Method of degrading dye wastewater by iron-based amorphous alloy/hydrogen peroxide Fenton-like system
An iron-based amorphous alloy and hydrogen peroxide technology, which is applied in water/sewage treatment, reduced water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of single pollutant composition and low pollutant removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
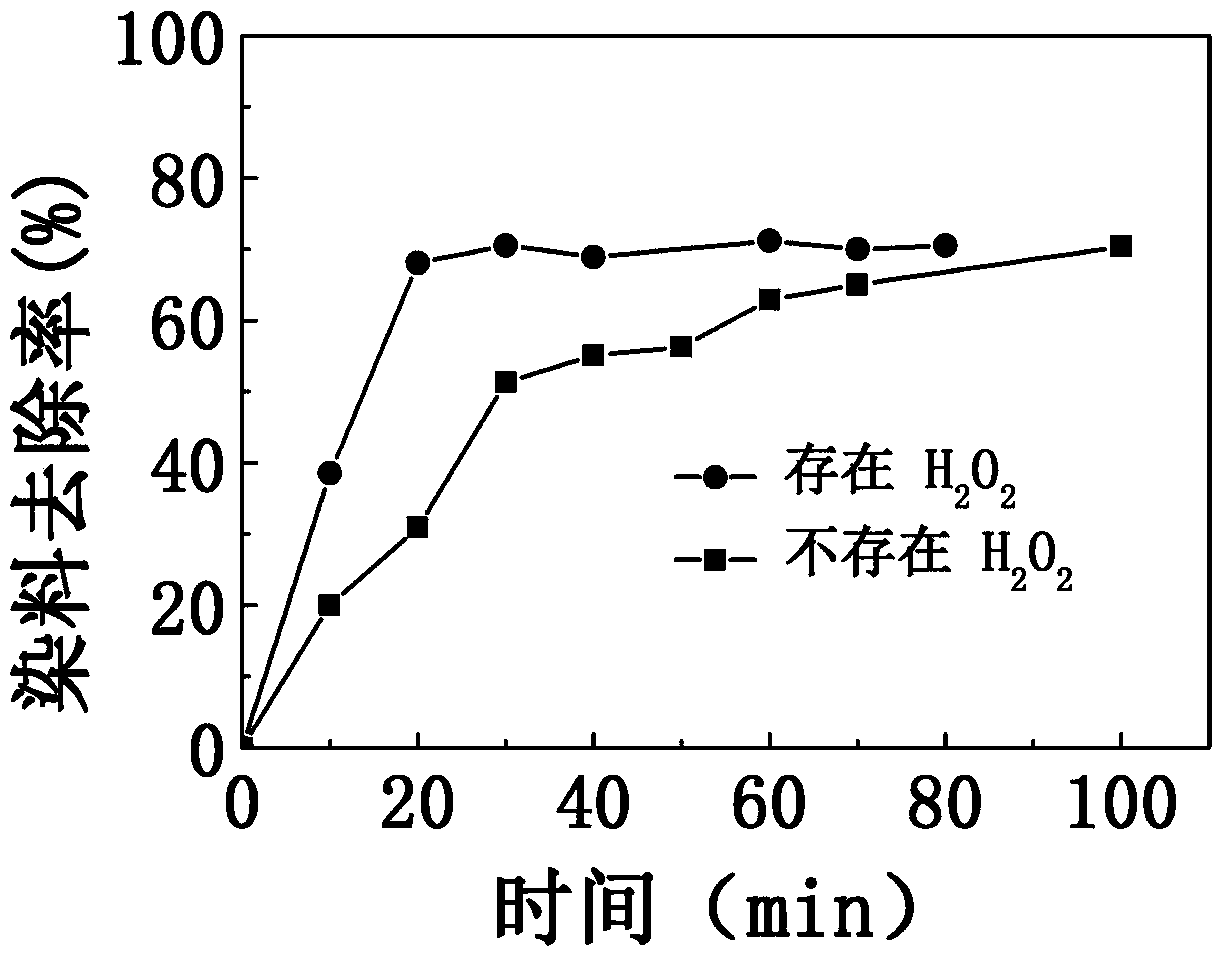
[0020] At 25°C, to an initial concentration of 10mg·L -1 100g of methylene blue dye solution was added with 1g of iron-based amorphous alloy strip slices and H 2 o 2 The mass fraction is 30% hydrogen peroxide, and then magnetically stirred for 80 minutes at a stirring rate of 200 rpm. The mass ratio of methylene blue dye solution to iron-based amorphous alloy slices is 100:1; after adding hydrogen peroxide, H 2 o 2 The molar concentration in the dye solution mixture is 10mmol L -1 . The change of the dye removal rate in the dye solution with time is as follows: figure 1 The circular data points in the middle are shown.
