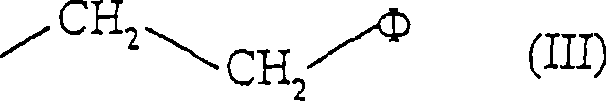Patents
Literature
41 results about "Cell chemotaxis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). [GOC:dph]
Injectable cross-linked polymeric preparations and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050003010A1Promote regenerationFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCross-linkDamages tissue
A composition for promoting repair of damaged tissues, being a cross-linked alginate solution, which can be maintained in liquid form indefinitely (under constant conditions) and only gels in vivo. This cross-linked alginate solution is an ideal material to be used for tissue repair. Injection of said material into cardiac tissue post-myocardial infarct induced tissue regeneration. The invention provides such injectable solution, as well as compositions and method of preparation thereof. The invention also provides various methods and uses of the cross-linked alginate solution, for cardiac tissue regeneration, induction of neo-vascularization, enhancing SDF-1 expression and guiding stem cell chemotaxis, among others. A kit for tissue repair is also provided.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
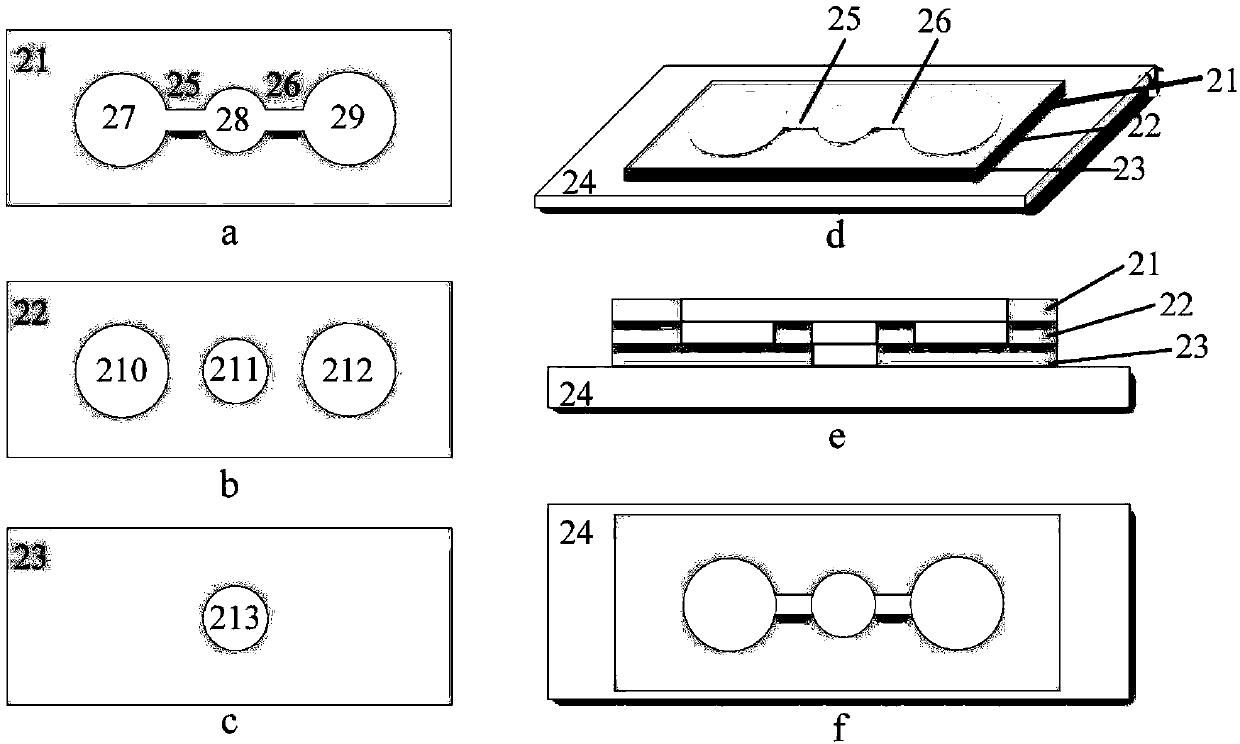
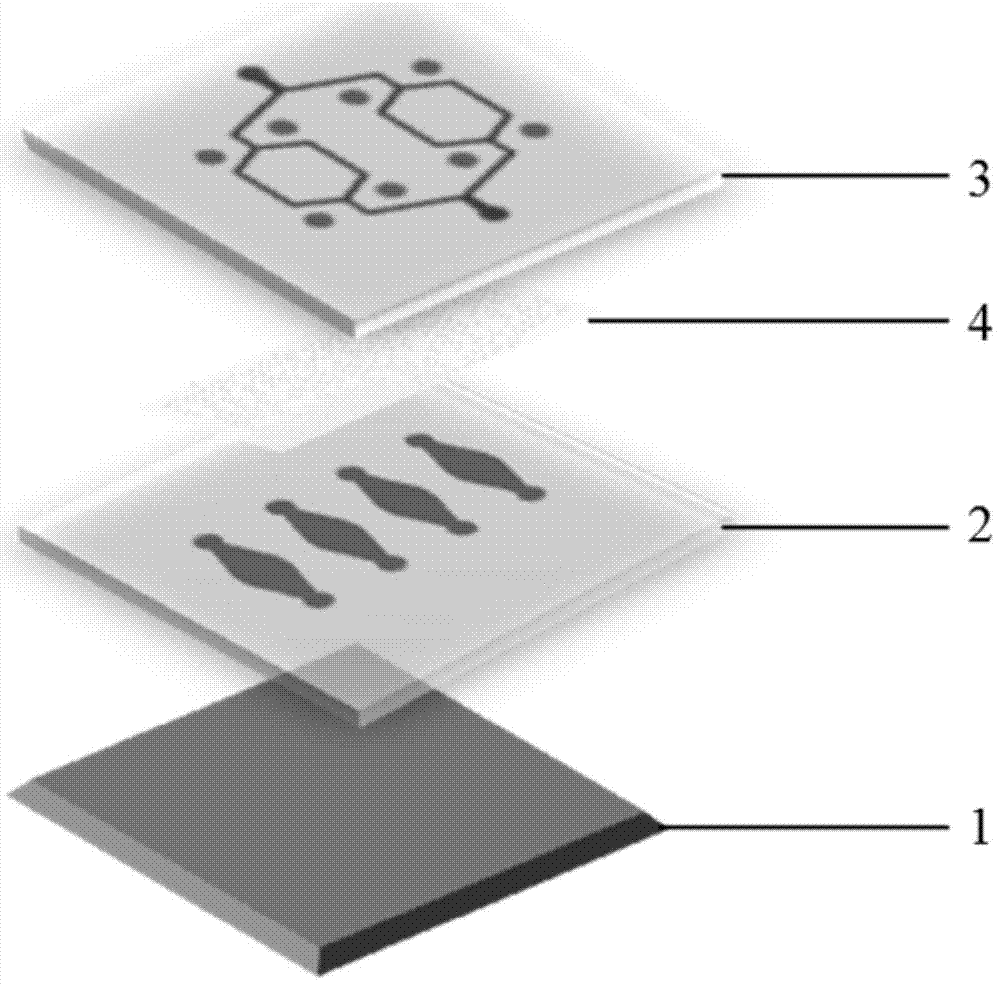
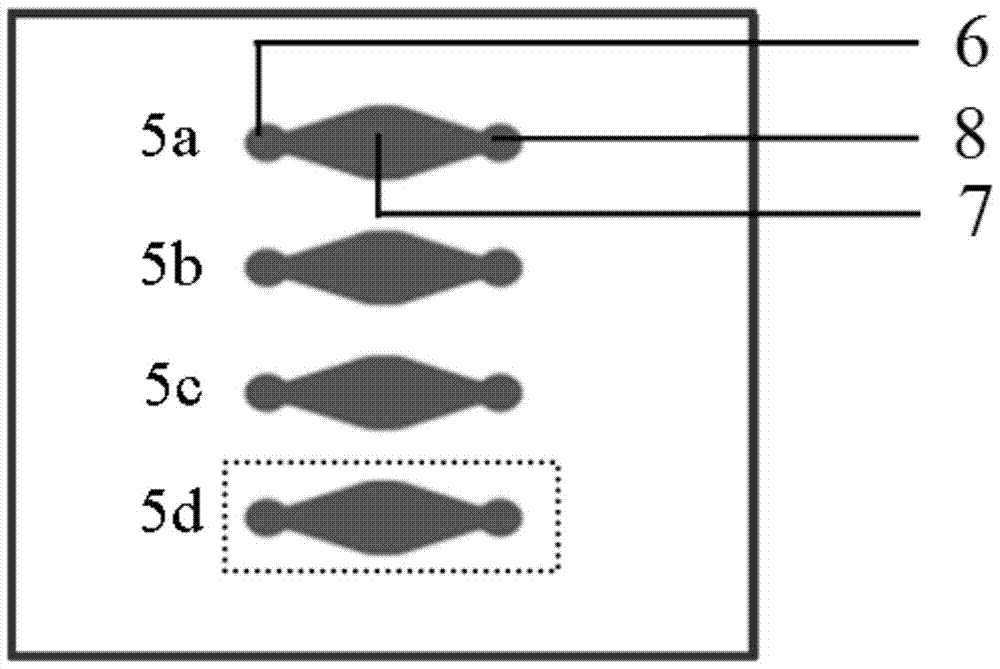
Micro-fluidic chip and cell chemotaxis movement research method
ActiveCN103952300ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiochemical engineeringPorous membrane
The aim of the invention is to provide a micro-fluidic chip and a cell chemotaxis movement research method. The micro-fluidic chip is characterized in that the micro-fluidic chip comprises a glass substrate, a first diaphragm and a second diaphragm; the first diaphragm is provided with culturing units; the second diaphragm is provided with micro-channels; a porous membrane exists between the culturing units of the first diaphragm and the micro-channels of the second diaphragm; the number of the culturing units of the first diaphragm is same to the number of the micro-channels of the second; and the micro-channels on the second diaphragm are respectively located above the culturing units of the first diaphragm. The micro-fluidic chip can be used in the research of the selective chemotaxis movement condition of cells in the micro-channels when the cells flow through the culturing units. The micro-fluidic chip likes a bionic model characterized in that a branching capilary goes through organs; and compared with the traditional cell chemotaxis research methods, the research method is a new method for researching the selective chemotaxis movement of the cells in the flowing process, and has important biomedical research values and economic values.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
