Nonvolatile memory
A non-volatile, memory technology, applied in the field of memory, can solve the problems affecting the performance of resistive memory, etc., and achieve the effect of good rectification effect and high reading discrimination.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
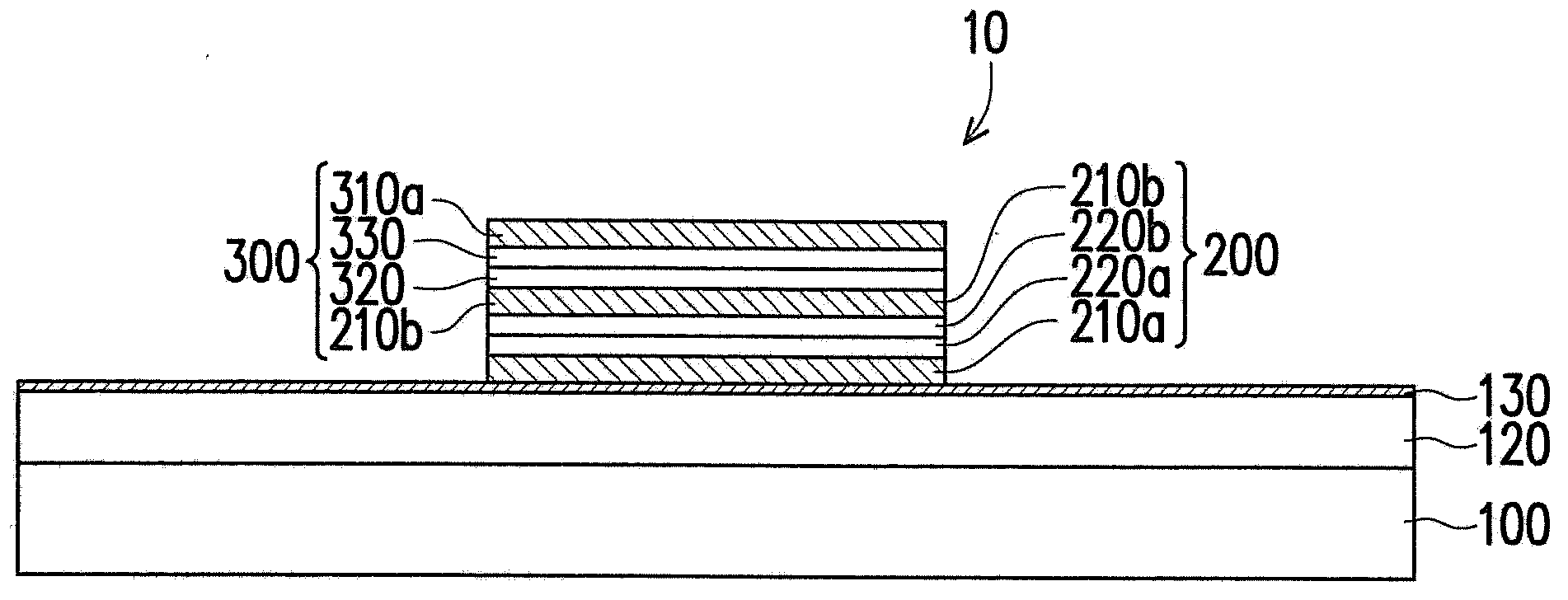
[0039] figure 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the nonvolatile memory according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to figure 1 , the nonvolatile memory 10 includes a unipolar resistive memory unit 200 and a diode unit 300 . The unipolar resistive memory cell 200 is disposed on the substrate 100 . The substrate 100 is, for example, a silicon substrate. In addition, the dielectric layer 120 is disposed between the unipolar resistive memory unit 200 and the substrate 100 . The material of the dielectric layer 120 is, for example, oxide, and its thickness is, for example, between 10 nm and 500 nm. The dielectric layer 120 is used to electrically isolate the unipolar resistive memory cell 200 from the substrate 100 . In addition, the adhesion layer 130 is selectively disposed between the unipolar resistive memory unit 200 and the dielectric layer 120 . The material of the adhesion layer 130 is, for example, titanium, and its thickness is, f...
