Micro-fluidic chip and cell chemotaxis movement research method
A microfluidic chip and cell technology, applied in the field of biomedical research, can solve the problems that do not have the characteristics of the closed space of microvessels, can not be used to study cell biological processes, and cannot reproduce the chemotaxis process of cells in microvessels, etc., to achieve wide application foreground effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The microfluidic chip used was designed and manufactured by our laboratory.
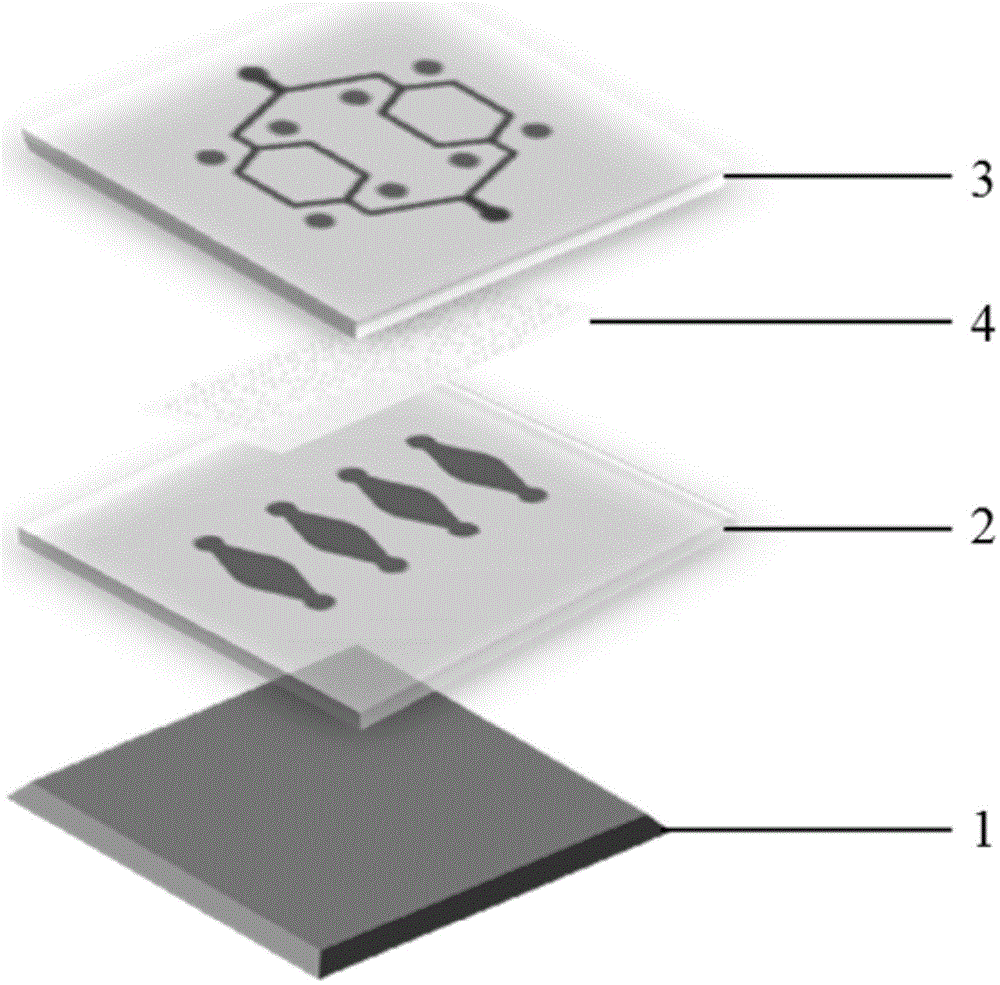
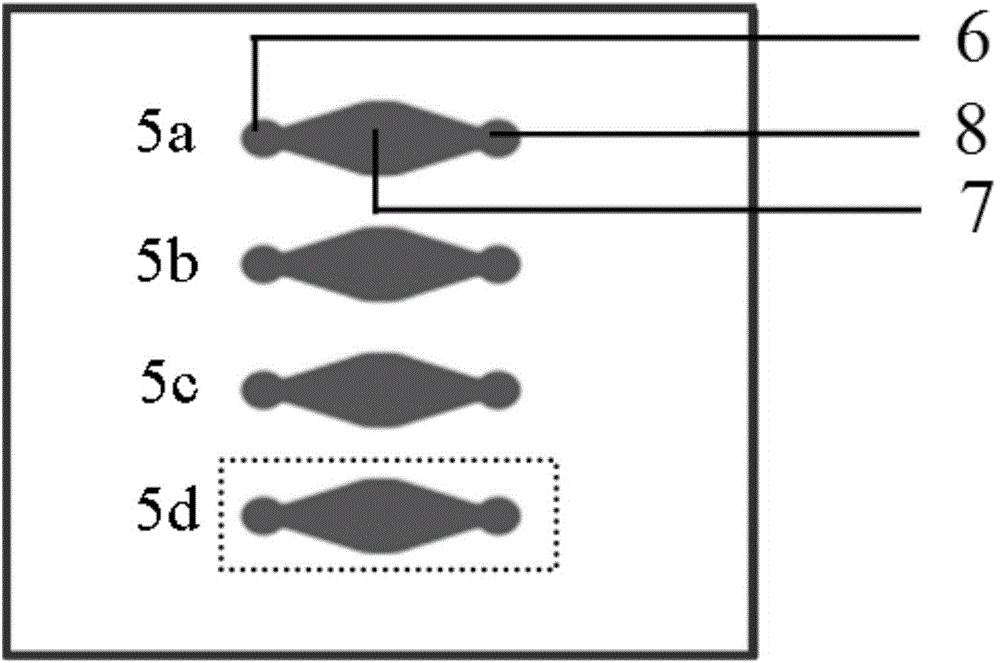
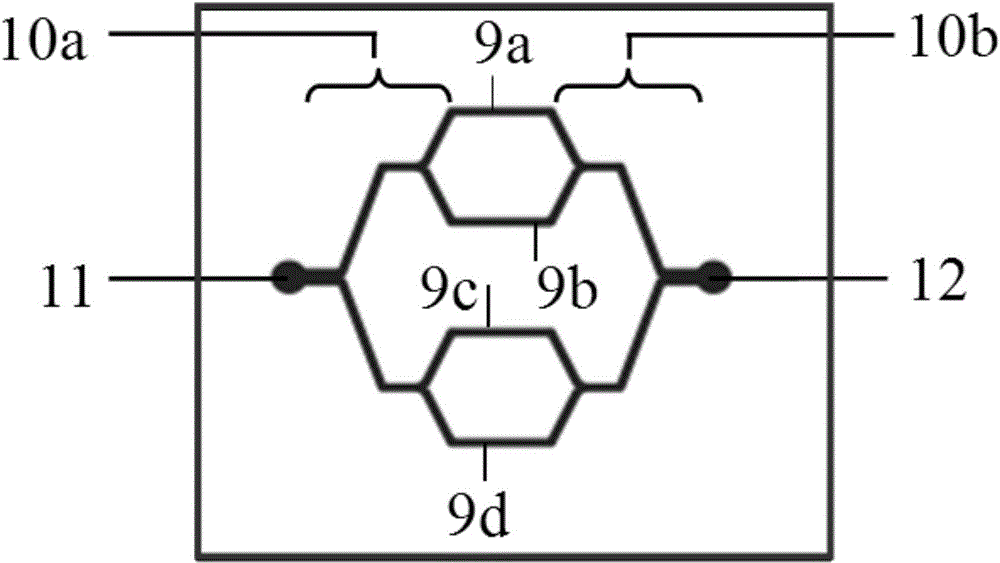
[0029] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, the microfluidic chip of the present invention is composed of a glass substrate 1, a first membrane 2, a second membrane 3 and a porous membrane 4, wherein the material of the first membrane 2 and the second membrane 3 is polydimethylform base siloxane, and the porous membrane 4 is a polycarbonate membrane. There are four parallel and independent culture units (5a, 5b, 5c, 5d) on the first diaphragm 2, and each culture unit (5a, 5b, 5c, 5d) has an independent liquid inlet-6 and liquid outlet respectively Port one 8, a culture pool 7 is arranged between the liquid inlet one 6 and the liquid outlet one 8; there are four parallel microchannels (9a, 9b, 9c, 9d) on the second diaphragm 3, one of the microchannels One side is collected in the liquid inlet 2 11 through a group of branched connection channels 10a on one floor, and the other side is collected in t...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The chip described in Example 1 was used for research: FITC-Dextran (molecular weight is about 12KD) was added into the culture pool 7 through the liquid inlet 6, and as time went on, FITC-Dextran diffused through the porous membrane 4 and vascular endothelial cells into the microchannel of the second diaphragm 3 ( Figure 6 ).
Embodiment 3
[0035]The chip described in Example 1 is used for research: through the liquid inlet 6, add the concentration of 0ng / ml, 25ng / ml, 50ng / ml, and 100ng / ml respectively in the four culture pools 7 of the first membrane 2. Chemokine CXCL12, incubated for 2 hours. Add the red fluorescent probe-labeled tumor cell line (ACC-M) into the microchannel through the liquid inlet 2 11 . Drive the red fluorescent probe-labeled tumor cell line (ACC-M) through the syringe pump 13 connected to the liquid inlet 2 11 to make it flow in the microchannel of the second diaphragm 3, stop after 30 minutes, and use phosphate After gently rinsing with buffer, take pictures under a fluorescent microscope to record the adhesion of ACC-M cells to vascular endothelial cells ( Figure 7 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com