Organic light emission diode device and fabrication method thereof
An electroluminescence device and electroluminescence technology, which are applied in the directions of organic semiconductor devices, materials of organic semiconductor devices, and electric solid devices, etc., can solve the problem of high manufacturing cost, the polarizing film is easily affected by humidity and ambient temperature, and the brightness of light output is low. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
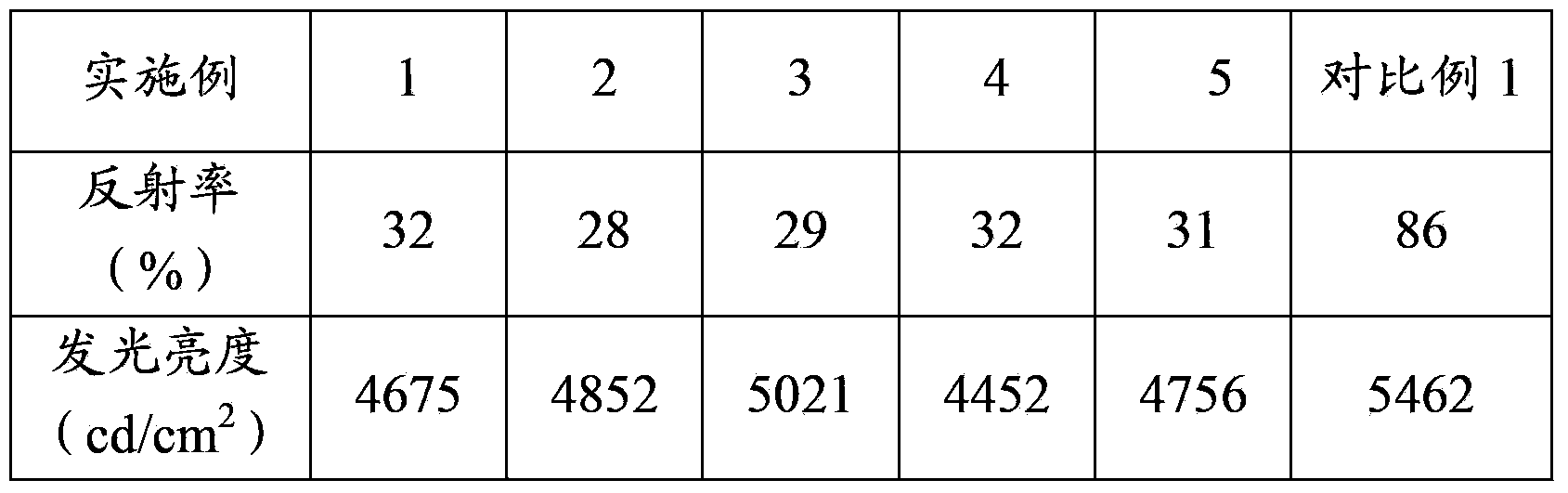
Embodiment 1
[0060] A method for preparing an organic electroluminescent device, comprising the following steps:
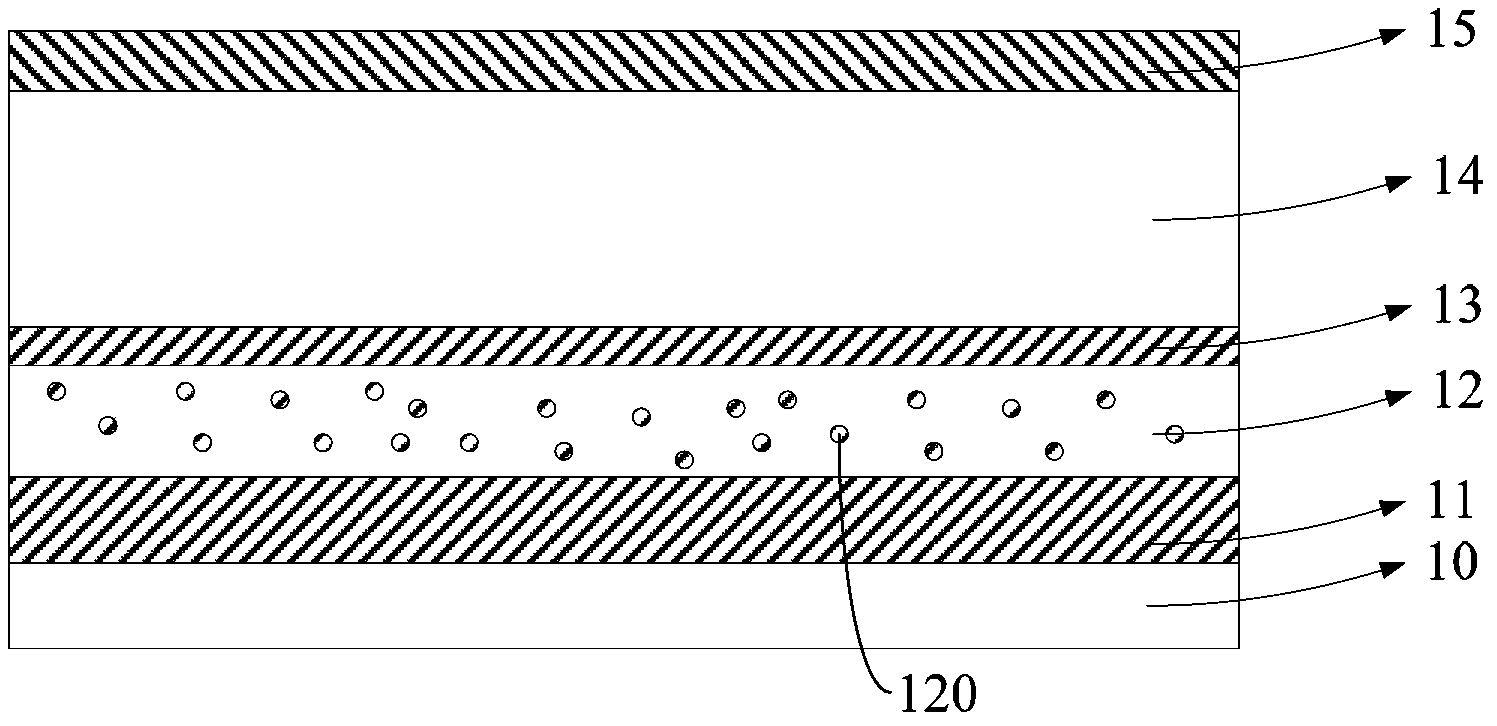
[0061] (1) Place the glass substrate on a 1×10 -4 In the vacuum coating chamber of Pa, a metal Ag film with a thickness of 500nm was prepared on the surface of the substrate by vacuum evaporation as a reflective electrode;
[0062] (2) A light-scattering layer with a thickness of 100 μm is formed on the surface of the reflective electrode by a screen printing process. The material of the light-scattering layer includes titanium dioxide nanospheres and photocurable acrylic resin with a mass ratio of 50:100. The particle size is 50nm, and the screen printing process uses screen printing with a mesh number of 200 to form a film;
[0063] (3) A layer of ITO film with a thickness of 200nm was sputtered on the surface of the light scattering layer by magnetron sputtering as the first transmission electrode, and the sputtering speed was 0.2nm / s; Prepare a light-emitting functional ...
