Preparation method of high-coking resistance selective-hydrogenation catalyst
A technology for selective hydrogenation and catalysts, applied in the fields of hydrogenation to hydrocarbons, chemical instruments and methods, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing catalyst coking, reducing green oil production and prolonging service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
[0045] Adjust the pH value of the Ni precursor aqueous solution, prepare a Ni microemulsion at 20°C, put 100 g of the burnt carrier into the prepared microemulsion for impregnation, and dry the filtered solid after impregnation, roast, and then Prepare a Pd aqueous solution, adjust its pH to 2.0, add the calcined Ni-containing carrier into the Pd aqueous solution for impregnation, dry and calcinate after the impregnation, and obtain the required catalysts 1-3. The specific parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0046] Table 1 embodiment catalyst preparation concrete parameter
[0047]
[0048]
[0049] Measure Pd content and nickel content in embodiment 1~3 with atomic absorption spectrometry, in embodiment 1, the content of Pd is 0.03%, and nickel content is 0.079%; Among the embodiment 2, Pd content is 0.038%, and nickel content is 0.35%; Pd content is 0.045% among the embodiment 3, and nickel content is 3.5%. The catalyst prepared in Examples 1-3 is placed in a fixed-be...
Embodiment 1
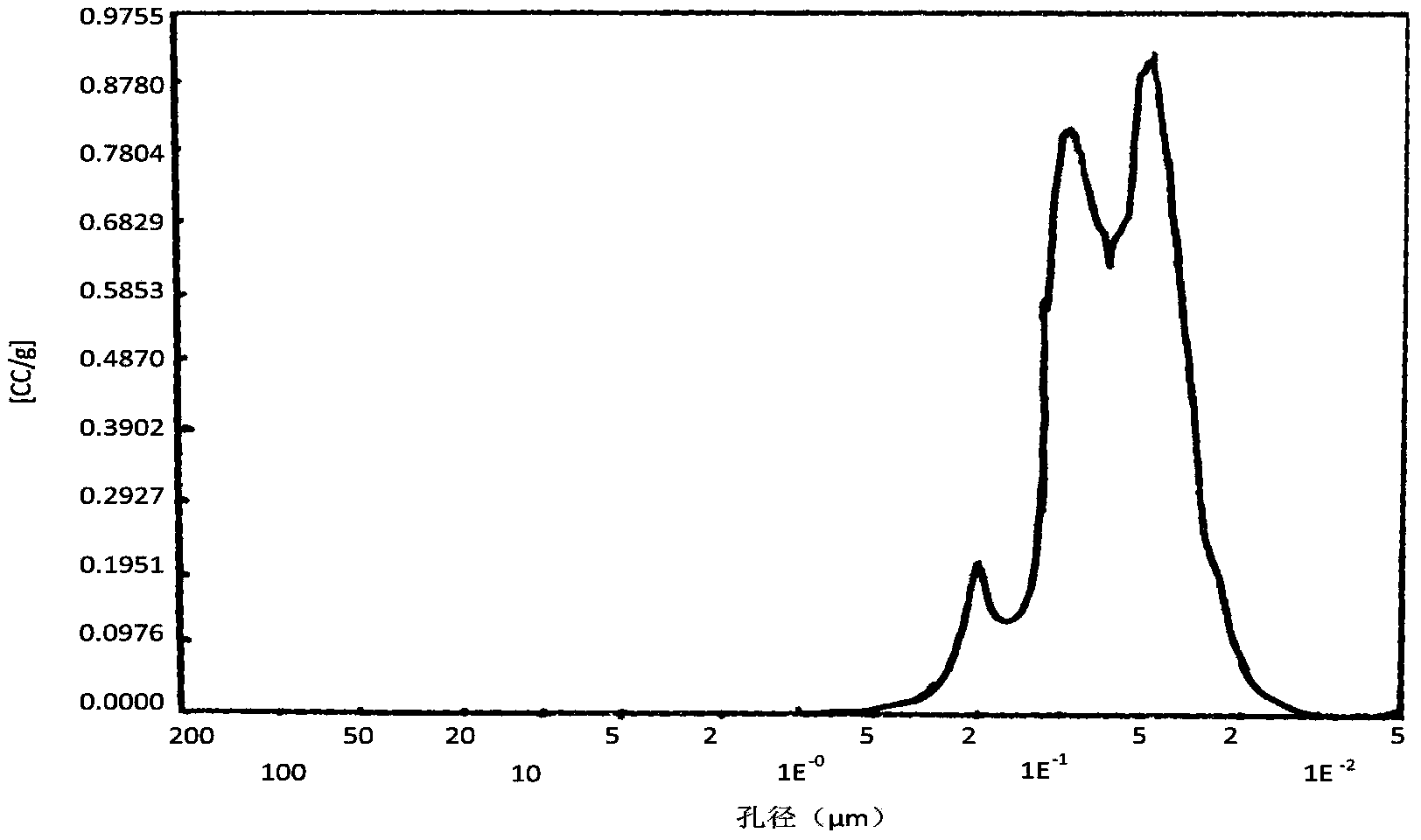
[0070] Except for the carrier used in Example 1 and contrast agent 1, the rest of the preparation methods and active components are the same. As can be seen from the performance comparison of Example 1 and comparative catalyst 1, when the active component content is the same, the initial conversion rate of both acetylene is the same, and the catalyst provided by the present invention has higher selectivity than the contrast agent, and after the catalyst runs for 1000h, The conversion and selectivity of both catalysts decreased, but the activity and selectivity of catalyst 1 of the present invention decreased much less than that of contrast agent 1, and the coking amount of the catalyst of the present invention after 1000 hours of operation was significantly smaller than that of contrast agent 1. This shows that the present invention agent adopts the carrier of bimodal pore distribution, has reduced the impact of gas diffusion on catalyst performance, and catalyst selectivity im...
Embodiment 2
[0071]Example 2 and contrast agent 2 both used the same bimodal pore distribution carrier, and no Ni was added to contrast agent 2. By the performance comparison of embodiment 2 and comparative catalyst 2, it can be seen that using the same carrier, under the same situation of catalyst active component content, the initial conversion rate and selectivity of the two are the same, and after 1000 hours of operation, both Activity and selectivity all have decline, but contrast agent 2 is much less than the activity and selectivity decline of catalyst 2 of the present invention, and the coking amount of comparison catalyst 2 after running 1000 hours is far greater than catalyst 2 of the present invention, this It shows that the addition of Ni has a significant effect on reducing the coking of the catalyst, and the coking of the catalyst will seriously affect his activity and selectivity.
[0072] Embodiment 3 and comparative example 3 all adopt identical carrier, and active compone...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com