[0021] The chemical composition molecular formula of the iron-based amorphous alloy strip slice used in this embodiment is Fe 78 Si 9 B 13 , the slice width was 4 mm, the thickness was 40 μm, and the length was 10 mm.
Embodiment 2
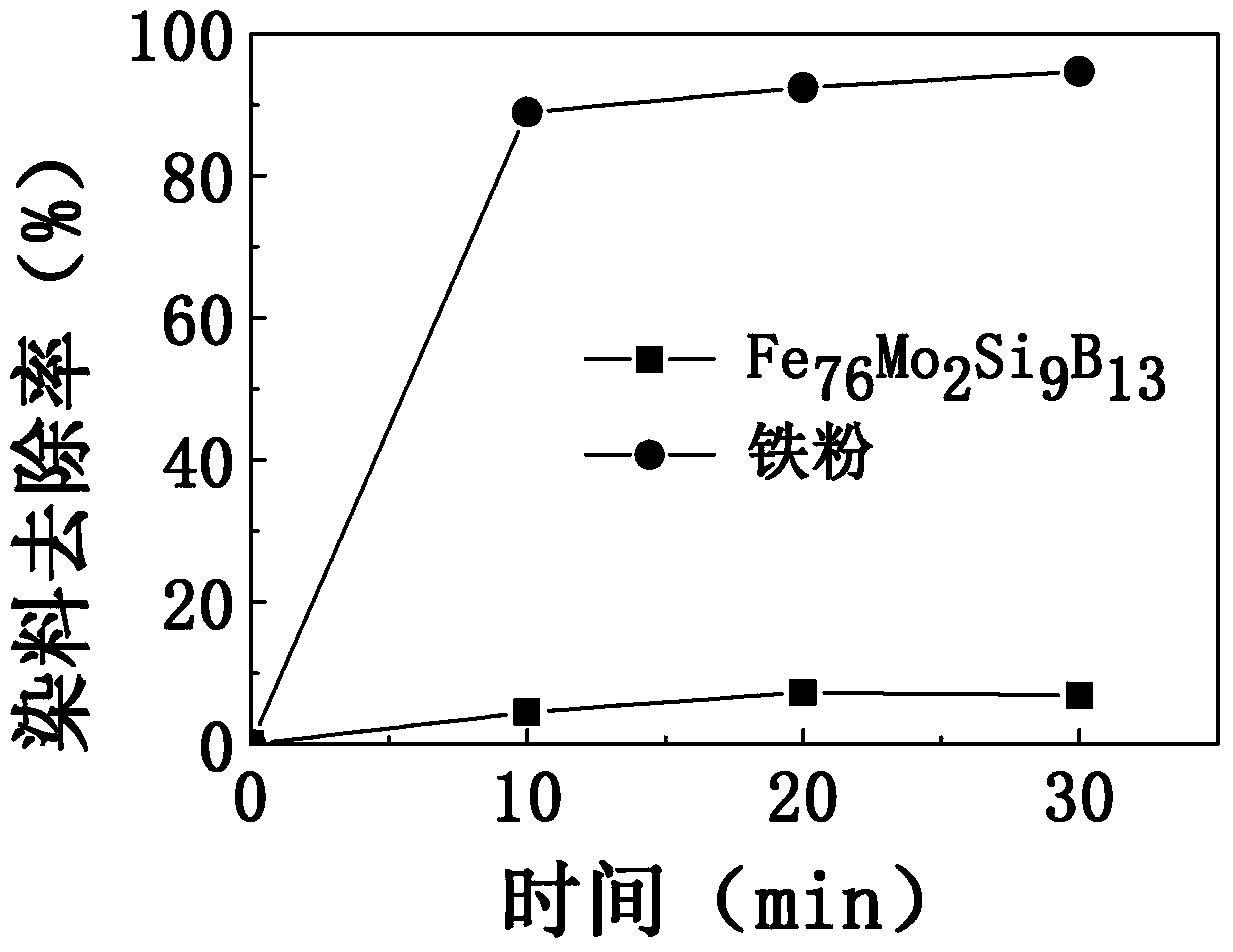
[0027] At 25°C, to an initial concentration of 10mg·L -1 100g of the methylene blue dye solution was added with 1g of iron-based amorphous alloy strip slices and 30% hydrogen peroxide, and then magnetically stirred for 30 minutes at a stirring rate of 200rpm. The mass ratio of dye solution to iron-based amorphous alloy slices is 100:1; after adding hydrogen peroxide, H 2 o 2 The molar concentration in the dye solution mixture is 10mmol L -1 . The change of the dye removal rate in the dye solution with time is as follows: figure 2 The data points in the middle triangle are shown.
[0028] The chemical composition molecular formula of the iron-based amorphous alloy strip slice used in this embodiment is Fe 76 Mo 2 Si 9 B 13 , the slice width was 4 mm, the thickness was 40 μm, and the length was 10 mm.