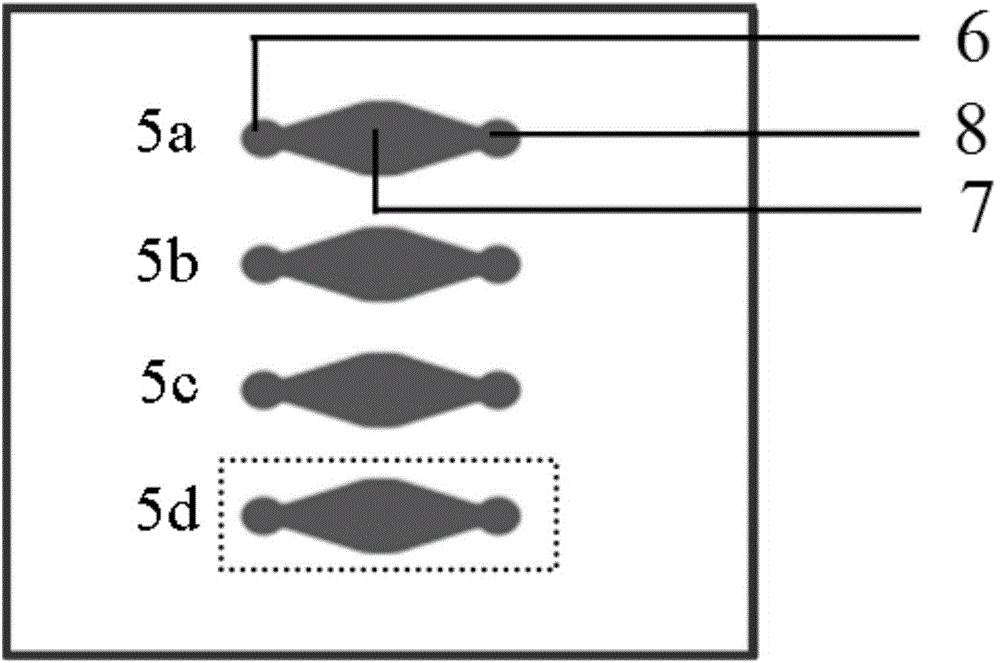
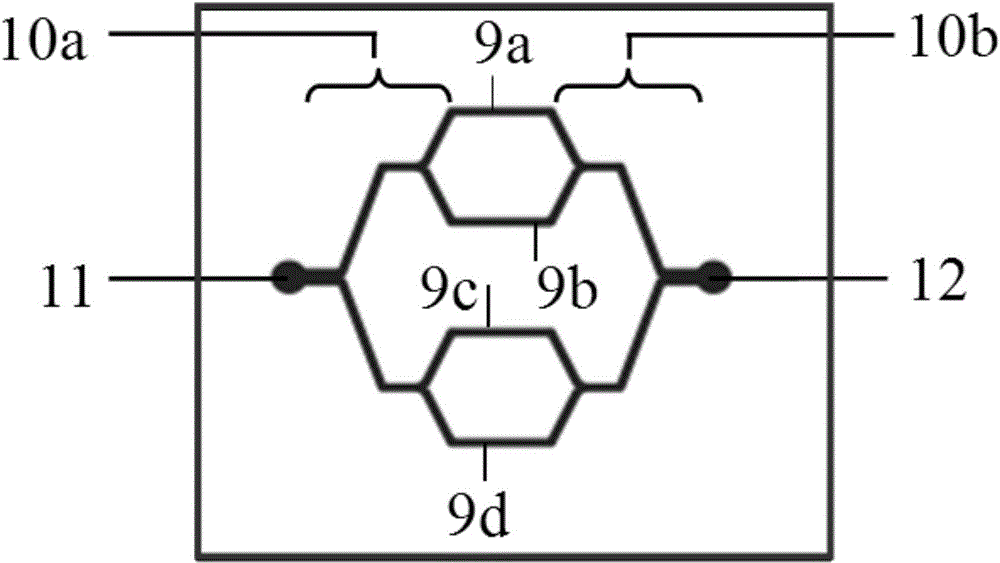
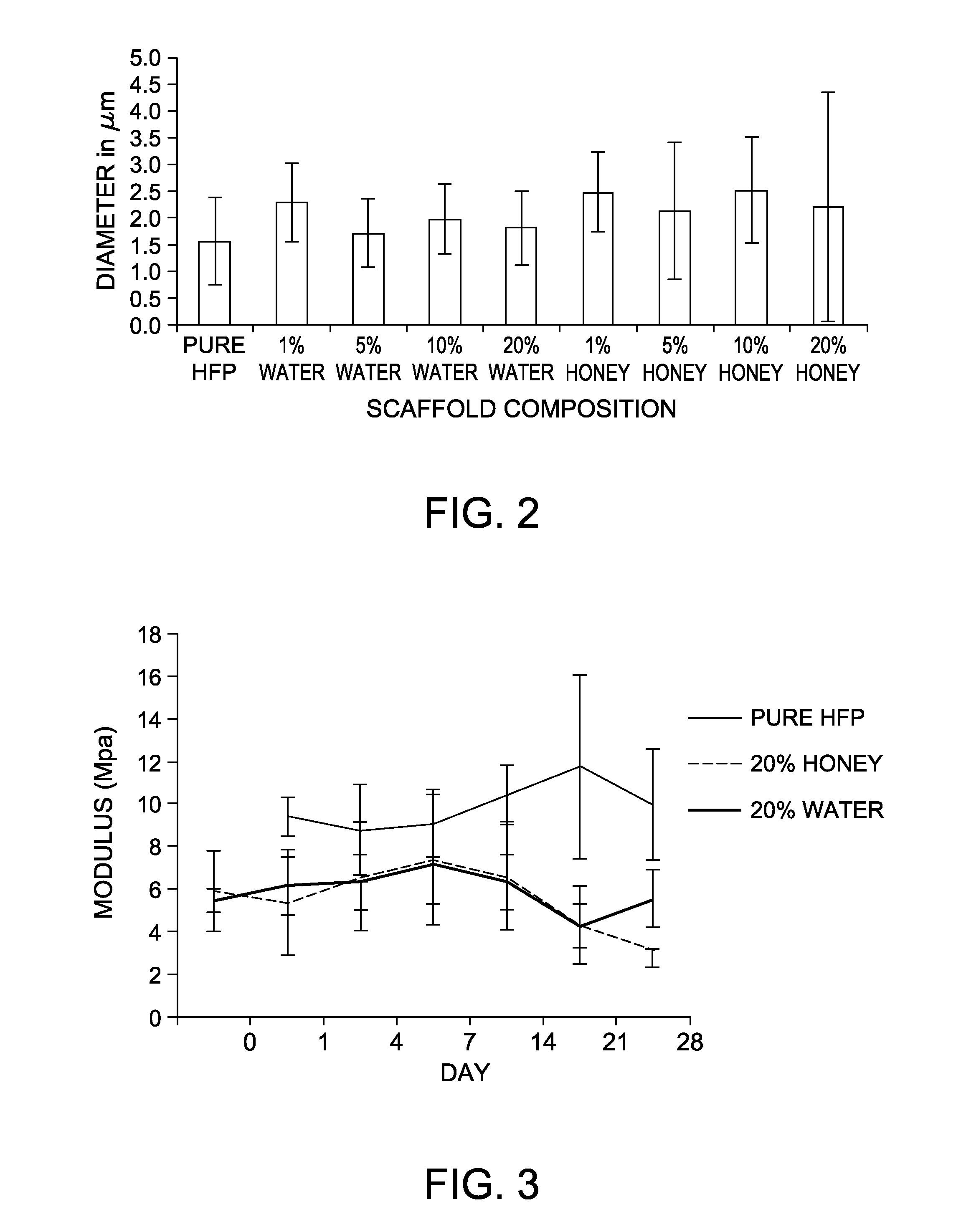
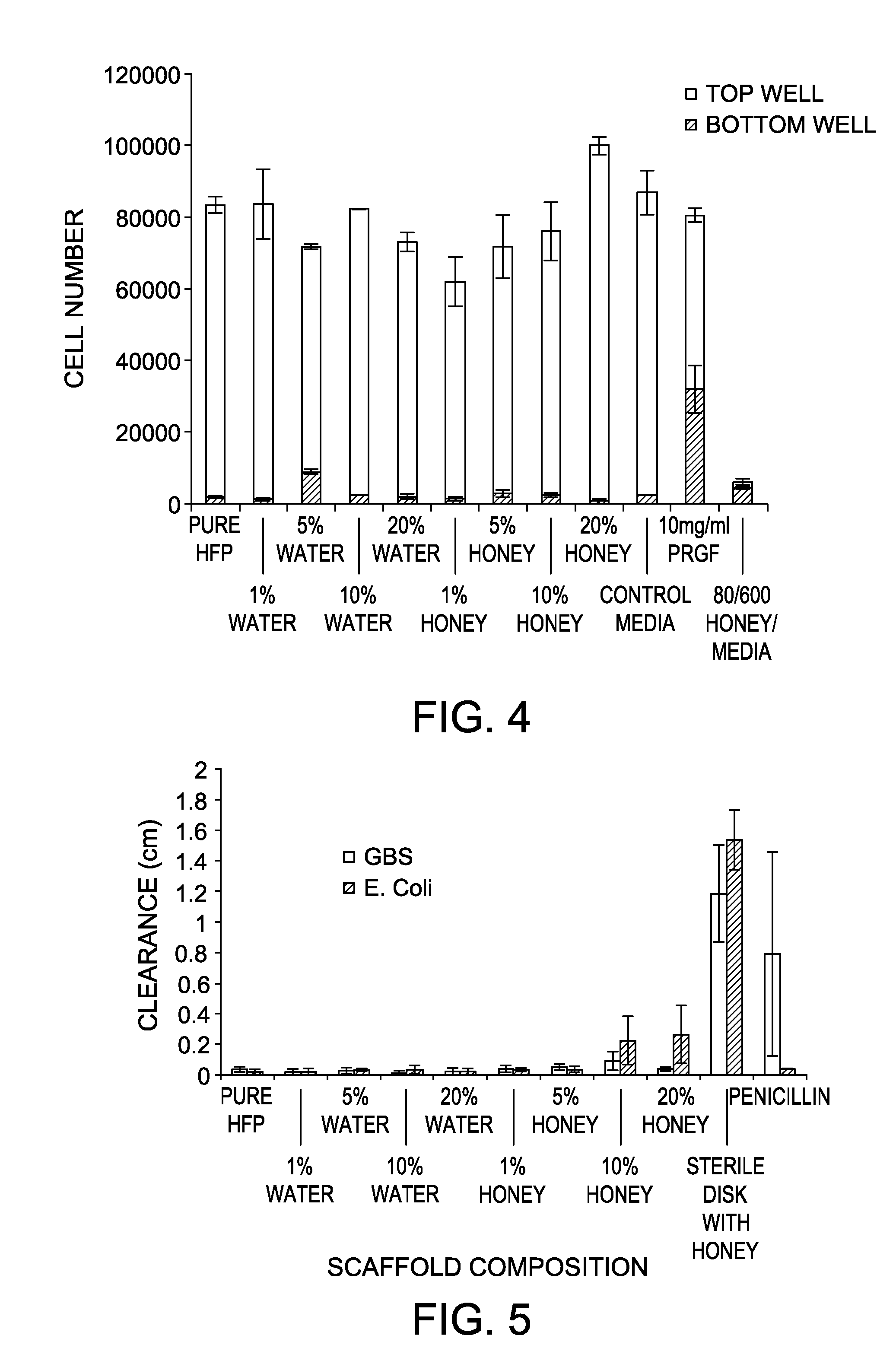
Honey and growth factor eluting scaffold for wound healing and tissue engineering
InactiveUS20150030688A1Sustained releaseAnthropod material medical ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberCell-Extracellular Matrix
Tissue engineering structures with biologically favorable structural and chemical properties are disclosed. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to tissue engineered scaffolds having a fiber support and honey. The tissue engineered scaffolds having a fiber support and honey can further include at least one biomolecule. The tissue engineered scaffolds can be used to promote cellular chemotaxis, enhance cell proliferation, enhance extracellular matrix production, increase angiogenesis, and provide antimicrobial activity. The nature of the tissue engineered scaffolds provides a template for cellular infiltration and guide tissue regeneration. The tissue engineered scaffolds can be used in the treatment of dermal wounds (burns, chronic wounds, etc.) or as a tissue engineering scaffold in a wide range of applications.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
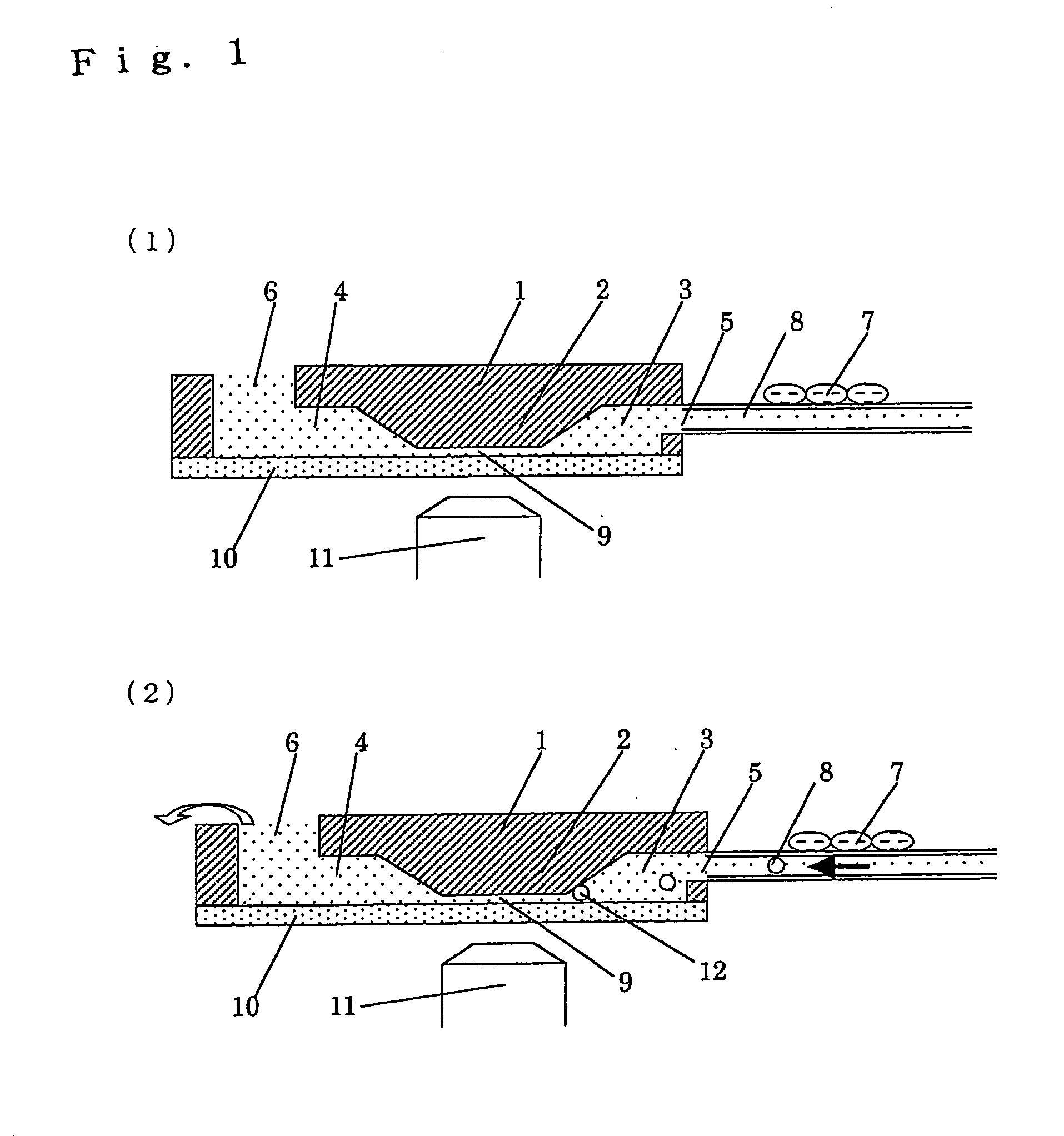
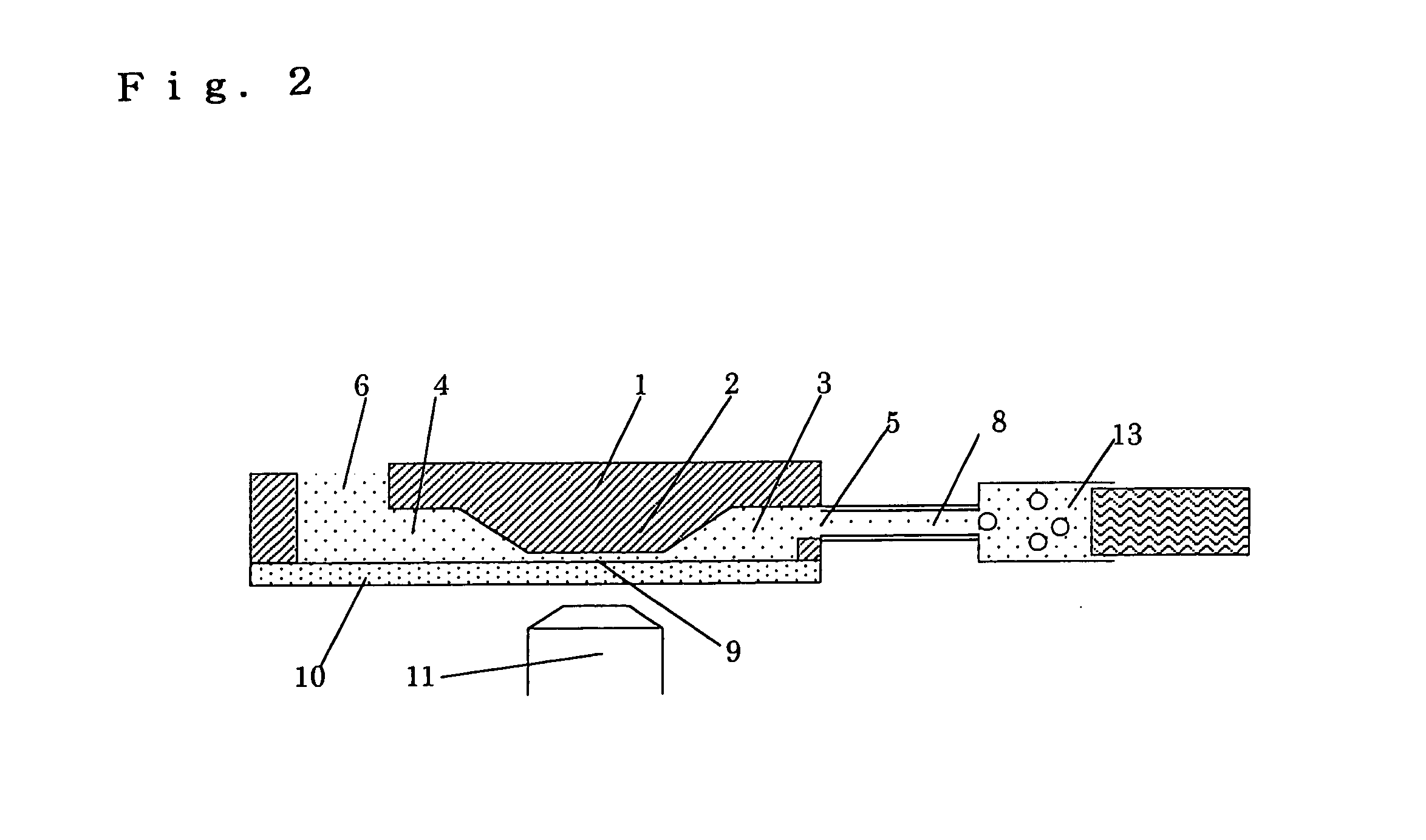
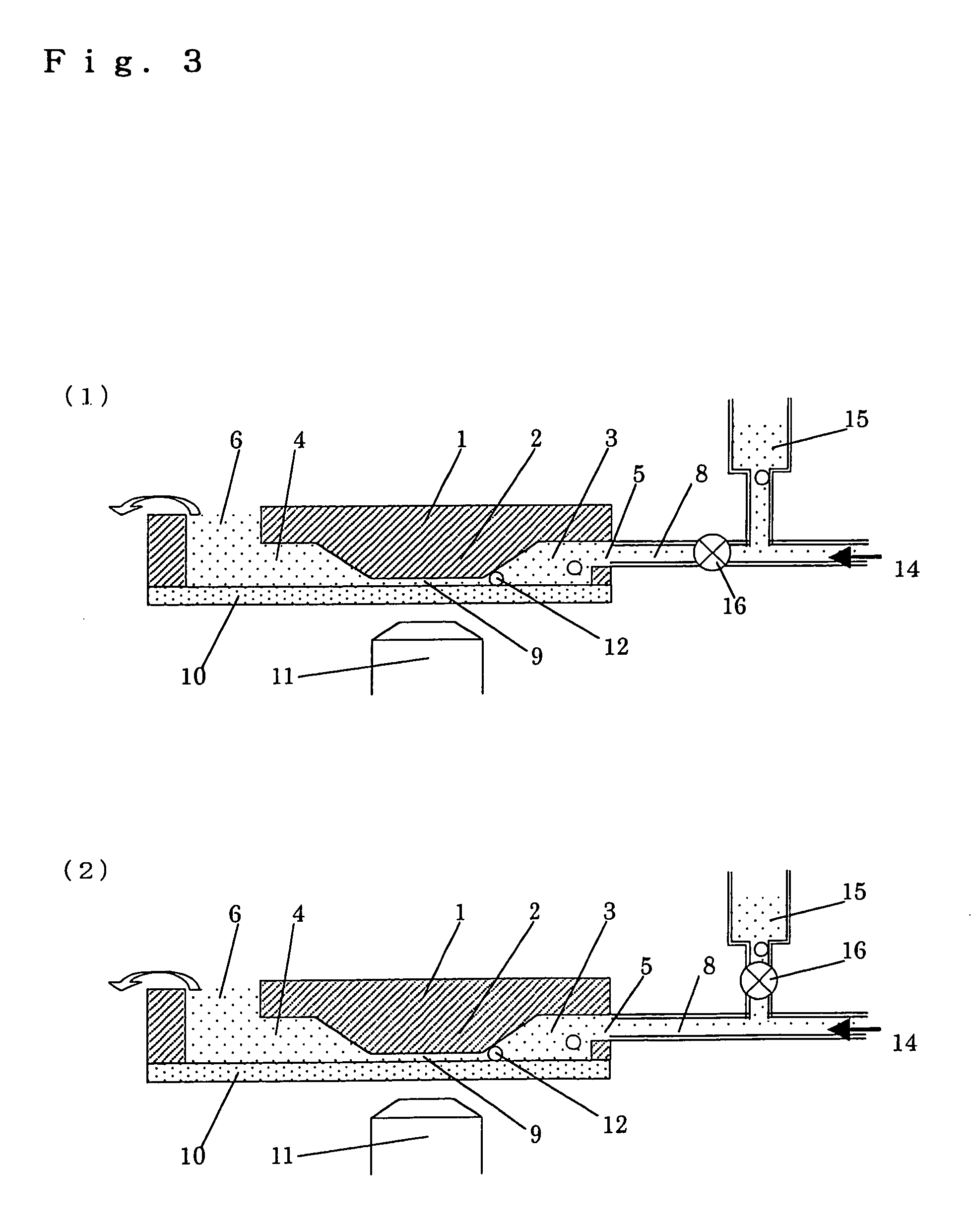
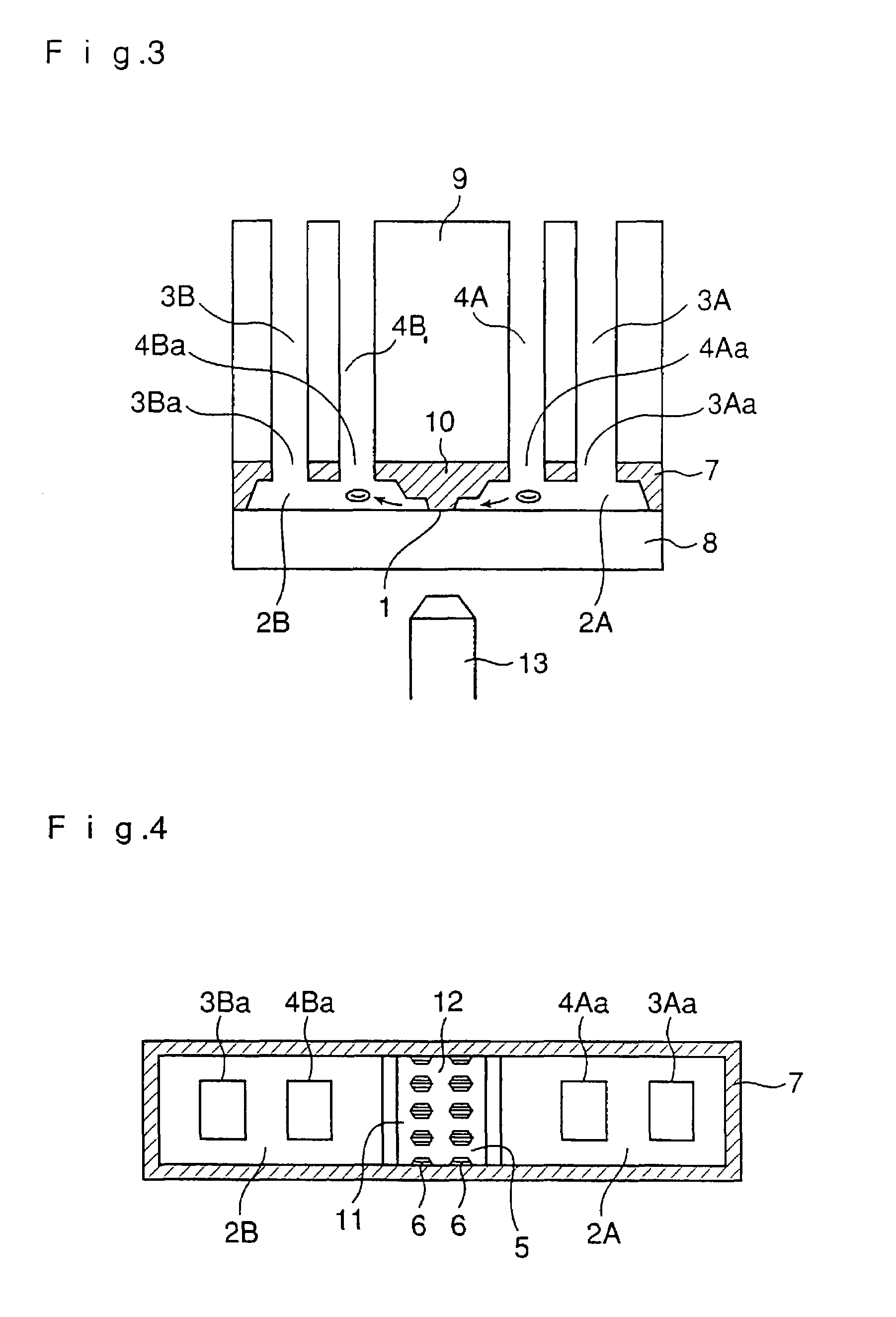
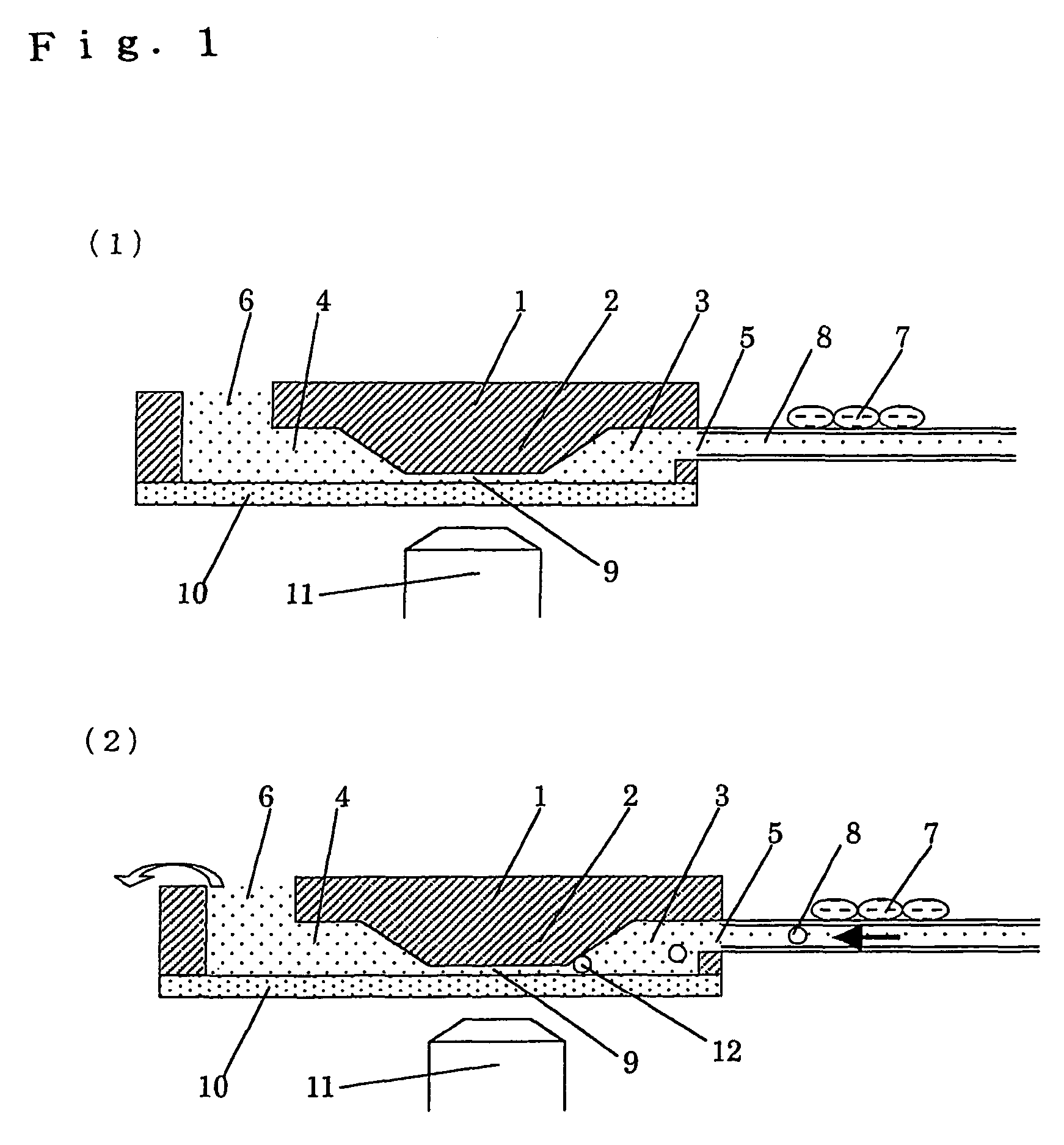
Apparatus for detecting cell chemotaxis
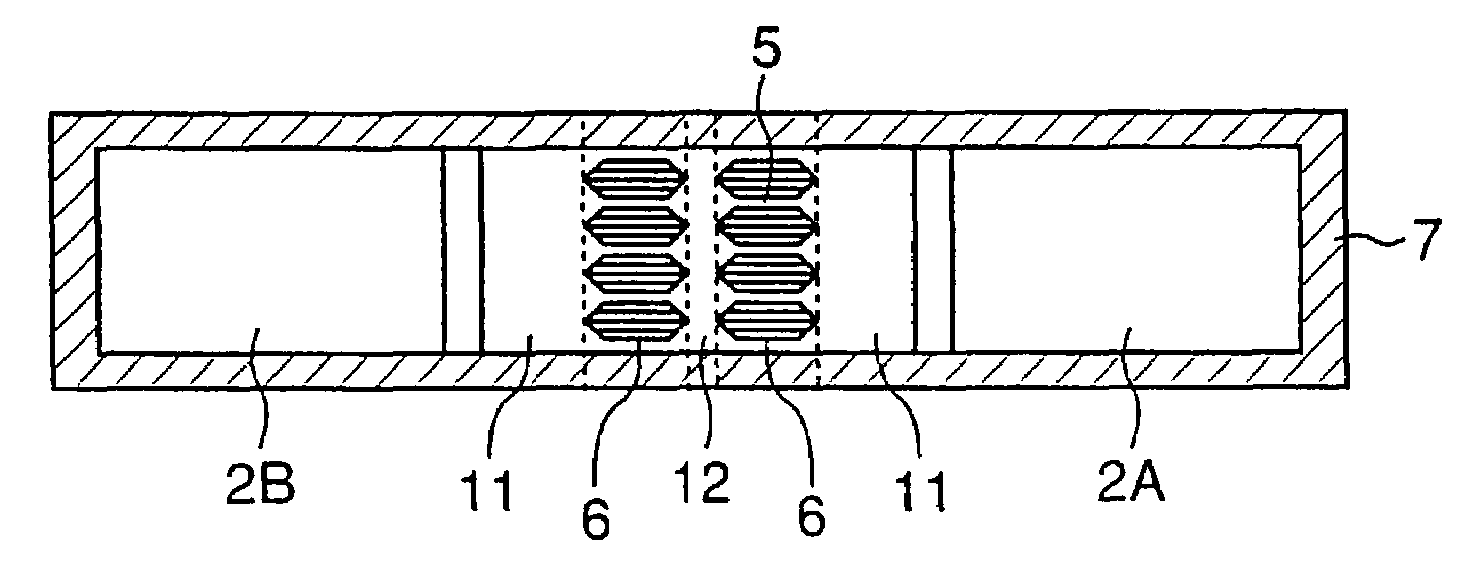
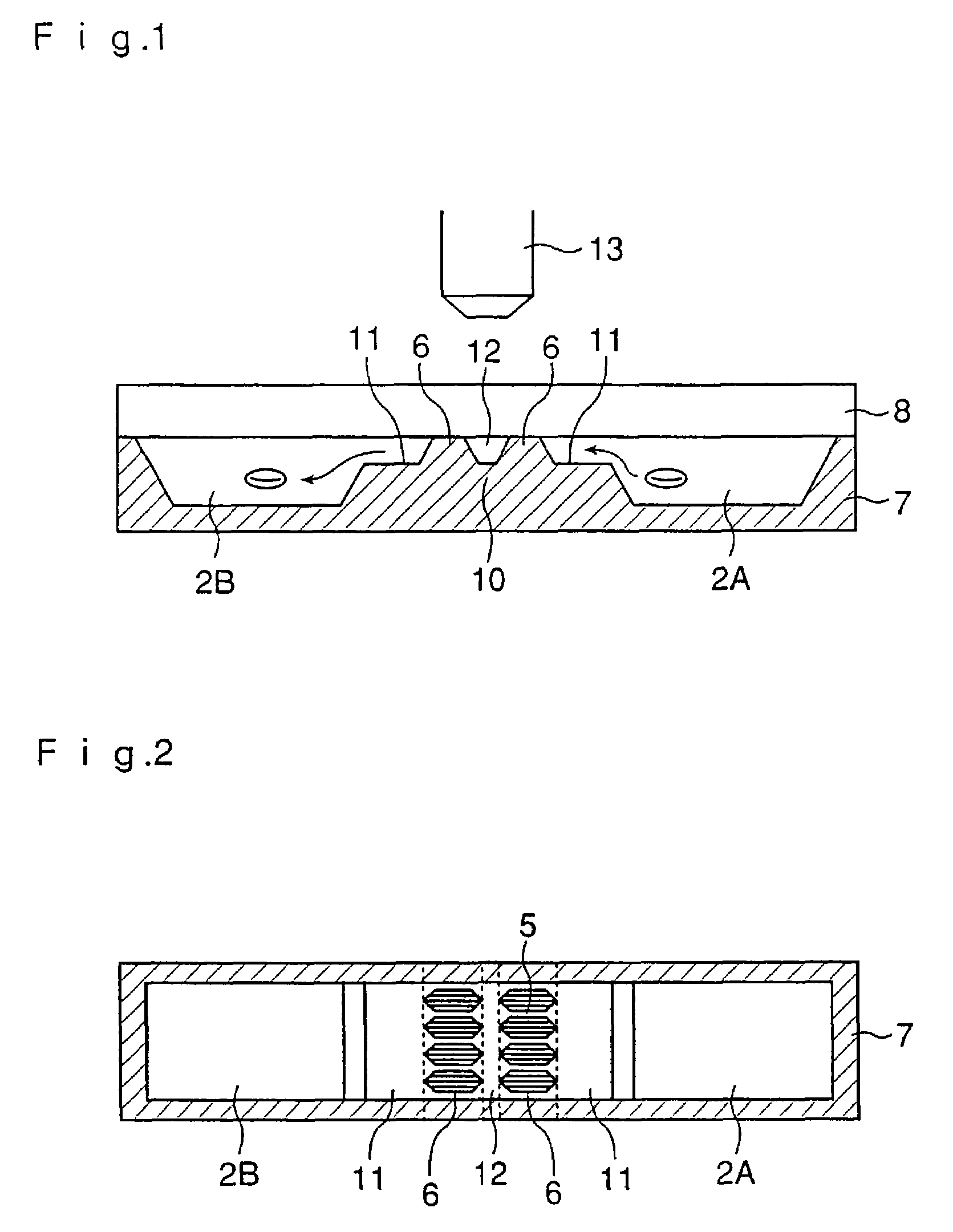
InactiveUS20060121600A1Improve automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiffusionConcentration gradient
The present invention relates to an improvement in an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells. It aims at providing a structure for detecting chemotaxis of cells at an elevated accuracy with the use of a microquantity of cells. That is to say, an object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells by which cell injection and position control can be easily carried out while ensuring the prevention of unexpected migration of the cells definitely positioned in a well or the injected sample so that a stable concentration gradient due to the diffusion of the specimen can be maintained and which ensures further automated operation and controlling. Namely, an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells with a structure wherein two wells are connected to each other via a channel having resistance to the passage of cells and each well has an opening for injecting cells or a specimen, characterized by having (1) a means of transporting a liquid and a means of stopping the transportation after the injection or the aspiration discharge of the liquid and (2) a means of sealing the opening(s) in one or both of the cell-injection side and the specimen-injection side.
