Low-resistance BaM<II><x>Bi<1-x>O3 negative-temperature-coefficient thermosensitive thick-film material and preparation method thereof
A bamiixbi1-xo3, negative temperature coefficient technology, applied in the field of electronic information functional materials, can solve the problems of reducing the room temperature resistivity of thick films, low thermal constants, and high room temperature resistivity, and achieve great practicability and promotion prospects. Synthetic system Single, low room temperature resistivity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
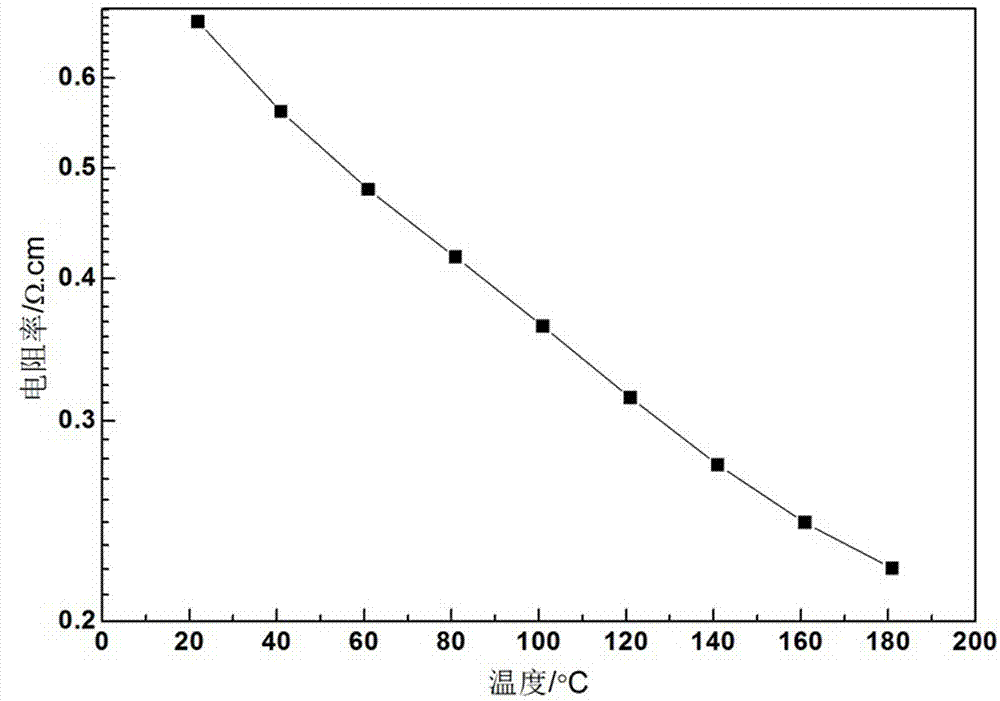
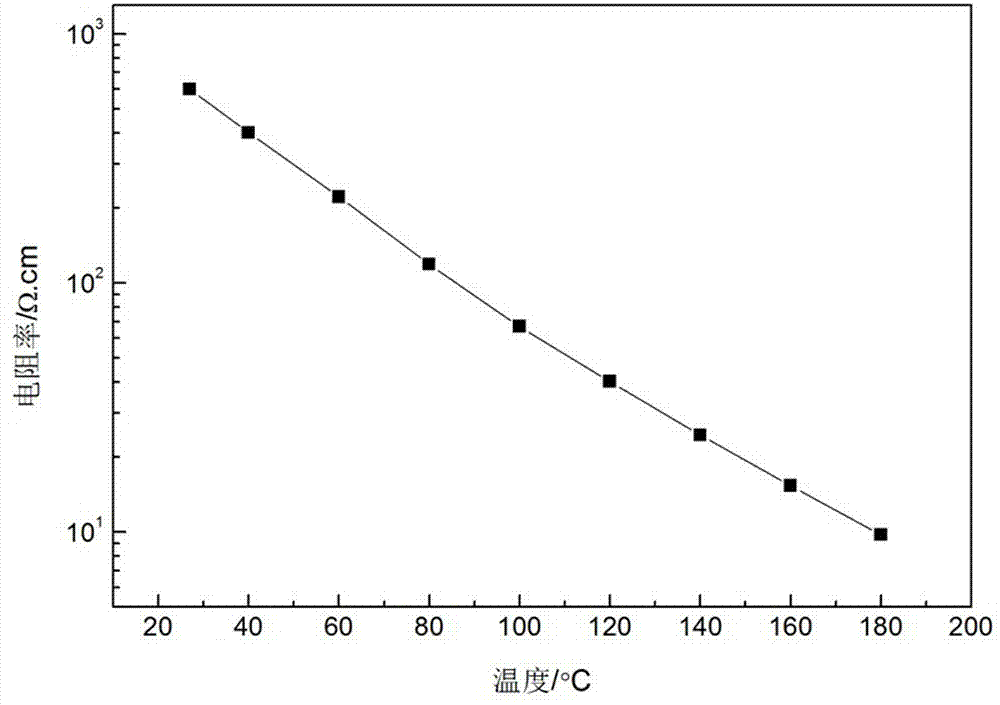
[0023] A low-resistance negative temperature coefficient heat-sensitive thick film material, its composition formula is: BaCo II 0.02 Bi 0.98 o 3 .
