Low-temperature inorganic phase-change heat storage material and preparation method thereof
A heat storage material, inorganic phase change technology, applied in heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to meet production requirements, and achieve the effects of suitable phase change temperature, stable performance and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0020] The preparation method of the above-mentioned low-temperature inorganic phase-change thermal storage material comprises the following steps:
[0021] 1) Put the test tube containing disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate into hot water at a constant temperature of 50°C, and stir until completely melted;
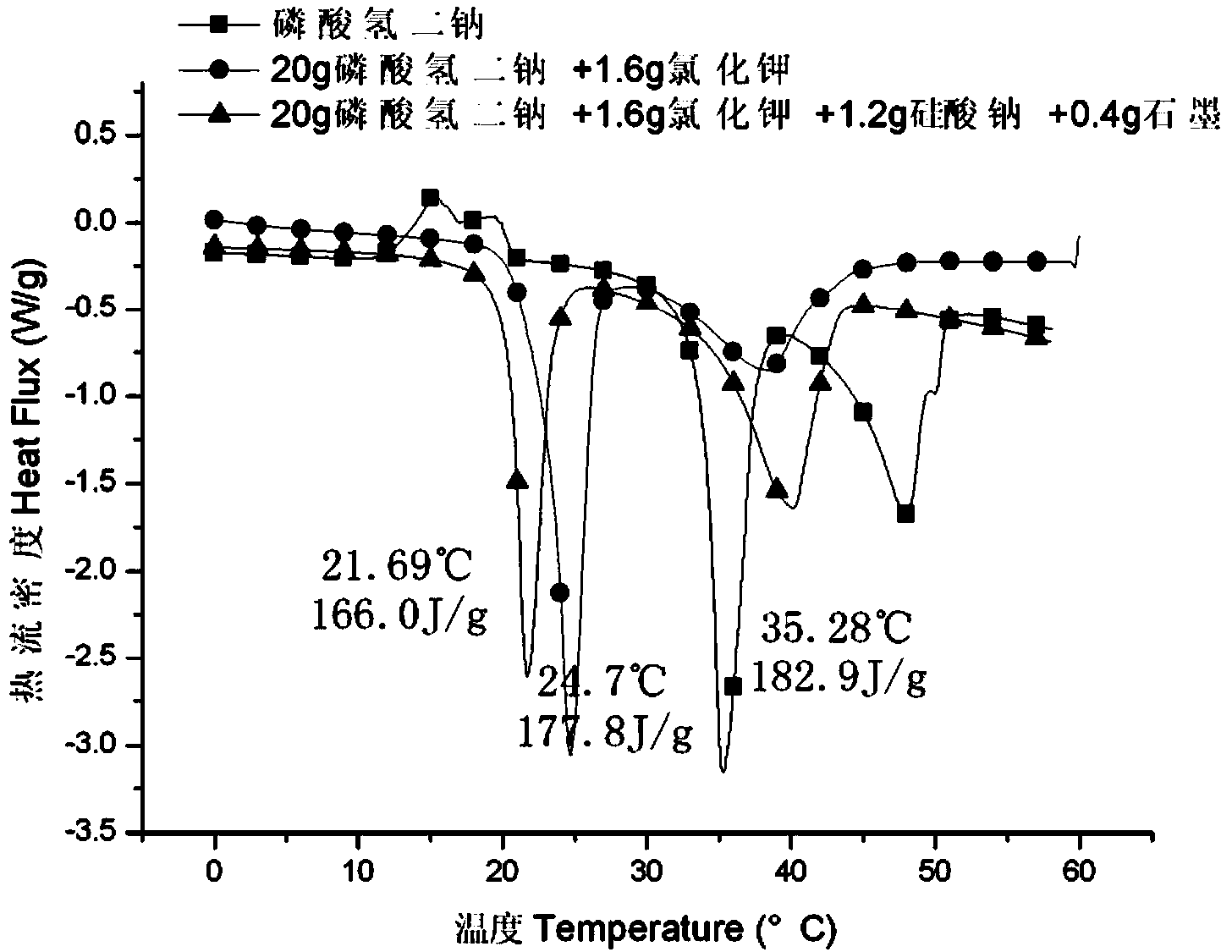
[0022] 2) then add the Potassium Chloride of recipe amount in dodecahydrate disodium hydrogen phosphate, melt, obtain dodecahydrate disodium hydrogen phosphate and potassium chloride mixture, the dodecahydrate disodium hydrogen phosphate and potassium chloride mixture The phase transition temperature drops to 26.5°C, and the supercooling degree is 10.7°C;
[0023] 3) Add nucleating agent graphite and thickener sodium metasilicate nonahydrate to the mixture of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate and potassium chloride, heat and melt to prepare a phase transition temperature of about 25°C, and a phase transition latent heat value of 170J / g or so, supercooling ...
Embodiment 1
[0029] The low-temperature phase-change heat storage material prepared in this embodiment is composed of the following raw materials in mass percentage: Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O: 86.2%; Potassium chloride: 6.9%; Graphite: 1.7%; Sodium metasilicate nonahydrate: 5.2%.
[0030] Tested by the applicant, the low-temperature inorganic phase change heat storage material prepared in this example has a latent heat value of 166 J / g, a melting temperature of 24.7°C, an undercooling degree of less than 0.5°C, no phase separation, and stable performance. The endothermic and exothermic performances are stable after 3000 cycles.
Embodiment 2
[0032] The low-temperature phase-change heat storage material prepared in this embodiment is composed of the following raw materials in mass percentage: Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O: 86.6%; Potassium chloride: 6.8%; Graphite: 1.3%; Sodium metasilicate nonahydrate: 5.3%.
[0033] Tested by the applicant, the low-temperature inorganic phase change heat storage material prepared in this example has a latent heat value of 169 J / g, a melting temperature of 25.3°C, an undercooling degree of less than 0.5°C, no phase separation, and stable performance. The endothermic and exothermic performances are stable after 3000 cycles.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Phase change latent heat value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Latent heat value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com