Owner:ECI
Microfluidic chip group used for screening formyl peptide receptor agonist and screening method
InactiveCN101782569AAvoid influenceReal-time monitoring of the transient flow of calcium ionsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceScreening methodAgonist
The invention provides a microfluidic chip group used for screening a formyl peptide receptor agonist and a screening method. The microfluidic chip group consists of three microfluidic chip units, i.e. a cell chemotaxis detection unit, a receptor endocytosis detection unit and a calcium ion transient flow process monitoring unit. The invention designs a group of chips by aiming to the characteristics of different cell function analytical experiments, can respectively carry out cell chemotaxis, receptor endocytosis detection and calcium ion transient flow (release) process monitoring, and judges biologic activity thereof by comprehensively evaluating influence on the formyl peptide receptor signal conduction path by an alternative compound. Compared with the traditional technology, the invention realizes real-time monitoring of the intracellular calcium ion releasing process and saves a series of complex operations, such as film laying, film obtaining, cell doctoring, fixing, dying andthe like, thereby greatly saving the analysis time and lowering the detection cost.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
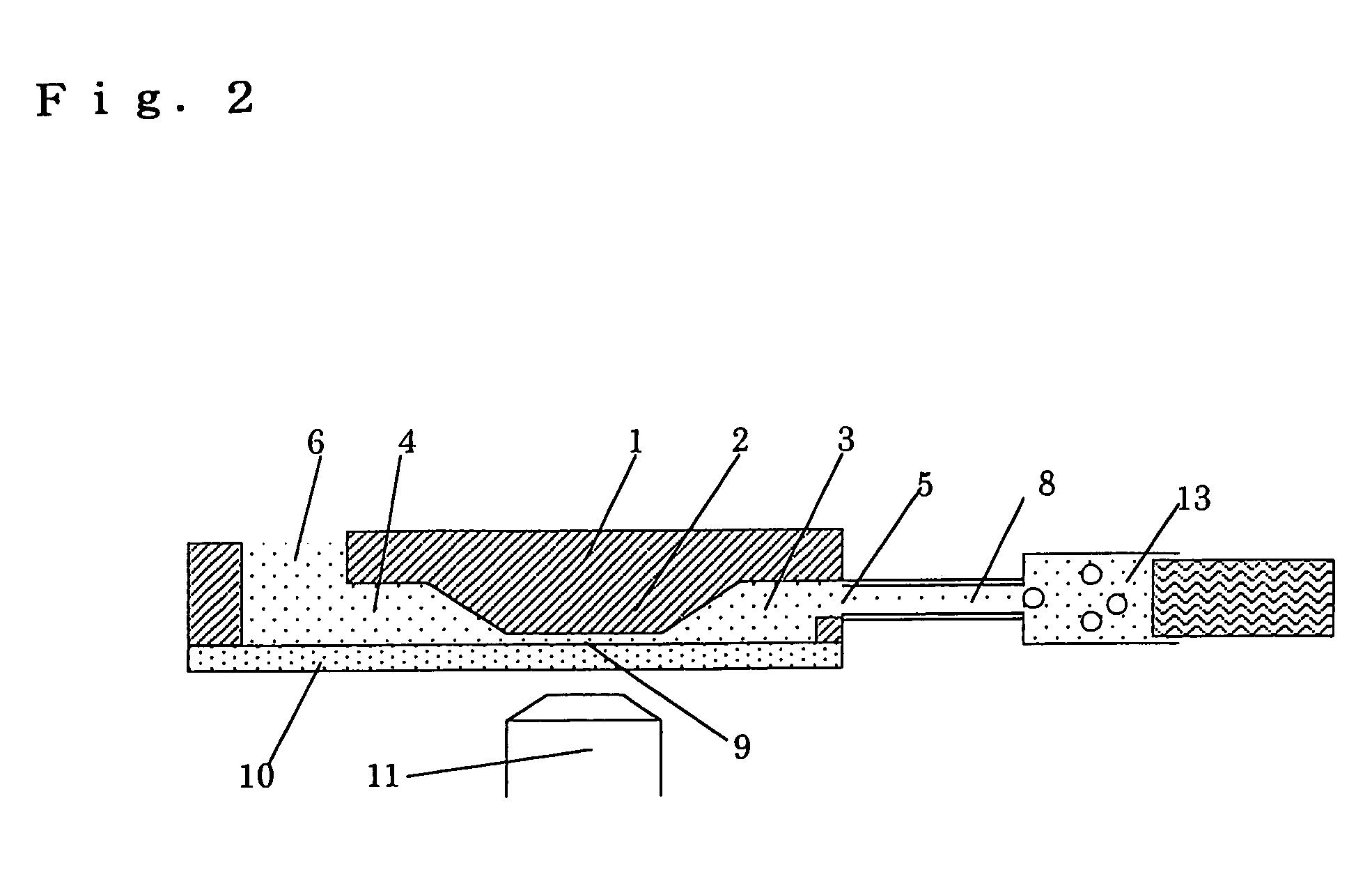
Well unit for detecting cell chemotaxis and separating chemotactic cells
InactiveUS7022516B2High-precision detectionConfirm effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringChemokinesis
The present invention aims at providing a well unit to be used in fabricating an apparatus whereby movements of cells based on their own actions can be accurately and easily detected, in detecting the chemotaxis of cells due to a chemotactic factor or the inhibition of the chemotaxis of cells by an inhibitor.Accordingly, the present invention provides a well unit to be used in an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells and separating cells characterized in that a plural number of wells, in which a liquid sample can be held in a resting state, are connected to each other via a channel, the channel is provided with a bank, and, in the upper part of the bank, barriers constituting one or more grooves having a width and / or a depth fit for the diameter or deformability of cells are provided or a plane is provided so as to give a gap having a depth fit for the diameter or deformability of cells between the plane and the glass substrate.
