Production method of biodegradable polymer support
A technology for degrading polymers and polymer materials, applied in the field of preparation of biodegradable polymer stents, can solve the problems of inability to slow down the physical aging of materials, the stent is prone to fracture, and the technical advantages are not obvious, and achieves improved strength and toughness, It is not easy to break, and the effect of reducing the breakage phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] The present invention generally provides a method for preparing a biodegradable polymer scaffold, comprising the following steps:
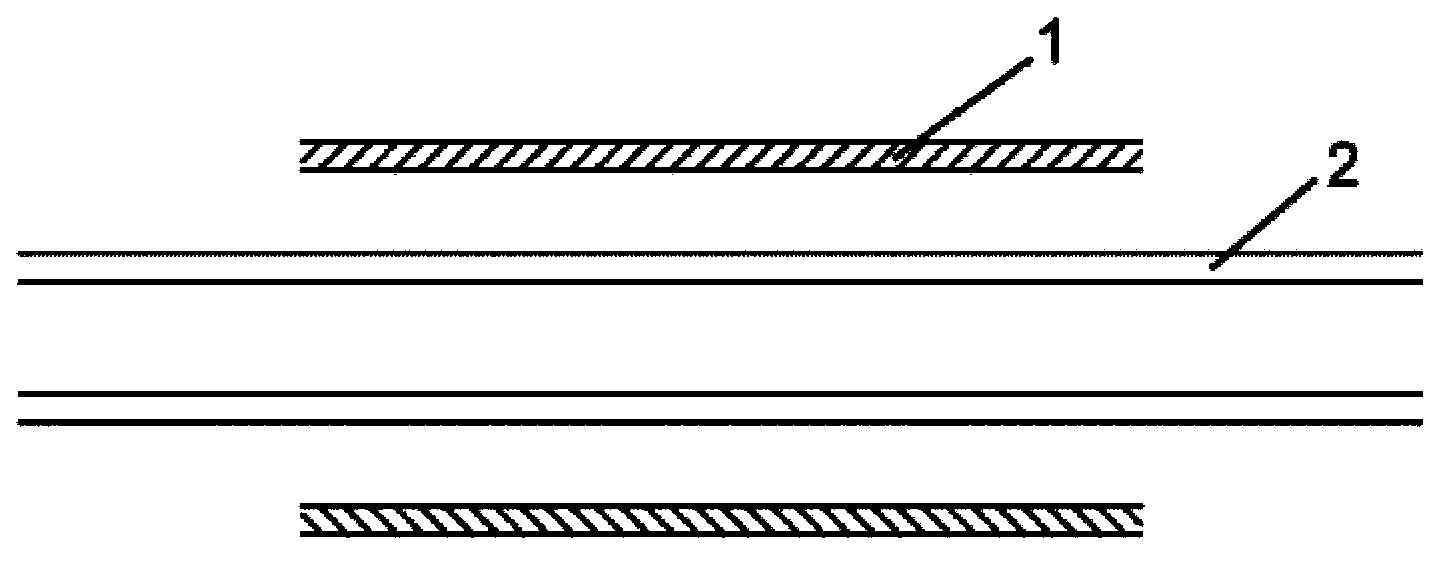
[0044] Step 1): preparing the biodegradable polymer original pipe 2 from the biodegradable polymer material;
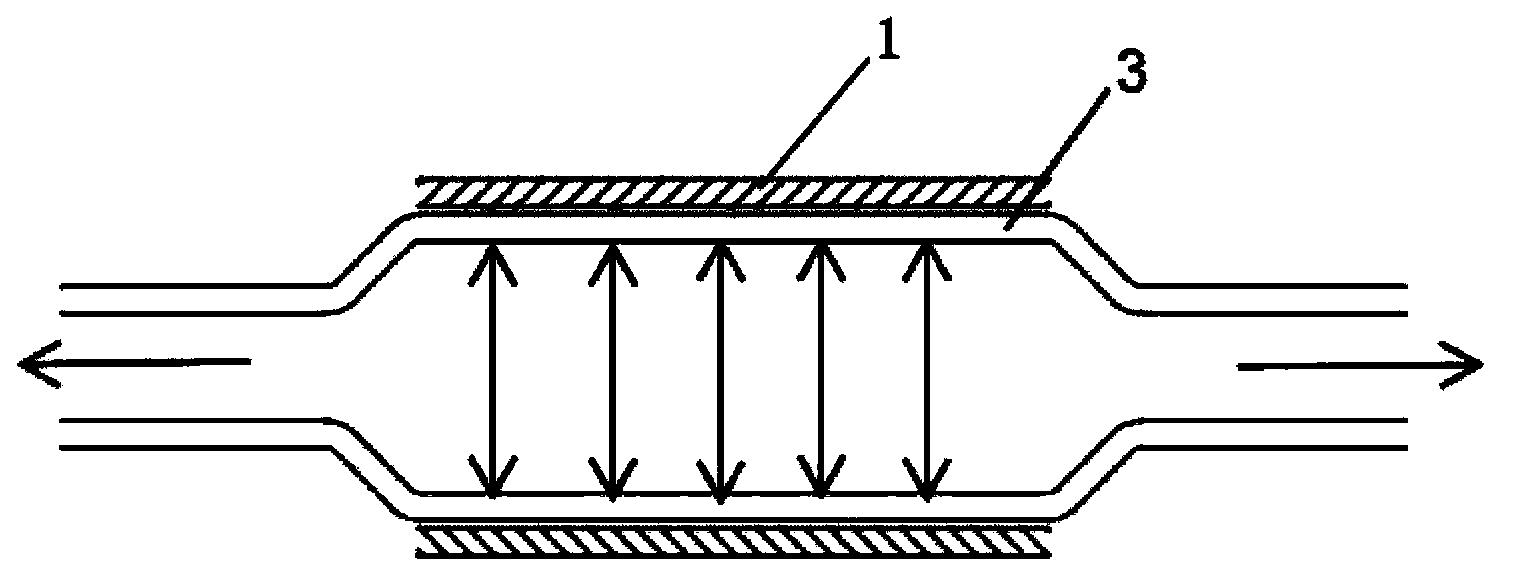
[0045] Step 2): Put the original pipe material 2 prepared in the step 1) into the tubular mold 1 (such as figure 1 As shown, the original pipe material 2 is inserted into the inner hole of the tubular mold 1), the original pipe material 2 is heated, and high-pressure gas is injected into the original pipe material 2 to move along the radial direction of the original pipe material 2 Inflate the original pipe material 2 so that the outer diameter of the pipe material 3 after inflation is equal to the inner diameter of the tubular mold 1 (such as figure 2 shown), so that the tube can be highly oriented in the radial direction; and, the tube can be axially stretched along the axial direction of the tube before blowing the tube along ...
example 1