Embodiment 3
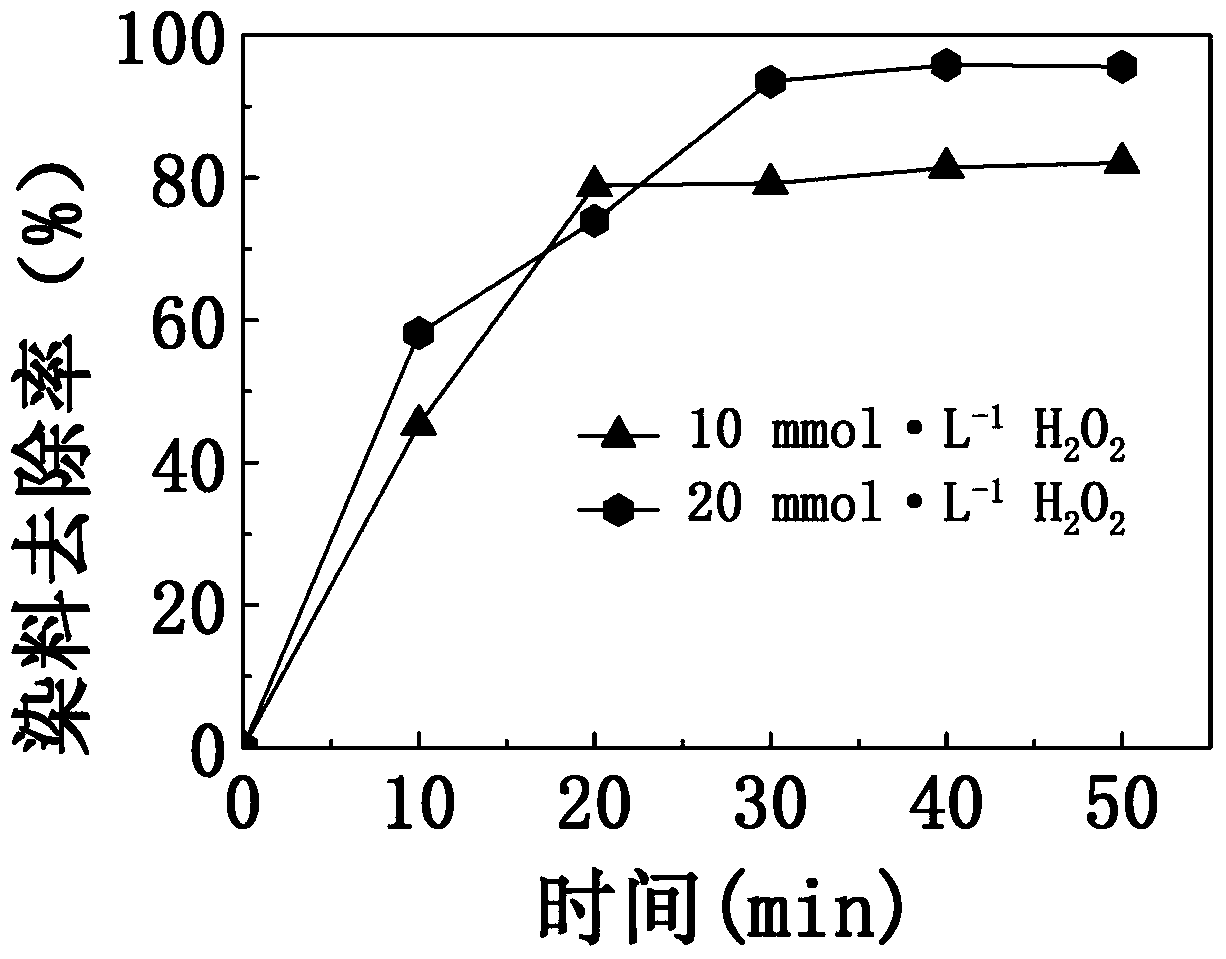
[0033] At 25°C, to an initial concentration of 10mg·L -1 100g of the methylene blue dye solution was added with 1g of iron-based amorphous alloy strip slices and 30% hydrogen peroxide, and then magnetically stirred for 50 minutes at a stirring rate of 200rpm. The mass ratio of dye solution to iron-based amorphous alloy slices is 100:1; after adding hydrogen peroxide, H 2 o 2 The molar concentration in the dye solution mixture is 10mmol L -1 . The change of the dye removal rate in the dye solution with time is as follows: image 3 The data points in the middle triangle are shown.
[0034] The chemical composition molecular formula of the iron-based amorphous alloy strip slice used in this embodiment is Fe 75 Mo 3 Si 9 B 13 , the slice width was 4 mm, the thickness was 40 μm, and the length was 10 mm.
[0035] Such as image 3As shown, the dye removal rate reached 80% after 50 minutes of reaction.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com