Dynamic cooperative coverage method among base stations
A technology between base stations and base stations, which is applied in the field of dynamic cooperative coverage between base stations, can solve the problems of not considering the number of users, the random time-varying characteristics of user positions, and the difficult energy-saving communication mode, and achieve the effect of less power increase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
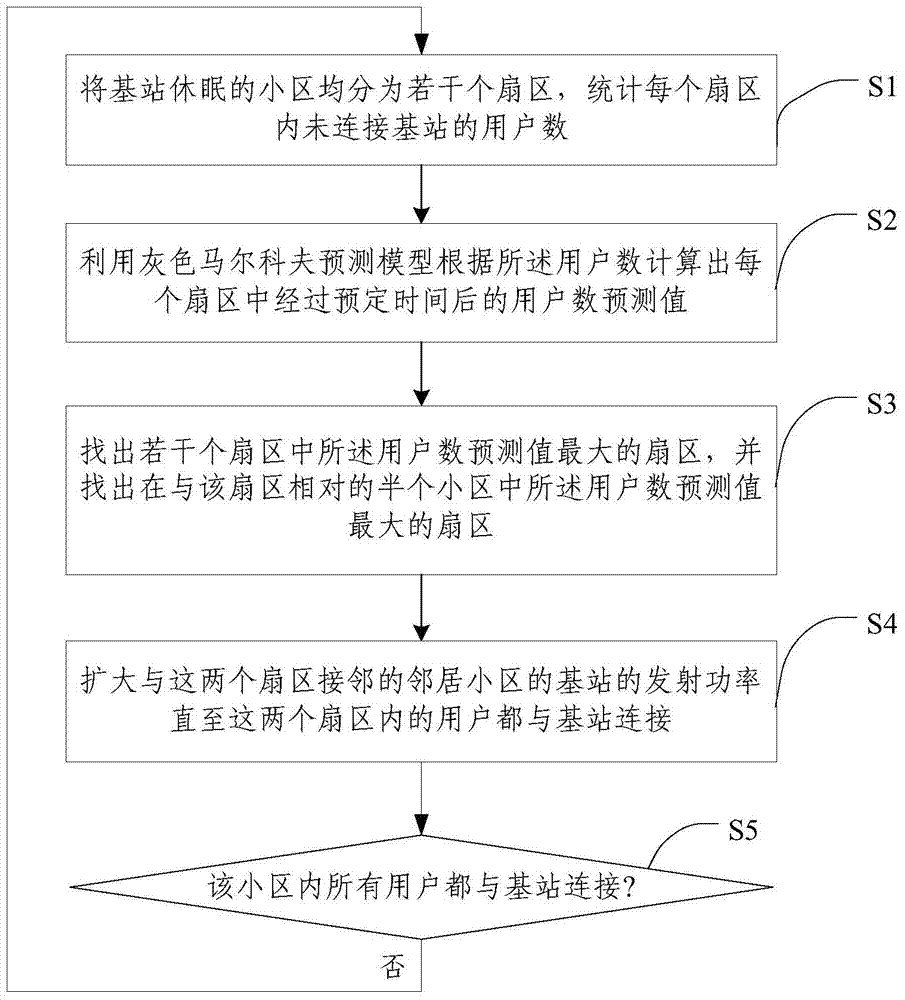
[0049] The embodiment of the present invention proposes a dynamic coordinated coverage method between base stations, see figure 1 , the method includes:
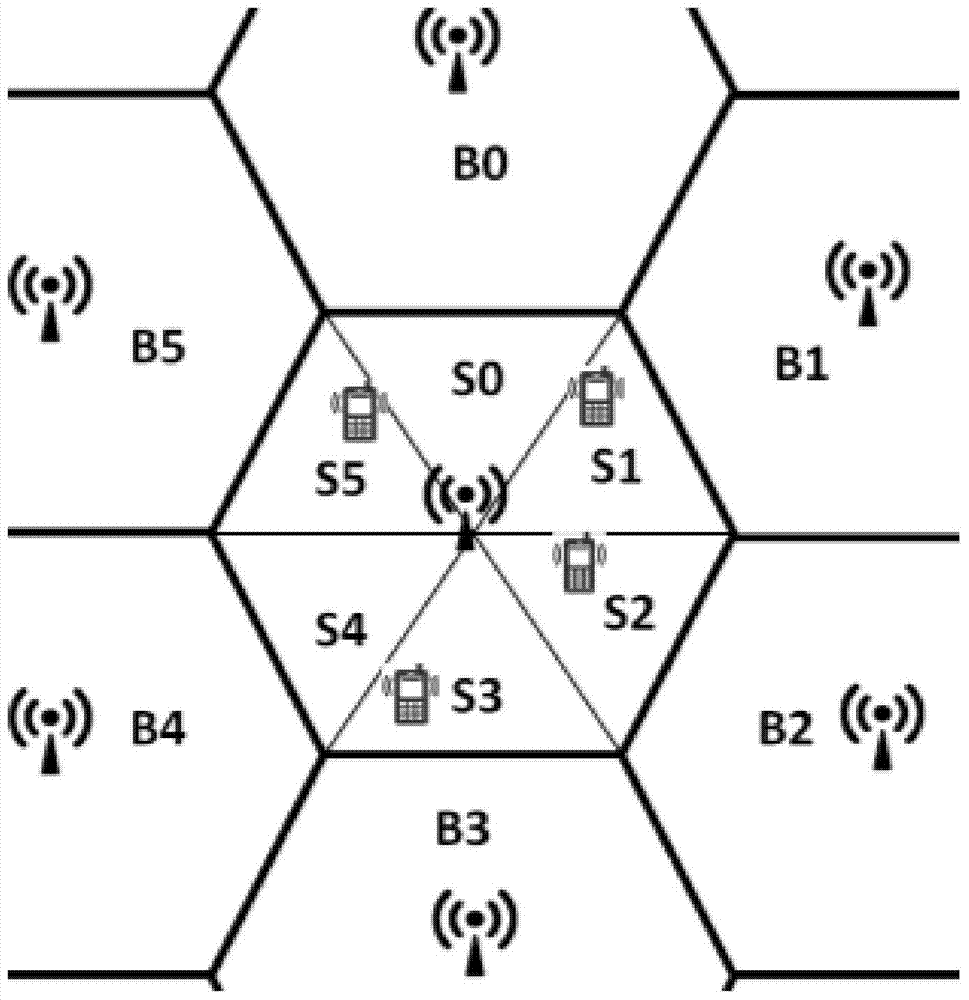
[0050] Step S1: divide the dormant cell of the base station into several sectors, and count the number of users not connected to the base station in each sector;
[0051] Step S2: Using the gray Markov prediction model to calculate the predicted value of the number of users in each sector after a predetermined period of time according to the number of users not connected to the base station;
[0052] Step S3: Find the sector with the largest predicted value of the number of users among several sectors, and find the sector with the largest predicted value of the number of users in the half of the cell opposite to the sector;