[0064] The polymer material of the original tubing 2 selected in this example is polylactic acid, a biodegradable polymer material. The polylactic acid particles were extruded to obtain a raw pipe 2 with an outer diameter of 1.5 mm and a wall thickness of 0.5 mm. Put this original pipe 2 into a stainless steel tubular mold 1 with an internal diameter of 2.5mm, such as figure 1 shown in . One end of the polylactic acid original pipe material 2 is closed, and the other end is connected with a high-pressure gas circuit. First, heat the original pipe 2 and the tubular mold 1 to raise the temperature to 120°C, then fill the original pipe 2 with high-pressure nitrogen at a pressure of 200 psi (pounds per square inch), and at the same time carry out axial Stretch, the stretching distance is 40mm. The original pipe 2 is prepared under the conditions of high temperature, high pressure and stretching into a pipe with an outer diameter of 2.5 mm and a wall thickness of 0.15 mm, that i...
example 2
[0069] The polymer material of the original pipe 2 selected in this example is polylactic-polyglycolic acid copolymer (PLGA), a biodegradable polymer material, with a copolymerization ratio of 85:15. The copolymerized particles were injection-molded to obtain an original pipe material 2 with an outer diameter of 1.2 mm and a wall thickness of 0.3 mm. This raw pipe material 2 was put into a stainless steel tubular mold 1 with an inner diameter of 2.5 mm. One end of the PLGA original pipe 2 is closed, and the other end is connected with a high-pressure gas circuit. First, the original pipe 2 and the tubular mold 1 are heated to 80° C., and then the original pipe 2 is filled with high-pressure helium at a pressure of 400 psi. The original pipe 2 was prepared under high temperature and high pressure conditions into a pipe with an outer diameter of 2.5 mm and a wall thickness of 0.15 mm. Afterwards, the entire system is rapidly cooled to 20° C., and then the pressure is released,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com