Owner:ECI
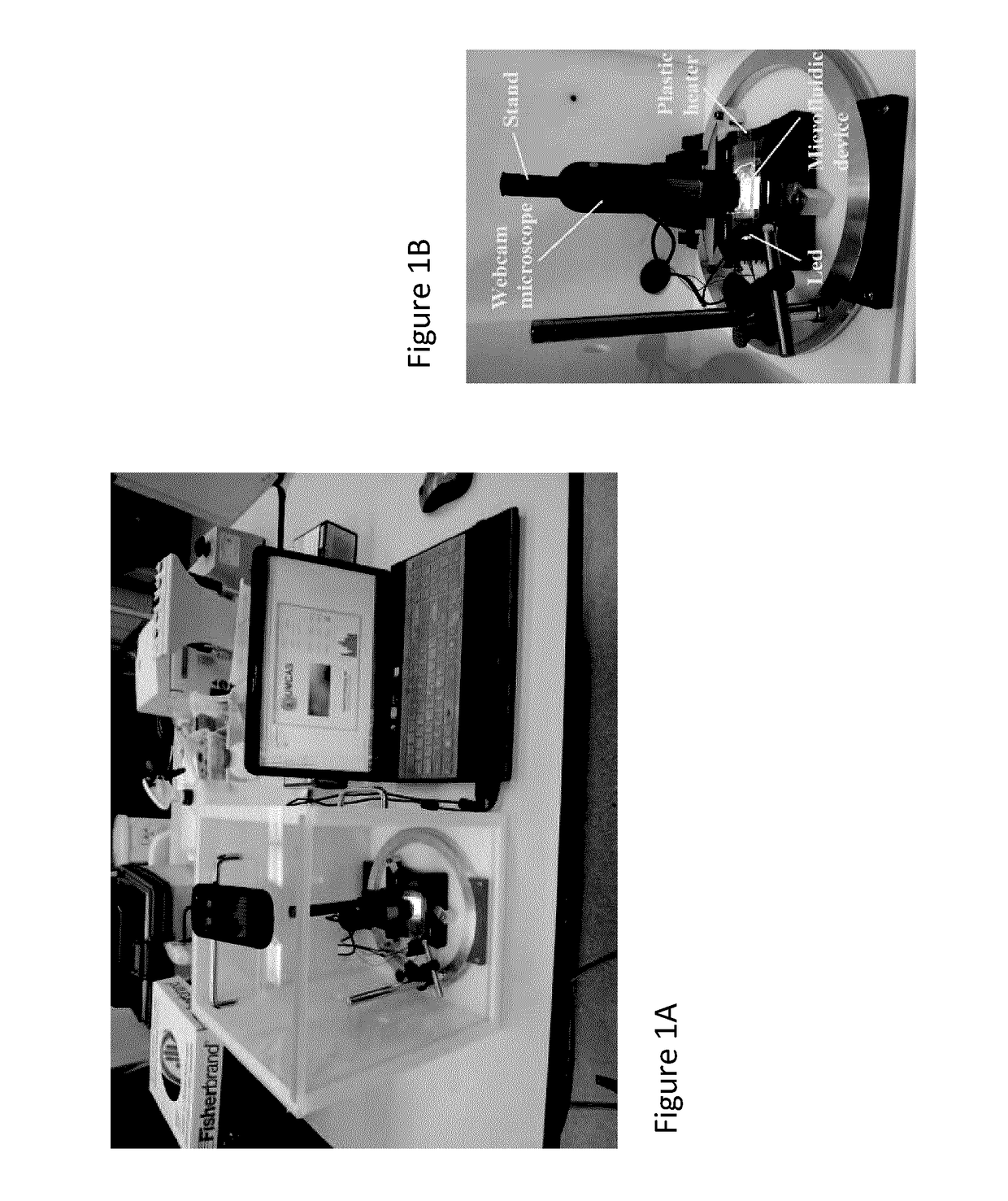
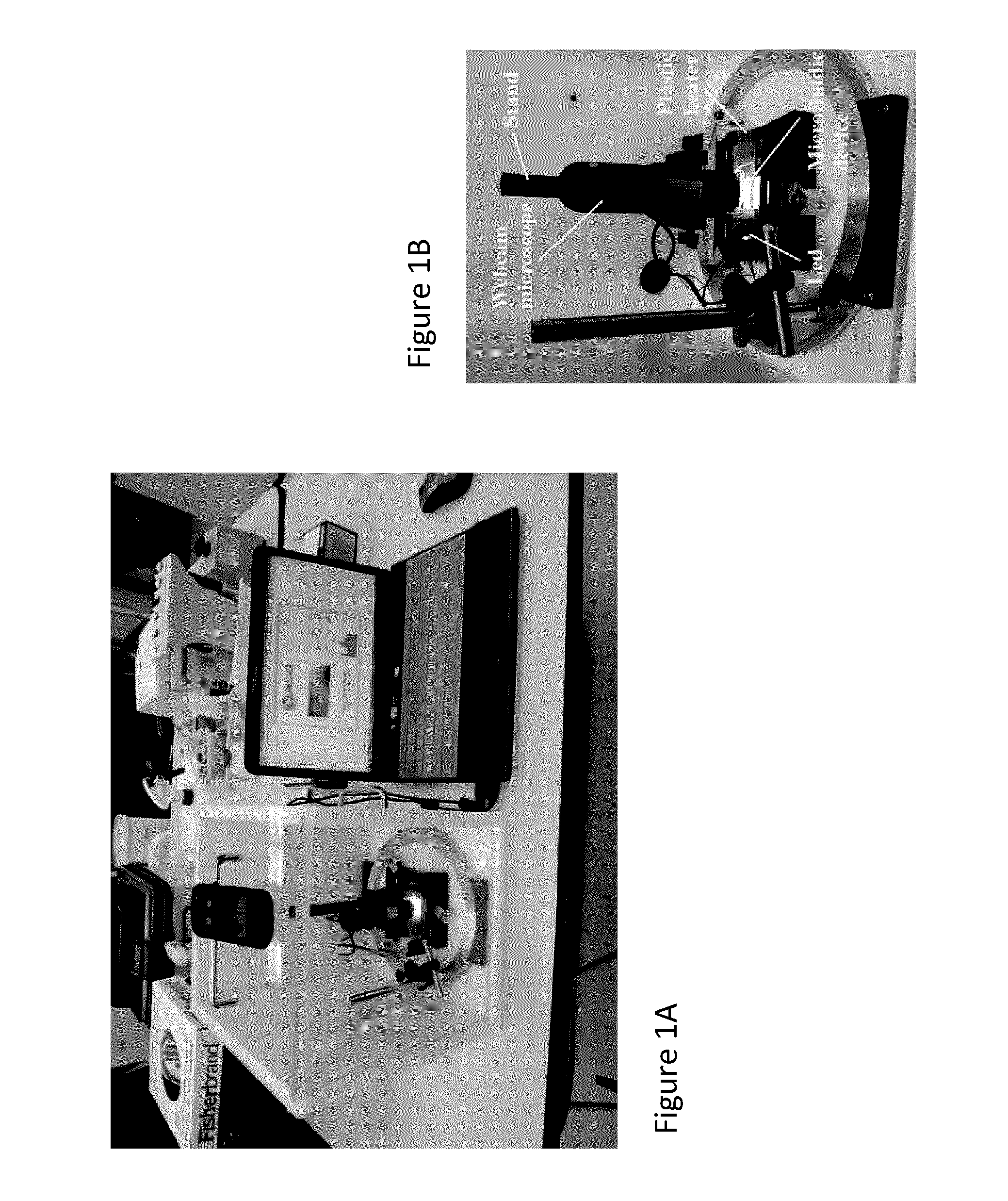
Low-cost portable microfluidic system for cell migration
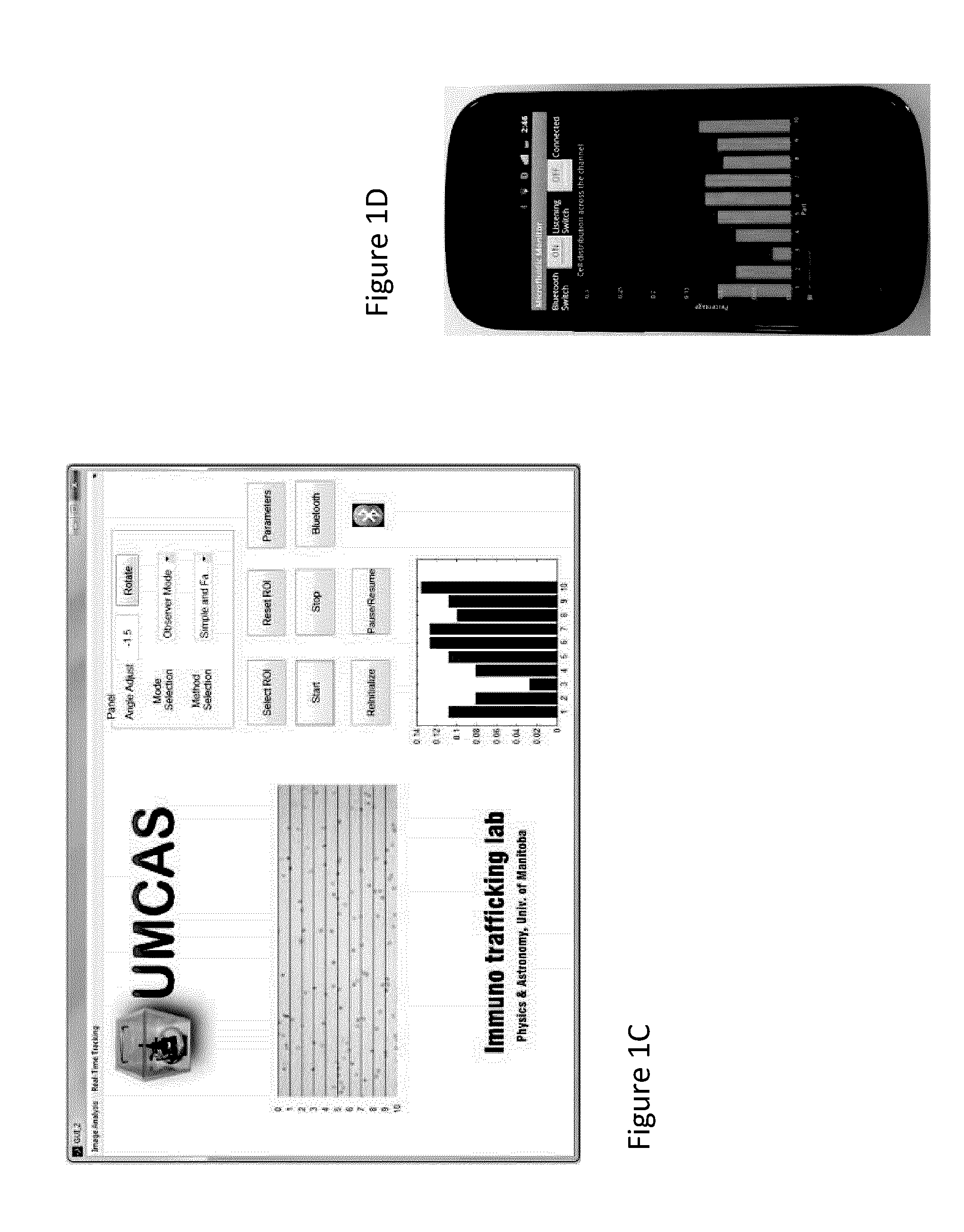
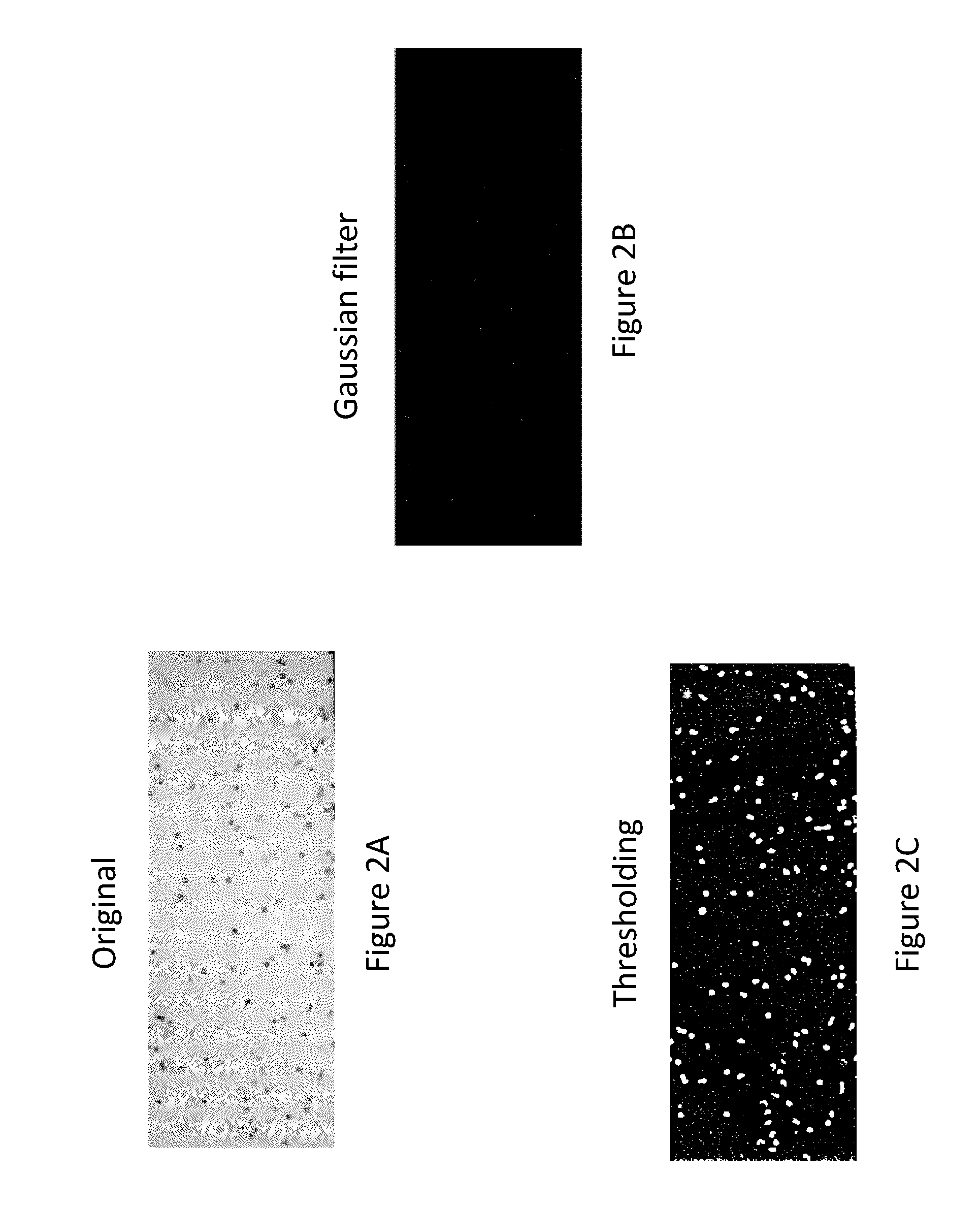
Low-cost and portable microfluidic systems are needed for cell migration research and Point of Care (POC) testing. This study introduces a low-cost and portable USB Microscope Microfluidic Chemotaxis Analysis System (UMCAS) for rapid analysis of cell chemotaxis studies. A standalone microfluidic gradient generator is also developed for rapid generation of chemical gradient in microfluidic device without need of any peripheral perfusion apparatus. A smart phone based application program was developed for the real-time remote monitoring of the migration data. This system is validated by observing the neutrophil migration in three different conditions: 1) medium control, 2) uniform IL-8 control, and 3) IL-8 gradient. The results show that neutrophils exhibit random migration in both medium and uniform IL-8 control experiments, while they show strong directional migration to the IL-8 gradient. These results successfully validated the developed UMCAS system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Low-Cost Portable Microfluidic System for Cell Migration
InactiveUS20150212070A1Image enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPoint of careMedia controls
Low-cost and portable microfluidic systems are needed for cell migration research and Point of Care (POC) testing. This study introduces a low-cost and portable USB Microscope Microfluidic Chemotaxis Analysis System (UMCAS) for rapid analysis of cell chemotaxis studies. A standalone microfluidic gradient generator is also developed for rapid generation of chemical gradient in microfluidic device without need of any peripheral perfusion apparatus. A smart phone based application program was developed for the real-time remote monitoring of the migration data. This system is validated by observing the neutrophil migration in three different conditions: 1) medium control, 2) uniform IL-8 control, and 3) IL-8 gradient. The results show that neutrophils exhibit random migration in both medium and uniform IL-8 control experiments, while they show strong directional migration to the IL-8 gradient. These results successfully validated the developed UMCAS system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Biological patch for tympanic membrane repair and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110448730AEfficient removalConducive to chemotaxisTissue regenerationProsthesisCell membraneBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
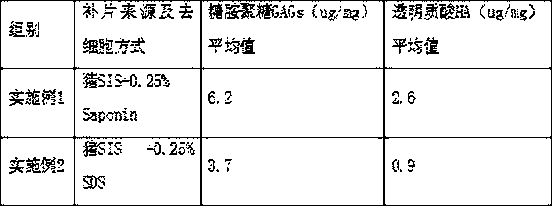
The invention belongs to the field of otology repair materials, and relates to a biological patch for tympanic membrane repair and a preparation method thereof. The otology repair patch of the invention overcomes the shortcomings of the prior patch due to an improper decellularizing process and a complicated process, and causes serious loss of effective active ingredients in the ECM. The biological patch adopts the plant-derived saponin as a decellularizing reagent, which avoids the residue and toxicity of a chemical reagent, and the mild decellularizing reagent is highly targeted and mainly binds to the cell membrane lipid; the decellularizing reagent has little damage on an ECM stereoscopic three-dimensional structure and the active components thereof; and more biologically active components such as glycosaminoglycan (including hyaluronic acid) can be retained. The patch of the invention has a better ECM scaffold structure and more active components, and has stronger ability to induce cell chemotaxis and proliferation, is beneficial to faster and better repair of the tympanic membrane, and also has a certain anti-infective effect; at the same time, the method of the invention issimple and convenient to operate, and has no damage to the ECM.
Owner:上海白衣缘生物工程有限公司
Otology biological material
PendingCN110801533AVarious dosage formsFlexible and diverse methods of useTissue regenerationProsthesisBiotechnologyBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to an otology biological material which can be used for repairing ear wounds including ear drum membrane injury. The material is prepared in the mode that young stock tissue suchas small intestinal submucosa of weaned piglets is used, and tender tissue of young stock is subjected to decellularization under the low-temperature condition through mild plant-derived reagents such as saponin. According to the obtained otology biological material, an ECM three-dimensional structure of the otology biological material is complete, the content of bioactive components is obviouslyhigher than that of an existing product, especially the content of hyaluronic acid is high, cell chemotaxis, growth and proliferation can be better promoted, and otology wound surface healing is facilitated; meanwhile, the otology biological material is easy to degrade and absorb and has an anti-infection effect; the defects of few active ingredients, much ECM structure damage, weak healing promoting capability and slow degradation of the existing product are overcome; and in addition, the dosage form of the otology biological material can be further made into different shapes such as powder,and thus use is more flexible, even simpler, more convenient and painless.
