Thermoelectric material, method for producing same, and thermoelectric conversion module using same
A technology of thermoelectric materials and thermoelectric layers, which is applied in the manufacture/processing of thermoelectric devices, materials for the junction leads of thermoelectric devices, thermoelectric devices that only use the Peltier or Seebeck effect, etc., can solve the problems of thermal conductivity reduction and achieve increased Effect of power factor and conductivity improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
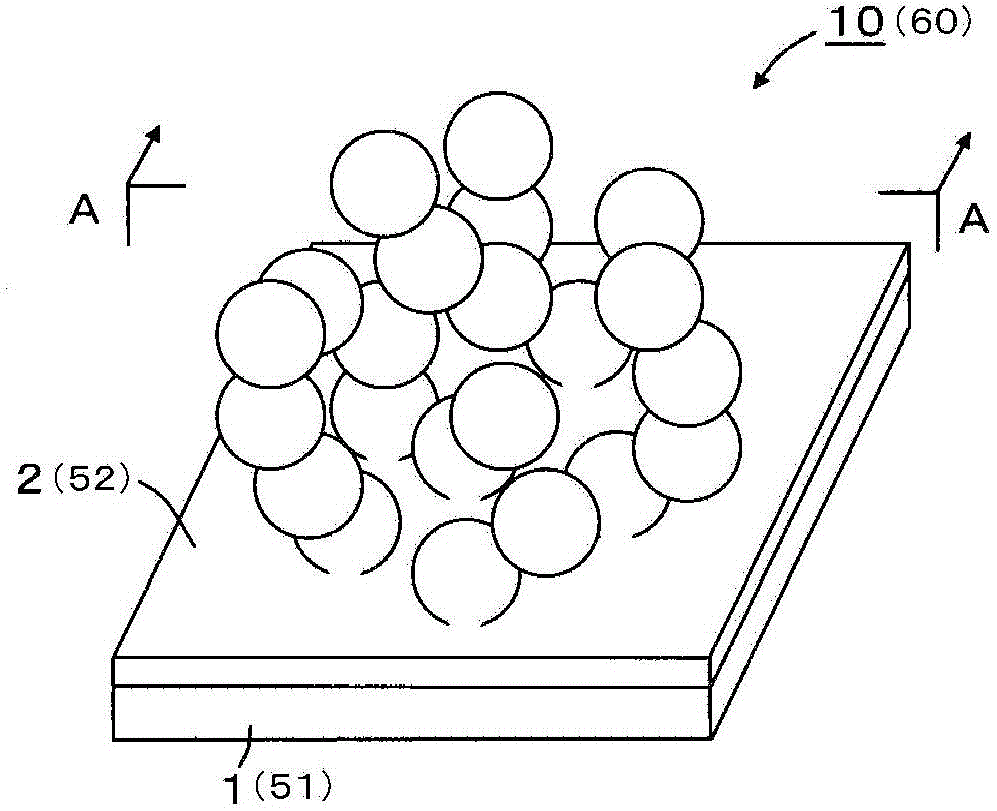
[0066] will refer to figure 1 and 2 A thermoelectric material 10 according to a first embodiment of the present invention is described.
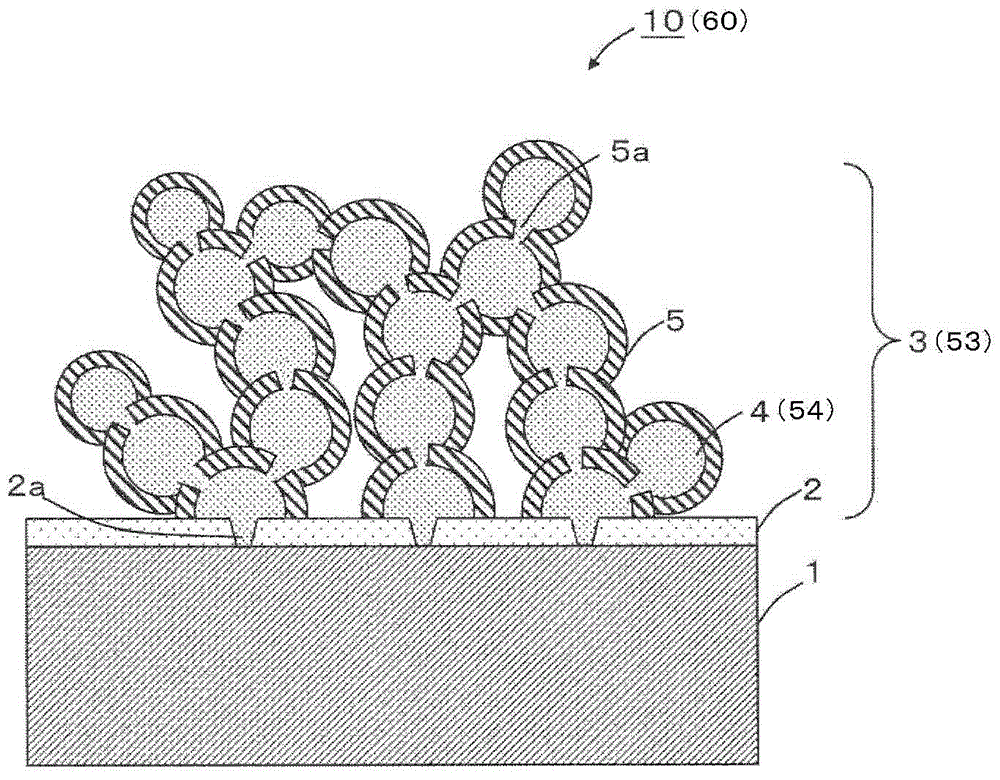
[0067] as in figure 1 and 2 As shown in , the thermoelectric material 10 includes a silicon substrate 1 , a silicon oxide film 2 formed on the silicon substrate 1 , and a thermoelectric layer 3 disposed on the silicon oxide film 2 . As the silicon substrate 1, a single crystal silicon substrate is preferably used. The silicon oxide film 2 is preferably an ultra-thin oxide film as thick as about a single layer or double layers of Si. The thermoelectric layer 3 has a configuration in which a plurality of semiconductor nanodots 4 each surrounded by a barrier layer (hereinafter, referred to as a barrier layer) 5 are stacked so as to form a particle-filled structure.
