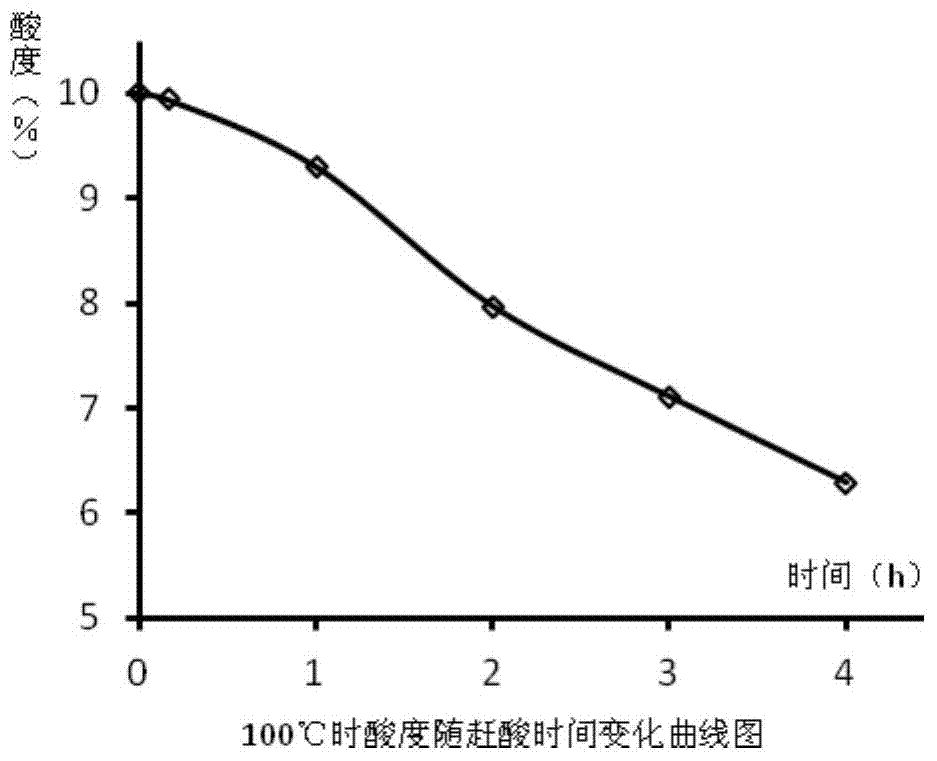
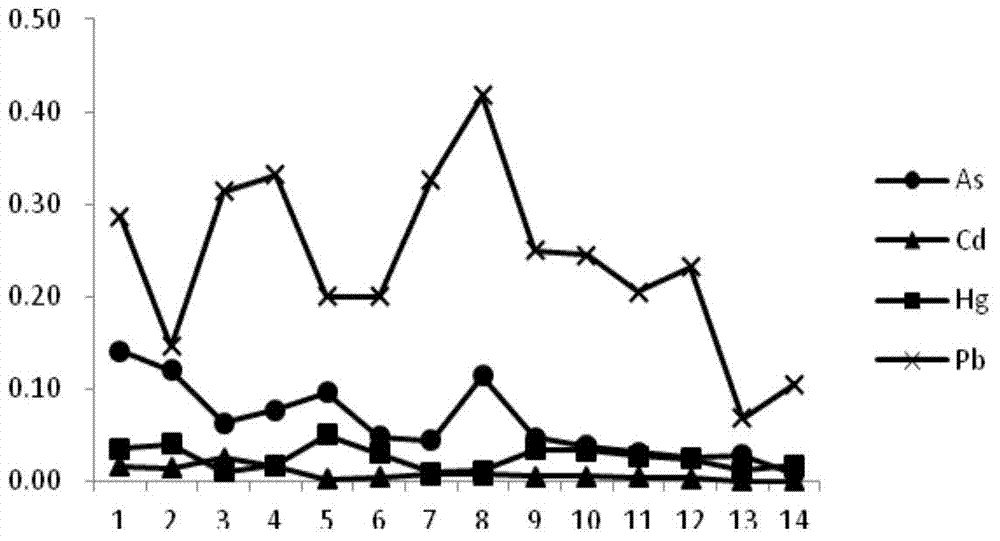
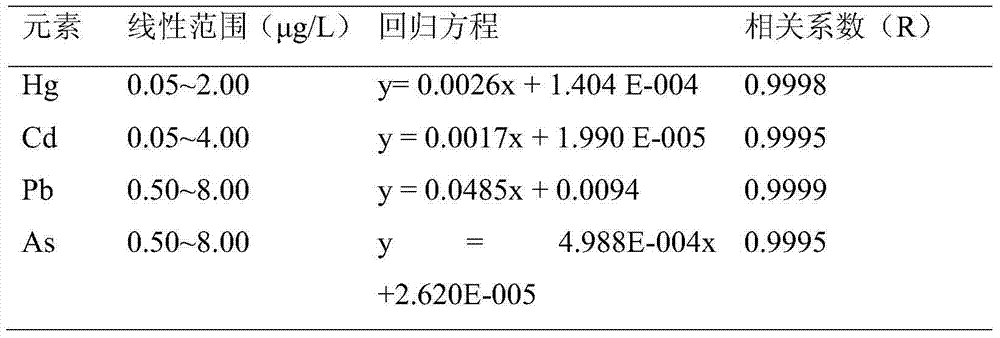
Method for determining traces of mercury, cadmium, lead and arsenic in food by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS)
An ICP-MS, food technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, material analysis by electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of sensitivity, precision, and accuracy that cannot meet the requirements of trace analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] Main instruments and reagents
[0013] American Agilent7700X inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer with ORS 3 Collision cell and HMI sampling system; Beijing Sartorius CP225D electronic balance with a sensitivity of 0.1 mg; Italian Milestone Ethos One microwave digestion instrument with a 41-position polytetrafluoroethylene microwave digestion tank with an inner diameter of 23.7 mm and an outer diameter of 23.7 mm. Diameter 29.8mm, tank height 151mm; Beijing Labtech VB24 type acid catcher, 24 holes, hole diameter 30.8mm, hole depth 60.0mm.
[0014] The analysis water is the first-class water specified in GB / T6682, with a resistivity ≥ 18.2MΩ.cm; nitric acid, high-grade pure; nitric acid solution, measure 100mL of nitric acid, dilute to 1000mL with water, mix well and set aside. Gold solution [GSB04-1715-2004] is 1000mg / L; 10mg / L gold solution, absorb 1mL of 1000mg / L gold solution, dilute to 100mL with 20% hydrochloric acid, mix well and set aside. Argon, liquid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com