Owner:上海白衣缘生物工程有限公司
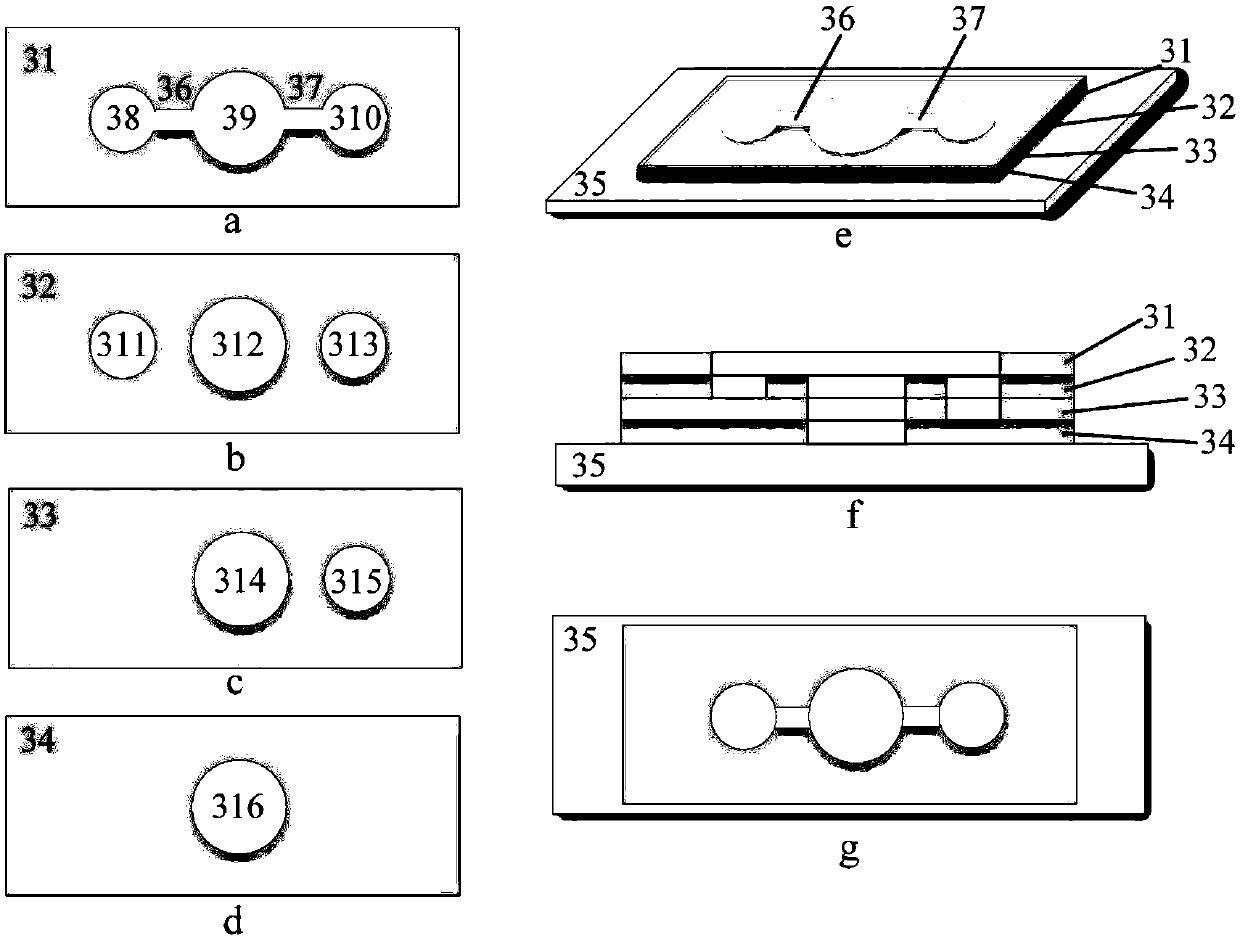
Micro-fluidic chip and method for studying cell chemotaxis
ActiveCN107904168AReduce volumeObserve migration in real timeMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue/virus culture apparatusConcentration gradientCellular Migration Process
The invention relates to a micro-fluidic chip and a method for studying cell chemotaxis. The micro-fluidic chip is of a multi-layer structure and comprises a substrate layer, cell culture layers and acell migration layer, wherein the layers are sealed together in sequence; reservoirs for cell culture are arranged on the cell culture layers; different cells are cultured on different layers; the cell migration layer is provided with reservoirs and communicating areas; cell chemotaxis observation and study are implemented in the communicating areas. By adopting the micro-fluidic chip, indirect contact type coculture of multiple cells can be achieved, stable concentration gradients can be achieved, and cell chemotaxis under the action of cell factors is studied. The micro-fluidic chip has theadvantages of being flexible in design, simple to manufacture, simple and convenient to operate, low in use amount of cells and reagents, possible in real-time observation on cell migration process,and the like, and can be applied to various studies on cell indirect contact type coculture, cell chemotaxis, cell migration and the like.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
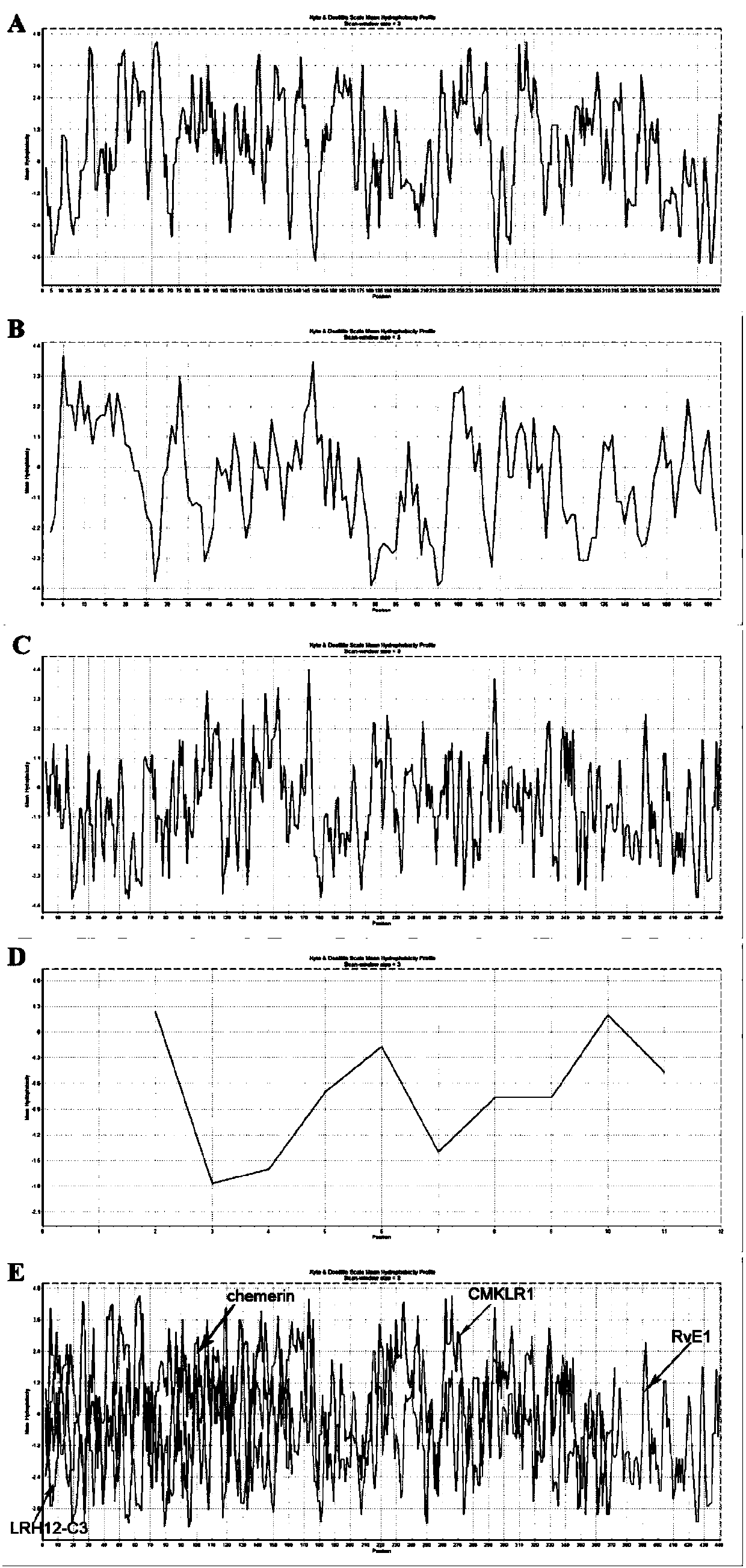
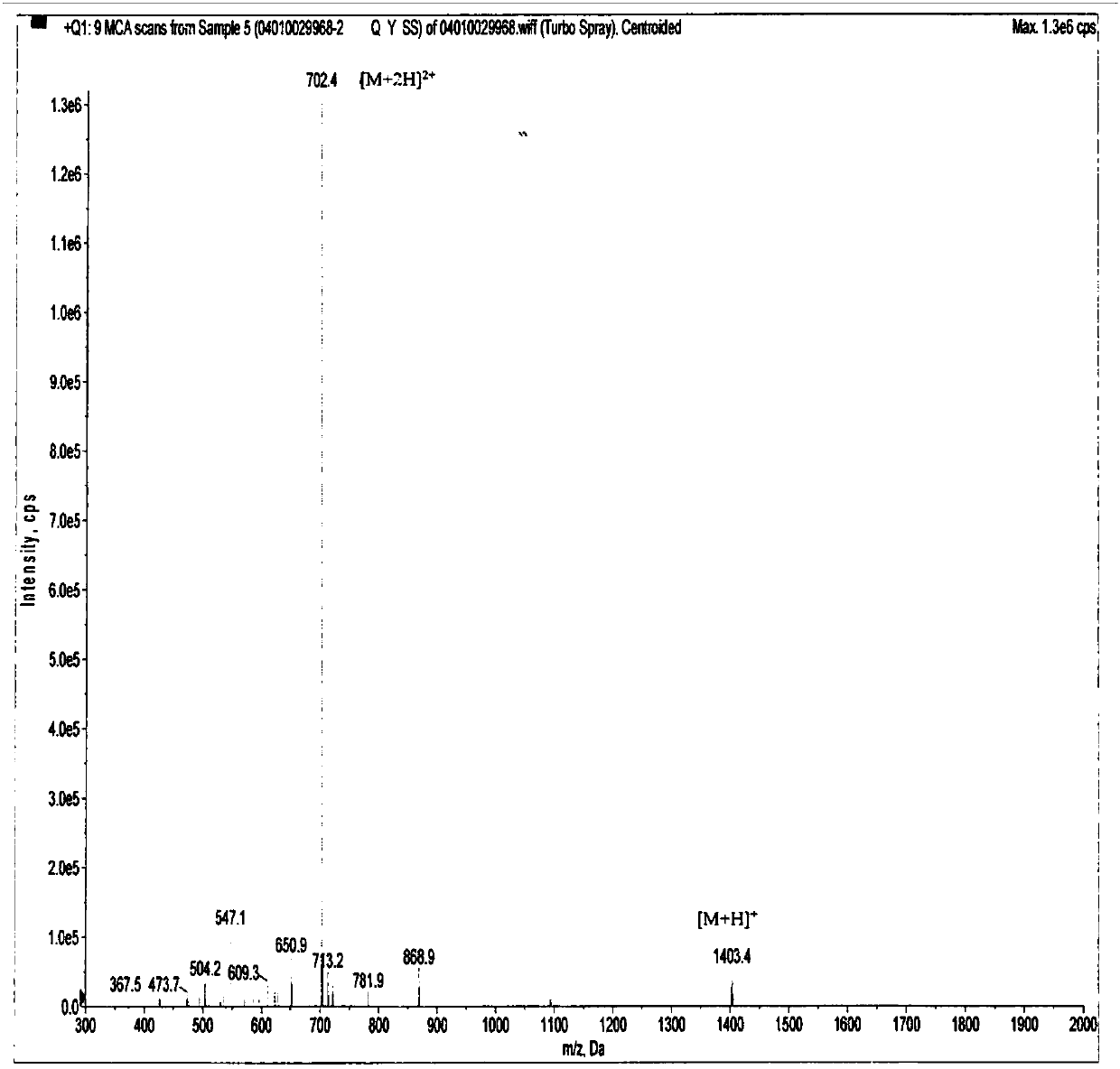
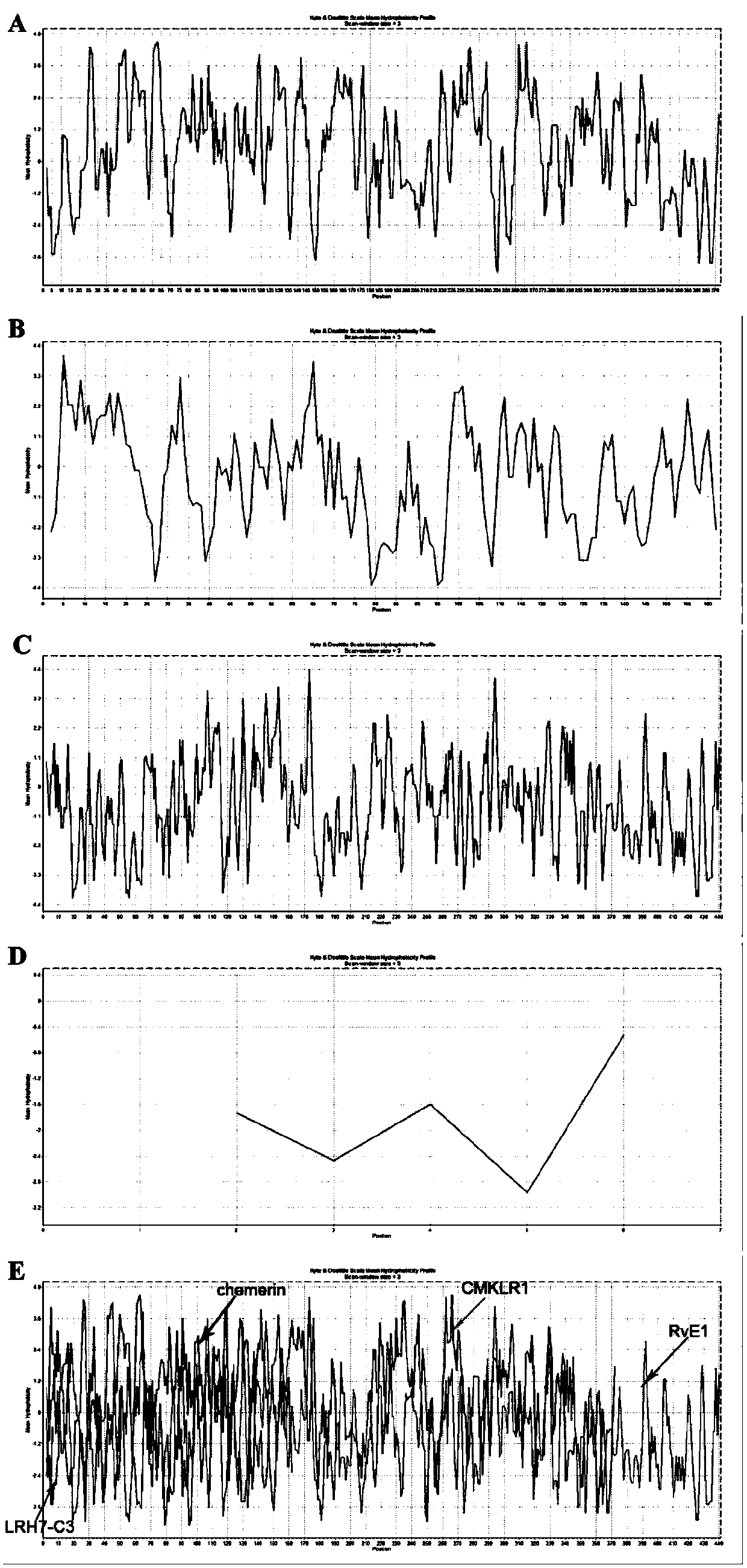
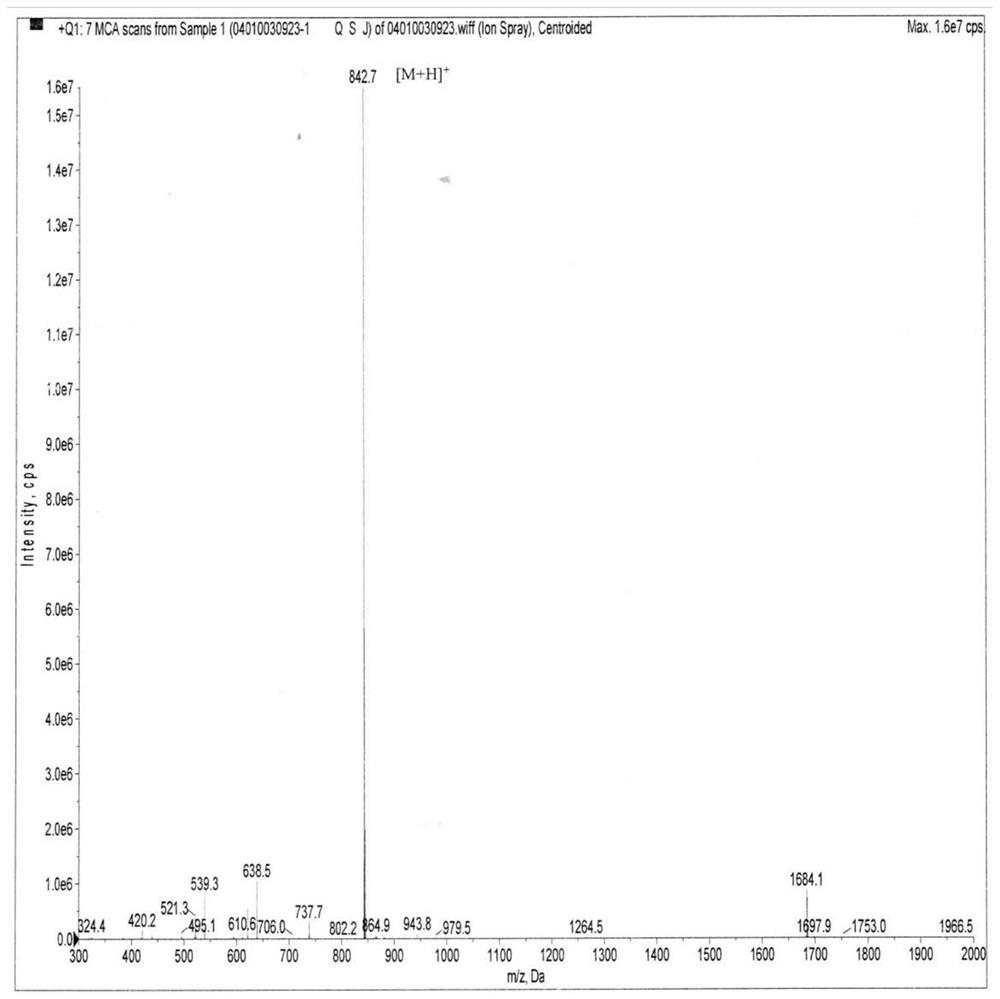
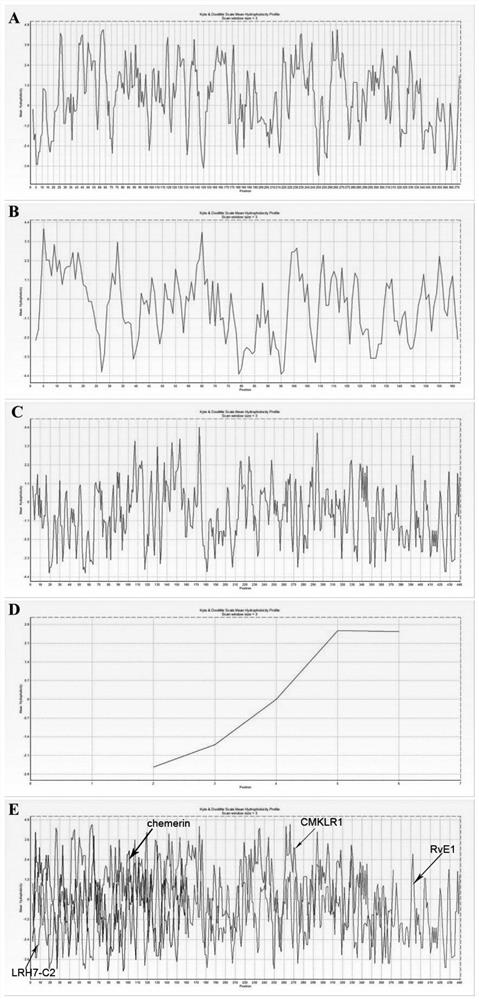
CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivatives and application thereof
The invention discloses a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivatives and application thereof, and particularly relates to analogs of the CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide shown in sequences SEQ IDNO.1-21 and derivatives thereof. The derivatives of the binding peptide are products obtained after conventional modification of amino terminals or carboxyl terminals on CMKLR1 binding peptide amino acid side chain groups and CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide fragments or products obtained by bonding labels for polypeptide or protein detection or purification with the CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide. The binding peptide and the derivatives thereof can be bonded with CMKLR1 in vitro, and by blocking the bond of chemerin / RvE1 and CMKLR1, cAMP concentration increase is promoted, calcium influx caused by chemerin is inhibited, cell chemotaxis caused by chemerin is inhibited, and effective small-molecular treatment drugs are provided for high-expression CMKLR1 receptor diseases such as breast cancer and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
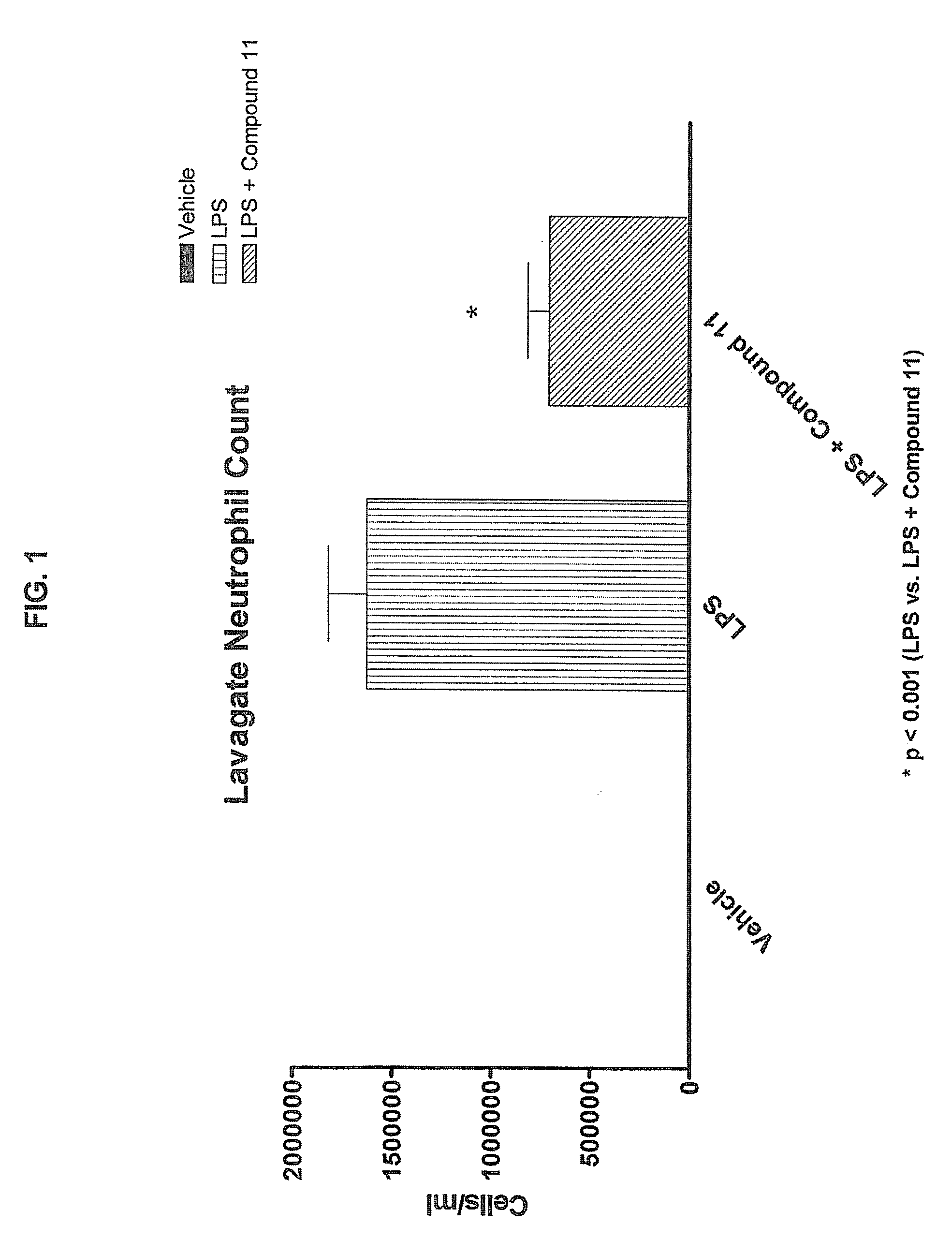
Method of treating inflammation
InactiveUS20070249556A1Inhibit inflammationInhibition of chemotaxisBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseWhite blood cell
This invention provides methods of preventing and / or treating diseases or conditions associated with inflammation in a mammal, particularly a human. The method comprises administering to a mammal in need thereof an effective amount of a compound of Formula I, IA, or IB, wherein said amount is effective to inhibit inflammation. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting chemotaxis of leukocytes.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA
CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN109942676APeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAmino acid side chainBinding peptide
The invention discloses a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and a derivative and application thereof and particularly relates to a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide shown in SEQ ID No.1-9 and a derivativethereof. The derivative of the binding peptide is a product obtained in the mode that conventional modification is conducted on a CMKLR1 binding peptide amino acid side chain group and an amino terminal or a carboxyl terminal of a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide fragment or a product obtained in the mode that a label for detection or purification of polypeptide or protein is linked to the CMKLR1antagonistic polypeptide. The binding peptide and the derivative thereof can be combined with CMKLR1 in vitro, by stopping combination of chemerin / RvE1 and CMKLR1, the cAMP concentration is changed, the calcium influx caused by chemerin and cell chemotaxis caused by chemerin are inhibited, and effective micromolecule treatment drugs are provided for diseases of high-expression CMKLR1 receptors.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN109942684APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAmino acid side chainBinding peptide
The invention discloses a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and a derivative and application thereof and particularly relates to a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide shown in SEQ ID No.1-24 and a derivative thereof. The derivative of the binding peptide is a product obtained in the mode that conventional modification is conducted on a CMKLR1 binding peptide amino acid side chain group and an amino terminal or a carboxyl terminal of a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide fragment or a product obtained in the mode that a label for detection or purification of polypeptide or protein is linked to the CMKLR1antagonistic polypeptide. The binding peptide and the derivative thereof can be combined with CMKLR1 in vitro, by stopping combination of chemerin / RvE1 and CMKLR1, increase of the cAMP concentrationis promoted, the calcium influx caused by chemerin and cell chemotaxis caused by chemerin are inhibited, proliferation of ovarian carcinoma cells can be inhibited, apoptosis of the ovarian carcinoma cells is promoted, and effective micromolecule treatment drugs are provided for female reproductive diseases such as ovarian cancer.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Cell invasion chemotaxis model and preparation method thereof