[0053] Step S4: Enlarging the transmit power of the base stations of the neighboring cells adjacent to the two sectors until all users in the two sectors are connected to the base station;
[0054] St...
Embodiment 2
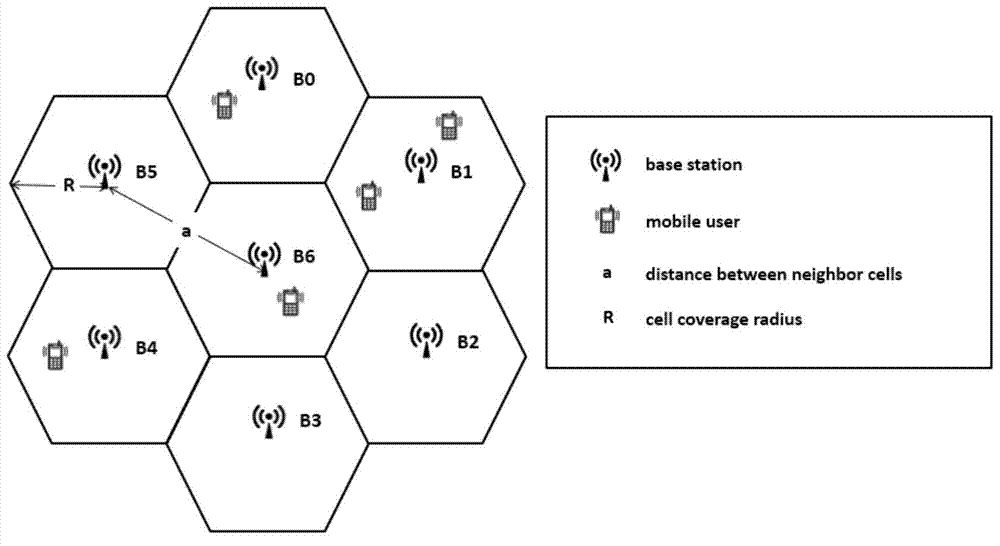
[0061] The embodiment of the present invention proposes a method for dynamic coordinated coverage between base stations in a cellular network, see figure 2 , consider that in a cellular network, a cell and 6 adjacent cells together form a management domain, and a base station (base station) is set in the center of each cell, mobile users (mobile users) are randomly distributed, and the distance between base stations (distance between neighbor cells) is a, and the coverage radius (cell coverage radius) of each base station is R.
[0062] The energy consumption of the base station is mainly composed of two parts, the signal transmission power consumption and the basic operation power consumption of the base station. The basic operating power consumption of the base station includes cooling fan energy consumption, power amplifier energy consumption, core equipment energy consumption, power system loss, signal processing energy consumption, etc. Based on the goal of saving netwo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com