[0024] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0025] (1) Synthesis of BaCo II 0.02 Bi 0.98 o 3 Heat-sensitive phase powder: press BaCo first II 0.02 Bi 0.98 o 3 Stoichiometric ratio as BaCO 3 :Co II O: Bi 2 o 3 =1:0.02:0.49 molar ratio mixing;
[0026] (2) Ball milling, sieving, drying, and heat preservation at 700°C for 6 hours for pre-sintering synthesis, and the obtained pre-sintered powder was subjected to secondary ball milling, sieving and drying to obtain BaCo II 0.02 Bi 0.98 o 3 Thermosensitive phase powder;
[0027] (3) Preparation of thick film resistor paste: the BaCo obtained in step (2) II 0.02 Bi 0.98 o 3 The heat-sensitive phase powder and the organic carrier are mixed uniformly at a mass ratio of 74:26 to form a heat-sensitive thick film resistor slurry; the composition raw...
Embodiment 2
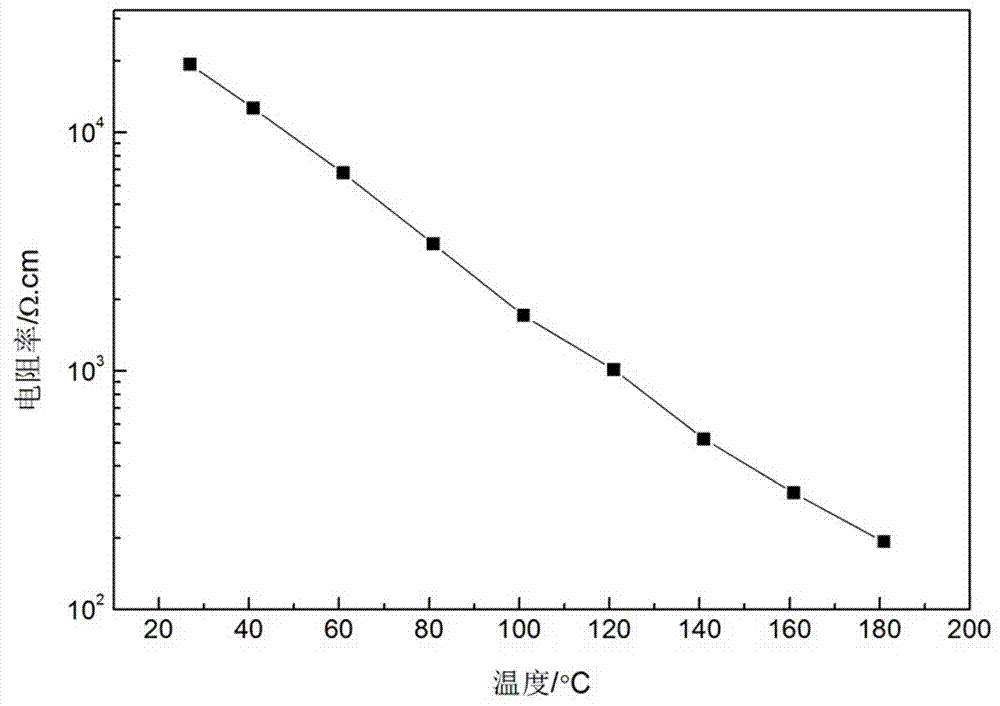
[0033] A low-resistance negative temperature coefficient heat-sensitive thick film material, its composition formula is: BaCo II 0.01 Bi 0.99 o 3 .
[0034] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0035] (1) Synthesis of BaCo II 0.01 Bi 0.99 o 3 Heat-sensitive phase powder: press BaCo first II 0.01 Bi 0.99 o 3 Stoichiometric ratio as BaCO 3 :Co II O: Bi 2 o 3 =1:0.01:0.495 molar ratio mixing;
[0036] (2) Ball milling, sieving, drying, and heat preservation at 700°C for 6 hours for pre-sintering synthesis, and the obtained pre-sintered powder was subjected to secondary ball milling, sieving and drying to obtain BaCo II 0.01 Bi 0.99 o 3 Thermosensitive phase powder;
[0037] (3) Preparation of thick film resistor paste: the BaCo obtained in step (2) II 0.01 Bi 0.99 o 3 The heat-sensitive phase powder and the organic carrier are mixed uniformly at a mass ratio of 74:26 to form a heat-sensitive thick film resistor slurry; the composition raw ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A low-resistance negative temperature coefficient heat-sensitive thick film material, its composition formula is: BaCo II 0.05 Bi 0.95 o 3 .
[0044] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0045] (1) Synthesis of BaCo II 0.05 Bi 0.95 o 3 Heat-sensitive phase powder: press BaCo first II 0.05 Bi 0.95 o 3 Stoichiometric ratio as BaCO 3 :Co II O: Bi 2 o 3 =1:0.05:0.475 molar ratio mixing;
[0046] (2) Ball milling, sieving, drying, and heat preservation at 700°C for 6 hours for pre-sintering synthesis, and the obtained pre-sintered powder was subjected to secondary ball milling, sieving and drying to obtain BaCo II 0.05 Bi 0.95 o 3 Thermosensitive phase powder;
[0047] (3) Preparation of thick film resistor paste: the BaCo obtained in step (2) II 0.05 Bi 0.95 o 3 The heat-sensitive phase powder and the organic carrier are mixed uniformly at a mass ratio of 74:26 to form a heat-sensitive thick film resistor slurry; the composition ra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com