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivatives and application thereof
ActiveCN109942682APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAmino acid side chainChemerin
The invention discloses a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivatives and application thereof, and particularly relates to analogs of the CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide shown in sequences SEQ IDNO.1-17 and derivatives thereof. The derivatives of the binding peptide are products obtained after conventional modification of amino terminals or carboxyl terminals on CMKLR1 binding peptide amino acid side chain groups and CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide fragments. The binding peptide and the derivatives thereof can be bonded with CMKLR1 in vitro, and by blocking the bond of chemerin and CMKLR1, cAMP concentration increase is promoted, calcium influx caused by chemerin is inhibited and cell chemotaxis caused by chemerin is inhibited. Besides, proliferation of ovarian cancer cells can be inhibited, the cell cycle is blocked, apoptosis of the ovarian cancer cells is promoted, and effective small-molecular treatment drugs are provided for female reproductive diseases such as ovarian cancer.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Stem cell biological product for treating liver cirrhosis and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN110946877AImprove specific homing abilityIncrease the number ofGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemCCR9Mesenchymal stem cell
In order to overcome a problem that an existing conventional treatment method for liver cirrhosis has a poor effect, the invention provides a stem cell biological product. The stem cell biological product comprises mesenchymal stem cells, wherein the mesenchymal stem cells are transfected into a vector, and the vector comprises a CCR9 gene sequence. Furthermore, the invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the stem cell biological product. The stem cell biological products utilizes that combination of CCL25 and receptor CCR9 has an effect of cell chemotaxis, improves aspecific homing ability of the mesenchymal stem cells at a focal part of liver cirrhosis, increases number of local stem cells, and effectively improves a therapeutic effect of the mesenchymal stem cells on liver cirrhosis.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN ISTEM REGENERATIVE MEDICINE SCI TECH CO LTD +1
Hydrogel motor for guiding T cell chemotaxis and application thereof
ActiveCN112957316AArrive accuratelyIncrease capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnergy modified materialsWireless controlBiocompatibility
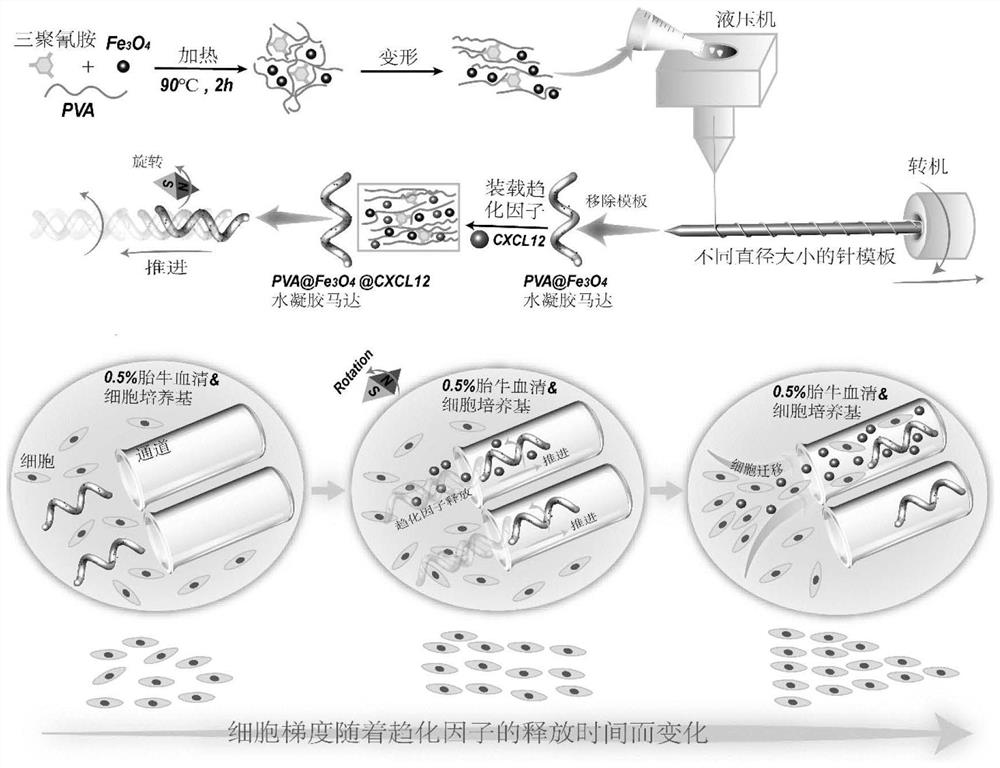
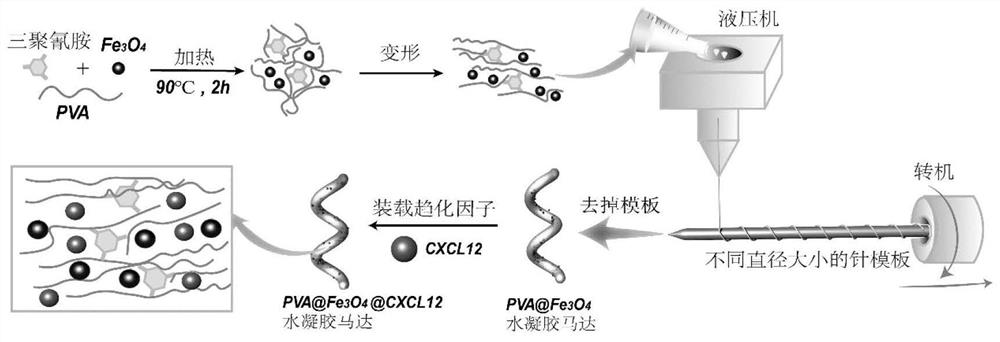
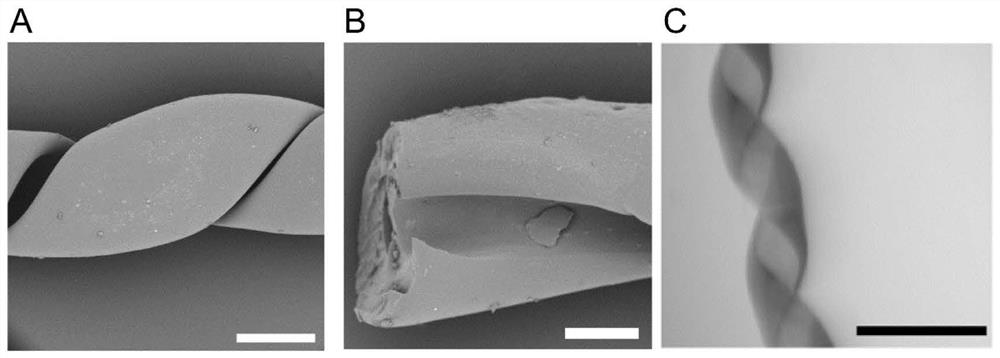
The invention discloses a hydrogel motor for guiding T cell chemotaxis and application of the hydrogel motor. The hydrogel motor comprises a chemotactic factor. The invention designs a spiral hydrogel magnetic micromotor through a device which is easy to manufacture and is universal, and magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles arranged in the hydrogel motor allow remote magnetic field driving and control. The wireless control provides good biocompatibility and excellent control precision, a porous hydrogel structure also provides high capacity of chemotactic factor loading and retention release. The spiral motor driven by a rotating magnetic field can accurately reach a target lesion site, and sends a chemotactic factor signal to an immune following cell to generate directed T cell chemotaxis or recruitment towards a chemotactic factor release site.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Apparatus for detecting cell chemotaxis
InactiveUS7807451B2Improve automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiffusionConcentration gradient
The present invention relates to an improvement in an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells. It aims at providing a structure for detecting chemotaxis of cells at an elevated accuracy with the use of a microquantity of cells. That is to say, an object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells by which cell injection and position control can be easily carried out while ensuring the prevention of unexpected migration of the cells definitely positioned in a well or the injected sample so that a stable concentration gradient due to the diffusion of the specimen can be maintained and which ensures further automated operation and controlling.Namely, an apparatus for detecting chemotaxis of cells with a structure wherein two wells are connected to each other via a channel having resistance to the passage of cells and each well has an opening for injecting cells or a specimen, characterized by having (1) a means of transporting a liquid and a means of stopping the transportation after the injection or the aspiration discharge of the liquid and (2) a means of sealing the opening(s) in one or both of the cell-injection side and the specimen-injection side.