no. 2 example
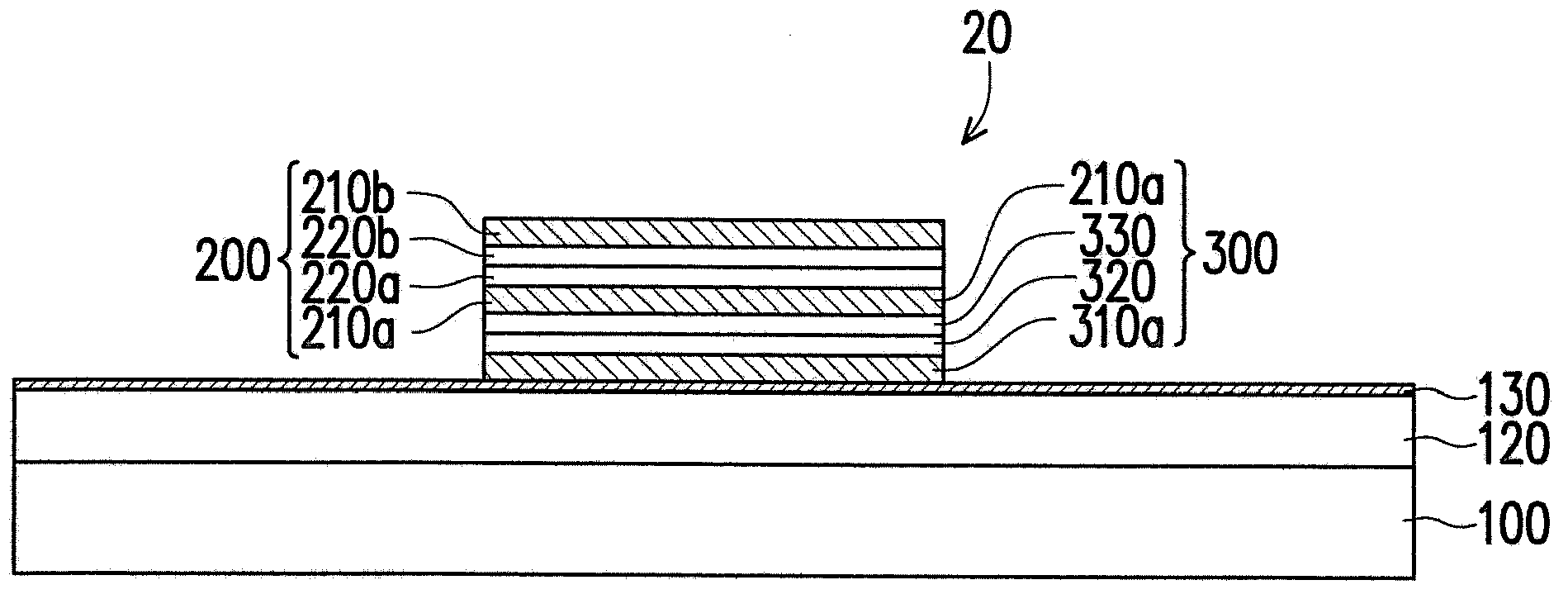
[0046] figure 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the nonvolatile memory according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to figure 2 The difference between the nonvolatile memory 20 and the nonvolatile memory 10 is that in the nonvolatile memory 20, the diode unit 300 is disposed on the adhesion layer 130, while the unipolar resistive memory unit 200 is disposed on the diode unit 300, and both share the electrode 210a.
no. 3 example
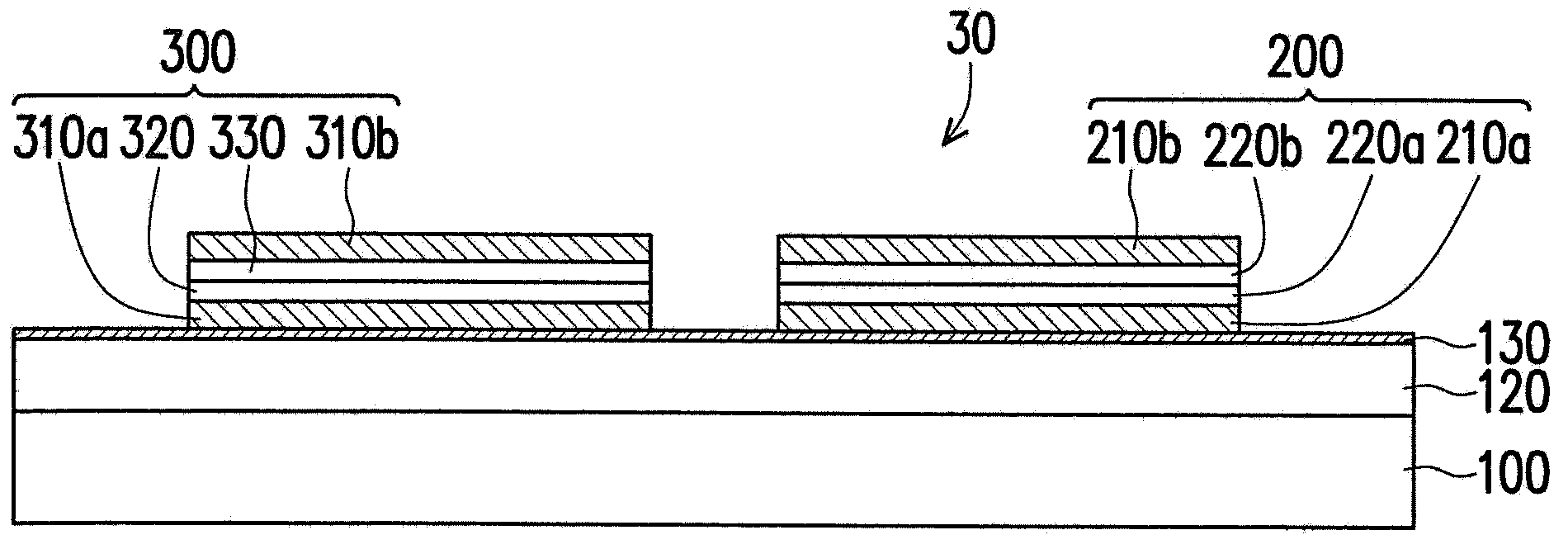
[0048] image 3 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the non-volatile memory according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to image 3, the difference between the nonvolatile memory 30 and the nonvolatile memory 10 is that: in the nonvolatile memory 30, the diode unit 300 and the unipolar resistive memory unit 200 are both arranged on the adhesion layer 130, and the diode unit The 300 and the unipolar resistive memory cell 200 are electrically connected to each other, for example, through interconnection lines (not shown). In this embodiment, the unipolar resistive memory cell 200 and the diode unit 300 each have a pair of electrodes, that is, the unipolar resistive memory cell 200 has an electrode 210a and an electrode 210b, and the diode unit 300 has an electrode 310a and an electrode 310b . In the unipolar resistive memory cell 200 , the electrode 210 a , the transition layer 220 a , the transition layer 220 b and the electrode 210 b are sequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com