[0068] Nanodots herein refer to nanocrystals having nanoscale dimensions having a substantially spherical or substantially elliptical shape. It is to be noted that the nanodo...
no. 2 approach
[0104] Reference will be made to describe the first embodiment figure 1 etc. describe the thermoelectric material 60 according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
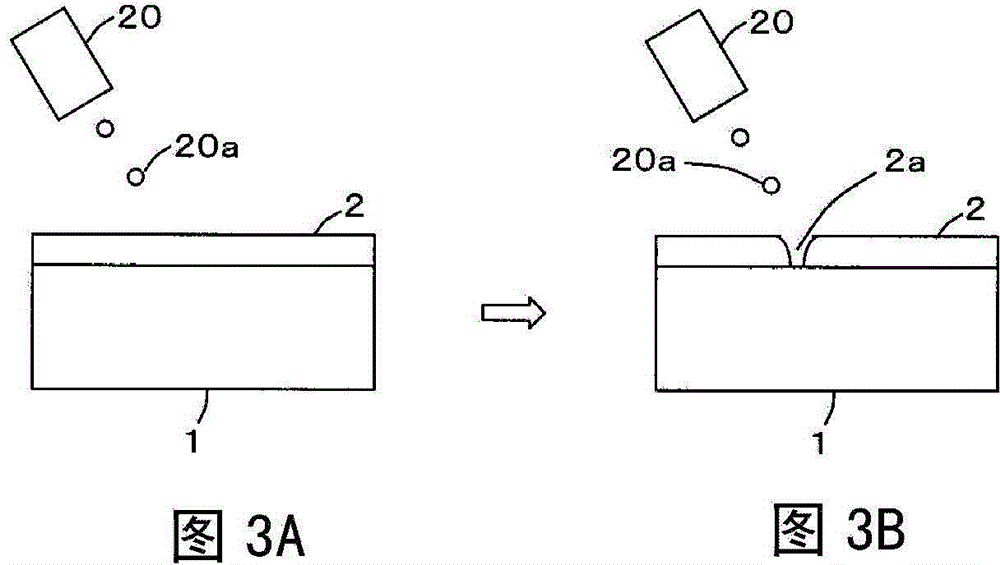
[0105] In the growing step S4 of the method for manufacturing a thermoelectric material according to the first embodiment, irradiation is performed with a molecular beam of the material (eg, Si, Ge, SiGe, or silicide of nanodots 4) (see Figures 4A to 4C ). Meanwhile, in the growing step S4 according to this embodiment, irradiation is performed with a molecular beam of a dopant (ie, a donor atom or an acceptor atom other than the molecular beam of the material of the nanodots 54 ). Thus, the nanodots 54 of the thermoelectric layer 53 are doped, and the thermoelectric material 60 functions as a p-type semiconductor or an n-type semiconductor. Except for the above, the configuration of the thermoelectric material 60 and the steps of the method of manufacturing the thermoelectric material 60 are the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com