Device and method for measuring magnetostriction coefficient through linear frequency modulation multi-beam laser heterodyne second harmonic method
A technology of magnetostriction coefficient and linear frequency modulation, applied in the field of optical measurement, can solve the problem of low measurement accuracy of ferromagnetic material length variation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
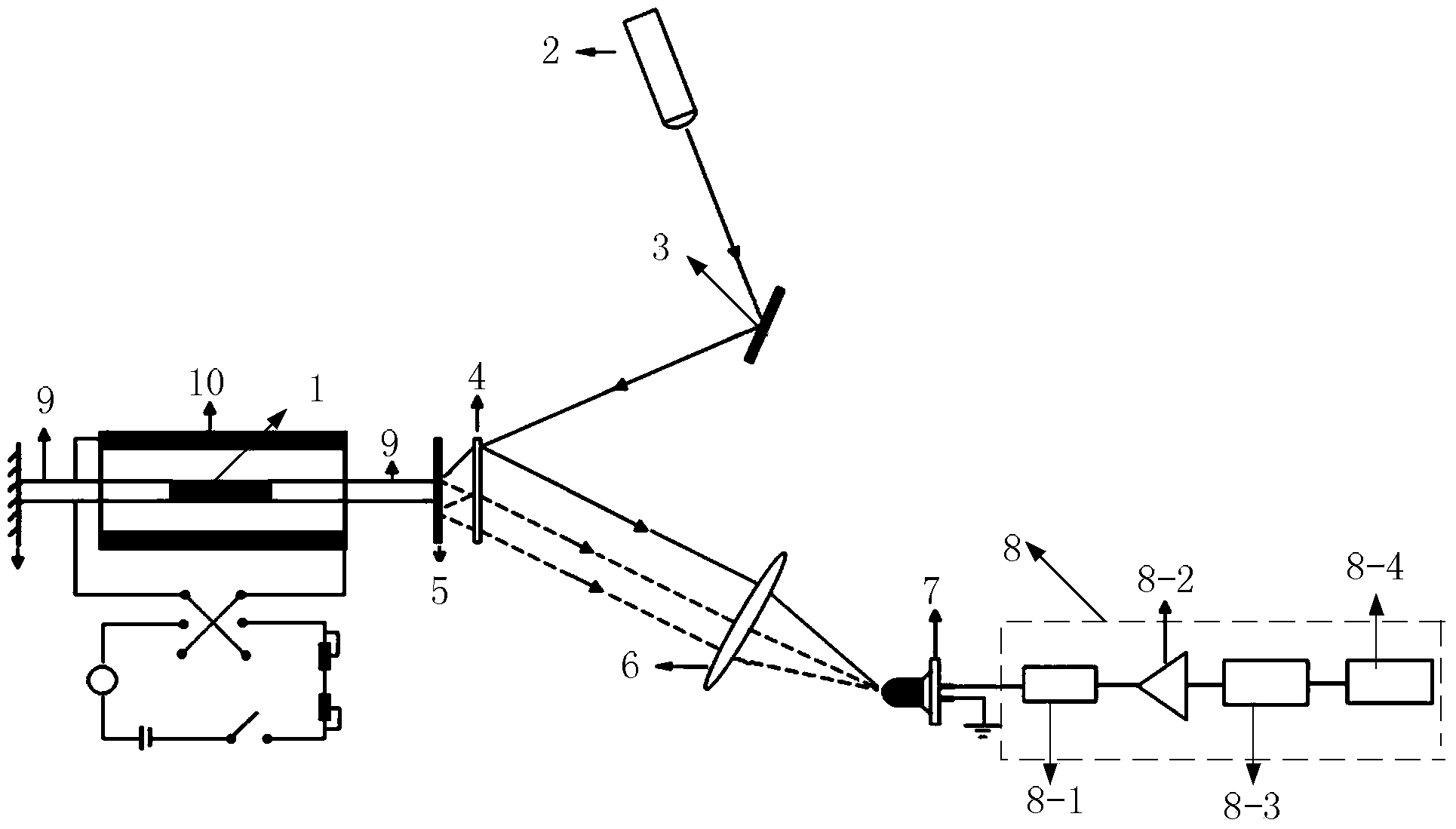
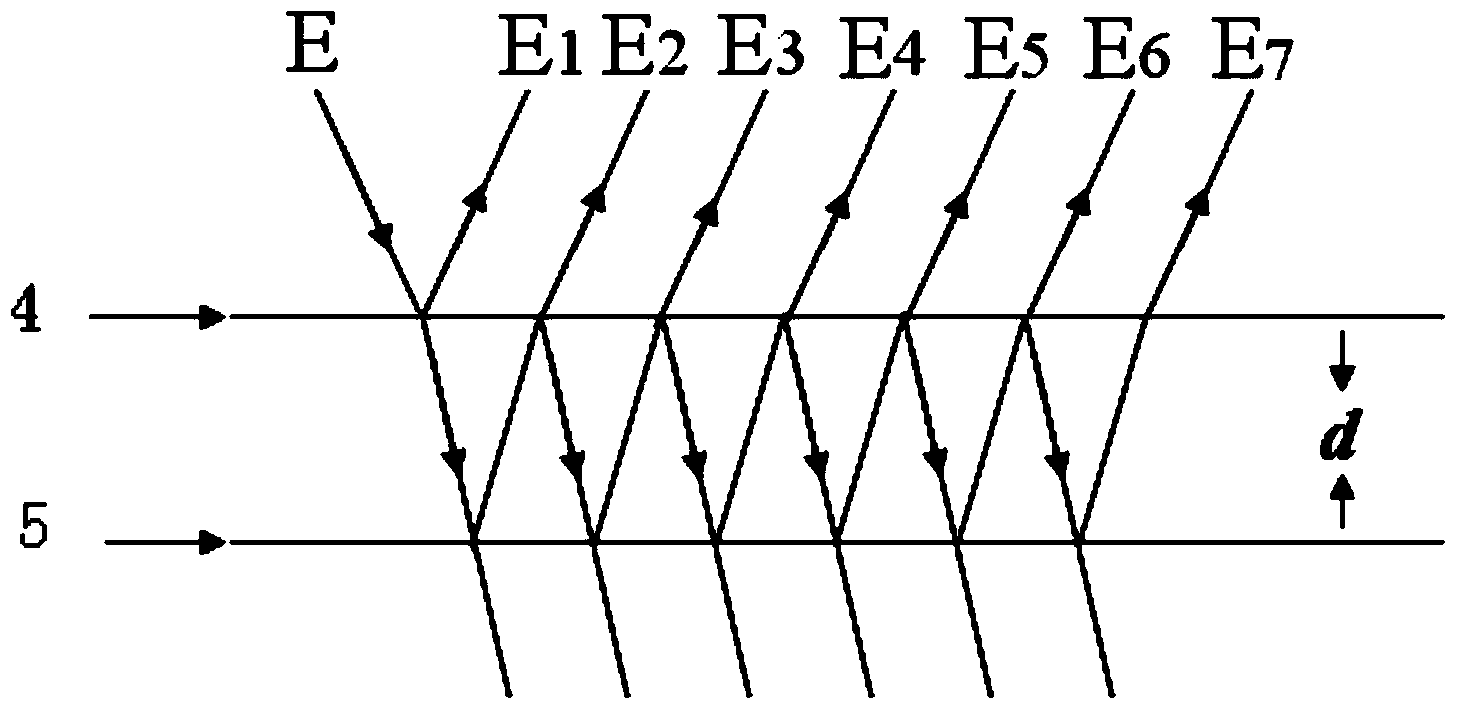
[0057] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe the present embodiment, the device for measuring the magnetostriction coefficient by the chirp multi-beam laser heterodyne second harmonic method described in the present embodiment, it includes the ferromagnetic material sample 1 to be measured, and it also includes the chirp laser 2, the first plane mirror 