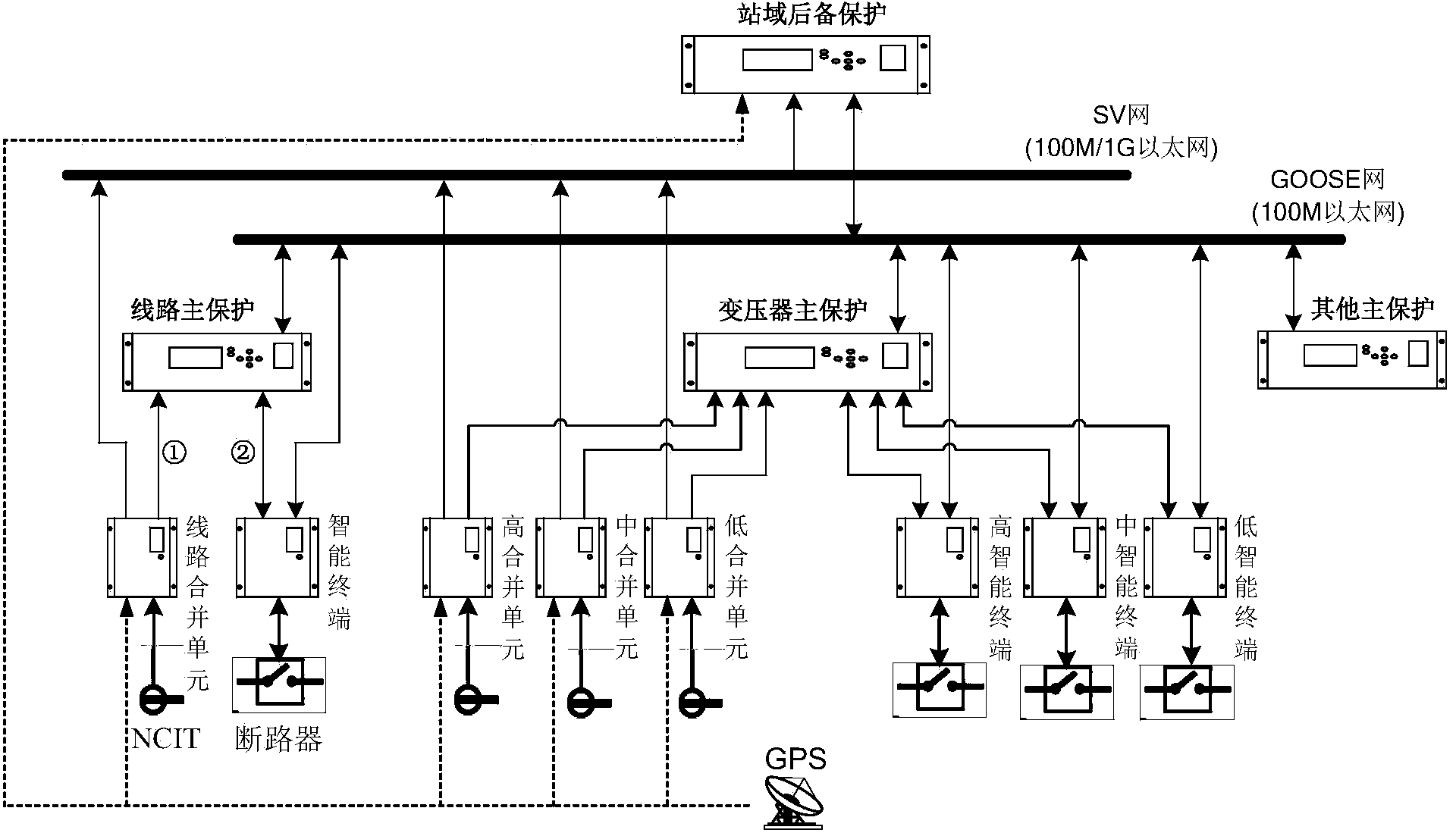
Substation area backup protection method based on combination of direction comparison and current differential
A backup protection, current differential technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of high bandwidth and reliability requirements of communication networks, increased calculation, and high economic costs, and achieves simplified configuration and tuning. The effect of shortening the action time and increasing the action speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
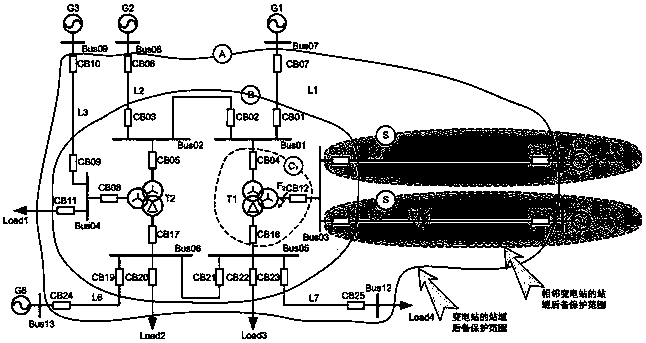
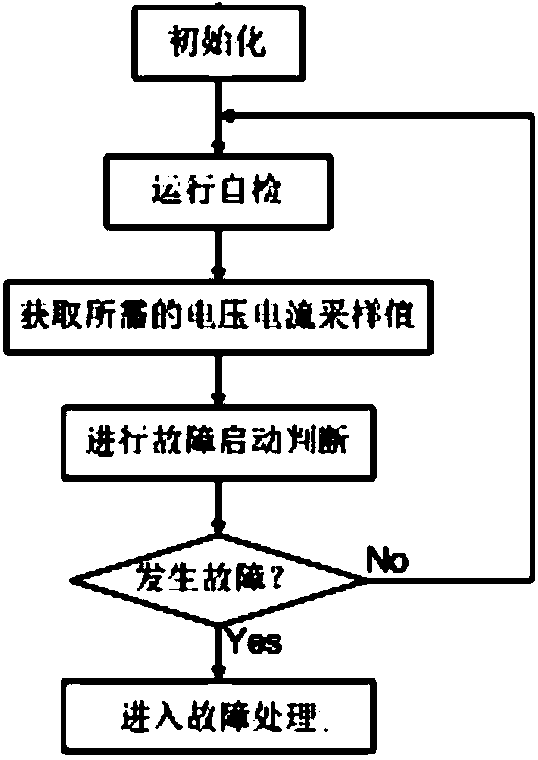
[0052] Take the working condition of line L5 fault and main protection refusing to operate as an example. When F 1 If a fault occurs at any point, the fault starting element will act, and the backup protection of the station domain will enter the fault handling procedure. After calculating the current differential criterion, it is detected that the differential zone B of the substation is in the braking state of the differential criterion, so it is judged that the fault occurs outside the substation. There are two situations at this time: in the first case, the fault is located on the outgoing line of the substation; in the second case, the fault is located outside the protection range of the station domain backup protection. The station domain backup protection judges the directional element according to the collected bus voltage and outgoing current. The judgment result of the direction of the outgoing line L5 is the positive direction, while the direction judgment results ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: Take the internal failure of transformer T1 and the refusal of circuit breaker CB12 as an example to illustrate the specific process:
[0054] f 2 A fault occurs at the fault, the fault start element acts, and the station domain backup protection enters the fault processing procedure:
[0055] After the calculation of the current differential criterion, it is detected that the differential zone B of the substation is in the action state of the differential criterion, and it is determined that the faulty element is located inside the substation;
[0056] Enter the traversal program of the extended differential area for component faults in the station, and remove the busbars Bus01, Bus02, Bus03, Bus04, Bus05, Bus06 and transformer T2 in the differential area B in the station in sequence, and the extended differential area formed during this process Zones are all in the action state of the differential criterion, so it is determined that the fault is located...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com