Owner:ECI INC
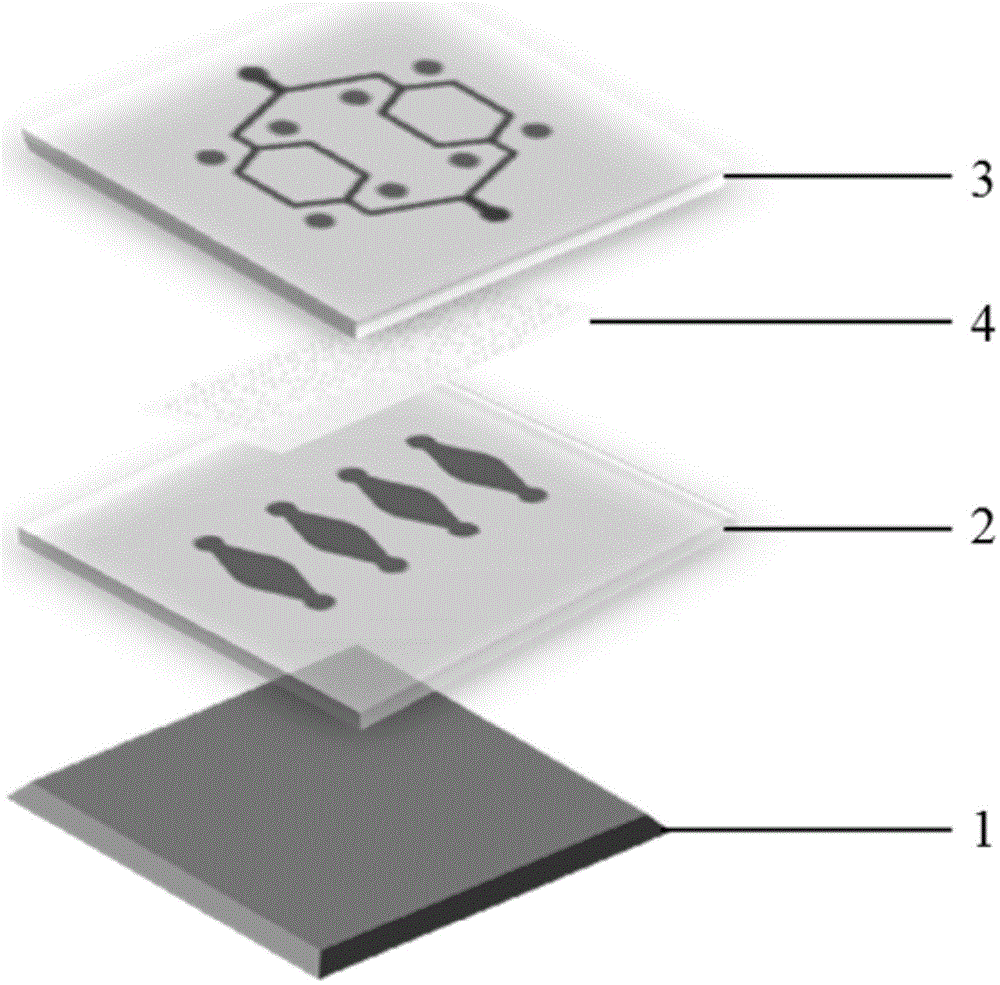
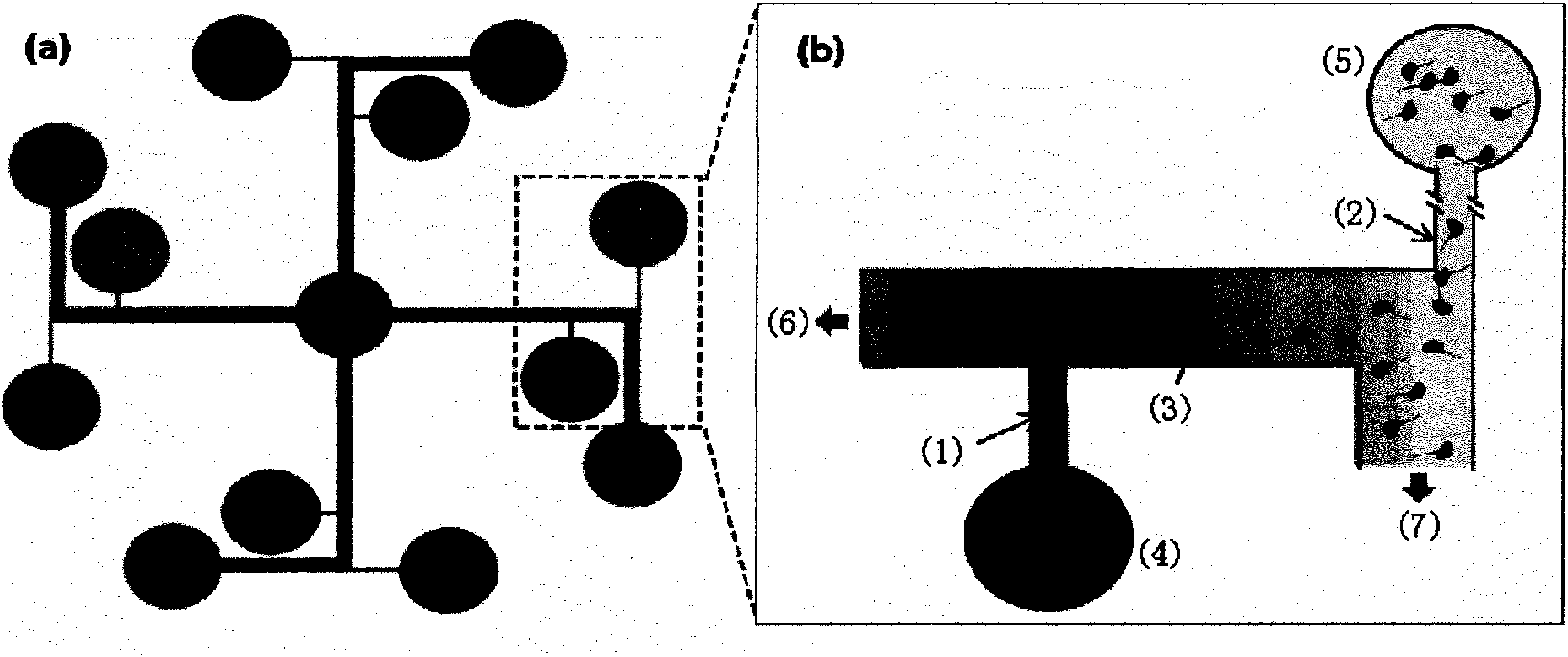
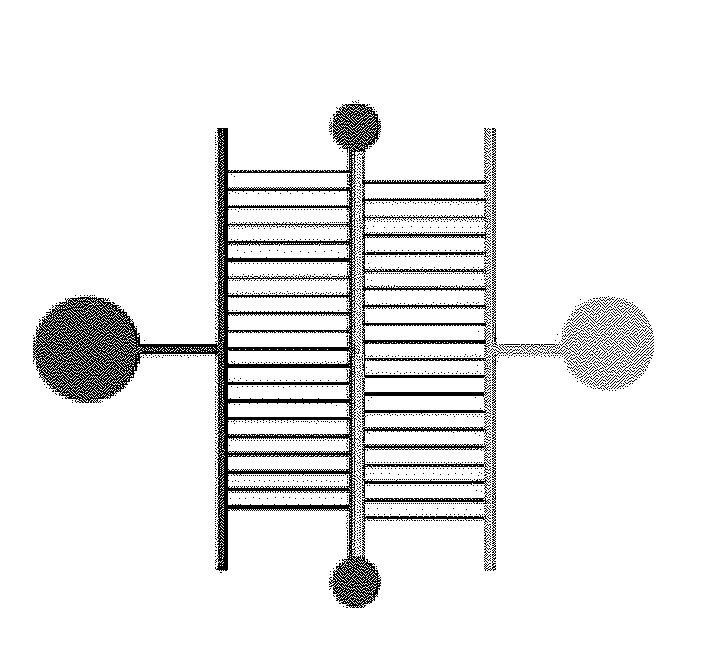
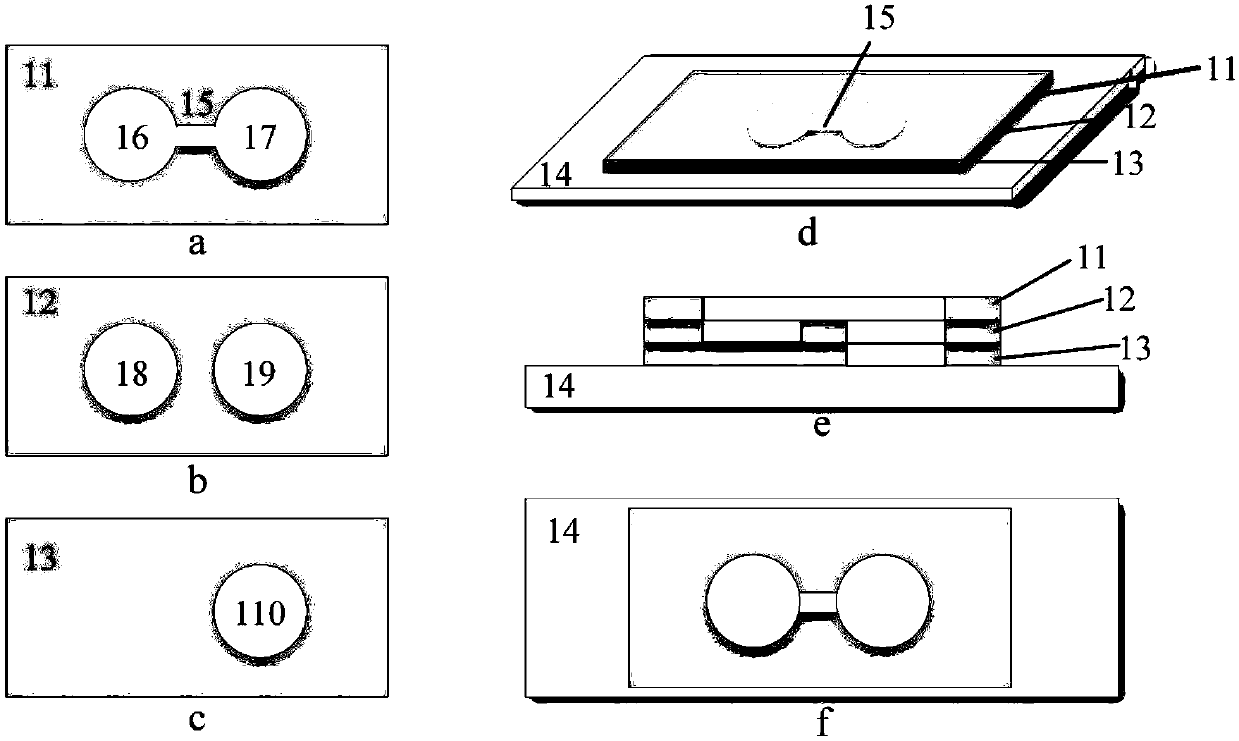
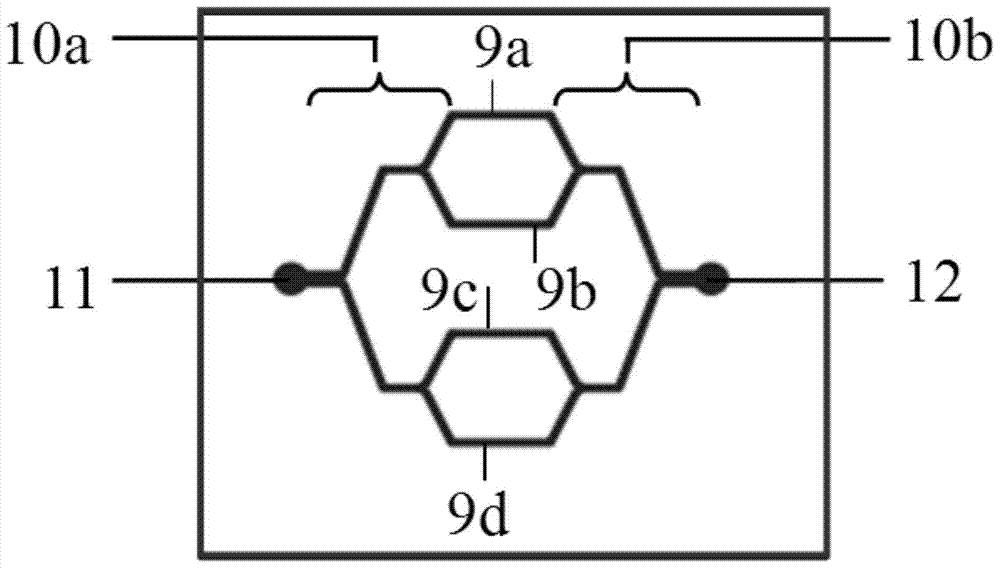
Cell chemotaxis analysis chip and device as well as use method and preparation method of cell chemotaxis analysis chip
InactiveCN103361263BConvenient quantitative observationConvenient researchBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringConcentration gradient
Owner:PEKING UNIV
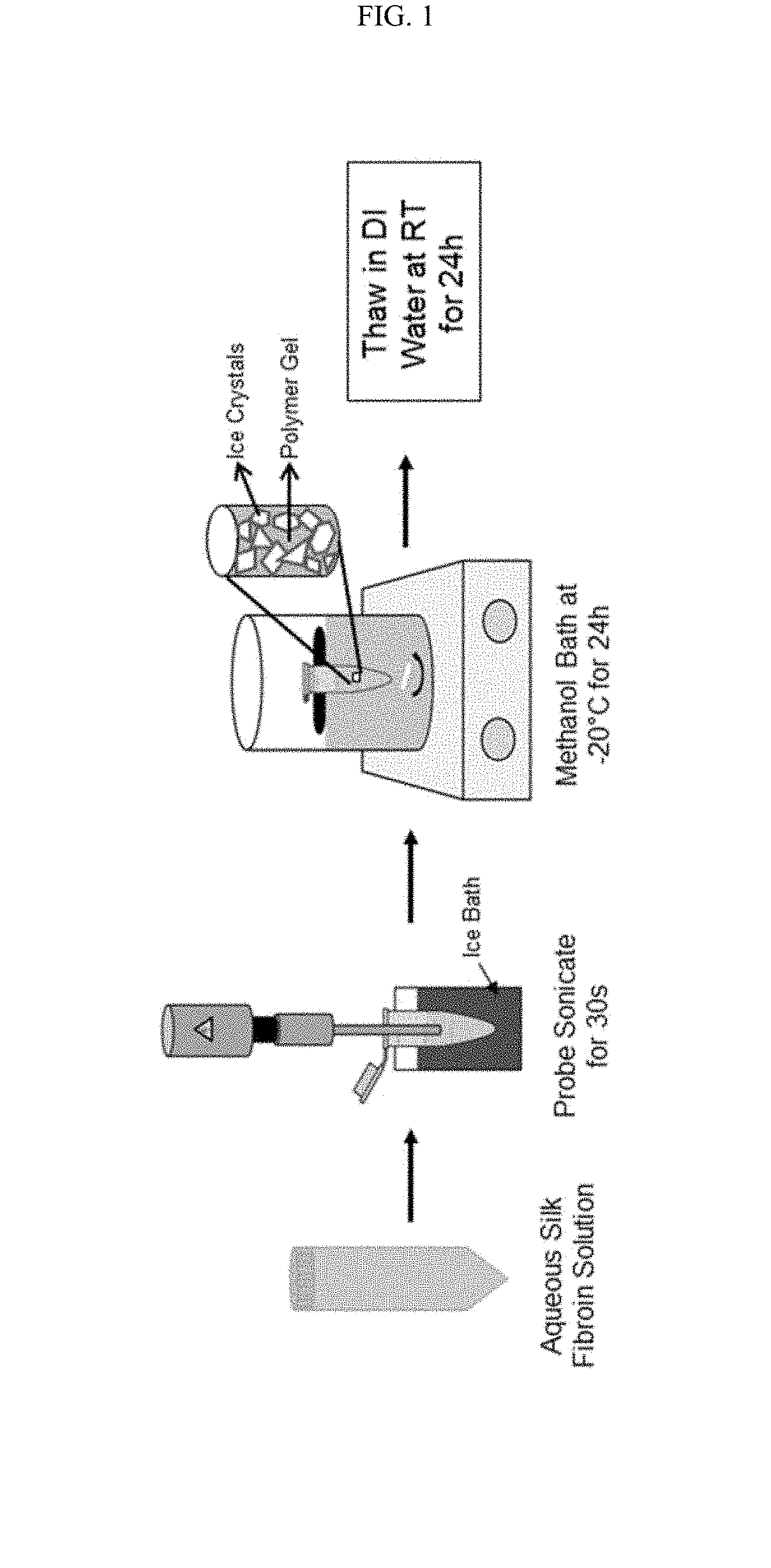
Silk fibroin cryogels
InactiveUS20180243475A1Improve mechanical stabilityBroad and significant impactTissue regenerationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBone tissue engineering
Disclosed are silk fibroin cryogels and methods for preparing silk fibroin cryogels. The silk fibroin cryogels can be used to promote cellular chemotaxis, enhance cell proliferation, enhance extracellular matrix production, promote calcified matrix production, and increase angiogenesis. The silk fibroin cryogels can further be used in the treatment of dermal wounds (burns, chronic wounds, etc.), bone tissue engineering and oral and maxillofacial repair.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN109942677APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisMetabolism disorderAntipyreticAmino acid side chainApoptosis
The invention discloses a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and a derivative and application thereof and particularly relates to a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide shown in SEQ ID No.1-15 and a derivative thereof. The derivative of the binding peptide is a product obtained in the mode that conventional modification is conducted on a CMKLR1 binding peptide amino acid side chain group and an amino terminal or a carboxyl terminal of a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide fragment or a product obtained in the mode that a label for detection or purification of polypeptide or protein is linked to the CMKLR1antagonistic polypeptide. The binding peptide and the derivative thereof can be combined with CMKLR1 in vitro, by stopping combination of chemerin / RvE1 and CMKLR1, the cAMP concentration is changed,the calcium influx caused by chemerin and cell chemotaxis caused by chemerin are inhibited, proliferation of ovarian carcinoma cells can be inhibited, apoptosis of the ovarian carcinoma cells is promoted, and effective micromolecule treatment drugs are provided for female reproductive diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
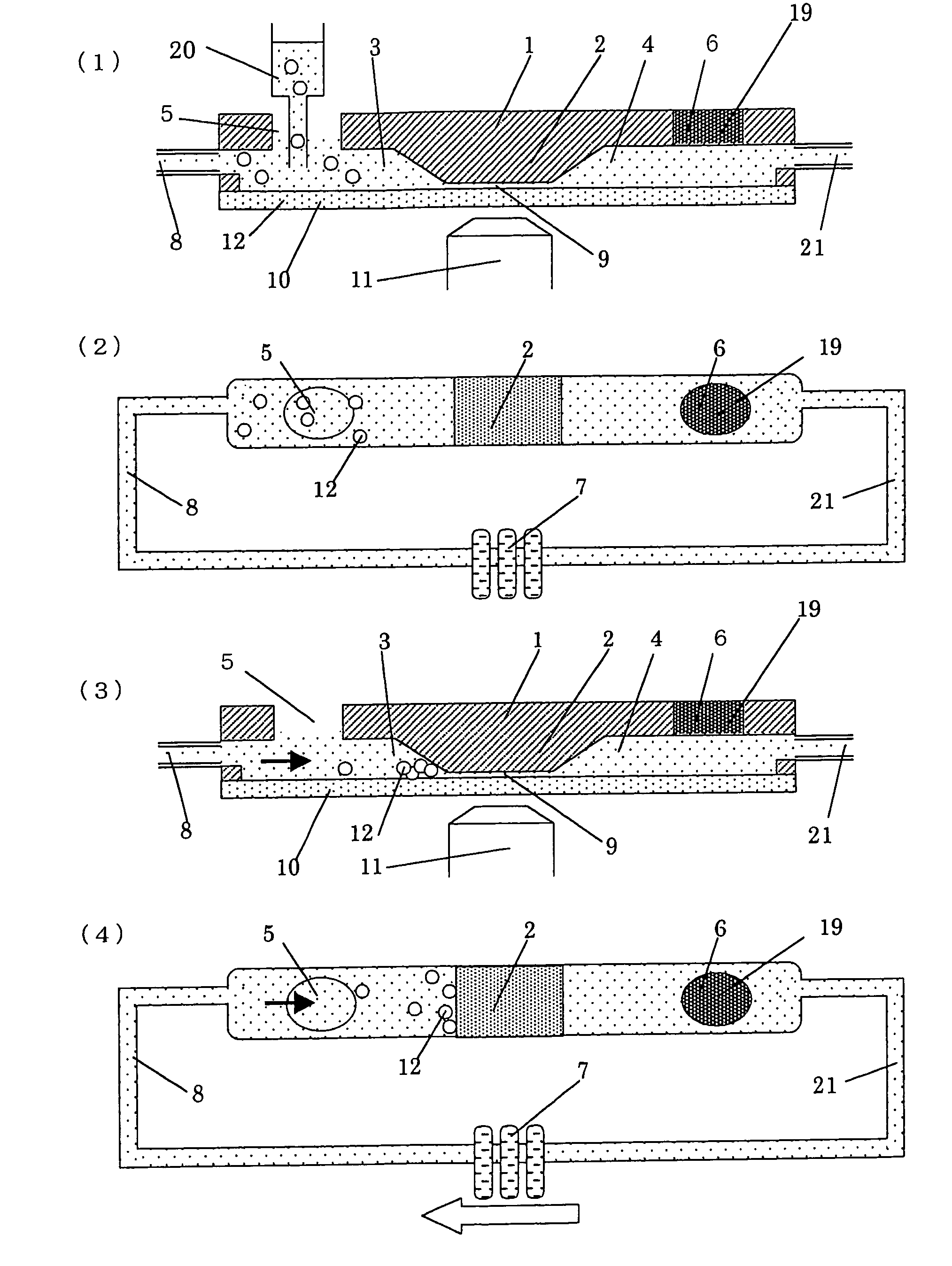
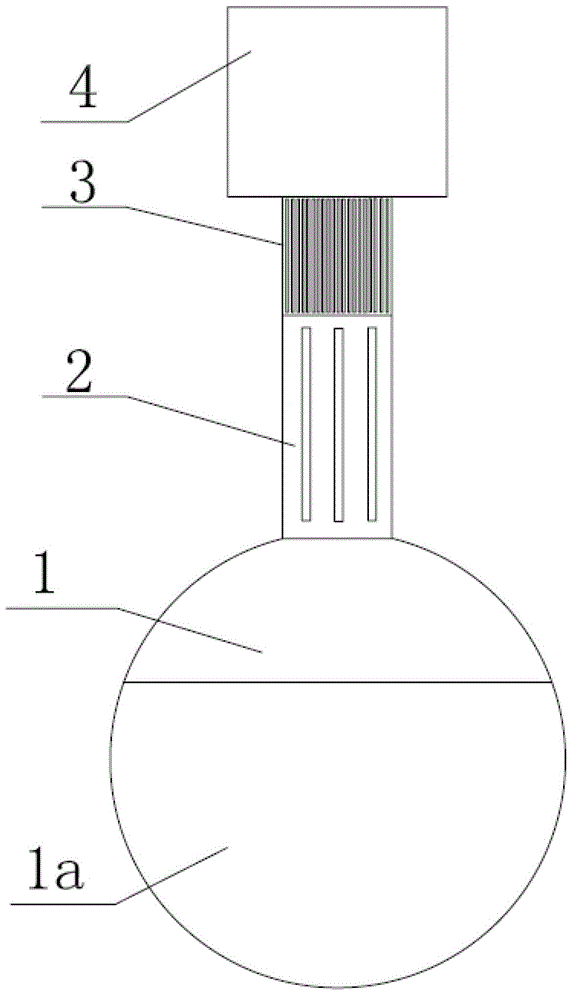
Cell chemotaxis detection device
PendingCN113046238AImprove injection abilityImprove job stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringControl theory
The invention discloses a cell chemotaxis detection device, and belongs to the technical field of cell chemotaxis detection devices. The cell chemotaxis detection device comprises a base, a first sliding rail, a second sliding rail, a cell operating frame, a cell operating floor and a cell injection frame. The first sliding rail and the second sliding rail are fixedly connected to the base, the cell operating frame is slidably connected to the side, away from the base, of the first sliding rail and the second sliding rail, the cell operating floor is fixedly connected into the cell operating frame, and the cell injection frame is fixedly connected to the cell operating floor. The base is further fixedly connected with a first fixing assembly and a second fixing assembly. The cell chemotaxis detection device is simple in structure, and the concentration gradient formed by chemotactic factors and other sample samples in a flow path can be stably kept; and meanwhile, the working stability of the cell injection frame can be improved through cooperation of the first fixing assembly and the second fixing assembly.
