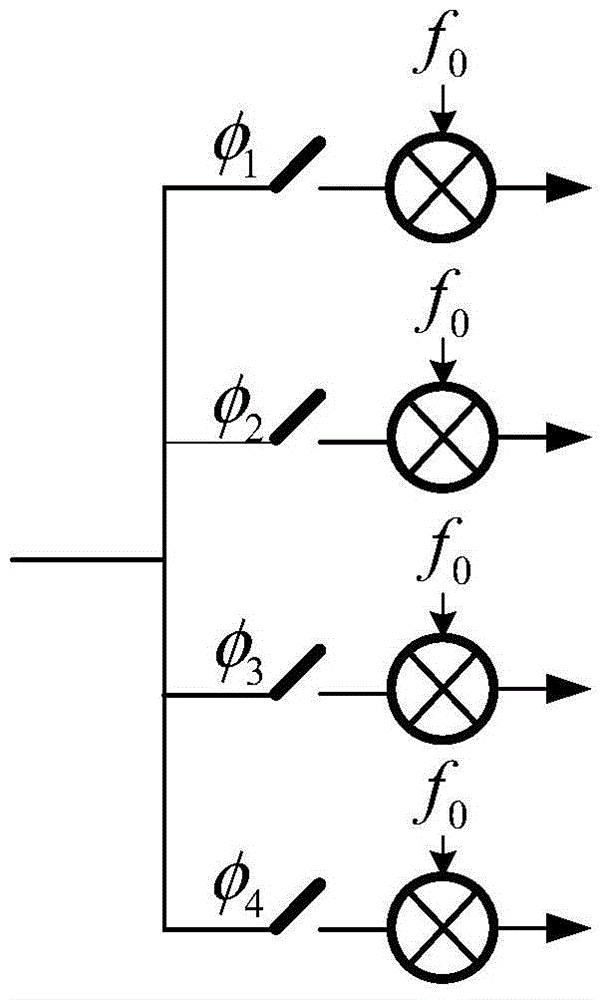
[0043]Specific embodiment three: this embodiment will further explain embodiment one, the first time division frequency division multiplexing unit 108 and the second time division frequency division multiplexing unit 109 have the same structure, both are composed of a switch network and a summation unit, so The above switch network is a group of time switches φ 1 , φ 2 , φ 3 , φ 4 ; Controlled by a time-sharing switch, and load the multiplexing signal through the summation unit;
[0044] Time division switch φ in the first time division frequency division multiplexing unit 108 1 , φ 2 , φ 3 , φ 4 Control the loading of differential capacitors C1, C2, C3 and C4 respectively;
[0045] Time division switch φ in the second time division frequency division multiplexing unit 109 1 , φ 2 , φ 3 , φ 4 Control the loading of differential capacitors C5, C6, C7 and C8 respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com