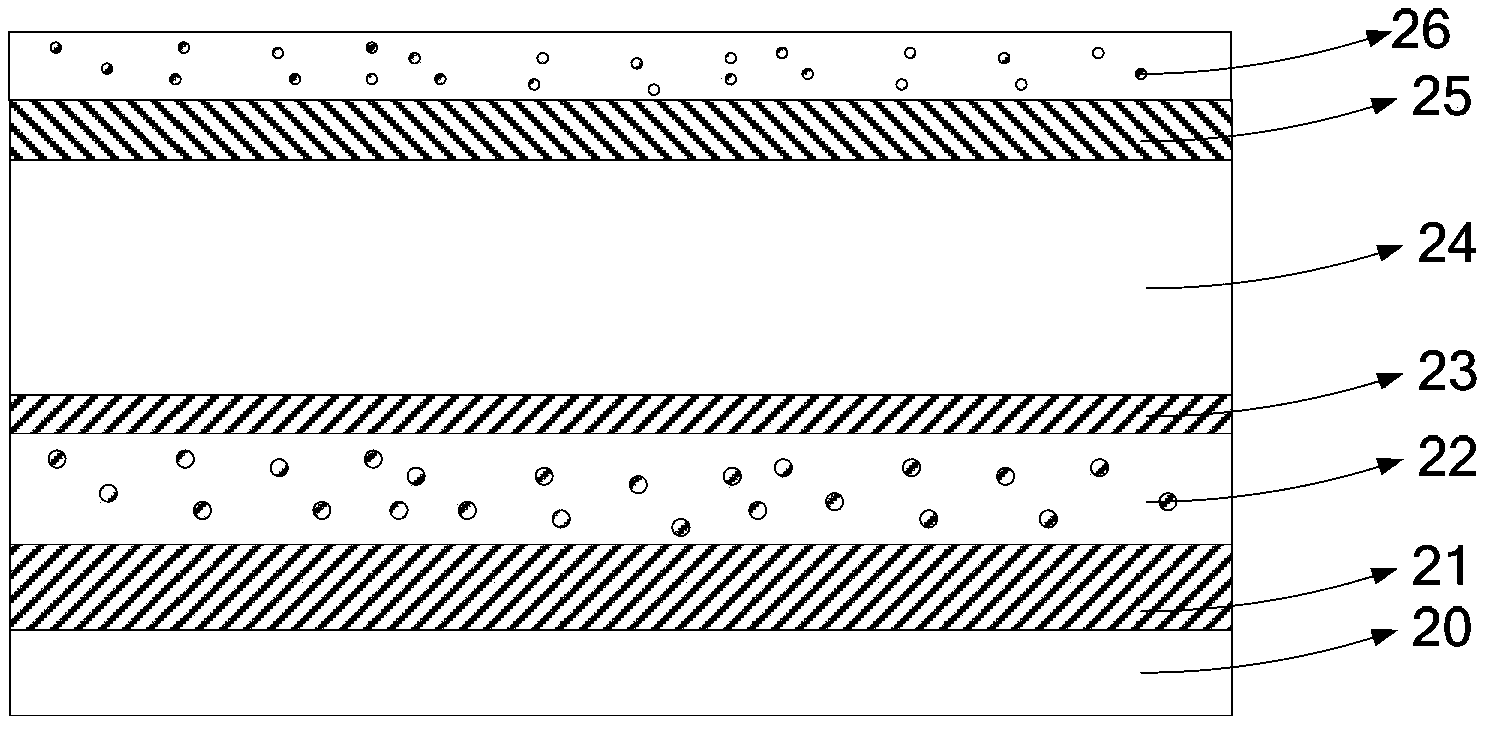
Embodiment 2
[0068] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the material of the light scattering layer includes titanium dioxide nano-microspheres and photocurable acrylic resin with a mass ratio of 20:100, the particle size of the titanium dioxide nano-microspheres is 100nm, and the screen printing process adopts mesh A film was formed by screen printing with a mesh of 1000, and the thickness of the light scattering layer was 80 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the material of the light scattering layer includes titanium dioxide nano-microspheres and photocurable acrylic resin with a mass ratio of 20:100, the particle size of the titanium dioxide nano-microspheres is 250nm, and the screen printing process adopts a mesh A film was formed by screen printing with a mesh of 400, and the thickness of the light scattering layer was 20 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mesh | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com