3, thin glass plate 4, second plane mirror 5, converging lens 6, photodetector 7, signal processing system 8, two fixed rods 9 and excitation coil 10,
[0058] The two ends of the ferromagnetic material sample 1 to be tested are respectively bonded with a fixed rod 9, the free end of one fixed rod 9 is fixed by a fixing piece, and the free end of the other fixed rod 9 is bonded and fixed to the back of the second plane reflector 5 ; The ferromagnetic material sample 1 to be tested is placed in the center of the excitation coil 10; the excitation coil 10 is powered by a DC stabilized power ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
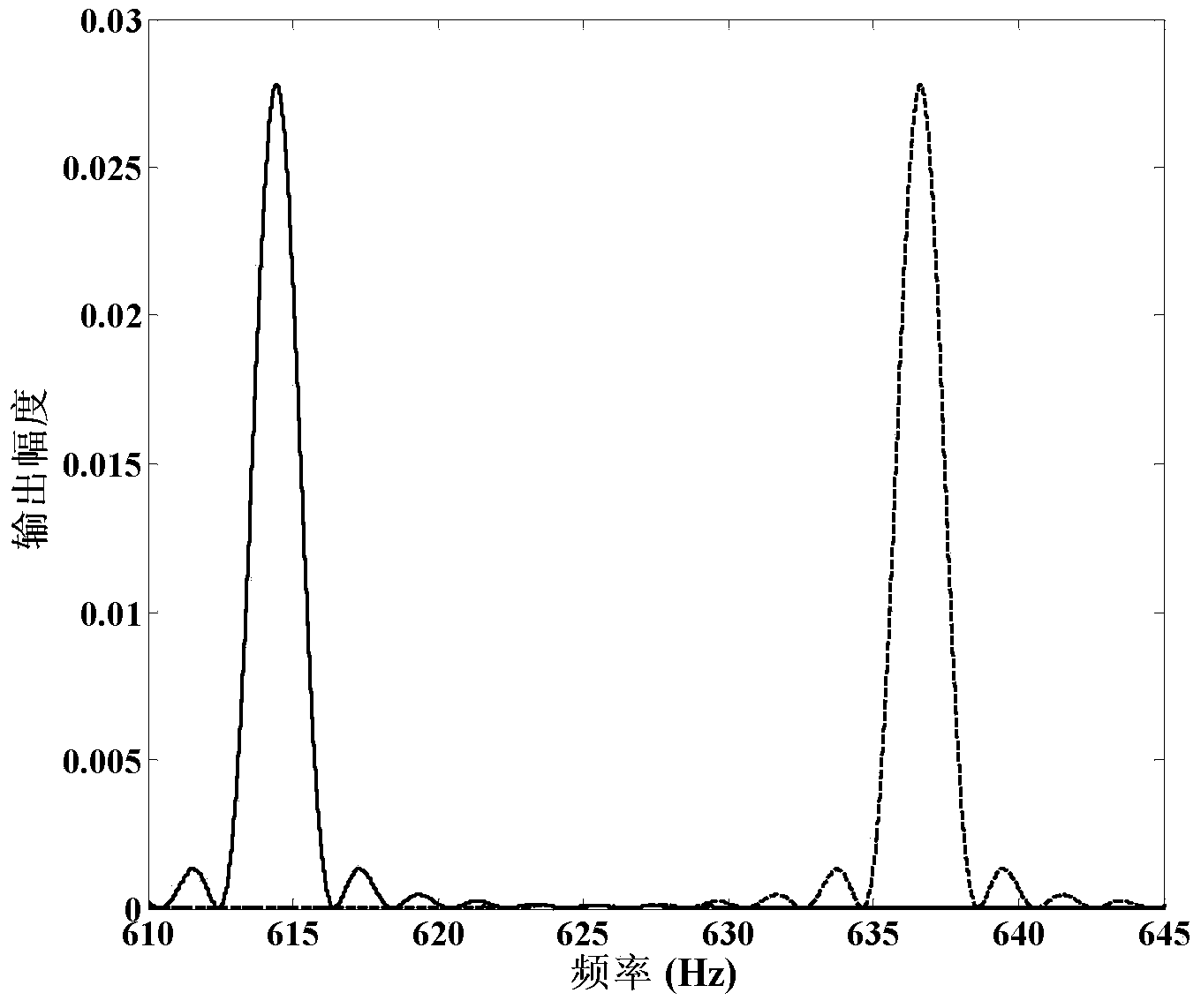
[0061] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 1 Illustrate this embodiment, this embodiment will further illustrate embodiment one, the signal processing system 8 described in this embodiment is made up of filter 8-1, preamplifier 8-2, analog-to-digital converter 8-3 and digital signal processor 8-4 composition,
[0062] The filter 8-1 is used to receive the photocurrent signal output by the photodetector 8, the filter 8-1 outputs the filtered signal to the preamplifier 8-2, and the analog signal amplified by the preamplifier 8-2 is sent to the analog-to-digital conversion 8-3, the analog signal is converted into a digital signal by the analog-to-digital converter 8-3 and then sent to the digital signal processor 8-4.
[0063] Filter 8-1 is a low pass filter.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: This embodiment further describes Embodiment 1 or 2. The initial distance between the thin glass plate 4 and the second flat mirror 5 in this embodiment is 30 mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com