Owner:河南和泽干细胞基因工程有限公司
A cmklr1 antagonistic polypeptide and its derivatives and applications
The invention discloses a CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide and its derivatives and applications, specifically related to the sequence of SEQ ID No.1‑9 and its derivatives. The derivatives of the binding peptide are CMKLR1 binding peptide amino acid side chain group, CMKLR1 The product obtained by conventional modification of the amino-terminal or carboxyl-terminal of the antagonistic polypeptide fragment, or the product obtained by linking a tag for polypeptide or protein detection or purification on the CMKLR1 antagonistic polypeptide; the binding peptide and its derivatives can bind CMKLR1 in vitro , by blocking the combination of chemerin / RvE1 and CMKLR1 to change the concentration of cAMP, inhibit the calcium influx caused by chemerin, and inhibit the cell chemotaxis caused by chemerin, and provide effective therapeutic small molecule drugs for diseases with high expression of CMKLR1 receptors.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
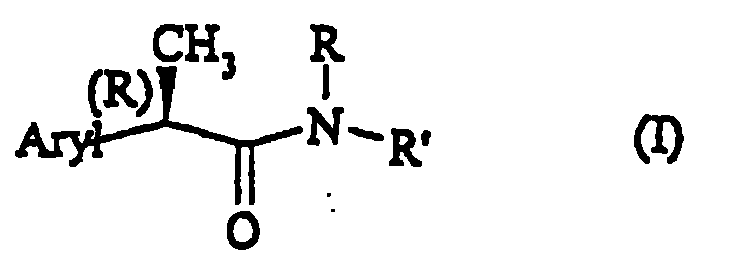
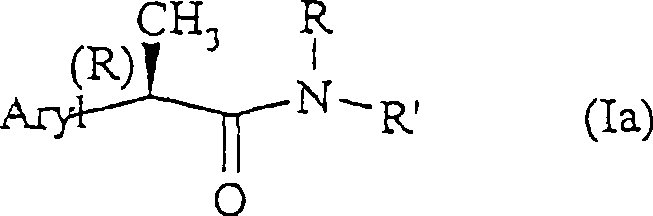
Amide for inhibition of IL-8-induced chemiotaxis of neutrophil leucocytes
InactiveCN100513386CHigh amide activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticWhite blood cellFibrosis
N-(2-arylpropionyl)-amides represented by the general formula (I) are described. The present invention also describes its preparation method and its pharmaceutical preparation. The amides of the present invention are used to prevent and treat tissue damage caused by the acute recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (leukocytes PMN) at the site of inflammation. Specifically, the present invention relates to the R enantiomer of N-(2-aryl-propionyl)amide represented by general formula (I) for inhibiting neutrophils induced by interleukin 8 (IL-8). Cell chemotaxis. The compounds of the invention are useful in the treatment of psoriasis, ulcerative cholelithitis, glomerulonephritis, acute respiratory insufficiency, spontaneous fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:DOMPE FARM SPA
HIV-encoded chemoattractant
InactiveUS20050158341A1Improve stability and persistenceEasy and inexpensive to produceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseLocalized disease
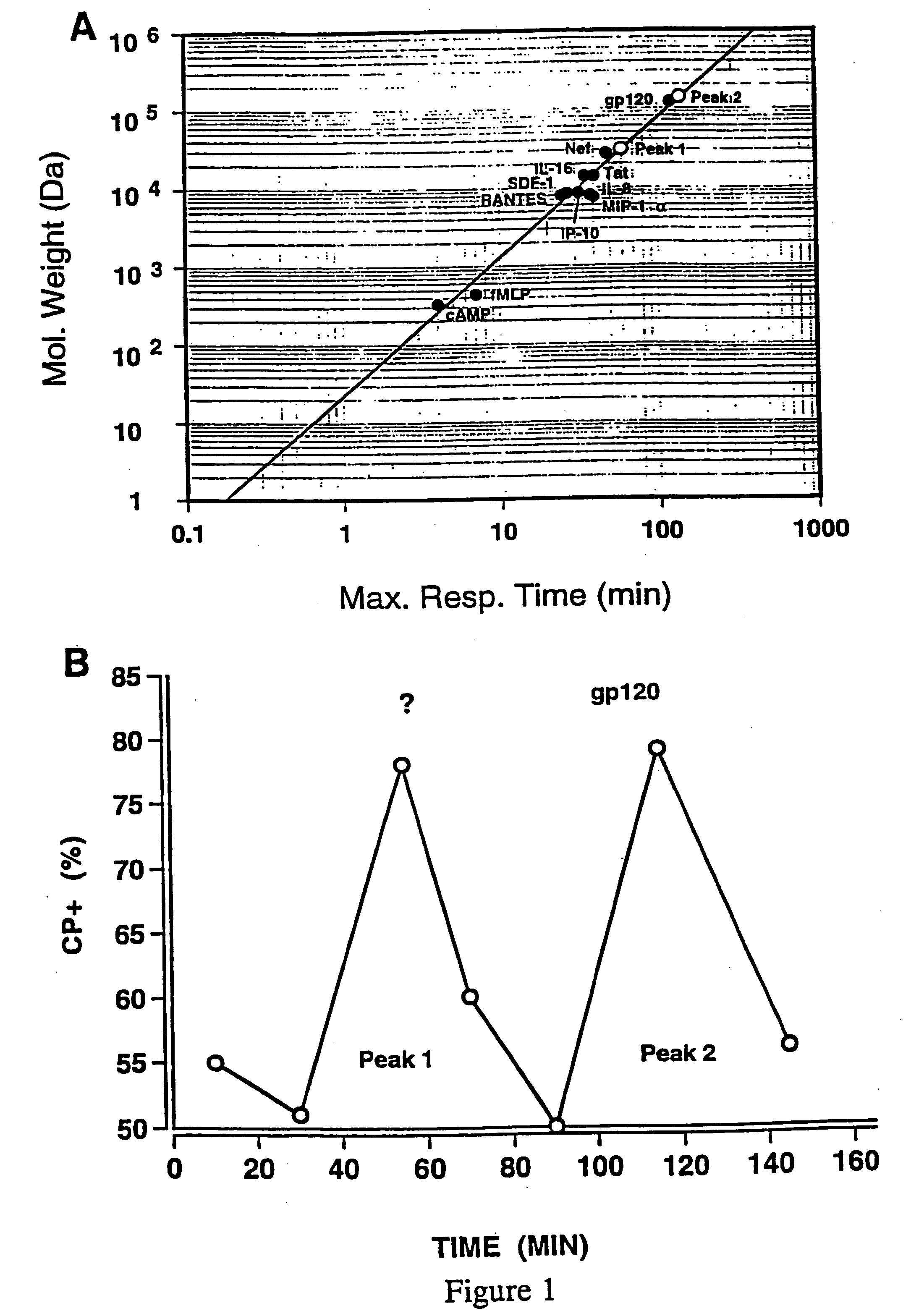
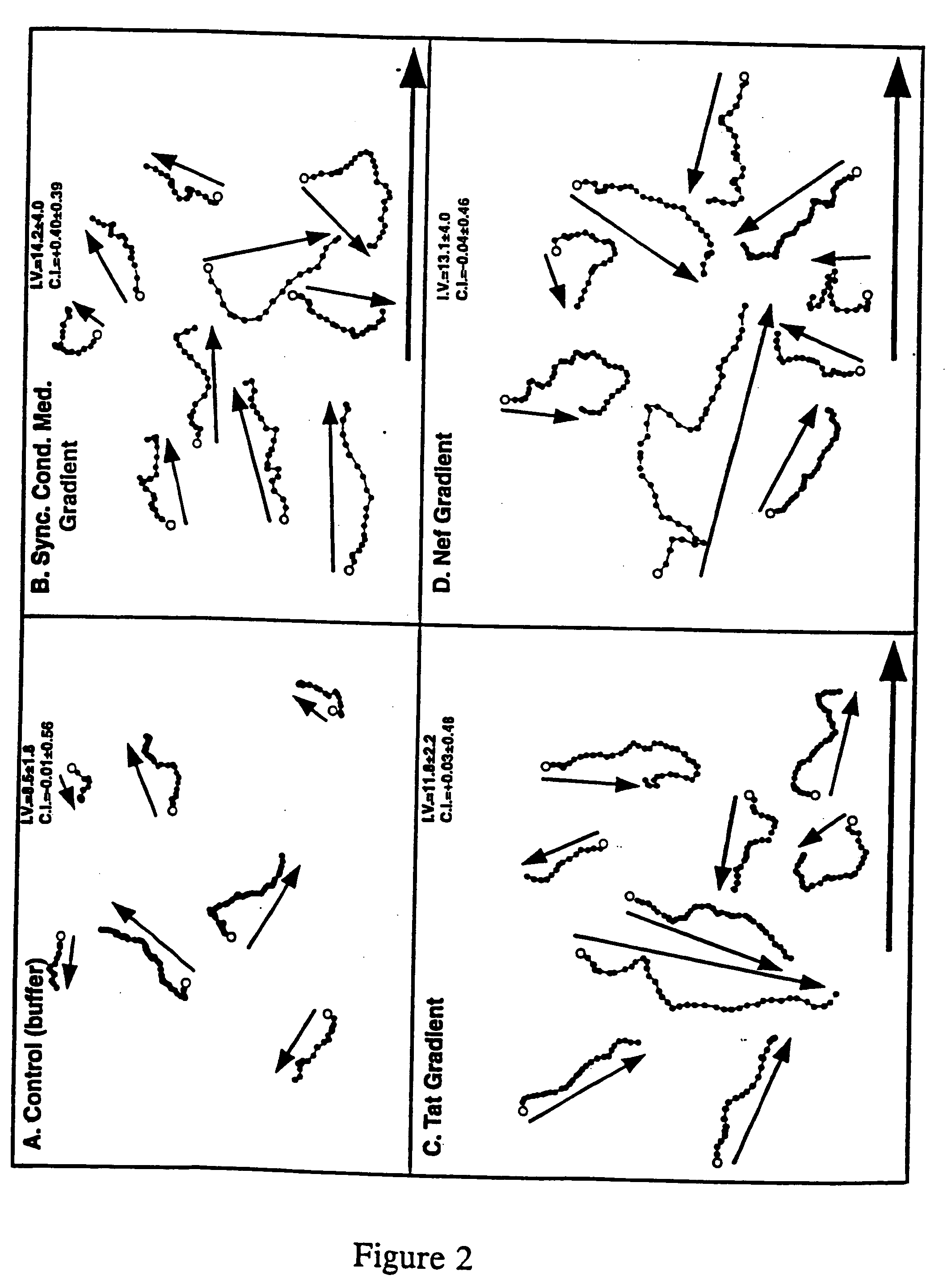
The combination of HIV proteins Tat and Nef is chemotactic for CD4+ cells. Utilizing the capacity of Tat and Nef to modulate CD4+ cell trafficking and infiltration, the invention provides various treatment modes for individuals infected with HIV. The invention further provides treatment modes for other localized diseases by controlling CD4+ cell trafficking and infiltration. In particular, the invention provides methodology for promoting CD4+ cell chemotaxis to a localized site of infection as a means of augmenting the efficacy of extant chemotherapeutic methods. The invention further provides methodology for diverting CD4+ cell infiltration from a localized site where the presence of CD4+ cells is detrimental to the clinical outcome, by providing a composition comprising Tat and Nef at a distinct site, such as blood, within the individual where the accumulation of CD4+ cells is less detrimental.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
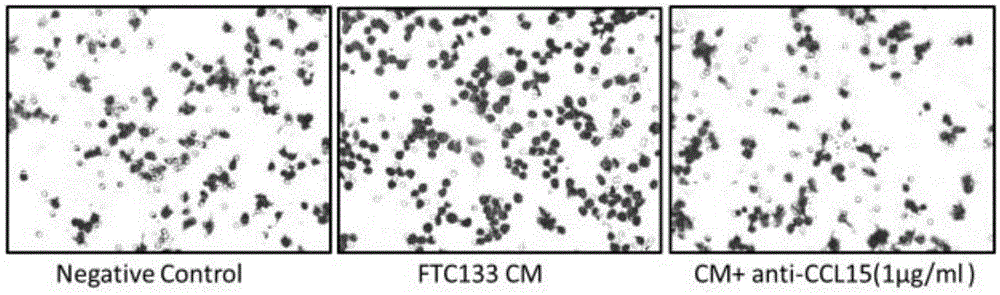
Application of reagents for detecting ccl15 chemokines in preparation of reagents for screening thyroid follicular carcinoma
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A microfluidic chip and a research method for cell chemotaxis
ActiveCN103952300BBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous membraneStudy methods
The aim of the invention is to provide a micro-fluidic chip and a cell chemotaxis movement research method. The micro-fluidic chip is characterized in that the micro-fluidic chip comprises a glass substrate, a first diaphragm and a second diaphragm; the first diaphragm is provided with culturing units; the second diaphragm is provided with micro-channels; a porous membrane exists between the culturing units of the first diaphragm and the micro-channels of the second diaphragm; the number of the culturing units of the first diaphragm is same to the number of the micro-channels of the second; and the micro-channels on the second diaphragm are respectively located above the culturing units of the first diaphragm. The micro-fluidic chip can be used in the research of the selective chemotaxis movement condition of cells in the micro-channels when the cells flow through the culturing units. The micro-fluidic chip likes a bionic model characterized in that a branching capilary goes through organs; and compared with the traditional cell chemotaxis research methods, the research method is a new method for researching the selective chemotaxis movement of the cells in the flowing process, and has important biomedical research values and economic values.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
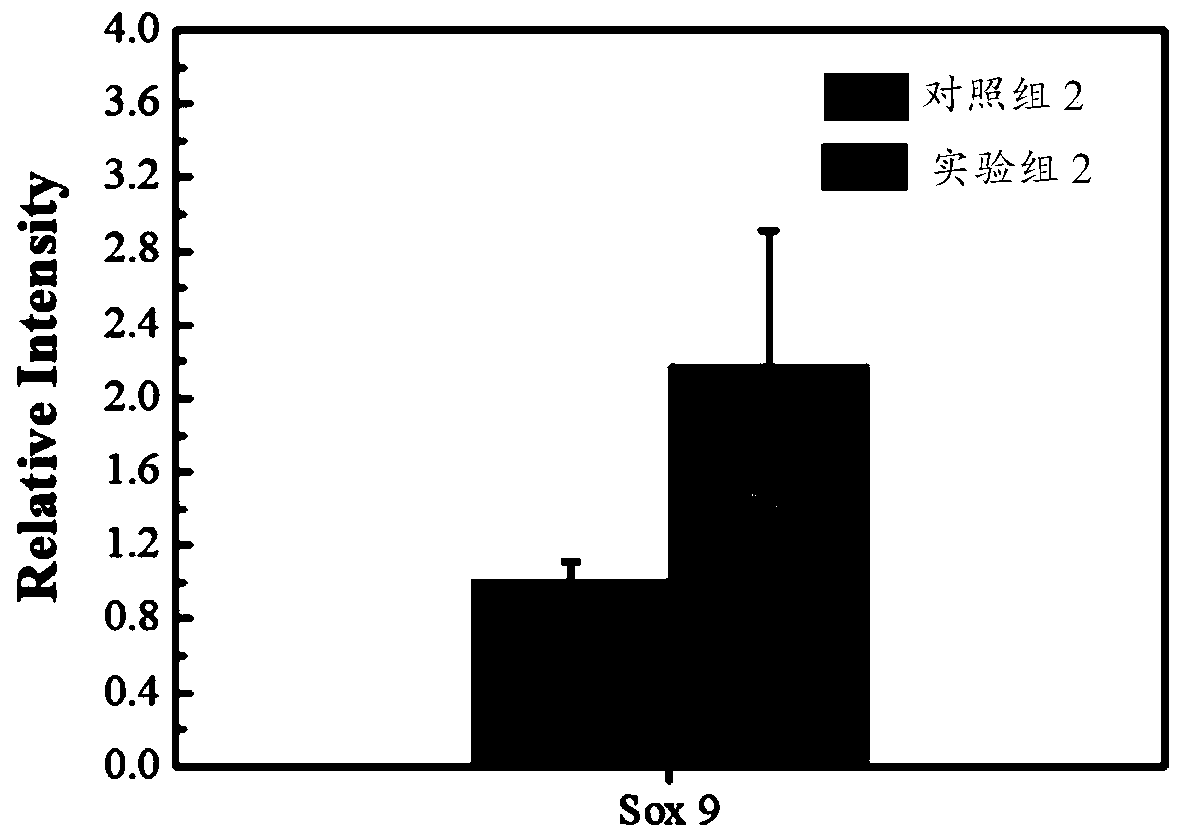
Endogenous cell chemotaxis and chondrogenic differentiation induction bioactive scaffold and application thereof
InactiveCN109350767AImprove repair effectSolve the shortcomings of low differentiation efficiencyTissue regenerationProsthesisFreeze-dryingCell chemotaxis
The invention discloses an endogenous cell chemotaxis and chondrogenic differentiation induction bioactive scaffold and a preparation method and application thereof in preparation of cartilage defectrepair materials. The bioactive scaffold comprises SDF-1, TGF-beta, fibroin and a porous scaffold. The bioactive scaffold takes natural fibroin as a medium, and by a freeze drying technique, a gene cell derived factor (SDF-1) with a chemotaxis effect, a transforming growth factor-beta (TFG-beta) and fibroin are fixed into the porous scaffold through crystal phase transition. When the scaffold is transplanted to a cartilage injury / or defect area, the chemotaxis factor SDF-1 can be released for a long time to enable chemotaxis migration of autologous endogenous cells to the injury area while chondrogenic differentiation can be induced by TGF-beta in long-term controlled release, and accordingly endogenous cell attraction and implementation of effective cartilage injury repair are realized.
Owner:陈元峰 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com