Method for inducing and culturing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into nerve cells
A technology of stem cells and nerve cells, applied in the field of neurobiology, can solve the problems of low differentiation efficiency of nerve cells, long induction period and low cell differentiation, and achieve the effect of high cell differentiation uniformity and short induction period.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1. Acquisition and cultivation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0029] Neonatal umbilical cords authorized with maternal consent were used as a source of mesenchymal stem cells.
[0030] The neonatal umbilical cord was washed three times in physiological saline containing 1% double antibody to remove the blood stains on the surface, and then cut into small pieces about 1 cm long. Use ophthalmic scissors to cut the umbilical cord longitudinally along the direction parallel to the blood vessels, and peel off the 2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein from the umbilical cord. Peel off the amniotic membrane on the surface, wash the Huatong glue part with normal saline containing 1% double antibody for 3 times, and cut it into pieces to about 1mm 3 size. Evenly spread the shredded tissue blocks on the 75cm 2 Place in the culture bottle at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to make the tissue pieces stick tightly. Add 5ml of medium containing DMEM / F12,...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2. Directed differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro 1
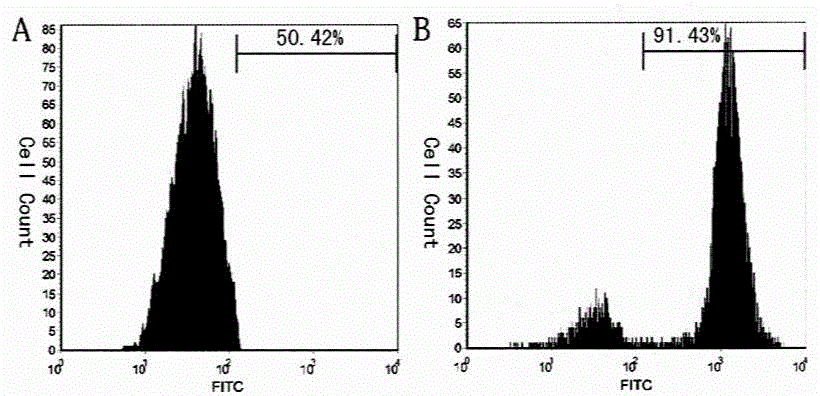
[0033] Freshly passaged P3-6 umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells were used in 5×10 4 Inoculate in a 24-well plate with poly-lysine-coated coverslips per ml, 1ml / well, replace the pre-induction culture medium after 3 days of adherent culture, change the medium in half after 3 days, and terminate the induction on the 3rd day .
[0034] The pre-induction culture medium is DMEM as the base medium, which also contains 50nmol vitamin C, 20U / ml human leukocyte inhibitory factor, 8mM L-glutamine, 5mM thioglycerol (MTG), 80U / ml penicillin, 80μg / ml streptomycin.
[0035] The cells obtained from the pre-induction culture were divided into 5×10 4 Inoculate at a cell density of / ml for monolayer adherent induction culture, replace the induction medium for induction culture after 2 days of adherence culture, change the medium for half of the amount after 3 days, terminate the induction on ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3. Directed differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro 2
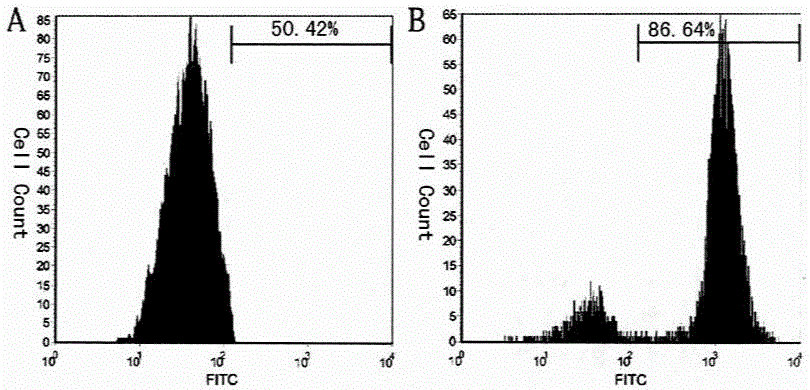
[0039] Freshly passaged P3-6 umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells were used in 5×10 4 Inoculate in a 24-well plate with poly-lysine-coated coverslips, 1ml / well, replace the pre-induction culture medium after 3 days of adherent culture, change the medium in half after 3 days, and terminate the induction on the 4th day .
[0040] The pre-induction culture medium is DMEM as the base medium, which also contains 20nmol vitamin C, 10U / ml human leukocyte inhibitory factor, 1mM L-glutamine, 2mM thioglycerol (MTG), 100U / ml penicillin, 100μg / ml streptomycin.
[0041] The cells obtained from the pre-induction culture were divided into 5×10 4Inoculate at a cell density of / ml for monolayer adherent induction culture, replace the induction medium for induction culture after 2 days of adherence culture, change the medium in half after 3 days, terminate the induction on the 6th day, and obta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com